Nacos 服务注册源码分析
微信公众号:运维开发故事,作者:郑哥
本文我们一起以源码的维度来分析 Nacos 做为服务注册中心的服务注册过程,我会以服务端、客户端两个角度来进行分析,Nacos 客户端我主要是采用 spring-cloud-alibaba 作为核心的客户端组件。对于 Nacos 服务端我会讲解到, Nacos 如何实现 AP/CP 两种模式共存的,以及如何区分的。最后还会分享我在源码调试过程中如何定位核心类的一点经验。
下面我先对我的环境做一个简单的介绍:
-
Jdk 1.8 -
nacos-server-1.4.2 -
spring-boot-2.3.5.RELEASE -
spring-cloud-Hoxton.SR8 -
spring-cloiud-alibab-2.2.5.RELEASE
Nacos 服务架构
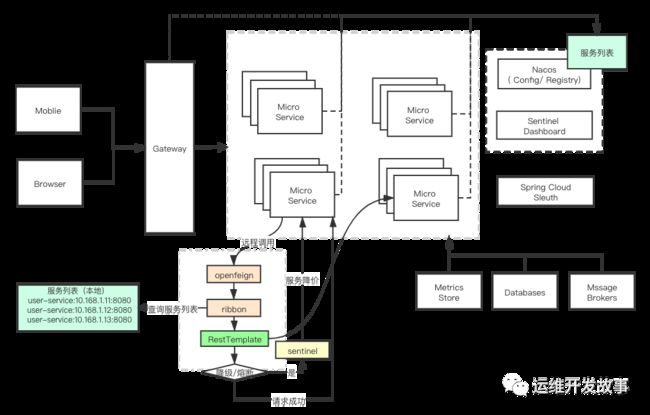
以 Spring-Boot 为服务基础搭建平台, Nacos 在服务架构中的位置如下图所示:
总的来说和 Nacos 功能类似的中间件有 Eureka、Zookeeper、Consul 、Etcd 等。Nacos 最大的特点就是既能够支持 AP、也能够支持 CP 模式,在分区一致性方面使用的是 Raft 协议来实现。
Nacos 客户端
服务注册客户端
添加依赖
Nacos 服务注册是客户端主动发起,利用 Spring 启完成事件进行拓展调用服务注册方法。首先我们需要导入spring-cloud-starter-alibaba-nacos-discovery依赖:
com.alibaba.cloud
spring-cloud-starter-alibaba-nacos-discovery
分析源码
对于 spring-boot 组件我们首先先找它的 META-INF/spring.factories 文件
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.EnableAutoConfiguration=\
com.alibaba.cloud.nacos.discovery.NacosDiscoveryAutoConfiguration,\
com.alibaba.cloud.nacos.ribbon.RibbonNacosAutoConfiguration,\
com.alibaba.cloud.nacos.endpoint.NacosDiscoveryEndpointAutoConfiguration,\
com.alibaba.cloud.nacos.registry.NacosServiceRegistryAutoConfiguration,\
com.alibaba.cloud.nacos.discovery.NacosDiscoveryClientConfiguration,\
com.alibaba.cloud.nacos.discovery.reactive.NacosReactiveDiscoveryClientConfiguration,\
com.alibaba.cloud.nacos.discovery.configclient.NacosConfigServerAutoConfiguration,\
com.alibaba.cloud.nacos.NacosServiceAutoConfiguration
org.springframework.cloud.bootstrap.BootstrapConfiguration=\
com.alibaba.cloud.nacos.discovery.configclient.NacosDiscoveryClientConfigServiceBootstrapConfiguration
通过我的分析发现 NacosServiceRegistryAutoConfiguration 是咱们服务注册的核心配置类,该类中定义了三个核心的 Bean 对象:
-
NacosServiceRegistry -
NacosRegistration -
NacosAutoServiceRegistration
NacosAutoServiceRegistration
NacosAutoServiceRegistration 实现了服务向 Nacos 发起注册的功能,它继承自抽象类 AbstractAutoServiceRegistration 。
在抽象类 AbstractAutoServiceRegistration 中实现 ApplicationContextAware、ApplicationListener 接口。在容器启动、并且上下文准备就绪过后会调用 onApplicationEvent 方法。
public void onApplicationEvent(WebServerInitializedEvent event) {
bind(event);
}
再调用 bind(event) 方法:
public void bind(WebServerInitializedEvent event) {
ApplicationContext context = event.getApplicationContext();
if (context instanceof ConfigurableWebServerApplicationContext) {
if ("management".equals(((ConfigurableWebServerApplicationContext) context)
.getServerNamespace())) {
return;
}
}
this.port.compareAndSet(0, event.getWebServer().getPort());
this.start();
}
然后调用 start() 方法
public void start() {
if (!isEnabled()) {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Discovery Lifecycle disabled. Not starting");
}
return;
}
// only initialize if nonSecurePort is greater than 0 and it isn't already running
// because of containerPortInitializer below
if (!this.running.get()) {
this.context.publishEvent(
new InstancePreRegisteredEvent(this, getRegistration()));
register();
if (shouldRegisterManagement()) {
registerManagement();
}
this.context.publishEvent(
new InstanceRegisteredEvent<>(this, getConfiguration()));
this.running.compareAndSet(false, true);
}
}
最后调用 register(); 在内部去调用 serviceRegistry.register() 方法完成服务注册。
private final ServiceRegistry serviceRegistry;
protected void register() {
this.serviceRegistry.register(getRegistration());
}
NacosServiceRegistry
NacosServiceRegistry 类主要的目的就是实现服务注册
public void register(Registration registration) {
if (StringUtils.isEmpty(registration.getServiceId())) {
log.warn("No service to register for nacos client...");
return;
}
// 默认情况下,会通过反射返回一个 `com.alibaba.nacos.client.naming.NacosNamingService` 的实例
NamingService namingService = namingService();
// 获取 serviceId , 默认使用配置: spring.application.name
String serviceId = registration.getServiceId();
// 获取 group , 默认 DEFAULT_GROUP
String group = nacosDiscoveryProperties.getGroup();
// 创建 instance 实例
Instance instance = getNacosInstanceFromRegistration(registration);
try {
// 注册实例
namingService.registerInstance(serviceId, group, instance);
log.info("nacos registry, {} {} {}:{} register finished", group, serviceId,
instance.getIp(), instance.getPort());
}
catch (Exception e) {
log.error("nacos registry, {} register failed...{},", serviceId,
registration.toString(), e);
// rethrow a RuntimeException if the registration is failed.
// issue : https://github.com/alibaba/spring-cloud-alibaba/issues/1132
rethrowRuntimeException(e);
}
}
我们可以看到最后调用的是 namingService.registerInstance(serviceId, group, instance); 方法。
public void registerInstance(String serviceName, String groupName, Instance instance) throws NacosException {
NamingUtils.checkInstanceIsLegal(instance);
String groupedServiceName = NamingUtils.getGroupedName(serviceName, groupName);
if (instance.isEphemeral()) {
BeatInfo beatInfo = beatReactor.buildBeatInfo(groupedServiceName, instance);
beatReactor.addBeatInfo(groupedServiceName, beatInfo);
}
serverProxy.registerService(groupedServiceName, groupName, instance);
}
然后再调用 serverProxy.registerService(groupedServiceName, groupName, instance); 方法进行服务注册,通过 beatReactor.addBeatinfo() 创建 schedule 每间隔 5s 向服务端发送一次心跳数据
public void registerService(String serviceName, String groupName, Instance instance) throws NacosException {
NAMING_LOGGER.info("[REGISTER-SERVICE] {} registering service {} with instance: {}", namespaceId, serviceName,
instance);
final Map params = new HashMap(16);
params.put(CommonParams.NAMESPACE_ID, namespaceId);
params.put(CommonParams.SERVICE_NAME, serviceName);
params.put(CommonParams.GROUP_NAME, groupName);
params.put(CommonParams.CLUSTER_NAME, instance.getClusterName());
params.put("ip", instance.getIp());
params.put("port", String.valueOf(instance.getPort()));
params.put("weight", String.valueOf(instance.getWeight()));
params.put("enable", String.valueOf(instance.isEnabled()));
params.put("healthy", String.valueOf(instance.isHealthy()));
params.put("ephemeral", String.valueOf(instance.isEphemeral()));
params.put("metadata", JacksonUtils.toJson(instance.getMetadata()));
// POST: /nacos/v1/ns/instance 进行服务注册
reqApi(UtilAndComs.nacosUrlInstance, params, HttpMethod.POST);
}
服务注册服务端
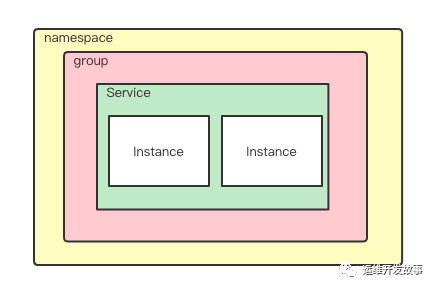
Nacos 做为服务注册中心,既可以实现AP ,也能实现 CP 架构。来维护我们服务中心的服务列表。下面是我们服务列表一个简单的数据模型示意图:
其实就和咱们 NacosServiceRegistry#registry 构建 Instance 实例的过程是一致的。继续回到我们源码分析我们直接来看服务端的 /nacos/v1/ns/instance 接口,被定义在 InstanceController#register 方法。
服务注册
在 InstanceController#register 方法中,主要是解析 request 参数然后调用 serviceManager.registerInstance , 如果返回 ok 就表示注册成功。
@CanDistro
@PostMapping
@Secured(parser = NamingResourceParser.class, action = ActionTypes.WRITE)
public String register(HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception {
final String namespaceId = WebUtils
.optional(request, CommonParams.NAMESPACE_ID, Constants.DEFAULT_NAMESPACE_ID);
final String serviceName = WebUtils.required(request, CommonParams.SERVICE_NAME);
NamingUtils.checkServiceNameFormat(serviceName);
final Instance instance = parseInstance(request);
serviceManager.registerInstance(namespaceId, serviceName, instance);
return "ok";
}
registerInstance 方法的调用
public void registerInstance(String namespaceId, String serviceName, Instance instance) throws NacosException {
createEmptyService(namespaceId, serviceName, instance.isEphemeral());
Service service = getService(namespaceId, serviceName);
if (service == null) {
throw new NacosException(NacosException.INVALID_PARAM,
"service not found, namespace: " + namespaceId + ", service: " + serviceName);
}
addInstance(namespaceId, serviceName, instance.isEphemeral(), instance);
}
再调用 addInstance() 方法
@Resource(name = "consistencyDelegate")
private ConsistencyService consistencyService;
public void addInstance(String namespaceId, String serviceName, boolean ephemeral, Instance... ips)
throws NacosException {
String key = KeyBuilder.buildInstanceListKey(namespaceId, serviceName, ephemeral);
Service service = getService(namespaceId, serviceName);
synchronized (service) {
List instanceList = addIpAddresses(service, ephemeral, ips);
Instances instances = new Instances();
instances.setInstanceList(instanceList);
consistencyService.put(key, instances);
}
}
调用 consistencyService.put(key, instances); 刷新 service 中的所有 instance。我们通过 consistencyService 的定义可以知道它将调用 DelegateConsistencyServiceImpl 类的 put 方法。在这个地方有一个 AP/CP 模式的选择我们可以通过
@Override
public void put(String key, Record value) throws NacosException {
mapConsistencyService(key).put(key, value);
}
// AP 或者 CP 模式的选择, AP 模式采用 Distro 协议, CP 模式采用 Raft 协议。
private ConsistencyService mapConsistencyService(String key) {
return KeyBuilder.matchEphemeralKey(key) ? ephemeralConsistencyService : persistentConsistencyService;
}
AP 模式
Nacos 默认就是采用的 AP 模式使用 Distro 协议实现。实现的接口是 EphemeralConsistencyService 对节点信息的持久化主要是调用 put 方法
@Override
public void put(String key, Record value) throws NacosException {
// 数据持久化
onPut(key, value);
// 通知其他服务节点
distroProtocol.sync(new DistroKey(key, KeyBuilder.INSTANCE_LIST_KEY_PREFIX), DataOperation.CHANGE,
globalConfig.getTaskDispatchPeriod() / 2);
}
在调用 doPut 来保存数据并且发通知
public void onPut(String key, Record value) {
if (KeyBuilder.matchEphemeralInstanceListKey(key)) {
Datum datum = new Datum<>();
datum.value = (Instances) value;
datum.key = key;
datum.timestamp.incrementAndGet();
// 数据持久化
dataStore.put(key, datum);
}
if (!listeners.containsKey(key)) {
return;
}
notifier.addTask(key, DataOperation.CHANGE);
}
在 notifier.addTask 主要是通过 tasks.offer(Pair.with(datumKey, action)); 向阻塞队列 tasks 中放注册实例信息。通过 Notifier#run 方法来进行异步操作以保证效率
public class Notifier implements Runnable {
@Override
public void run() {
Loggers.DISTRO.info("distro notifier started");
for (; ; ) {
try {
Pair pair = tasks.take();
handle(pair);
} catch (Throwable e) {
Loggers.DISTRO.error("[NACOS-DISTRO] Error while handling notifying task", e);
}
}
}
private void handle(Pair pair) {
// 省略部分代码
for (RecordListener listener : listeners.get(datumKey)) {
count++;
try {
if (action == DataOperation.CHANGE) {
listener.onChange(datumKey, dataStore.get(datumKey).value);
continue;
}
if (action == DataOperation.DELETE) {
listener.onDelete(datumKey);
continue;
}
} catch (Throwable e) {
Loggers.DISTRO.error("[NACOS-DISTRO] error while notifying listener of key: {}", datumKey, e);
}
}
}
}
如果是 DataOperation.CHANGE 类型的事件会调用 listener.onChange(datumKey, dataStore.get(datumKey).value); 其实我们的 listener 就是我们的 Service 对象。
public void onChange(String key, Instances value) throws Exception {
Loggers.SRV_LOG.info("[NACOS-RAFT] datum is changed, key: {}, value: {}", key, value);
for (Instance instance : value.getInstanceList()) {
if (instance == null) {
// Reject this abnormal instance list:
throw new RuntimeException("got null instance " + key);
}
if (instance.getWeight() > 10000.0D) {
instance.setWeight(10000.0D);
}
if (instance.getWeight() < 0.01D && instance.getWeight() > 0.0D) {
instance.setWeight(0.01D);
}
}
updateIPs(value.getInstanceList(), KeyBuilder.matchEphemeralInstanceListKey(key));
recalculateChecksum();
}
updateIPs 方法会将服务实例信息,更新到注册表的内存中去,并且会以 udp 的方式通知当前服务的订阅者。
public void updateIPs(Collection instances, boolean ephemeral) {
Map> ipMap = new HashMap<>(clusterMap.size());
for (String clusterName : clusterMap.keySet()) {
ipMap.put(clusterName, new ArrayList<>());
}
for (Instance instance : instances) {
try {
if (instance == null) {
Loggers.SRV_LOG.error("[NACOS-DOM] received malformed ip: null");
continue;
}
if (StringUtils.isEmpty(instance.getClusterName())) {
instance.setClusterName(UtilsAndCommons.DEFAULT_CLUSTER_NAME);
}
if (!clusterMap.containsKey(instance.getClusterName())) {
Loggers.SRV_LOG
.warn("cluster: {} not found, ip: {}, will create new cluster with default configuration.",
instance.getClusterName(), instance.toJson());
Cluster cluster = new Cluster(instance.getClusterName(), this);
cluster.init();
getClusterMap().put(instance.getClusterName(), cluster);
}
List clusterIPs = ipMap.get(instance.getClusterName());
if (clusterIPs == null) {
clusterIPs = new LinkedList<>();
ipMap.put(instance.getClusterName(), clusterIPs);
}
clusterIPs.add(instance);
} catch (Exception e) {
Loggers.SRV_LOG.error("[NACOS-DOM] failed to process ip: " + instance, e);
}
}
for (Map.Entry> entry : ipMap.entrySet()) {
//make every ip mine
List entryIPs = entry.getValue();
// 更新服务列表
clusterMap.get(entry.getKey()).updateIps(entryIPs, ephemeral);
}
setLastModifiedMillis(System.currentTimeMillis());
// 推送服务订阅者消息
getPushService().serviceChanged(this);
StringBuilder stringBuilder = new StringBuilder();
for (Instance instance : allIPs()) {
stringBuilder.append(instance.toIpAddr()).append("_").append(instance.isHealthy()).append(",");
}
Loggers.EVT_LOG.info("[IP-UPDATED] namespace: {}, service: {}, ips: {}", getNamespaceId(), getName(),
stringBuilder.toString());
}
CP 模式
Nacos 默认就是采用的 CP 模式使用 Raft 协议实现。实现类是 PersistentConsistencyServiceDelegateImpl
首先我们先看他的 put 方法
public void put(String key, Record value) throws NacosException {
checkIsStopWork();
try {
raftCore.signalPublish(key, value);
} catch (Exception e) {
Loggers.RAFT.error("Raft put failed.", e);
throw new NacosException(NacosException.SERVER_ERROR, "Raft put failed, key:" + key + ", value:" + value,
e);
}
}
调用 raftCore.signalPublish(key, value); 主要的步骤如下
-
判断是否是 Leader 节点,如果不是 Leader 节点将请求转发给 Leader 节点处理;
-
如果是 Leader 节点,首先执行
onPublish(datum, peers.local());方法,内部首先通过raftStore.updateTerm(local.term.get());方法持久化到文件,然后通过NotifyCenter.publishEvent(ValueChangeEvent.builder().key(datum.key).action(DataOperation.CHANGE).build());异步更新到内存; -
通过 CountDownLatch 实现了一个过半机制
new CountDownLatch(peers.majorityCount())只有当成功的节点大于 N/2 + 1 的时候才返回成功。 -
调用其他的 Nacos 节点的
/raft/datum/commit同步实例信息。
public void signalPublish(String key, Record value) throws Exception {
if (stopWork) {
throw new IllegalStateException("old raft protocol already stop work");
}
if (!isLeader()) {
ObjectNode params = JacksonUtils.createEmptyJsonNode();
params.put("key", key);
params.replace("value", JacksonUtils.transferToJsonNode(value));
Map parameters = new HashMap<>(1);
parameters.put("key", key);
final RaftPeer leader = getLeader();
raftProxy.proxyPostLarge(leader.ip, API_PUB, params.toString(), parameters);
return;
}
OPERATE_LOCK.lock();
try {
final long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
final Datum datum = new Datum();
datum.key = key;
datum.value = value;
if (getDatum(key) == null) {
datum.timestamp.set(1L);
} else {
datum.timestamp.set(getDatum(key).timestamp.incrementAndGet());
}
ObjectNode json = JacksonUtils.createEmptyJsonNode();
json.replace("datum", JacksonUtils.transferToJsonNode(datum));
json.replace("source", JacksonUtils.transferToJsonNode(peers.local()));
onPublish(datum, peers.local());
final String content = json.toString();
final CountDownLatch latch = new CountDownLatch(peers.majorityCount());
for (final String server : peers.allServersIncludeMyself()) {
if (isLeader(server)) {
latch.countDown();
continue;
}
final String url = buildUrl(server, API_ON_PUB);
HttpClient.asyncHttpPostLarge(url, Arrays.asList("key", key), content, new Callback() {
@Override
public void onReceive(RestResult result) {
if (!result.ok()) {
Loggers.RAFT
.warn("[RAFT] failed to publish data to peer, datumId={}, peer={}, http code={}",
datum.key, server, result.getCode());
return;
}
latch.countDown();
}
@Override
public void onError(Throwable throwable) {
Loggers.RAFT.error("[RAFT] failed to publish data to peer", throwable);
}
@Override
public void onCancel() {
}
});
}
if (!latch.await(UtilsAndCommons.RAFT_PUBLISH_TIMEOUT, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS)) {
// only majority servers return success can we consider this update success
Loggers.RAFT.error("data publish failed, caused failed to notify majority, key={}", key);
throw new IllegalStateException("data publish failed, caused failed to notify majority, key=" + key);
}
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
Loggers.RAFT.info("signalPublish cost {} ms, key: {}", (end - start), key);
} finally {
OPERATE_LOCK.unlock();
}
}
判断 AP 模式还是 CP 模式
如果注册 nacos 的 client 节点注册时 ephemeral=true,那么 nacos 集群对这个 client 节点的效果就是 ap 的采用 distro,而注册nacos 的 client 节点注册时 ephemeral=false,那么nacos 集群对这个节点的效果就是 cp 的采用 raft。根据 client 注册时的属性,ap,cp 同时混合存在,只是对不同的 client 节点效果不同
Nacos 源码调试
Nacos 启动文件
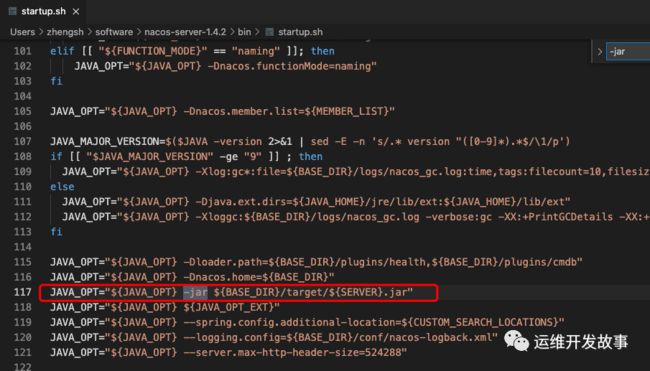
首先我们需要找到 Nacos 的启动类,首先需要找到启动的 jar.
然后我们在解压 target/nacos-server.jar
解压命令:
# 解压 jar 包tar -zxvf nacos-server.jar# 查看 MANIFEST.MF 内容cat META-INF/MANIFEST.MFManifest-Version: 1.0Implementation-Title: nacos-console 1.4.2Implementation-Version: 1.4.2Archiver-Version: Plexus ArchiverBuilt-By: xiweng.yySpring-Boot-Layers-Index: BOOT-INF/layers.idxSpecification-Vendor: Alibaba GroupSpecification-Title: nacos-console 1.4.2Implementation-Vendor-Id: com.alibaba.nacosSpring-Boot-Version: 2.5.0-RC1Implementation-Vendor: Alibaba GroupMain-Class: org.springframework.boot.loader.PropertiesLauncherSpring-Boot-Classpath-Index: BOOT-INF/classpath.idxStart-Class: com.alibaba.nacos.NacosSpring-Boot-Classes: BOOT-INF/classes/Spring-Boot-Lib: BOOT-INF/lib/Created-By: Apache Maven 3.6.3Build-Jdk: 1.8.0_231Specification-Version: 1.4.2
通过 MANIFEST.MF 中的配置信息,我们可以找到 Start-Class 这个配置这个类就是 Spring-Boot 项目的启动类 com.alibaba.nacos.Nacos
Nacos 调试
通过 com.alibaba.nacos.Nacos 的启动类,我们可以通过这个类在 Idea 中进行启动,然后调试。
参考链接
http://nacos.io
https://github.com/alibaba/nacos/issues/3000