如何让代码更加容易复用。
继承
在传统的 OOP 里面,我们通常会提到继承(Inheritance)和多态(Polymorphism)。继承是用来在父类的基础上创建一个子类,来继承父类的属性和方法。多态则允许我们在子类里面调用父类的构建者,并且覆盖父类里的方法。
Javascript 如何通过继承多态重用?
从 ES6 开始,通过 extends 的方式来做继承
class Widget {
appName = "核心微件";
getName () {
return this.appName;
}
}
class Calendar extends Widget {}
var calendar = new Calendar();
console.log(calendar.hasOwnProperty("appName")); // 返回 true
console.log(calendar.getName()); // 返回 "核心微件"
calendar.appName = "日历应用"
console.log(typeof calendar.getName); // 返回 function
console.log(calendar.getName()); // 返回 “日历应用”从 ES6 开始,我们可以通过 super 在子类构建者里面调用父类的构建者,并且覆盖父类里的属性。
class Widget {
constructor() {
this.appName = "核心微件";
}
getName () {
return this.appName;
}
}
class Calendar extends Widget {
constructor(){
super();
this.appName = "日历应用";
}
}
var calendar = new Calendar();
console.log(calendar.hasOwnProperty("appName")); // 返回 true
console.log(calendar.getName()); // 返回 "日历应用"
console.log(typeof calendar.getName); // 返回 function
console.log(calendar.getName()); // 返回 “日历应用”通过继承 React.Component 来创建一个 WelcomeMessage 的子类。
class WelcomeMessage extends React.Component {
render() {
return Hello, {this.props.name}
;
}
}授权
作为个体对象可以授权给一个平台或者他人来一起做一件事。
如何通过授权做到重用?
通过原型本身来做授权会更符合直觉。
Object.create() 实现
var Widget = {
setCity : function(City) {this.city = City; },
outputCity : function() {return this.city;}
};
var Weather = Object.create(Widget);
Weather.setWeather = function (City, Tempreture) {
this.setCity(City);
this.tempreture = Tempreture;
};
Weather.outputWeather = function() {
console.log(this.outputCity()+ ", " + this.tempreture);
}
var weatherApp1 = Object.create(Weather);
var weatherApp2 = Object.create(Weather);
weatherApp1.setWeather("北京","26度");
weatherApp2.setWeather("南京","28度");
weatherApp1.outputWeather(); // 北京, 26度
weatherApp2.outputWeather(); // 南京, 28度通过 class 来实现
class SetLikeMap {
// 初始化字典
constructor() { this.map = new Map(); }
// 自定义集合接口
count(key) { /*...*/ }
add(key) { /*...*/ }
delete(key) { /*...*/ }
// 迭代返回字典中的键
[Symbol.iterator]() { return this.map.keys(); }
// 部分功能授权给字典
keys() { return this.map.keys(); }
values() { return this.map.values(); }
entries() { return this.map.entries(); }
}组合
关于授权,广义上其实就是一种组合。但是这种组合更像是“个体和平台的合作”;而另一种组合更像是“团队内部的合作”,它也有很多的应用和实现方式: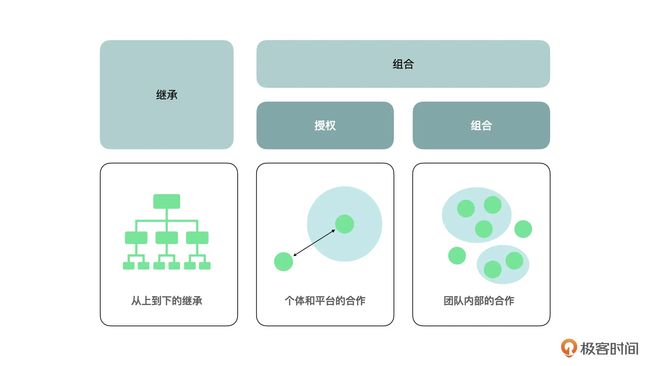
如何通过借用做到重用?
在 JavaScript 中,函数有自带的 apply 和 call 功能。我们可以通过 apply 或 call 来“借用”一个功能。这种方式,也叫隐性混入(Implicit mixin)。
Array.slice()
如何通过拷贝赋予重用?
显性混入
通过Object.assign()
“浅度拷贝”和“深度拷贝”浅拷贝通过延展操作符
// 数组浅拷贝
var a = [ 1, 2 ];
var b = [ ...a ];
b.push( 3 );
a; // [1,2]
b; // [1,2,3]
// 对象浅拷贝
var o = {
x: 1,
y: 2
};
var p = { ...o };
p.y = 3;
o.y; // 2
p.y; // 3通过 for in 循环
function shallowCopy(parent, child) {
var i;
child = child || {};
for (i in parent) {
if (parent.hasOwnProperty(i)) {
child[i] = parent[i];
}
}
return child;
}深拷贝通过JSON.stringify()其他方法:
function deepCopy(parent, child) {
var i,
toStr = Object.prototype.toString,
astr = "[object Array]";
child = child || {};
for (i in parent) {
if (parent.hasOwnProperty(i)) {
if (typeof parent[i] === "object") {
child[i] = (toStr.call(parent[i]) === astr) ? [] : {};
deepCopy(parent[i], child[i]);
} else {
child[i] = parent[i];
}
}
}
return child;
}如何通过组合做到重用?
React 中的组合优于继承
在 React 当中,我们也可以看到组合优于继承的无处不在,并且它同样体现在我们前面讲过的两个方面,一个是“团队内部的合作”,另一个是“个体与平台合作”。下面,我们先看看“团队内部的合作”的例子。
团队内部的合作
function FancyBorder(props) {
return (
{props.children}
);
}
function WelcomeDialog() {
return (
Welcome
Thank you for visiting our spacecraft!
);
}个体与平台合作
function Dialog(props) {
return (
{props.title}
{props.message}
);
}
function WelcomeDialog() {
return (
);
}