Python-Numpy入门
Python-Numpy入门
NumPy是一个开源的Python科学计算基础库,包含:
- 一个强大的N维数组对象ndarray
- 广播功能函数
- 整合C/C++/Fortran代码的工具
- 线性代数、傅里叶变换、随机数生成等功能
NumPy的引用
import numpy as np
N维数组对象:ndarray
- 数组对象可以去掉元素间运算所需的循环,使一维向量更像单个数据
- 设置专门的数组对象,经过优化,可以提升这类应用的运算速度
- 数组对象采用相同的数据类型,有助于节省运算和存储空间
ndarray是一个多维数组对象,由两部分构成:
- 实际的数据
- 描述这些数据的元数据(数据维度、数据类型等)
ndarray在程序中的别名是:array
>>> a=np.array([[1,2,3],[4,5,6]])
>>> a
array([[1, 2, 3],
[4, 5, 6]])
>>> print(a)
[[1 2 3]
[4 5 6]]
ndarray对象的属性
| 属性 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| .ndim | 秩,即轴的数量或维度的数量 |
| .shape | ndarray对象的尺度,对于矩阵,n行m列 |
| .size | ndarray对象元素的个数,相当于.shape中n*m的值 |
| .dtype | ndarray对象的元素类型 |
| .itemsize | ndarray对象中每个元素的大小,以字节为单位 |
>>> a.ndim
2
>>> a.shape
(2, 3)
>>> a.size
6
>>> a.dtype
dtype('int32')
>>> a.itemsize
4
ndarray的元素类型
| 数据类型 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| bool | 布尔类型,True或False |
| intc | 与C语言中的int类型一致,一般是int32或int64 |
| intp | 用于索引的整数,与C语言中ssize_t一致,int32或int64 |
| int8 | 字节长度的整数,取值:[‐128, 127] |
| int16 | 16位长度的整数,取值:[‐32768, 32767] |
| int32 | 32位长度的整数,取值:[‐231, 231‐1] |
| int64 | 64位长度的整数,取值:[‐263, 263‐1] |
| uint8 | 8位无符号整数,取值:[0, 255] |
| uint16 | 16位无符号整数,取值:[0, 65535] |
| uint32 | 32位无符号整数,取值:[0, 232‐1] |
| uint64 | 32位无符号整数,取值:[0, 264‐1] |
| float16 | 16位半精度浮点数:1位符号位,5位指数,10位尾数 |
| float32 | 32位半精度浮点数:1位符号位,8位指数,23位尾数 |
| float64 | 64位半精度浮点数:1位符号位,11位指数,52位尾数 |
| complex64 | 复数类型,实部和虚部都是32位浮点数 |
| complex128 | 复数类型,实部和虚部都是64位浮点数 |
Python语法仅支持整数、浮点数和复数3种类型
ndarray支持如此多种元素类型?
- 科学计算涉及数据较多,对存储和性能都有较高要求
- 对元素类型精细定义,有助于NumPy合理使用存储空间并优化性能
- 对元素类型精细定义,有助于程序员对程序规模有合理评估
非同质ndarray对象无法有效发挥NumPy优势,尽量避免使用
ndarray数组的创建
- 从Python中的列表、元组等类型创建ndarray数组
x = np.array(list/tuple)
x = np.array(list/tuple,dtype=np.float32)
当不指定dtype,Numpy会根据数据实际情况关联一个dtype类型
>>> x=np.array([0,1,2,3])
>>> print(x)
[0 1 2 3]
>>> x=np.array((1,2,3,4,5))
>>> print(x)
[1 2 3 4 5]
>>> x=np.array([[1,2,3],[4,5,6],[7,8,9]])
>>> print(x)
[[1 2 3]
[4 5 6]
[7 8 9]]
- 使用NumPy中函数创建ndarray数组,如:arange, ones, zeros等
| 函数 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| np.arange(n) | 类似range()函数,返回ndarray类型,元素从0到n‐1 |
| np.ones(shape) | 根据shape生成一个全1数组,shape是元组类型 |
| np.zeros(shape) | 根据shape生成一个全0数组,shape是元组类型 |
| np.full(shape,val) | 根据shape生成一个数组,每个元素值都是val |
| np.eye(n) | 创建一个正方的n*n单位矩阵,对角线为1,其余为0 |
>>> np.zeros((3,6),dtype=np.int32)
array([[0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0],
[0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0],
[0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0]])
>>> np.eye(5)
array([[1., 0., 0., 0., 0.],
[0., 1., 0., 0., 0.],
[0., 0., 1., 0., 0.],
[0., 0., 0., 1., 0.],
[0., 0., 0., 0., 1.]])
>>> np.arange(10)
array([0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9])
>>> np.ones((3,6))
array([[1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1.],
[1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1.],
[1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1.]])
| 函数 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| np.ones_like(a) | 根据数组a的形状生成一个全1数组 |
| np.zeros_like(a) | 根据数组a的形状生成一个全0数组 |
| np.full_like(a,val) | 根据数组a的形状生成一个数组,每个元素值都是val |
| np.linspace() | 根据起止数据等间距地填充数据,形成数组 |
| np.concatenate() | 将两个或多个数组合并成一个新的数组 |
>>> a
array([[1., 0., 0., 0., 0.],
[0., 1., 0., 0., 0.],
[0., 0., 1., 0., 0.],
[0., 0., 0., 1., 0.],
[0., 0., 0., 0., 1.]])
>>> np.ones_like(a)
array([[1., 1., 1., 1., 1.],
[1., 1., 1., 1., 1.],
[1., 1., 1., 1., 1.],
[1., 1., 1., 1., 1.],
[1., 1., 1., 1., 1.]])
#
>>> a=np.linspace(1,10,4)
>>> a
array([ 1., 4., 7., 10.])
>>> b=np.linspace(1,10,4,endpoint=False)
>>> b
array([1. , 3.25, 5.5 , 7.75])
>>> c=np.concatenate((a,b))
>>> c
array([ 1. , 4. , 7. , 10. , 1. , 3.25, 5.5 , 7.75])
ndarray数组的变换
对于创建后的ndarray数组,可以对其进行维度变换和元素类型变换
ndarray数组的维度变换
| 方法 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| .reshape(shape) | 不改变数组元素,返回一个shape形状的数组,原数组不变 |
| .resize(shape) | 与.reshape()功能一致,但修改原数组 |
| .swapaxes(ax1,ax2) | 将数组n个维度中两个维度进行调换 |
| .flatten() | 对数组进行降维,返回折叠后的一维数组,原数组不变 |
>>> a=np.ones((2,3,4),dtype=np.int32)
>>> a
array([[[1, 1, 1, 1],
[1, 1, 1, 1],
[1, 1, 1, 1]],
[[1, 1, 1, 1],
[1, 1, 1, 1],
[1, 1, 1, 1]]])
>>> a.reshape((3,8))
array([[1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1],
[1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1],
[1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1]])
>>> a.resize((3,8))
>>> a
array([[1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1],
[1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1],
[1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1]])
>>> a.flatten()
array([1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1,
1, 1])
ndarray数组的类型变换
new_a= a.astype(new_type)
astype()方法一定会创建新的数组(原始数据的一个拷贝),即使两个类型一致
>>> b=a.astype(np.float)
>>> b
array([[1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1.],
[1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1.],
[1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1.]])
>>> b.dtype
dtype('float64')
ndarray数组向列表的转换
ls = a.tolist()
>>> c=b.tolist()
>>> c
[[1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0], [1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0], [1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0]]
ndarray数组的操作
数组的索引和切片
索引:获取数组中特定位置元素的过程
切片:获取数组元素子集的过程
一维数组的索引和切片:与Python的列表类似
>>> a=np.array([9,8,7,6,5])
>>> a[2]
7
>>> a[1:4:2]
array([8, 6])
多维数组的索引:每个维度一个索引值,逗号分割
>>> a=np.arange(24).reshape((2,3,4))
>>> a
array([[[ 0, 1, 2, 3],
[ 4, 5, 6, 7],
[ 8, 9, 10, 11]],
[[12, 13, 14, 15],
[16, 17, 18, 19],
[20, 21, 22, 23]]])
>>> a[1,2,3]
23
>>> a[-1,-2,-3]
17
#多维数组切片
>>> a[:,:,::2]
array([[[ 0, 2],
[ 4, 6],
[ 8, 10]],
[[12, 14],
[16, 18],
[20, 22]]])
ndarray数组的运算
数组与标量之间的运算
数组与标量之间的运算作用于数组的每一个元素
NumPy一元函数
对ndarray中的数据执行元素级运算的函数
| 函数 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| np.rint(x) | 计算数组各元素的四舍五入值 |
| np.modf(x) | 将数组各元素的小数和整数部分以两个独立数组形式返回 |
| np.cos(x) np.cosh(x) np.sin(x) np.sinh(x) np.tan(x) np.tanh(x) | 计算数组各元素的普通型和双曲型三角函数 |
| np.exp(x) | 计算数组各元素的指数值 |
| np.sign(x) | 计算数组各元素的符号值,1(+), 0, ‐1(‐) |
| np.abs(x) np.fabs(x) | 计算数组各元素的绝对值 |
| np.sqrt(x) | 计算数组各元素的平方根 |
| np.square(x) | 计算数组各元素的平方 |
| np.log(x) np.log10(x) np.log2(x) | 计算数组各元素的自然对数、10底对数和2底对数 |
| np.ceil(x) np.floor(x) | 计算数组各元素的ceiling值或floor值 |
NumPy二元函数
| 函数 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| +‐* / ** | 两个数组各元素进行对应运算 |
| np.maximum(x,y) np.fmax() np.minimum(x,y)np.fmin() | 元素级的最大值/最小值计算 |
| np.mod(x,y) | 元素级的模运算 |
| np.copysign(x,y) | 将数组y中各元素值的符号赋值给数组x对应元素 |
| >< >= <= == ! = | 算术比较,产生布尔型数组 |
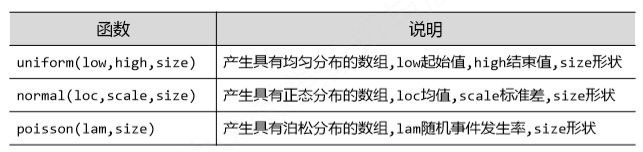
Numpy的随机数函数字库
NumPy的random子库 np.random.*
| 函数 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| rand(d0,d1,…,dn) | 根据d0‐dn创建随机数数组,浮点数,[0,1),均匀分布 |
| randn(d0,d1,…,dn) | 根据d0‐dn创建随机数数组,标准正态分布 |
| randint(low[,high,shape]) | 根据shape创建随机整数或整数数组,范围是[low, high) |
| seed(s) | 随机数种子,s是给定的种子值 |
>>> a=np.random.rand(3,4,5)
>>> a
array([[[0.05634508, 0.23282427, 0.97323879, 0.57125055, 0.31443504],
[0.63496895, 0.88520873, 0.98213933, 0.85760826, 0.89756098],
[0.75591832, 0.99073097, 0.22627046, 0.65524722, 0.75661298],
[0.92475593, 0.48066909, 0.84691563, 0.82388277, 0.60752717]],
[[0.01765494, 0.27591181, 0.68354883, 0.62560336, 0.48458496],
[0.27518994, 0.5134795 , 0.75454143, 0.40991304, 0.52873799],
[0.56319705, 0.42336783, 0.42504597, 0.79090525, 0.83288663],
[0.17305841, 0.94027144, 0.75059357, 0.47371894, 0.39481083]],
[[0.11607009, 0.6345432 , 0.79418343, 0.38497282, 0.28560523],
[0.8823346 , 0.95018567, 0.32477007, 0.19077357, 0.12261713],
[0.98872221, 0.1084761 , 0.45498204, 0.01817987, 0.80057172],
[0.27032861, 0.35974023, 0.96219735, 0.24607752, 0.64934941]]])
数据存取函数
CSV******文件
np.loadtxt()
np.savetxt()
多维数据存取
a.tofile()
np.fromfile()
np.save()
np.savez()
np.load()
随机函数
np.random.rand() np.random.randn()
np.random.randint() np.random.seed()
np.random.shuffle() np.random.permutation()
np.random.choice()
小结
根据Doctor.ht-wang的理解,numpy和panda之类的库初步学习过一遍可以做什么,之后在实际项目中,用到的时候查表就好。于是将老师的课件整理成文章,供后续使用。