基于Seq2Seq模型的机器翻译
如标题所见,这篇博客的主题就是基于Seq2Seq模型的机器翻译,它的主要任务就是将一种语言翻译为另一种语言,在这里我们以英语翻译成法语为例子,如I'm a student.---->>>Je suis étudiant.
这份数据是公开,可以直接下载的,下载地址为:翻译语料下载地址
模型结构
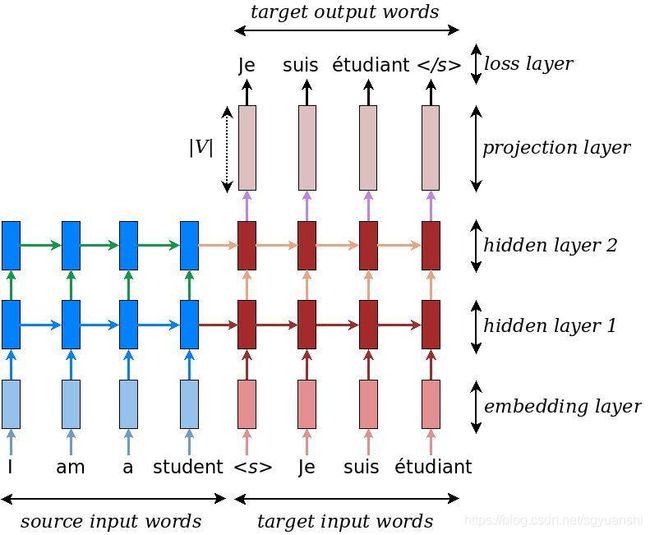
首先,我们先了解一下模型的结构:
- 首先,第一部分是编码器
Encoder,它接收source sentence,然后Encoder将其转换为一个包含具体语义信息的中间向量; - 接着,是一个解码器
Decoder,接收Encoder传递过来的中间向量,最后通过Decoder输出最终的翻译结果。
具体思路
第一步:将source input words即待英语单词,进行词向量Embedding;
第二步:词向量作为Encoder的输入,Encoder通常是一个RNN、LSTM或GRU的网络;
第三步:target input words即法语单词,同样进行进行Embedding,在Embedding之前,需要做预处理:在句子的最前面加上开始标识,句子的最后加上结束标识,如 “Je suis étudiant” ===>>>“ Je suis étudiant ”;
第四步:将target input words的词向量作为Decoder的输入,Decoder网络类型跟Encoder同理。不仅如此,还需要将Encoder最后一个输出和state,可对应为下图的hidden layer 1和hidden layer 2,作为Decoder的初始状态;
第五步:使用一种"teacher forcing"的方法,将target input words向后偏移一个timestamp,即原来的
“ Je suis étudiant ”
变为===>>>
“Je suis étudiant ”,得到target output words,这便是模型训练样本的真实标签;
最后:根据Decoder所有时刻的输出,再通过softmax进行概率归一化,与target output words计算loss,迭代训练模型。
模型推理
上面提到的其实是模型的训练方法,但是在模型推理即线上翻译时是不同的,因为我们没有完整的target input words,即Decoder缺失输入,不过Encoder训练和推理时时一样的。
(其实如果有了target input words,还需要翻译吗?这不就是翻译结果了吗!)
所以,
- 首先,还是将待翻译文本source input words的词向量作为Encoder的输入,然后将其最后一个输出和state传递给Decoder,作为其初始状态;
- 这时我们会将 开始标识
作为Decoder的输入,即整个target input words只有一个单词; - 然后我们去预测下一个单词是什么;
- 接着,预测的单词的词向量又作为下一轮Decoder的输入,上一轮Decoder的输出和state又作为下一轮Decoder的初始状态;
- 如此循环,直到预测的单词为结束标识即。
- 最后,将所有预测的单词拼接起来即可。
代码实现
import numpy as np
import tensorflow as tf
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from google.colab import drive
import os
class Seq2Seq:
batch_size = 64 # Batch size for training.
epochs = 50 # Number of epochs to train for.
latent_dim = 256 # Latent dimensionality of the encoding space.
num_samples = 80000 # Number of samples to train on.
# Path to the data txt file on disk.
# data_path = "fra.txt"
max_seq_len = 64 # 这里是简单化处理,将encoder和decoder的最大长度设为同一个值
embedding_size = 128 # 词向量的size
num_decoder_tokens = None
num_encoder_tokens = None
# weight_initializer = tf.truncated_normal_initializer(stddev=0.02)
def __init__(self, lr):
self.lr = lr
# colab google云盘挂载
drive.mount('/gdrive')
self.data_path = "/gdrive/My Drive/sequence-to-sequence/fra.txt"
def get_dataset(self):
# 将array格式的数据转化为tf的dataset格式
def tf_dataset(encoder_input_data, decoder_input_data, decoder_target_data):
inputs = tf.data.Dataset.from_tensor_slices((encoder_input_data, decoder_input_data))
# decoder_target_data = tf.one_hot(decoder_target_data, depth=self.num_decoder_tokens)
labels = tf.data.Dataset.from_tensor_slices(decoder_target_data)
dataset = tf.data.Dataset.zip((inputs, labels)).shuffle(1024).repeat(-1).batch(self.batch_size)
return dataset
encoder_inputs, decoder_inputs, decoder_targets = self.data_preprocess(self.data_path)
encoder_inputs_train, encoder_inputs_val, decoder_inputs_train, decoder_inputs_val, decoder_targets_train, decoder_targets_val = train_test_split(
encoder_inputs, decoder_inputs, decoder_targets, test_size=0.2)
train_dataset = tf_dataset(encoder_inputs_train, decoder_inputs_train, decoder_targets_train)
val_dataset = tf_dataset(encoder_inputs_val, decoder_inputs_val, decoder_targets_val)
return train_dataset, val_dataset
def data_preprocess(self, data_path):
# 数据预处理.
encoder_input_data = []
decoder_input_data = []
decoder_target_data = []
encoder_length = []
decoder_length = []
input_char_map = dict()
target_char_map = dict()
num_encoder_tokens = 1
num_decoder_tokens = 1
with open(data_path, "r", encoding="utf-8") as f:
lines = f.read().split("\n")
for line in lines[:self.num_samples]:
data = line.split("\t")
if len(data) < 2:
continue
input_text, target_text = data[0], data[1]
target_text = "\t" + target_text + "\n"
input_index = [0] * self.max_seq_len
target_index = [0] * self.max_seq_len
encoder_length.append(len(input_text))
decoder_length.append(len(target_text))
for i, char in enumerate(input_text.split(" ")):
if i >= self.max_seq_len:
break
if input_char_map.get(char):
input_index[i] = input_char_map.get(char)
else:
input_index[i] = num_encoder_tokens
input_char_map[char] = num_encoder_tokens
num_encoder_tokens += 1
for i, char in enumerate(target_text.split(" ")):
if i >= self.max_seq_len:
break
if target_char_map.get(char):
target_index[i] = target_char_map.get(char)
else:
target_index[i] = num_decoder_tokens
target_char_map[char] = num_decoder_tokens
num_decoder_tokens += 1
encoder_input_data.append(input_index)
decoder_input_data.append(target_index)
decoder_target_data.append(target_index[1:] + [0])
self.num_decoder_tokens = num_decoder_tokens
self.num_encoder_tokens = num_encoder_tokens
print("num_decoder_tokens: ", num_decoder_tokens)
print("num_encoder_tokens: ", num_encoder_tokens)
print("encoder_input_data: ", encoder_input_data[0], "......")
print("decoder_input_data: ", decoder_input_data[0], "......")
print("decoder_target_data: ", decoder_target_data[0], "......")
return np.array(encoder_input_data), np.array(decoder_input_data), np.array(
decoder_target_data)
def build_net(self, lr):
# 用LSTM作为encoder和decoder的网络结构
def custom_loss(y_true, r_pred):
# 自定义loss,加入mask机制
mask = tf.math.logical_not(tf.math.equal(y_true, 0))
loss_ = tf.keras.losses.sparse_categorical_crossentropy(y_true, r_pred,
from_logits=False)
mask = tf.cast(mask, dtype=loss_.dtype)
loss_ *= mask
return tf.reduce_sum(loss_) / tf.reduce_sum(mask)
encoder_input = tf.keras.Input(shape=[self.max_seq_len], name='encoder_input')
decoder_input = tf.keras.Input(shape=[self.max_seq_len], name='decoder_input')
encoder = Encoder(self.num_encoder_tokens, self.embedding_size, self.latent_dim)
_, encoder_state_h, encoder_state_c = encoder(encoder_input)
encoder_state = [encoder_state_h, encoder_state_c]
decoder = Decoder(self.num_decoder_tokens, self.embedding_size, self.latent_dim)
decoder_output, _, _ = decoder(decoder_input, state=encoder_state)
model = tf.keras.Model([encoder_input, decoder_input], decoder_output)
model.compile(optimizer=tf.keras.optimizers.Adam(),
loss=custom_loss,
metrics=[AccuracyWithMask()]
# metrics="accuracy"
)
return model
def train(self, strategy=None):
train_dataset, val_dataset = self.get_dataset()
# callbacks = [
# tf.keras.callbacks.ModelCheckpoint(
# # Path where to save the model
# # The two parameters below mean that we will overwrite
# # the current checkpoint if and only if
# # the `val_loss` score has improved.
# # The saved model name will include the current epoch.
# filepath="model",
# save_best_only=True, # Only save a model if `val_loss` has improved.
# monitor="val_loss",
# verbose=1,
# )
# ]
if strategy: # 是否使用TPU
with strategy.scope():
model = self.build_net(0.01)
else:
model = self.build_net(0.01)
model.fit(train_dataset,
# callbacks=callbacks,
# verbose=2,
validation_data=val_dataset, epochs=self.epochs,
steps_per_epoch=int(self.num_samples/self.batch_size),
validation_steps=self.epochs)
def inference(self, text):
pass
class Encoder(tf.keras.Model):
def __init__(self, vocab_size, embedding_size, hidden_size):
super(Encoder, self).__init__()
self.embedding = tf.keras.layers.Embedding(vocab_size, embedding_size)
self.lstm = tf.keras.layers.LSTM(hidden_size, return_state=True, return_sequences=True)
def call(self, inputs, **kwargs):
x = self.embedding(inputs)
output, state_h, state_c = self.lstm(x)
return output, state_h, state_c
class Decoder(tf.keras.Model):
def __init__(self, vocab_size, embedding_size, hidden_size):
super(Decoder, self).__init__()
self.embedding = tf.keras.layers.Embedding(vocab_size, embedding_size)
self.lstm = tf.keras.layers.LSTM(hidden_size, return_state=True, return_sequences=True)
self.fc = tf.keras.layers.Dense(vocab_size, activation="softmax")
def call(self, inputs, **kwargs):
state = kwargs.get('state')
x = self.embedding(inputs)
output, state_h, state_c = self.lstm(x, initial_state=state)
output = self.fc(output)
return output, state_h, state_c
class AccuracyWithMask(tf.keras.metrics.Metric):
# 自定义accuracy,加入mask机制
def __init__(self, name="accuracy", **kwargs):
super(AccuracyWithMask, self).__init__(name=name, **kwargs)
self.true_samples = self.add_weight(name="ctp", initializer="zeros")
self.all_samples = self.add_weight(name="ctp2", initializer="zeros")
def update_state(self, y_true, y_pred, sample_weight=None):
mask = tf.math.logical_not(tf.math.equal(y_true, 0))
y_pred = tf.argmax(y_pred, axis=-1)
values = tf.cast(y_true, "int32") == tf.cast(y_pred, "int32")
values = tf.cast(values, "float32")
values = tf.boolean_mask(values, mask)
# if sample_weight is not None:
# sample_weight = tf.cast(sample_weight, "float32")
# values = tf.multiply(values, sample_weight)
self.true_samples.assign_add(tf.reduce_sum(values))
self.all_samples.assign_add(tf.cast(tf.size(values), "float32"))
def result(self):
return self.true_samples / self.all_samples
def reset_states(self):
# The state of the metric will be reset at the start of each epoch.
self.true_samples.assign(0.0)
self.all_samples.assign(0.0)
# class CustomLoss(tf.keras.losses.Loss):
# def __init__(self, name="CustomLoss"):
# super().__init__(name=name)
#
# def call(self, y_true, r_pred):
# loss_object = tf.keras.losses.SparseCategoricalCrossentropy(
# from_logits=True, reduction='none')
# mask = tf.math.logical_not(tf.math.equal(y_true, 0))
# loss_ = loss_object(y_true, r_pred)
#
# mask = tf.cast(mask, dtype=loss_.dtype)
# loss_ *= mask
#
# return tf.reduce_mean(loss_)
if __name__ == '__main__':
model = Seq2Seq(0.01)
model.train(strategy)