.NET代码混淆实践
今天突然对反编译、混淆感兴趣,在网上查了一些资料,文章大部分内容来源http://www.cnblogs.com/hsapphire/archive/2010/11/21/1883514.html。
1,名称混淆
1.1控制台程序
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
string userID="asldjf3333djf";
string pwd = GetPassword(userID);
ChangeInfo(userID, pwd);
}
public static string GetPassword(string userID)
{
return "123456";
}
public static void ChangeInfo(string userID,string pwd)
{
}
}
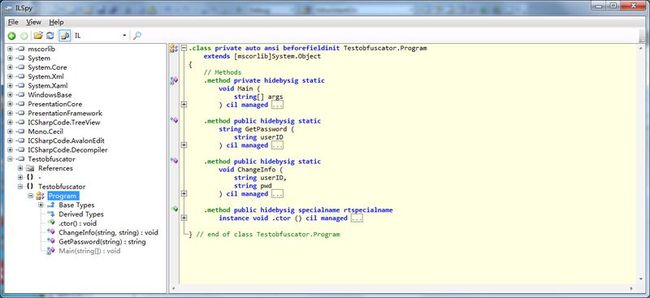
使用ILSPY进行反编译,界面如下:
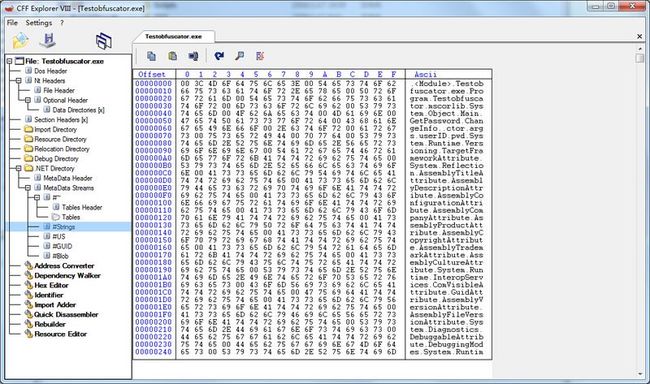
1.2 使用PE文件查看工具CFF载入可执行文件。定位到#Strings流(程序集的类型、引用类型、成员等的定义都在该字符串中),使用CFF来修改#Strings流的内容。查找到字符串“ChangeInfo”和字符串“GetPassword”,随意替换,保存后双击程序,运行验证是否有问题。
结果显示能够正常运行。然后用ILSPY打开后,显示原先的“ChangeInfo”和“GetPassword”为乱码(图略,使用ILSPY时需要重新打开exe文件)
1.3作者的总结:
- 第一种替换方法为无意义替换。我们知道在实际的开发过程中,我们都必须遵守一定的命名规范来为类型、属性、字段命名。但是当我们对编译成功的代码进行名称混淆的时候就是要将这些规范的、规律的名称变得毫无意义,毫无规律可循。
- 第二种替换方法称为不可打印字符替换。在UNICODE字符集中,一些特殊字符,目前无法得到正确的显示,比如从0x01到0x20之间的字符。如果把名称替换成这些字符,显示出来的就是奇怪的乱码。
- 第三种替换方法为空字符替换。空字符替换就是把名称替换为空串。但是这种方法并不适合实际的应用,因为如果名称都为空,那么势必要产生二义性。
2 流程混淆是指打乱方法的流程,让反编译软件无法将代码正确的反编译为高级语言。流程混淆即可保护代码又可增加破解者分析代码的难度。目前流程混淆基本上都是基于跳转实现的,我们在程序中使用的跳转有如下三种方式:
- 1) goto跳转;
- 2) if-else跳转
- 3) switch跳转。
.NET的流程混淆和传统windows应用程序的流程混淆本质上是有区别的。传统的流程混淆的目的是防止反汇编,而.NET流程混淆的目的是防止反编译。传统的流程混淆是基于汇编指令进行的,操作层次较低,可更改堆栈调用,可操作方式较多;.NET流程混淆是基于IL指令进行的,操作层次较高,不可触及堆栈调用,可操作方式较少。
2.1 测试流程混淆代码
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
string h = "hello";
if (h == "hell0")
{
OutString();
}
else
{
Console.WriteLine("There is no hello!");
}
}
public static void OutString()
{
Console.WriteLine("hello");
}
}
核心IL代码
.class private auto ansi beforefieldinit FlowObufscation.Program
extends [mscorlib]System.Object
{
.method private hidebysig static void Main(string[] args) cil managed
{
.entrypoint
.maxstack 2
.locals init ([0] string h,
[1] bool CS$4$0000)
IL_0000: nop
IL_0001: ldstr "hello"
IL_0006: stloc.0
IL_0007: ldloc.0
IL_0008: ldstr "hell0"
IL_000d: call bool [mscorlib]System.String::op_Equality(string, string)
IL_0012: ldc.i4.0
IL_0013: ceq
IL_0015: stloc.1
IL_0016: ldloc.1
IL_0017: brtrue.s IL_0023
IL_0019: nop
IL_001a: call void FlowObufscation.Program::OutString()
IL_001f: nop
IL_0020: nop
IL_0021: br.s IL_0030
IL_0023: nop
IL_0024: ldstr "There is no hello!"
IL_0029: call void [mscorlib]System.Console::WriteLine(string)
IL_002e: nop
IL_002f: nop
IL_0030: ret
} // end of method Program::Main
.method public hidebysig static void OutString() cil managed
{
// 代码大小 13 (0xd)
.maxstack 8
IL_0000: nop
IL_0001: ldstr "hello"
IL_0006: call void [mscorlib]System.Console::WriteLine(string)
IL_000b: nop
IL_000c: ret
} // end of method Program::OutString
.method public hidebysig specialname rtspecialname
instance void .ctor() cil managed
{
// 代码大小 7 (0x7)
.maxstack 8
IL_0000: ldarg.0
IL_0001: call instance void [mscorlib]System.Object::.ctor()
IL_0006: ret
} // end of method Program::.ctor
} // end of class FlowObufscation.Program
作者将Main方法的IL代码分成了三段,分段并没有什么依据,完全是随意的。下面将这三段代码重新组合,按照第一段、第三段、第二段的顺序排列,然后在第一段的结尾加上跳转语句“br IL_0012”,在第二段代码的后面加上跳转语句“br IL_0029”。修改之后的代码如下
.method private hidebysig static void Main(string[] args) cil managed
{
//第一段开始
.entrypoint
// 代码大小 49 (0x31)
.maxstack 2
.locals init ([0] string h,
[1] bool CS$4$0000)
IL_0000: nop
IL_0001: ldstr "hello"
IL_0006: stloc.0
IL_0007: ldloc.0
IL_0008: ldstr "hell0"
IL_000d: call bool [mscorlib]System.String::op_Equality(string, string)
br IL_0012
//第一段结束
//第三段开始
IL_0029: call void [mscorlib]System.Console::WriteLine(string)
IL_002e: nop
IL_002f: nop
IL_0030: ret
//第三段结束
//第二段开始
IL_0012: ldc.i4.0
IL_0013: ceq
IL_0015: stloc.1
IL_0016: ldloc.1
IL_0017: brtrue.s IL_0023
IL_0019: nop
IL_001a: call void FlowObufscation.Program::OutString()
IL_001f: nop
IL_0020: nop
IL_0021: br.s IL_0030
IL_0023: nop
IL_0024: ldstr "There is no hello!"
br IL_0029
//第二段结束
} // end of method Program::Main
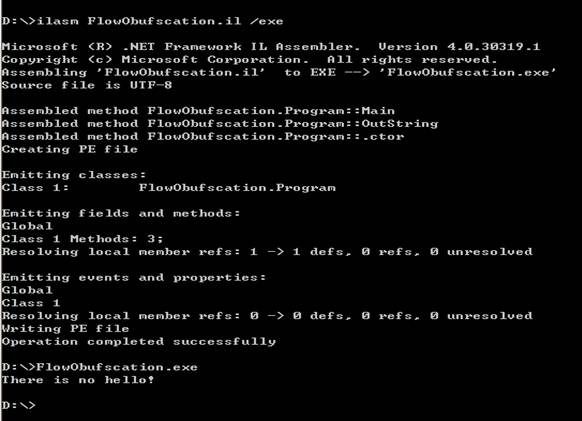
用ILASM重新编译修改后的IL代码(注意是ILASM,不是ILDASM)
这样就可以尝试反编译了。。原作者用Reflector测试抛出异常(可能因为版本等原因),我用的ILSPY竟然能够成功,没有异常。
原文中还有一个逻辑跳转的例子,但是测试没有成功,如果想尝试请参考文章开头的链接。
作者还有两篇文章,关于混淆和保护的一些观点,参考文章如下:
http://www.cnblogs.com/hsapphire/archive/2009/12/28/1634159.html
http://www.cnblogs.com/hsapphire/archive/2010/07/30/1788355.html
感谢原作者的分享。
附:
PE修改工具:
CFF,http://www.ntcore.com/exsuite.php
.NET 反编译:
ILSPY,http://ilspy.net/
dotPeek,http://www.jetbrains.com/decompiler/
JAVA反编译:
jd-gui,http://jd.benow.ca/