Python中的numpy.append()
Python numpy append() function is used to merge two arrays. This function returns a new array and the original array remains unchanged.
Python numpy append()函数用于合并两个数组。 该函数返回一个新数组,原始数组保持不变。
NumPy append()语法 (NumPy append() Syntax)
The function syntax is:
函数语法为:
numpy.append(arr, values, axis=None)- The arr can be an array-like object or a NumPy array. The values are appended to a copy of this array. arr可以是类似数组的对象或NumPy数组。 这些值将附加到此数组的副本中。
- The values are array-like objects and it’s appended to the end of the “arr” elements. 这些值是类似数组的对象,并附加到“ arr”元素的末尾。
- The axis specifies the axis along which values are appended. If the axis is not provided, both the arrays are flattened. 该轴指定沿其附加值的轴。 如果未提供轴,则将两个阵列展平。
Python numpy.append()示例 (Python numpy.append() Examples)
Let’s look at some examples of NumPy append() function.
让我们来看一些NumPy append()函数的示例。
1.展平两个数组 (1. Flattening Two Arrays)
import numpy as np
arr1 = np.array([[1, 2], [3, 4]])
arr2 = np.array([[10, 20], [30, 40]])
# no axis provided, array elements will be flattened
arr_flat = np.append(arr1, arr2)
print(arr_flat) # [ 1 2 3 4 10 20 30 40]2.沿轴合并 (2. Merging Along Axis)
import numpy as np
arr_merged = np.append([[1, 2], [3, 4]], [[10, 20], [30, 40]], axis=0)
print(f'Merged 2x2 Arrays along Axis-0:\n{arr_merged}')
arr_merged = np.append([[1, 2], [3, 4]], [[10, 20], [30, 40]], axis=1)
print(f'Merged 2x2 Arrays along Axis-1:\n{arr_merged}')Output:
输出:
Merged 2x2 Arrays along Axis-0:
[[ 1 2]
[ 3 4]
[10 20]
[30 40]]
Merged 2x2 Arrays along Axis-1:
[[ 1 2 10 20]
[ 3 4 30 40]]- When the 2×2 arrays are merged along the x-axis, the output array size is 4×2. 当2×2数组沿x轴合并时,输出数组大小为4×2。
- When the 2×2 arrays are merged along the y-axis, the output array size is 2×4. 当2×2数组沿y轴合并时,输出数组大小为2×4。
3.合并不同形状的数组 (3. Merging Arrays of different shapes)
The append() function throws ValueError if both the arrays are of different shape, excluding the axis.
如果两个数组的形状均不同(轴除外),则append()函数将引发ValueError。
Let’s understand this scenario with a simple example.
让我们用一个简单的例子来了解这种情况。
arr3 = np.append([[1, 2]], [[1, 2, 3], [1, 2, 3]])
print(arr3)
arr3 = np.append([[1, 2]], [[1, 2], [3, 4]], axis=0)
print(arr3)- In the first example, the array elements are flattened. So even if they have completely different size – 1×2 and 2×3, the append() works fine. 在第一个示例中,将数组元素展平。 因此,即使它们的大小完全不同-1×2和2×3,append()也可以正常工作。
- In the second example, the array shapes are 1×2 and 2×2. Since we are appending along the 0-axis, the 0-axis shape can be different. The other shapes should be the same, so this append() will also work fine. 在第二示例中,阵列形状是1×2和2×2。 由于我们沿0轴追加,因此0轴的形状可以不同。 其他形状应该相同,因此此append()也可以正常工作。
Output:
输出:
[1 2 1 2 3 1 2 3]
[[1 2]
[1 2]
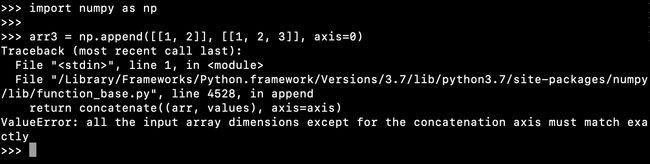
[3 4]]Let’s look at another example where ValueError will be raised.
让我们看另一个将引发ValueError的示例。
>>> import numpy as np
>>>
>>> arr3 = np.append([[1, 2]], [[1, 2, 3]], axis=0)
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "", line 1, in
File "/Library/Frameworks/Python.framework/Versions/3.7/lib/python3.7/site-packages/numpy/lib/function_base.py", line 4528, in append
return concatenate((arr, values), axis=axis)
ValueError: all the input array dimensions except for the concatenation axis must match exactly
>>>The array shapes are 1×2 and 2×3. Since the axis-1 shapes are different, ValueError is raised.
阵列形状为1×2和2×3。 由于1轴的形状不同,因此会引发ValueError。
Reference: API Doc
参考 : API文档
翻译自: https://www.journaldev.com/32780/numpy-append-in-python