每日学术速递1.27
CV - 计算机视觉 | ML - 机器学习 | RL - 强化学习
前沿推介:
ICLR 2023
ICLR 全称为国际学习表征会议(International Conference on Learning Representations),今年将举办的是第 11 届,预计将于 5 月 1 日至 5 日在卢旺达首都基加利线下举办。今年 ICLR 共接收近 5000 篇投稿,整体接收率为 31.8%,接近于去年的 32.26%。今年还有一个变化是接收论文的 tag 会有两个,一个是论文类型(oral、spotlight、poster),另一个是 presentation 的方式。
在机器学习社区中,ICLR 是较为「年轻」的学术会议,它由深度学习巨头、图灵奖获得者 Yoshua Bengio 和 Yann LeCun 牵头举办,2013 年才刚刚举办第一届。
不过 ICLR 很快就获得了学术研究者们的广泛认可,被认为是深度学习领域的顶级会议之一。在 Google Scholar 的学术会议 / 期刊排名中,ICLR 目前排名第 9 位,要高于 NeurIPS。
ICLR 2023会议论文:
Distilling Cognitive Backdoor Patterns within an Image
标题:提炼图像中的认知后门模式
作者:Hanxun Huang, Xingjun Ma, Sarah Erfani, James Bailey
文章链接:https://arxiv.org/abs/2301.10908v1
摘要:
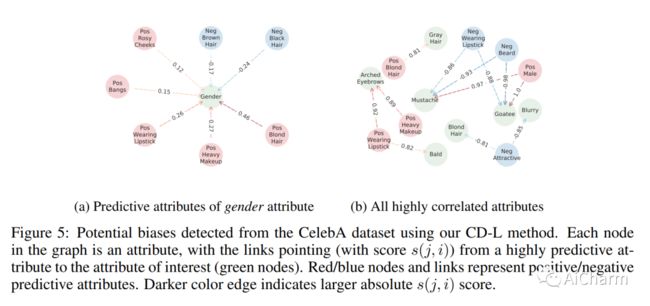
本文提出了一种简单的方法来提炼和检测图像中的后门模式。Cognitive Distillation(CD)。这个想法是为了从输入图像中提取对模型预测负责的 "最小本质"。CD优化一个输入掩码,从输入图像中提取一个可以导致相同模型输出的小模式(即对数或深度特征)。提取的模式可以帮助理解模型在干净图像与后门图像上的认知机制,因此被称为 emph{Cognitive Pattern}(CP)。利用CD和提炼出的CP,我们发现了后门攻击的一个有趣的现象:尽管不同的攻击所使用的触发模式的形式和大小各不相同,但后门样本的CP都是令人惊讶和怀疑的小。因此,人们可以利用学习到的掩码来检测并从中毒的训练数据集中删除后门样本。我们进行了广泛的实验,表明CD可以稳健地检测出广泛的高级后门攻击。我们还表明,CD有可能被用于帮助检测人脸数据集的潜在偏差。
代码在https://github.com/HanxunH/CognitiveDistillation
This paper proposes a simple method to distill and detect backdoor patterns within an image: \emph{Cognitive Distillation} (CD). The idea is to extract the "minimal essence" from an input image responsible for the model's prediction. CD optimizes an input mask to extract a small pattern from the input image that can lead to the same model output (i.e., logits or deep features). The extracted pattern can help understand the cognitive mechanism of a model on clean vs. backdoor images and is thus called a \emph{Cognitive Pattern} (CP). Using CD and the distilled CPs, we uncover an interesting phenomenon of backdoor attacks: despite the various forms and sizes of trigger patterns used by different attacks, the CPs of backdoor samples are all surprisingly and suspiciously small. One thus can leverage the learned mask to detect and remove backdoor examples from poisoned training datasets. We conduct extensive experiments to show that CD can robustly detect a wide range of advanced backdoor attacks. We also show that CD can potentially be applied to help detect potential biases from face datasets. Code is available at \url{https://github.com/HanxunH/CognitiveDistillation}.
TPAMI 期刊论文:
Learning Good Features to Transfer Across Tasks and Domains
标题:学习好的特征以跨任务和领域的转移
作者:Pierluigi Zama Ramirez, Adriano Cardace, Luca De Luigi, Alessio Tonioni, Samuele Salti, Luigi Di Stefano
文章链接:https://arxiv.org/abs/2301.11310
摘要:
标记数据的可用性是在新领域中部署计算机视觉任务的深度学习算法的主要障碍。许多用于解决不同任务的框架共享相同的架构,这一事实表明,应该有一种方法可以重复使用在特定环境中学习到的知识,以解决新的任务,只需有限的或没有额外的监督。在这项工作中,我们首先表明,这种知识可以通过学习特定领域中特定任务的深层特征之间的映射来实现跨任务共享。然后,我们表明,这个由神经网络实现的映射功能,能够泛化到未见过的新领域。此外,我们提出了一套策略来约束所学的特征空间,以缓解学习并提高映射网络的泛化能力,从而大大改善我们框架的最终性能。我们的建议通过在单眼深度估计和语义分割任务之间转移知识,在具有挑战性的合成到现实的适应场景中获得了引人注目的结果。
Availability of labelled data is the major obstacle to the deployment of deep learning algorithms for computer vision tasks in new domains. The fact that many frameworks adopted to solve different tasks share the same architecture suggests that there should be a way of reusing the knowledge learned in a specific setting to solve novel tasks with limited or no additional supervision. In this work, we first show that such knowledge can be shared across tasks by learning a mapping between task-specific deep features in a given domain. Then, we show that this mapping function, implemented by a neural network, is able to generalize to novel unseen domains. Besides, we propose a set of strategies to constrain the learned feature spaces, to ease learning and increase the generalization capability of the mapping network, thereby considerably improving the final performance of our framework. Our proposal obtains compelling results in challenging synthetic-to-real adaptation scenarios by transferring knowledge between monocular depth estimation and semantic segmentation tasks.
Others:
Cut and Learn for Unsupervised Object Detection and Instance Segmentation
标题:用于无监督物体检测和实例分割的切割和学习
作者:Xudong Wang, Rohit Girdhar, Stella X. Yu, Ishan Misra
文章链接:https://arxiv.org/abs/2301.11320
摘要:
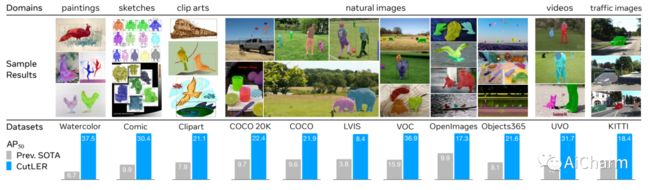
我们提出了Cut-and-LEaRn(CutLER),这是一种训练无监督的物体检测和分割模型的简单方法。我们利用自监督模型的特性,在没有监督的情况下 "发现 "物体,并放大它来训练最先进的定位模型,而不需要任何人类标签。CutLER首先使用我们提出的MaskCut方法为图像中的多个物体生成粗略的掩码,然后使用我们的稳健损失函数在这些掩码上学习一个检测器。我们通过对模型的预测进行自我训练来进一步提高性能。与之前的工作相比,CutLER更简单,与不同的检测架构兼容,并能检测多个物体。CutLER也是一个零拍摄的无监督检测器,在视频帧、绘画、素描等11个领域的基准上,检测性能AP50提高了2.7倍以上。通过微调,CutLER作为一个低照度检测器,在COCO上用5%的标签训练时,超过MoCo-v2 7.3%的APbox和6.6%的APmask。
We propose Cut-and-LEaRn (CutLER), a simple approach for training unsupervised object detection and segmentation models. We leverage the property of self-supervised models to 'discover' objects without supervision and amplify it to train a state-of-the-art localization model without any human labels. CutLER first uses our proposed MaskCut approach to generate coarse masks for multiple objects in an image and then learns a detector on these masks using our robust loss function. We further improve the performance by self-training the model on its predictions. Compared to prior work, CutLER is simpler, compatible with different detection architectures, and detects multiple objects. CutLER is also a zero-shot unsupervised detector and improves detection performance AP50 by over 2.7 times on 11 benchmarks across domains like video frames, paintings, sketches, etc. With finetuning, CutLER serves as a low-shot detector surpassing MoCo-v2 by 7.3% APbox and 6.6% APmask on COCO when training with 5% labels.