非极大值抑制(NMS)和soft-nms,及其代码实现
非极大值抑制(NMS)和soft-nms,及其代码实现
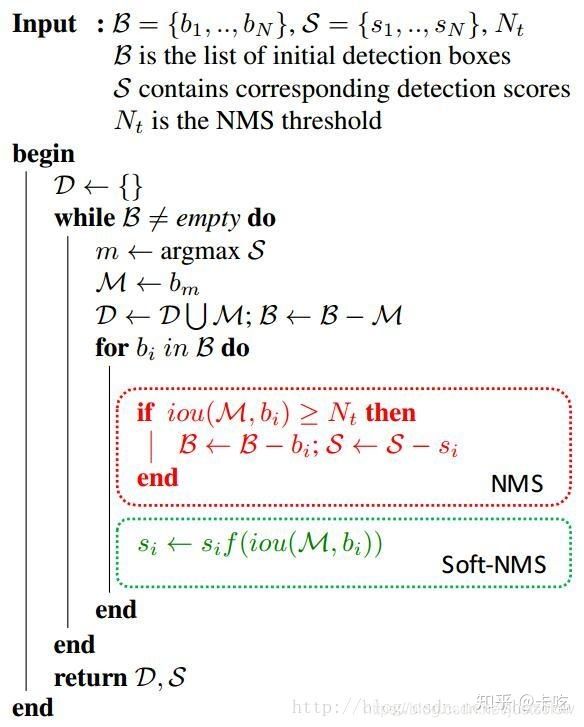
NMS算法的大致思想:对于有重叠的候选框:若大于规定阈值(某一提前设定的置信度)则删除,低于阈值的保留。对于无重叠的候选框:都保留。
注释很详细了,应该能看得懂。
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
def NMS(arr, thresh):
# 首先数据赋值和计算对应矩形框的面积
# arr的数据格式是arr = [[ xmin, ymin, xmax, ymax,scores]....]
x1 = arr[:, 0]
y1 = arr[:, 1]
x2 = arr[:, 2]
y2 = arr[:, 3]
score = arr[:, 4]
# 所有矩形框的面积
areas = (x2 - x1 + 1) * (y2 - y1 + 1)
# 取出分数从大到小排列的索引。.argsort()是从小到大排列,[::-1]是列表头和尾颠倒一下。
order = score.argsort()[::-1]
# 上面这两句比如分数score = [0.72 0.8 0.92 0.72 0.81 0.9 ]
# 对应的索引order = [2, 5, 4, 1, 3, 0]记住是取出索引,scores列表没变。
# 这边的keep用于存放,NMS后剩余的方框
keep = []
# order会剔除遍历过的方框,和合并过的方框
while order.size > 0:
# 取出第一个方框进行和其他方框比对,看有没有可以合并的,就是取最大score的索引
i = order[0]
# 因为我们这边分数已经按从大到小排列了。
# 所以如果有合并存在,也是保留分数最高的这个,也就是我们现在那个这个
# keep保留的是索引值,不是具体的分数。
keep.append(i)
# 计算交集的左上角和右下角
# 这里要注意,比如x1[i]这个方框的左上角x和所有其他的方框的左上角x的
xx1 = np.maximum(x1[i], x1[order[1:]])
yy1 = np.maximum(y1[i], y1[order[1:]])
xx2 = np.minimum(x2[i], x2[order[1:]])
yy2 = np.minimum(y2[i], y2[order[1:]])
# 这边要注意,如果两个方框相交,xx2-xx1和yy2-yy1是正的。
# 如果两个方框不相交,xx2-xx1和yy2-yy1是负的,我们把不相交的w和h设为0.
w = np.maximum(0, xx2-xx1+1)
h = np.maximum(0, yy2-yy1+1)
# 计算重叠面积就是上面说的交集面积。不相交因为W和H都是0,所以不相交面积为0
inter = w * h
# 这个就是IOU公式(交并比)。
# 得出来的ious是一个列表,里面拥有当前方框和其他所有方框的IOU结果。
ious = inter / (areas[i] + areas[order[1:]] - inter)
# 接下来是合并重叠度最大的方框,也就是合并ious中值大于thresh的方框
# 我们合并的操作就是把他们剔除,因为我们合并这些方框只保留下分数最高的。
# 我们经过排序当前我们操作的方框就是分数最高的,所以我们剔除其他和当前重叠度最高的方框
# 这里np.where(ious<=thresh)[0]是一个固定写法。
index = np.where(ious <= thresh)[0]
# 把留下来框在进行NMS操作
# 这边留下的框是去除当前操作的框,和当前操作的框重叠度大于thresh的框
# 每一次都会先去除当前操作框(n个框计算n-1个IOU值),所以索引的列表就会向前移动移位,要还原就+1,向后移动一位
order = order[index+1]
return keep
def plot_bbox(dets, c='k'):
x1 = dets[:, 0]
y1 = dets[:, 1]
x2 = dets[:, 2]
y2 = dets[:, 3]
plt.plot([x1, x2], [y1, y1], c)
plt.plot([x1, x1], [y1, y2], c)
plt.plot([x1, x2], [y2, y2], c)
plt.plot([x2, x2], [y1, y2], c)
plt.title(" nms")
if __name__ == '__main__':
boxes = np.array([[100, 100, 210, 210, 0.72],
[250, 250, 420, 420, 0.8],
[220, 220, 320, 330, 0.92],
[100, 100, 210, 210, 0.72],
[230, 240, 325, 330, 0.81],
[220, 230, 315, 340, 0.9]])
plt.figure(1)
ax1 = plt.subplot(1, 2, 1)
ax2 = plt.subplot(1, 2, 2)
plt.sca(ax1)
plot_bbox(boxes, 'k') # before nms
keep = NMS(boxes, thresh=0.7)
plt.sca(ax2)
plot_bbox(boxes[keep], 'r') # after nms
plt.show()
soft-nms就是在nms的基础上进行了一定程度的改进。
nms有什么问题呢?看一下下面这张图片:
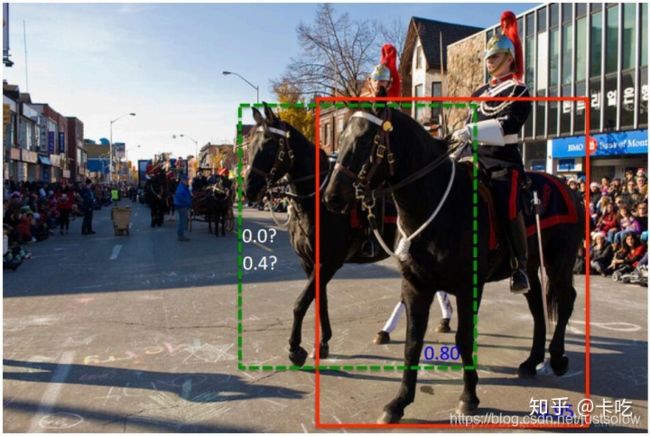
红色框和绿色框是当前的检测结果,二者的得分分别是0.95和0.80。如果按照传统的NMS进行处理,首先选中得分最高的红色框,然后绿色框就会因为与之重叠面积过大而被删掉。另一方面,NMS的阈值也不太容易确定,设小了会出现下图的情况(绿色框因为和红色框重叠面积较大而被删掉),设置过高又容易增大误检。
解决思路:不要粗鲁地删除所有IOU大于阈值的框,而是降低其置信度。
soft NMS算法的大致思路为:M为当前得分最高框,bi 为待处理框,bi 和M的IOU越大,bi 的得分si 就下降的越厉害。
NMS中置信度的公式为:

soft-nms中:
(1)线性加权:
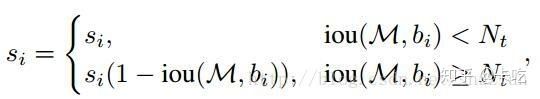
(2)高斯加权:
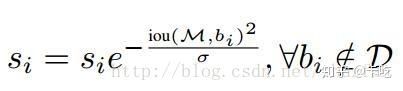
soft NMS仍然有问题:其阈值仍然需要手工设定
soft NMS的相关代码如下:
作者:IronMan
链接:https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/42018282
来源:知乎
著作权归作者所有。商业转载请联系作者获得授权,非商业转载请注明出处。
# coding:utf-8
import numpy as np
def soft_nms(boxes, sigma=0.5, Nt=0.1, threshold=0.001, method=1):
N = boxes.shape[0]
pos = 0
maxscore = 0
maxpos = 0
for i in range(N):
maxscore = boxes[i, 4]
maxpos = i
tx1 = boxes[i,0]
ty1 = boxes[i,1]
tx2 = boxes[i,2]
ty2 = boxes[i,3]
ts = boxes[i,4]
pos = i + 1
# get max box
while pos < N:
if maxscore < boxes[pos, 4]:
maxscore = boxes[pos, 4]
maxpos = pos
pos = pos + 1
# add max box as a detection
boxes[i,0] = boxes[maxpos,0]
boxes[i,1] = boxes[maxpos,1]
boxes[i,2] = boxes[maxpos,2]
boxes[i,3] = boxes[maxpos,3]
boxes[i,4] = boxes[maxpos,4]
# swap ith box with position of max box
boxes[maxpos,0] = tx1
boxes[maxpos,1] = ty1
boxes[maxpos,2] = tx2
boxes[maxpos,3] = ty2
boxes[maxpos,4] = ts
tx1 = boxes[i,0]
ty1 = boxes[i,1]
tx2 = boxes[i,2]
ty2 = boxes[i,3]
ts = boxes[i,4]
pos = i + 1
# NMS iterations, note that N changes if detection boxes fall below threshold
while pos < N:
x1 = boxes[pos, 0]
y1 = boxes[pos, 1]
x2 = boxes[pos, 2]
y2 = boxes[pos, 3]
s = boxes[pos, 4]
area = (x2 - x1 + 1) * (y2 - y1 + 1)
iw = (min(tx2, x2) - max(tx1, x1) + 1)
if iw > 0:
ih = (min(ty2, y2) - max(ty1, y1) + 1)
if ih > 0:
ua = float((tx2 - tx1 + 1) * (ty2 - ty1 + 1) + area - iw * ih)
ov = iw * ih / ua #iou between max box and detection box
if method == 1: # linear
if ov > Nt:
weight = 1 - ov
else:
weight = 1
elif method == 2: # gaussian
weight = np.exp(-(ov * ov)/sigma)
else: # original NMS
if ov > Nt:
weight = 0
else:
weight = 1
boxes[pos, 4] = weight*boxes[pos, 4]
print(boxes[:, 4])
# if box score falls below threshold, discard the box by swapping with last box
# update N
if boxes[pos, 4] < threshold:
boxes[pos,0] = boxes[N-1, 0]
boxes[pos,1] = boxes[N-1, 1]
boxes[pos,2] = boxes[N-1, 2]
boxes[pos,3] = boxes[N-1, 3]
boxes[pos,4] = boxes[N-1, 4]
N = N - 1
pos = pos - 1
pos = pos + 1
keep = [i for i in range(N)]
return keep
boxes = np.array([[100, 100, 150, 168, 0.63],[166, 70, 312, 190, 0.55],[221, 250, 389, 500, 0.79],[12, 190, 300, 399, 0.9],[28, 130, 134, 302, 0.3]])
keep = soft_nms(boxes)
print(keep)
参考自:
https://www.zhihu.com/search?type=content&q=soft-nms
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/128125301