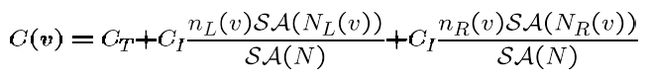前言:简单的数据结构的尝试,主要是为研究RTRT准备,折腾了不少时间。从我C++博客转过来的,希望大伙觉得有些价值。
kD 树是二叉树结构的一个变种,当前主要用于加速光纤跟踪的遍历过程。最简单的排序二叉树以各个元素的大小关系作为分割点,而 kD 树简而言之就是从数据中选择一个“维度”构造一个超平面对数据集进行分割。比如要对学生数据进行分割,找出哪些学生的生日小于 2 月 18 日,那么就只要遍历整个集合,把所有的数据分成。如果又要在符合第一次条件的学生中找出哪些学生是来自南京的,那么就只要再次进行比较规划就可以办到了。 kD 树的带来的性能提升很高,让我们看一下常用加速结构的复杂度 [1] ,从 O(N) 到 O(logN) :
Bounding Volumn Hierarchy
Grid
Octree (包括 Quadtree )
kD Tree
一般来说,构造 kD 树的方式有两种:排序和扫描。我们参考了一些加速构造 kD 树的方法,如采样,再结合实际的 3D 模型来为大家说明具体的操作方法。
基本概念:
由于 kD 树主要用于光线跟踪等 3D 图形学领域,所以很有必要把光线跟踪的基本方法弄清楚。我们知道场景都是由三角形组成,整个空间的三角形组成了模型的拓扑结构。传统的光栅化过程就是把所有变换过的三角形投射到屏幕上,也就是写入帧缓冲。而光线跟踪的最初概念来自于绘画。 15 世纪意大利 Albrecht Dűrer 发明了网格作画的方法,也就是在待画的物体前放一张同画布一样大小的纸质半透明网格,然后依次透过每个小格看物体,绘制那个小格子的图画,当把所有的小格子都画满了后,一幅画也就画好了。
我们由此可以想到暴力测试法,也就是从一个网格里发出光线后,检测场景中每个三角形,然后确定点亮那个网格(像素)的是什么颜色。 kD 树可以大幅度加速这个过程,类似于二叉树的遍历。
准备材料:
在真实的实现过程中,我们总是要面对许多模型的格式,比如 D3D 的 X 格式, QUAKE 系列所使用的 MD3/5 模型格式,以及诸多初学者所头疼的 3DS ASE 格式。需要补充的是,如果牵涉到在场景中使用骨骼动画,那么只有选择 MD5 或者 X 格式, 3DS/ASE 文件中没有记录骨骼动画所需要的权重节点等数据。
对于静态模型来说,主要数据包括:顶点数据,三角形索引,纹理坐标,顶点向量(有可能没有)。绘制模型的时候,用三角形索引来寻址,依次抽取顶点数组中的数据进行绘制。为了缩短开发周期,我们使用了来自 sourceforge.net 的 lib3ds[2] 开源库来处理 3DS 模型。如图:
这个 Hanana 模型由 10955 个顶点, 16221 个面(三角形)组成。我们用它来生成我们所需要的 kD 树加速结构。
思路优先:
我们的 kD 树的节点模型究竟应该是什么样子的呢?让我们看一下定义:
unsigned int flagDimAndOffset;
// bits 0..1 : 0 1 2代表x y z维
// bits 2..30 : offset to left child
// bit 31 : 是否是leaf
float splitCoordinates;
};
struct kDLeaf{
unsigned int flagAndOffset;
// bits 0..30 : 在三角形数组组中的偏移量
// bit 31 : 是否是leaf
unsigned int objectCount; // 三角形树的数目
};
typedef union{
kDLeaf leaf;
kDInner inner;
}kDNode; // 共用体,统inner和leaf统称为为Node
事实上,这样一上来就如此的精简并不方便构建kD树,我们先用普通的容易理解的定义表现一个Node
float SplitPos;
ulong AbsoluteOffset;
};
struct KDNode
{
KDNode * Left;
KDNode * Right;
offsetorsplitpos tag;
ulong Count;//当这个节电作为Inner使用的时候,Count储存了Dimsion
};
每个三角形的 AABB(Axis Aligned Bounding Box 即轴对称绑定盒 ) 也是必不可少的结构。 AABB 就很简单了,可以定义成这样:
struct AABB{
float min[3],max[3];
};
我们之所以要把每个三角形都打散,是为了计算合适的 Split Plane 位置,你可以想象为从什么地方把场景分成两半,也就是把一堆三角形分成两部分,代码级的思路就是,计算合适的数组偏移量。那么什么叫做合适的呢?请看下面的这个公式 [3] :
看似好像很复杂,其实可以化简为这样的公式: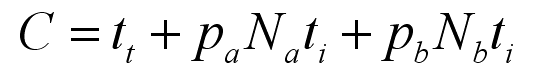
在这里, Ct 指遍历整个节点包含的三角形遍历时间,也就是渲染这一簇三角形的时间; Cl 指 Split Plane“ 左边”的三角形遍历时间,同理 Cr 是“右边”的遍历时间。引用的一些资料认为,
事实上, Cost(x) 是两个单调函数 Cl(x) 、 Cr(x) 的线性叠加。我们要尽量找到 Cost(x) 最小的某个空间位置,或者是某一个三角形边界,进而分割场景三角形。
显然,这肯定由三步组成:
1、选择合适的 Split Plane ,可以有三个维度,并且可以容易推断总共有 2n 个
2、数数看左边有多少个 AABBs
3、数数看右边有多少个 AABBs
下面我们开始讨论 2 种方法:排序与扫描。
Sort 排序
排序很容易理解。沿着轴将所有三角形的 AABB 排序(也就是对三角形索引数组进行排序)。排序后就可以直接把想要得位置和三角形数目带入公式计算,如果绘制为函数图像可以获得最光滑连续的图形。总花费为 O(nlogn) 。
Scan 扫描
扫描有些罗嗦,不过也很容易实现,最重要的是目前已经有成功的应用 [4] 。指定场景中的一个平面,遍历三角形比较大小,记录落在左边和右边的数目,再带入公式。如果要获得多个 Cost 数值,就必须要选择多个位置进行计算。每次都要遍历全部的三角形。经过处理后也可以达到 O(nlogn) 的复杂度,不过结合了采样技术后可以获得近似准确的结果,而且花费小的多。而且,这个过程是可以使用 SIMD 加速的。
还有一些技巧和疑问 [3] :
1、是否总是计算三个轴中最小的那个位置,还是总是从一个轴计算?
2、树需要细分到何种程度?每个 Leaf 需要有多少个三角形?
现在我们可以做进一步的推测,如果希望用光线跟踪一个动态的场景,那么每当我们变换过矩阵后,都需要重新构造一次 kD 树,所以为了达到实时交互式的速度,必须要对关键的步骤进行优化。而且生成树的质量与遍历的性能关系十分密切。
我们的思路有了,下面可以构思具体的实现过程
A. 准备三角形索引数组 Tris[] 。
B. 获得整个场景的 AABB V ,其中 V.min[0] 就是场景的左边界,以此类推。
C. 通过三角形索引数组读取 3 个顶点,构造每个三角形的 AABB ,储存到一个容器中 vector
D. 获得三角形 AABBs 的数目 N ,如果大于一个数值比如 1024 就用步骤 FG 计算 3 次,否则只计算一次。获得 AABBs 的开头和末尾指针(迭代器)。
E. 如果选择 Sort ,那么就要先对 AABBs 中的元素排序。这里我们采用 Scan 。
F. 在 (min[AXIS],max[AXIS]) 之间找几个固定平面,比如 8 个。 AXIS 指选择的坐标轴。
H. 带入公式计算,选择 Cost 最小的 Split Position ,生成 Node 。如果已经达到中止条件,那么就生成 Leaf Node ,否则生成 Inner Node 。把 v 从 Split Position 分成两个 Voxel Vl 与 Vr 。把 AABBs 分割为两个,从与 Split Position 最近的三角形开始。
G. 遍历 AABBs 容器,比较平面和每个元素的位置,记录 8 对数据。
I. 带入 Vl 与 Vr 分别从 D 开始迭代。
下面是分隔这个模型的输出信息:
Left Voxel has : 12377 Right Voxel has : 384
Left Voxel has : 2912 Right Voxel has : 946
Left Voxel has : 1025 Right Voxel has : 188
Left Voxel has : 415 Right Voxel has : 610
Left Voxel has : 128 Right Voxel has : 287
Left Voxel has : 68 Right Voxel has : 60
Leaf LEVEL : 5 Count : 128
Left Voxel has : 145 Right Voxel has : 142
Left Voxel has : 77 Right Voxel has : 68
Leaf LEVEL : 6 Count : 145
Left Voxel has : 61 Right Voxel has : 81
Leaf LEVEL : 6 Count : 142
Left Voxel has : 218 Right Voxel has : 392
Left Voxel has : 97 Right Voxel has : 121
Leaf LEVEL : 5 Count : 218
Left Voxel has : 211 Right Voxel has : 181
Left Voxel has : 114 Right Voxel has : 97
Leaf LEVEL : 6 Count : 211
Left Voxel has : 82 Right Voxel has : 99
Leaf LEVEL : 6 Count : 181
Left Voxel has : 772 Right Voxel has : 111
Left Voxel has : 373 Right Voxel has : 399
Left Voxel has : 194 Right Voxel has : 179
Left Voxel has : 82 Right Voxel has : 112
Leaf LEVEL : 6 Count : 194
Left Voxel has : 111 Right Voxel has : 68
Leaf LEVEL : 6 Count : 179
Left Voxel has : 190 Right Voxel has : 209
Left Voxel has : 99 Right Voxel has : 91
Leaf LEVEL : 6 Count : 190
Left Voxel has : 63 Right Voxel has : 146
Left Voxel has : 516 Right Voxel has : 599
Left Voxel has : 246 Right Voxel has : 270
Left Voxel has : 124 Right Voxel has : 122
Leaf LEVEL : 6 Count : 246
Left Voxel has : 126 Right Voxel has : 144
Left Voxel has : 285 Right Voxel has : 314
Left Voxel has : 150 Right Voxel has : 135
Left Voxel has : 152 Right Voxel has : 162
Left Voxel has : 4180 Right Voxel has : 528
Left Voxel has : 2220 Right Voxel has : 196
Left Voxel has : 1211 Right Voxel has : 100
Left Voxel has : 502 Right Voxel has : 709
Left Voxel has : 235 Right Voxel has : 267
Left Voxel has : 343 Right Voxel has : 366
Left Voxel has : 471 Right Voxel has : 538
Left Voxel has : 201 Right Voxel has : 270
Left Voxel has : 263 Right Voxel has : 275
Left Voxel has : 924 Right Voxel has : 103
Left Voxel has : 428 Right Voxel has : 496
Left Voxel has : 184 Right Voxel has : 244
Left Voxel has : 286 Right Voxel has : 210
Left Voxel has : 440 Right Voxel has : 596
Left Voxel has : 211 Right Voxel has : 229
Left Voxel has : 310 Right Voxel has : 286
Left Voxel has : 2437 Right Voxel has : 284
Left Voxel has : 1228 Right Voxel has : 120
Left Voxel has : 558 Right Voxel has : 670
Left Voxel has : 303 Right Voxel has : 255
Left Voxel has : 298 Right Voxel has : 372
Left Voxel has : 578 Right Voxel has : 631
Left Voxel has : 295 Right Voxel has : 283
Left Voxel has : 302 Right Voxel has : 329
Left Voxel has : 1466 Right Voxel has : 138
Left Voxel has : 805 Right Voxel has : 661
Left Voxel has : 430 Right Voxel has : 375
Left Voxel has : 346 Right Voxel has : 315
Left Voxel has : 653 Right Voxel has : 729
Left Voxel has : 347 Right Voxel has : 306
Left Voxel has : 367 Right Voxel has : 362
Left Voxel has : 2319 Right Voxel has : 152
Left Voxel has : 1413 Right Voxel has : 906
Left Voxel has : 825 Right Voxel has : 588
Left Voxel has : 437 Right Voxel has : 388
Left Voxel has : 180 Right Voxel has : 257
Left Voxel has : 98 Right Voxel has : 82
Leaf LEVEL : 6 Count : 180
Left Voxel has : 150 Right Voxel has : 107
Left Voxel has : 191 Right Voxel has : 197
Left Voxel has : 90 Right Voxel has : 101
Leaf LEVEL : 6 Count : 191
Left Voxel has : 68 Right Voxel has : 129
Left Voxel has : 294 Right Voxel has : 294
Left Voxel has : 150 Right Voxel has : 144
Left Voxel has : 91 Right Voxel has : 59
Leaf LEVEL : 6 Count : 150
Left Voxel has : 51 Right Voxel has : 93
Leaf LEVEL : 6 Count : 144
Left Voxel has : 153 Right Voxel has : 141
Left Voxel has : 105 Right Voxel has : 48
Leaf LEVEL : 6 Count : 153
Left Voxel has : 49 Right Voxel has : 92
Leaf LEVEL : 6 Count : 141
Left Voxel has : 457 Right Voxel has : 449
Left Voxel has : 214 Right Voxel has : 243
Left Voxel has : 124 Right Voxel has : 90
Leaf LEVEL : 5 Count : 214
Left Voxel has : 102 Right Voxel has : 141
Left Voxel has : 79 Right Voxel has : 62
Leaf LEVEL : 6 Count : 141
Left Voxel has : 196 Right Voxel has : 253
Left Voxel has : 99 Right Voxel has : 97
Leaf LEVEL : 5 Count : 196
Left Voxel has : 133 Right Voxel has : 120
Left Voxel has : 56 Right Voxel has : 77
Leaf LEVEL : 6 Count : 133
Left Voxel has : 791 Right Voxel has : 733
Left Voxel has : 462 Right Voxel has : 329
Left Voxel has : 228 Right Voxel has : 234
Left Voxel has : 129 Right Voxel has : 99
Left Voxel has : 64 Right Voxel has : 65
Leaf LEVEL : 6 Count : 129
Left Voxel has : 117 Right Voxel has : 117
Leaf LEVEL : 5 Count : 234
Left Voxel has : 171 Right Voxel has : 158
Left Voxel has : 90 Right Voxel has : 81
Leaf LEVEL : 5 Count : 171
Left Voxel has : 88 Right Voxel has : 70
Leaf LEVEL : 5 Count : 158
Left Voxel has : 423 Right Voxel has : 310
Left Voxel has : 205 Right Voxel has : 218
Left Voxel has : 114 Right Voxel has : 91
Leaf LEVEL : 5 Count : 205
Left Voxel has : 112 Right Voxel has : 106
Leaf LEVEL : 5 Count : 218
Left Voxel has : 177 Right Voxel has : 133
Left Voxel has : 86 Right Voxel has : 91
Leaf LEVEL : 5 Count : 177
Left Voxel has : 77 Right Voxel has : 56
Leaf LEVEL : 5 Count : 133
其中, C 可以用 foreach , H 可以用 partition ( stable_partition )等 STL 的算法。
核心的代码如下:
{
for ( AABB * itr = BeginItr ; itr != EndItr; itr ++ ){
( * Cl) += ( (itr -> max[Axis] < SplitPos ) ? 1 : 0 );
( * Cr) += ( (itr -> min[Axis] > SplitPos ) ? 1 : 0 );
}
};
{
if ( TriCount < 128 || Level > MAX_LEVEL){
return true ;
}
return false ;
};
{
float half_width = ( AABB.max[::gSplitAxis] - AABB.min[::gSplitAxis] ) * 0.5f ;
return (AABB.max[::gSplitAxis] - ::gSplitPos) < half_width ? true : false ;
};
float SAHCost(AXIS Axis, ulong * Cl, ulong * Cr,AABB & V, float SplitPos)
{
ulong Nl = * Cl;
ulong Nr = * Cr;
float Length = V.max[Axis] - V.min[Axis];
float L = SplitPos - V.min[Axis],R = SplitPos - V.max[Axis];
float Pl = L / Length;
float Pr = 1.0f - Pl;
float Tt = TRAVERSAL_TIME;
float Til = Nl * INTERSECTION_TIME,Tir = Nr * INTERSECTION_TIME;
return Tt + Pl * Nl * Til + Pr * Nr * Tir;
};
{
ulong TotalTriCount = EndItr - BeginItr;
if ( Terminate(TotalTriCount,Level) )
return ;
float SplitLoc[ 7 ];
float Cost[ 7 ];
ulong Cl = 0 ,Cr = 0 ;
float MinLoc = V.min[Axis],MaxLoc = V.max[Axis];
float step = (MaxLoc - MinLoc) / 8.0f ;
for ( int i = 0 ;i < 7 ;i ++ ){
SplitLoc[i] = MinLoc + step * float (i + 1 );
Count(BeginItr,EndItr,Axis,SplitLoc[i], & Cl, & Cr);
Cost[i] = SAHCost(Axis, & Cl, & Cr,V,SplitLoc[i]);
Cl = Cr = 0 ;
}
float * pGoodCostPtr = min_element(Cost,Cost + 7 );
size_t _Pos = pGoodCostPtr - Cost;
::gSplitPos = SplitLoc[_Pos];
::gSplitAxis = Axis;
AABB * MidItr = stable_partition(BeginItr,EndItr,IsUpboundSmaller);
Cl = MidItr - BeginItr;
Cr = EndItr - MidItr;
cout << " Left Voxel has : " << Cl << " \tRight Voxel has : " << Cr << endl;
AABB Vl,Vr;
if ( Cr > 128 || Cl > 128 ){
Root = new KDNode; // Root
Root -> Left = new KDNode;
Root -> Right = new KDNode;
Root -> tag.SplitPos = ::gSplitPos;
Root -> Count = Axis; // Ulong.MaxSize - Axis 代表坐标 因为Left Right肯定不是0
switch (Axis){
case X :
Vl.min[ 0 ] = V.min[ 0 ];
Vl.min[ 1 ] = V.min[ 1 ];
Vl.min[ 2 ] = V.min[ 2 ];
Vl.max[ 0 ] = ::gSplitPos;
Vl.max[ 1 ] = V.max[ 1 ];
Vl.max[ 2 ] = V.max[ 2 ];
Vr.min[ 0 ] = ::gSplitPos;
Vr.min[ 1 ] = V.min[ 1 ];
Vr.min[ 2 ] = V.min[ 2 ];
Vr.max[ 0 ] = V.max[ 0 ];
Vr.max[ 1 ] = V.max[ 1 ];
Vr.max[ 2 ] = V.max[ 2 ];
break ;
case Y :
Vl.min[ 0 ] = V.min[ 0 ];
Vl.min[ 1 ] = V.min[ 1 ];
Vl.min[ 2 ] = V.min[ 2 ];
Vl.max[ 0 ] = V.max[ 0 ];
Vl.max[ 1 ] = ::gSplitPos;
Vl.max[ 2 ] = V.max[ 2 ];
Vr.min[ 0 ] = V.min[ 0 ];
Vr.min[ 1 ] = ::gSplitPos;
Vr.min[ 2 ] = V.min[ 2 ];
Vr.max[ 0 ] = V.max[ 0 ];
Vr.max[ 1 ] = V.max[ 1 ];
Vr.max[ 2 ] = V.max[ 2 ];
break ;
case Z :
Vl.min[ 0 ] = V.min[ 0 ];
Vl.min[ 1 ] = V.min[ 1 ];
Vl.min[ 2 ] = V.min[ 2 ];
Vl.max[ 0 ] = V.max[ 0 ];
Vl.max[ 1 ] = V.max[ 1 ];
Vl.max[ 2 ] = ::gSplitPos;
Vr.min[ 0 ] = V.min[ 0 ];
Vr.min[ 1 ] = V.min[ 1 ];
Vr.min[ 2 ] = ::gSplitPos;
Vr.max[ 0 ] = V.max[ 0 ];
Vr.max[ 1 ] = V.max[ 1 ];
Vr.max[ 2 ] = V.max[ 2 ];
break ;
}
} else {
Root = new KDNode; // Leaf
Root -> Left = 0 ;Root -> Right = 0 ;
Root -> tag.AbsoluteOffset = BeginItr - ::gScenePtr;
Root -> Count = EndItr - BeginItr;
//cout << " Leaf LEVEL : " << Level << " \tCount : " << Root -> Count << endl;
return ;
}
++ Level;
KDTreeBuild(Root -> Left,Vl,BeginItr,MidItr,Axis,Level);
KDTreeBuild(Root -> Right,Vr,MidItr,EndItr,Axis,Level);
};
这样,我们就得到了一颗完整的基于SAH的KD树。下面就是遍历。
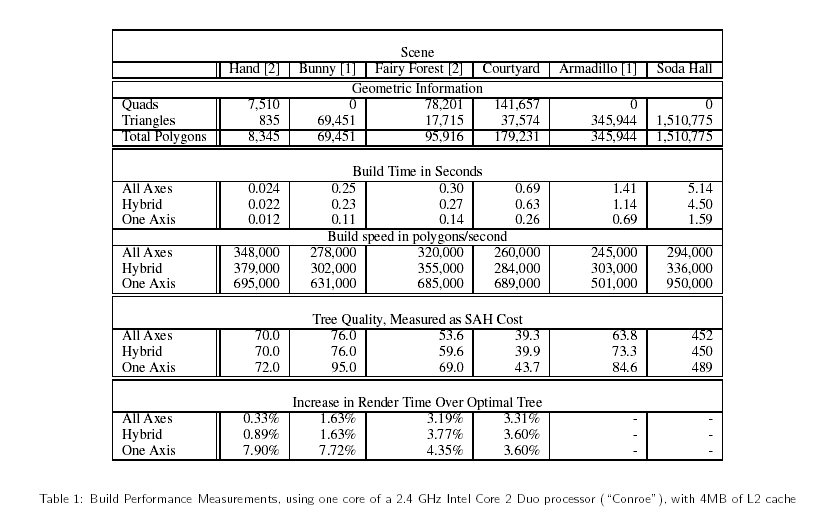
由于不同渲染要求的不同,遍历代码也大不相同。不过我们可以知道,kD树及适用于光线跟踪程序。目前在多款开源光线跟踪器,比如blender就采用了kD树作为加速结构。而且必须要提到的是,如果希望在Realtime Rendering的程序中使用光线跟踪技术 —— 虽然说在目前的情况下还不是很现实,不过这毕竟是个趋势,因为只有光线跟踪才能够精确的模拟物理全局光照,光栅化系统先天限制无法达到,虽然说Voxel渲染是一个折中的办法。我引用下面的这张表格[3]作为性能参照。
可是这里又会出现一个问题,就是在实时渲染程序中如何处理多纹理贴图?我们必须要模拟管线的处理过程。
A、如果场景中有运动的模型,标记出来
B、在世界坐标系统中对运动模型作矩阵变换,类似于OpenGL的MATRIX操作
C、把所有,各就各位的模型顶点、向量、纹理坐标、索引整合在一起。每当在这个链表中加入新的模型的时候,都要把现在模型的所有索引加上链表中已经加入的所有顶点的数目,构建一个好像是整体连续的单个模型。同时标记纹理,应该储存一个顶点偏移量以及三角形数目,用来标示这个纹理属于哪个模型。
D、根据视点,遍历kD树,把符合条件的三角形数目放入一个全局队列
E、渲染队列中的所有三角形,作为一个Frame。重复A。
目前由德国萨尔大学计算机科学系所开发的实时光线跟踪硬件与软件已经成功的问世,最令人振奋的莫过于表现了一个全部由光线跟踪引擎实现的Quake3游戏。有兴趣的朋友可以去[4]看看。
[1]Computer Graphics WS05/06 – kD-Tree and Optimization for Ray Tracing
[2]Lib3ds http://lib3ds.sf.net/
[3]Fast kd-tree Construction with an Adaptive Error-Bounded Heuristic