DynaSLAM-3 DynaSLAM中Mask R-CNN部分源码解析(Ⅱ)
目录
1.FPN
1.1 FPN层原理
1.2 FPN代码解析
2. 候选框的生成
2.1 根据特征图生成候选框
1.FPN
1.1 FPN层原理
在Faster R-CNN网络中,提取特征的时候,将原始数据经过一系列的卷积层,我们只用最后一层的特征图进行提取。
比如五层卷积神经网络,直接把第五层的output结果拿出来当作特征提取的结果了。
但是我们在进行特征提取的时候,我们认为网络层数越高提取信息越丰富。(随着卷积层的增加越往后的卷积层提取出来的特征越是包含整体的语义信息)(原因是越往后的卷积层感受野越大、特征融合越多)。但是越往后的特征层越容易忽略前面的原始图片的细节轮廓信息(小物体信息)。
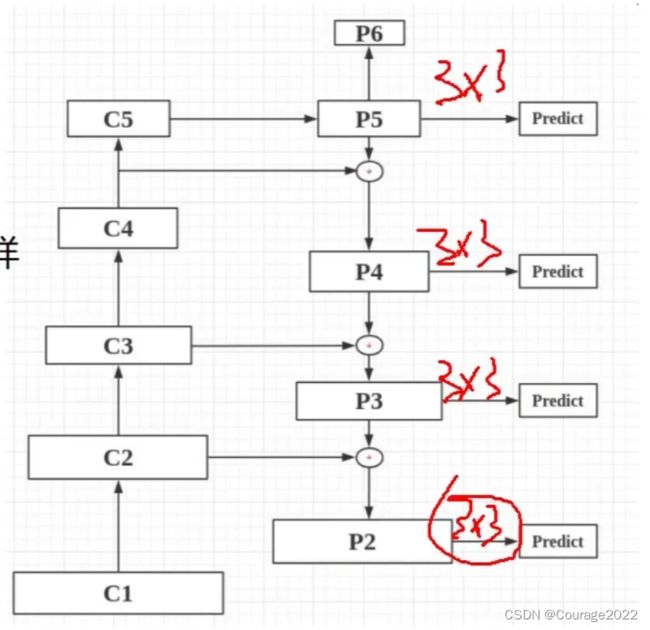
于是我们提出了FPN层:我们用多层特征层来得到特征提取的结果。
基本思想:将多个阶段特征图融合在一起,这就相当于既有了高层的语义特征,也有了低层的轮廓特征。理解阶段(在resnet网络中有多个“阶段”,有些特征图进行卷积之后它的特征图大小发生变化:
变成
,这叫做一个”阶段“,因此通过每一个阶段特征图融合在一起相当于既有高层的描述了整个原始图片的语义特征的信息既有低层的描述的单一的轮廓信息)。因此不是简单的做一个图像金字塔,而是对图像进行卷积特征提取后把不同阶段特征拿过来用。
融合:
这里C1-C5是resnet101的五个阶段的最后一层,每个阶段特征图尺寸不同。随着卷积的进行,特征图的个数越来越多特征图的大小越来越小。
C1的特征图大小为
,C2的特征图大小
.....,我们利用
的卷积核可以改变特征层的个数。这里比如C5是
的,我们通过
的卷积核对其进行卷积,得到的P5是
的。同理,P4是
的尺寸,他俩的大小规格不匹配怎么办呢?
进行自上而下的上采样!利用双线性插值的办法,让P5特征图尺寸变成
和P4进行加法操作进行融合.....。最终得到FPN的五个特征层Predict1、Predict2、Predict3、Predict4、Predict5。
1.2 FPN代码解析
在model.py中的MaskRCNN类中:
class MaskRCNN(): """Encapsulates the Mask RCNN model functionality. The actual Keras model is in the keras_model property. """ def __init__(self, mode, config, model_dir): """ mode: Either "training" or "inference" config: A Sub-class of the Config class model_dir: Directory to save training logs and trained weights """ assert mode in ['training', 'inference'] self.mode = mode self.config = config self.model_dir = model_dir self.set_log_dir() self.keras_model = self.build(mode=mode, config=config) def build(self, mode, config): """Build Mask R-CNN architecture. input_shape: The shape of the input image. mode: Either "training" or "inference". The inputs and outputs of the model differ accordingly. """ assert mode in ['training', 'inference'] # Image size must be dividable by 2 multiple times h, w = config.IMAGE_SHAPE[:2] if h / 2**6 != int(h / 2**6) or w / 2**6 != int(w / 2**6): raise Exception("Image size must be dividable by 2 at least 6 times " "to avoid fractions when downscaling and upscaling." "For example, use 256, 320, 384, 448, 512, ... etc. ") # Inputs input_image = KL.Input( shape=config.IMAGE_SHAPE.tolist(), name="input_image") input_image_meta = KL.Input(shape=[None], name="input_image_meta") if mode == "training": # RPN GT input_rpn_match = KL.Input( shape=[None, 1], name="input_rpn_match", dtype=tf.int32) input_rpn_bbox = KL.Input( shape=[None, 4], name="input_rpn_bbox", dtype=tf.float32) # Detection GT (class IDs, bounding boxes, and masks) # 1. GT Class IDs (zero padded) input_gt_class_ids = KL.Input( shape=[None], name="input_gt_class_ids", dtype=tf.int32) # 2. GT Boxes in pixels (zero padded) # [batch, MAX_GT_INSTANCES, (y1, x1, y2, x2)] in image coordinates input_gt_boxes = KL.Input( shape=[None, 4], name="input_gt_boxes", dtype=tf.float32) # Normalize coordinates h, w = K.shape(input_image)[1], K.shape(input_image)[2] image_scale = K.cast(K.stack([h, w, h, w], axis=0), tf.float32) gt_boxes = KL.Lambda(lambda x: x / image_scale)(input_gt_boxes) # 3. GT Masks (zero padded) # [batch, height, width, MAX_GT_INSTANCES] if config.USE_MINI_MASK: input_gt_masks = KL.Input( shape=[config.MINI_MASK_SHAPE[0], config.MINI_MASK_SHAPE[1], None], name="input_gt_masks", dtype=bool) else: input_gt_masks = KL.Input( shape=[config.IMAGE_SHAPE[0], config.IMAGE_SHAPE[1], None], name="input_gt_masks", dtype=bool) # Build the shared convolutional layers. # Bottom-up Layers # Returns a list of the last layers of each stage, 5 in total. # Don't create the thead (stage 5), so we pick the 4th item in the list. _, C2, C3, C4, C5 = resnet_graph(input_image, config.BACKBONE, stage5=True) # Top-down Layers # TODO: add assert to varify feature map sizes match what's in config P5 = KL.Conv2D(256, (1, 1), name='fpn_c5p5')(C5) P4 = KL.Add(name="fpn_p4add")([ KL.UpSampling2D(size=(2, 2), name="fpn_p5upsampled")(P5), KL.Conv2D(256, (1, 1), name='fpn_c4p4')(C4)]) P3 = KL.Add(name="fpn_p3add")([ KL.UpSampling2D(size=(2, 2), name="fpn_p4upsampled")(P4), KL.Conv2D(256, (1, 1), name='fpn_c3p3')(C3)]) P2 = KL.Add(name="fpn_p2add")([ KL.UpSampling2D(size=(2, 2), name="fpn_p3upsampled")(P3), KL.Conv2D(256, (1, 1), name='fpn_c2p2')(C2)]) # Attach 3x3 conv to all P layers to get the final feature maps. P2 = KL.Conv2D(256, (3, 3), padding="SAME", name="fpn_p2")(P2) P3 = KL.Conv2D(256, (3, 3), padding="SAME", name="fpn_p3")(P3) P4 = KL.Conv2D(256, (3, 3), padding="SAME", name="fpn_p4")(P4) P5 = KL.Conv2D(256, (3, 3), padding="SAME", name="fpn_p5")(P5) # P6 is used for the 5th anchor scale in RPN. Generated by # subsampling from P5 with stride of 2. P6 = KL.MaxPooling2D(pool_size=(1, 1), strides=2, name="fpn_p6")(P5) # Note that P6 is used in RPN, but not in the classifier heads. rpn_feature_maps = [P2, P3, P4, P5, P6] mrcnn_feature_maps = [P2, P3, P4, P5] # Generate Anchors self.anchors = utils.generate_pyramid_anchors(config.RPN_ANCHOR_SCALES, config.RPN_ANCHOR_RATIOS, config.BACKBONE_SHAPES, config.BACKBONE_STRIDES, config.RPN_ANCHOR_STRIDE) # RPN Model rpn = build_rpn_model(config.RPN_ANCHOR_STRIDE, len(config.RPN_ANCHOR_RATIOS), 256) # Loop through pyramid layers layer_outputs = [] # list of lists for p in rpn_feature_maps: layer_outputs.append(rpn([p])) # Concatenate layer outputs # Convert from list of lists of level outputs to list of lists # of outputs across levels. # e.g. [[a1, b1, c1], [a2, b2, c2]] => [[a1, a2], [b1, b2], [c1, c2]] output_names = ["rpn_class_logits", "rpn_class", "rpn_bbox"] outputs = list(zip(*layer_outputs)) outputs = [KL.Concatenate(axis=1, name=n)(list(o)) for o, n in zip(outputs, output_names)] rpn_class_logits, rpn_class, rpn_bbox = outputs # Generate proposals # Proposals are [batch, N, (y1, x1, y2, x2)] in normalized coordinates # and zero padded. proposal_count = config.POST_NMS_ROIS_TRAINING if mode == "training"\ else config.POST_NMS_ROIS_INFERENCE rpn_rois = ProposalLayer(proposal_count=proposal_count, nms_threshold=config.RPN_NMS_THRESHOLD, name="ROI", anchors=self.anchors, config=config)([rpn_class, rpn_bbox]) if mode == "training": # Class ID mask to mark class IDs supported by the dataset the image # came from. _, _, _, active_class_ids = KL.Lambda(lambda x: parse_image_meta_graph(x), mask=[None, None, None, None])(input_image_meta) if not config.USE_RPN_ROIS: # Ignore predicted ROIs and use ROIs provided as an input. input_rois = KL.Input(shape=[config.POST_NMS_ROIS_TRAINING, 4], name="input_roi", dtype=np.int32) # Normalize coordinates to 0-1 range. target_rois = KL.Lambda(lambda x: K.cast( x, tf.float32) / image_scale[:4])(input_rois) else: target_rois = rpn_rois # Generate detection targets # Subsamples proposals and generates target outputs for training # Note that proposal class IDs, gt_boxes, and gt_masks are zero # padded. Equally, returned rois and targets are zero padded. rois, target_class_ids, target_bbox, target_mask =\ DetectionTargetLayer(config, name="proposal_targets")([ target_rois, input_gt_class_ids, gt_boxes, input_gt_masks]) # Network Heads # TODO: verify that this handles zero padded ROIs mrcnn_class_logits, mrcnn_class, mrcnn_bbox =\ fpn_classifier_graph(rois, mrcnn_feature_maps, config.IMAGE_SHAPE, config.POOL_SIZE, config.NUM_CLASSES) mrcnn_mask = build_fpn_mask_graph(rois, mrcnn_feature_maps, config.IMAGE_SHAPE, config.MASK_POOL_SIZE, config.NUM_CLASSES) # TODO: clean up (use tf.identify if necessary) output_rois = KL.Lambda(lambda x: x * 1, name="output_rois")(rois) # Losses rpn_class_loss = KL.Lambda(lambda x: rpn_class_loss_graph(*x), name="rpn_class_loss")( [input_rpn_match, rpn_class_logits]) rpn_bbox_loss = KL.Lambda(lambda x: rpn_bbox_loss_graph(config, *x), name="rpn_bbox_loss")( [input_rpn_bbox, input_rpn_match, rpn_bbox]) class_loss = KL.Lambda(lambda x: mrcnn_class_loss_graph(*x), name="mrcnn_class_loss")( [target_class_ids, mrcnn_class_logits, active_class_ids]) bbox_loss = KL.Lambda(lambda x: mrcnn_bbox_loss_graph(*x), name="mrcnn_bbox_loss")( [target_bbox, target_class_ids, mrcnn_bbox]) mask_loss = KL.Lambda(lambda x: mrcnn_mask_loss_graph(*x), name="mrcnn_mask_loss")( [target_mask, target_class_ids, mrcnn_mask]) # Model inputs = [input_image, input_image_meta, input_rpn_match, input_rpn_bbox, input_gt_class_ids, input_gt_boxes, input_gt_masks] if not config.USE_RPN_ROIS: inputs.append(input_rois) outputs = [rpn_class_logits, rpn_class, rpn_bbox, mrcnn_class_logits, mrcnn_class, mrcnn_bbox, mrcnn_mask, rpn_rois, output_rois, rpn_class_loss, rpn_bbox_loss, class_loss, bbox_loss, mask_loss] model = KM.Model(inputs, outputs, name='mask_rcnn') else: # Network Heads # Proposal classifier and BBox regressor heads mrcnn_class_logits, mrcnn_class, mrcnn_bbox =\ fpn_classifier_graph(rpn_rois, mrcnn_feature_maps, config.IMAGE_SHAPE, config.POOL_SIZE, config.NUM_CLASSES) # Detections # output is [batch, num_detections, (y1, x1, y2, x2, class_id, score)] in image coordinates detections = DetectionLayer(config, name="mrcnn_detection")( [rpn_rois, mrcnn_class, mrcnn_bbox, input_image_meta]) # Convert boxes to normalized coordinates # TODO: let DetectionLayer return normalized coordinates to avoid # unnecessary conversions h, w = config.IMAGE_SHAPE[:2] detection_boxes = KL.Lambda( lambda x: x[..., :4] / np.array([h, w, h, w]))(detections) # Create masks for detections mrcnn_mask = build_fpn_mask_graph(detection_boxes, mrcnn_feature_maps, config.IMAGE_SHAPE, config.MASK_POOL_SIZE, config.NUM_CLASSES) model = KM.Model([input_image, input_image_meta], [detections, mrcnn_class, mrcnn_bbox, mrcnn_mask, rpn_rois, rpn_class, rpn_bbox], name='mask_rcnn') # Add multi-GPU support. if config.GPU_COUNT > 1: from parallel_model import ParallelModel model = ParallelModel(model, config.GPU_COUNT) return model def find_last(self): """Finds the last checkpoint file of the last trained model in the model directory. Returns: log_dir: The directory where events and weights are saved checkpoint_path: the path to the last checkpoint file """ # Get directory names. Each directory corresponds to a model dir_names = next(os.walk(self.model_dir))[1] key = self.config.NAME.lower() dir_names = filter(lambda f: f.startswith(key), dir_names) dir_names = sorted(dir_names) if not dir_names: return None, None # Pick last directory dir_name = os.path.join(self.model_dir, dir_names[-1]) # Find the last checkpoint checkpoints = next(os.walk(dir_name))[2] checkpoints = filter(lambda f: f.startswith("mask_rcnn"), checkpoints) checkpoints = sorted(checkpoints) if not checkpoints: return dir_name, None checkpoint = os.path.join(dir_name, checkpoints[-1]) return dir_name, checkpoint def load_weights(self, filepath, by_name=False, exclude=None): """Modified version of the correspoding Keras function with the addition of multi-GPU support and the ability to exclude some layers from loading. exlude: list of layer names to excluce """ import h5py from keras.engine import topology if exclude: by_name = True if h5py is None: raise ImportError('`load_weights` requires h5py.') f = h5py.File(filepath, mode='r') if 'layer_names' not in f.attrs and 'model_weights' in f: f = f['model_weights'] # In multi-GPU training, we wrap the model. Get layers # of the inner model because they have the weights. keras_model = self.keras_model layers = keras_model.inner_model.layers if hasattr(keras_model, "inner_model")\ else keras_model.layers # Exclude some layers if exclude: layers = filter(lambda l: l.name not in exclude, layers) if by_name: topology.load_weights_from_hdf5_group_by_name(f, layers) else: topology.load_weights_from_hdf5_group(f, layers) if hasattr(f, 'close'): f.close() # Update the log directory self.set_log_dir(filepath) def get_imagenet_weights(self): """Downloads ImageNet trained weights from Keras. Returns path to weights file. """ from keras.utils.data_utils import get_file TF_WEIGHTS_PATH_NO_TOP = 'https://github.com/fchollet/deep-learning-models/'\ 'releases/download/v0.2/'\ 'resnet50_weights_tf_dim_ordering_tf_kernels_notop.h5' weights_path = get_file('resnet50_weights_tf_dim_ordering_tf_kernels_notop.h5', TF_WEIGHTS_PATH_NO_TOP, cache_subdir='models', md5_hash='a268eb855778b3df3c7506639542a6af') return weights_path def compile(self, learning_rate, momentum): """Gets the model ready for training. Adds losses, regularization, and metrics. Then calls the Keras compile() function. """ # Optimizer object optimizer = keras.optimizers.SGD(lr=learning_rate, momentum=momentum, clipnorm=5.0) # Add Losses # First, clear previously set losses to avoid duplication self.keras_model._losses = [] self.keras_model._per_input_losses = {} loss_names = ["rpn_class_loss", "rpn_bbox_loss", "mrcnn_class_loss", "mrcnn_bbox_loss", "mrcnn_mask_loss"] for name in loss_names: layer = self.keras_model.get_layer(name) if layer.output in self.keras_model.losses: continue self.keras_model.add_loss( tf.reduce_mean(layer.output, keep_dims=True)) # Add L2 Regularization # Skip gamma and beta weights of batch normalization layers. reg_losses = [keras.regularizers.l2(self.config.WEIGHT_DECAY)(w) / tf.cast(tf.size(w), tf.float32) for w in self.keras_model.trainable_weights if 'gamma' not in w.name and 'beta' not in w.name] self.keras_model.add_loss(tf.add_n(reg_losses)) # Compile self.keras_model.compile(optimizer=optimizer, loss=[ None] * len(self.keras_model.outputs)) # Add metrics for losses for name in loss_names: if name in self.keras_model.metrics_names: continue layer = self.keras_model.get_layer(name) self.keras_model.metrics_names.append(name) self.keras_model.metrics_tensors.append(tf.reduce_mean( layer.output, keep_dims=True)) def set_trainable(self, layer_regex, keras_model=None, indent=0, verbose=1): """Sets model layers as trainable if their names match the given regular expression. """ # Print message on the first call (but not on recursive calls) if verbose > 0 and keras_model is None: log("Selecting layers to train") keras_model = keras_model or self.keras_model # In multi-GPU training, we wrap the model. Get layers # of the inner model because they have the weights. layers = keras_model.inner_model.layers if hasattr(keras_model, "inner_model")\ else keras_model.layers for layer in layers: # Is the layer a model? if layer.__class__.__name__ == 'Model': print("In model: ", layer.name) self.set_trainable( layer_regex, keras_model=layer, indent=indent + 4) continue if not layer.weights: continue # Is it trainable? trainable = bool(re.fullmatch(layer_regex, layer.name)) # Update layer. If layer is a container, update inner layer. if layer.__class__.__name__ == 'TimeDistributed': layer.layer.trainable = trainable else: layer.trainable = trainable # Print trainble layer names if trainable and verbose > 0: log("{}{:20} ({})".format(" " * indent, layer.name, layer.__class__.__name__)) def set_log_dir(self, model_path=None): """Sets the model log directory and epoch counter. model_path: If None, or a format different from what this code uses then set a new log directory and start epochs from 0. Otherwise, extract the log directory and the epoch counter from the file name. """ # Set date and epoch counter as if starting a new model self.epoch = 0 now = datetime.datetime.now() # If we have a model path with date and epochs use them if model_path: # Continue from we left of. Get epoch and date from the file name # A sample model path might look like: # /path/to/logs/coco20171029T2315/mask_rcnn_coco_0001.h5 regex = r".*/\w+(\d{4})(\d{2})(\d{2})T(\d{2})(\d{2})/mask\_rcnn\_\w+(\d{4})\.h5" m = re.match(regex, model_path) if m: now = datetime.datetime(int(m.group(1)), int(m.group(2)), int(m.group(3)), int(m.group(4)), int(m.group(5))) self.epoch = int(m.group(6)) + 1 # Directory for training logs self.log_dir = os.path.join(self.model_dir, "{}{:%Y%m%dT%H%M}".format( self.config.NAME.lower(), now)) # Path to save after each epoch. Include placeholders that get filled by Keras. self.checkpoint_path = os.path.join(self.log_dir, "mask_rcnn_{}_*epoch*.h5".format( self.config.NAME.lower())) self.checkpoint_path = self.checkpoint_path.replace( "*epoch*", "{epoch:04d}") def train(self, train_dataset, val_dataset, learning_rate, epochs, layers): """Train the model. train_dataset, val_dataset: Training and validation Dataset objects. learning_rate: The learning rate to train with epochs: Number of training epochs. Note that previous training epochs are considered to be done alreay, so this actually determines the epochs to train in total rather than in this particaular call. layers: Allows selecting wich layers to train. It can be: - A regular expression to match layer names to train - One of these predefined values: heaads: The RPN, classifier and mask heads of the network all: All the layers 3+: Train Resnet stage 3 and up 4+: Train Resnet stage 4 and up 5+: Train Resnet stage 5 and up """ assert self.mode == "training", "Create model in training mode." # Pre-defined layer regular expressions layer_regex = { # all layers but the backbone "heads": r"(mrcnn\_.*)|(rpn\_.*)|(fpn\_.*)", # From a specific Resnet stage and up "3+": r"(res3.*)|(bn3.*)|(res4.*)|(bn4.*)|(res5.*)|(bn5.*)|(mrcnn\_.*)|(rpn\_.*)|(fpn\_.*)", "4+": r"(res4.*)|(bn4.*)|(res5.*)|(bn5.*)|(mrcnn\_.*)|(rpn\_.*)|(fpn\_.*)", "5+": r"(res5.*)|(bn5.*)|(mrcnn\_.*)|(rpn\_.*)|(fpn\_.*)", # All layers "all": ".*", } if layers in layer_regex.keys(): layers = layer_regex[layers] # Data generators train_generator = data_generator(train_dataset, self.config, shuffle=True, batch_size=self.config.BATCH_SIZE) val_generator = data_generator(val_dataset, self.config, shuffle=True, batch_size=self.config.BATCH_SIZE, augment=False) # Callbacks callbacks = [ keras.callbacks.TensorBoard(log_dir=self.log_dir, histogram_freq=0, write_graph=True, write_images=False), keras.callbacks.ModelCheckpoint(self.checkpoint_path, verbose=0, save_weights_only=True), ] # Train log("\nStarting at epoch {}. LR={}\n".format(self.epoch, learning_rate)) log("Checkpoint Path: {}".format(self.checkpoint_path)) self.set_trainable(layers) self.compile(learning_rate, self.config.LEARNING_MOMENTUM) # Work-around for Windows: Keras fails on Windows when using # multiprocessing workers. See discussion here: # https://github.com/matterport/Mask_RCNN/issues/13#issuecomment-353124009 if os.name is 'nt': workers = 0 else: workers = max(self.config.BATCH_SIZE // 2, 2) self.keras_model.fit_generator( train_generator, initial_epoch=self.epoch, epochs=epochs, steps_per_epoch=self.config.STEPS_PER_EPOCH, callbacks=callbacks, validation_data=next(val_generator), validation_steps=self.config.VALIDATION_STEPS, max_queue_size=100, workers=workers, use_multiprocessing=True, ) self.epoch = max(self.epoch, epochs) def mold_inputs(self, images): """Takes a list of images and modifies them to the format expected as an input to the neural network. images: List of image matricies [height,width,depth]. Images can have different sizes. Returns 3 Numpy matricies: molded_images: [N, h, w, 3]. Images resized and normalized. image_metas: [N, length of meta data]. Details about each image. windows: [N, (y1, x1, y2, x2)]. The portion of the image that has the original image (padding excluded). """ molded_images = [] image_metas = [] windows = [] for image in images: # Resize image to fit the model expected size # TODO: move resizing to mold_image() molded_image, window, scale, padding = utils.resize_image( image, min_dim=self.config.IMAGE_MIN_DIM, max_dim=self.config.IMAGE_MAX_DIM, padding=self.config.IMAGE_PADDING) molded_image = mold_image(molded_image, self.config) # Build image_meta image_meta = compose_image_meta( 0, image.shape, window, np.zeros([self.config.NUM_CLASSES], dtype=np.int32)) # Append molded_images.append(molded_image) windows.append(window) image_metas.append(image_meta) # Pack into arrays molded_images = np.stack(molded_images) image_metas = np.stack(image_metas) windows = np.stack(windows) return molded_images, image_metas, windows def unmold_detections(self, detections, mrcnn_mask, image_shape, window): """Reformats the detections of one image from the format of the neural network output to a format suitable for use in the rest of the application. detections: [N, (y1, x1, y2, x2, class_id, score)] mrcnn_mask: [N, height, width, num_classes] image_shape: [height, width, depth] Original size of the image before resizing window: [y1, x1, y2, x2] Box in the image where the real image is excluding the padding. Returns: boxes: [N, (y1, x1, y2, x2)] Bounding boxes in pixels class_ids: [N] Integer class IDs for each bounding box scores: [N] Float probability scores of the class_id masks: [height, width, num_instances] Instance masks """ # How many detections do we have? # Detections array is padded with zeros. Find the first class_id == 0. zero_ix = np.where(detections[:, 4] == 0)[0] N = zero_ix[0] if zero_ix.shape[0] > 0 else detections.shape[0] # Extract boxes, class_ids, scores, and class-specific masks boxes = detections[:N, :4] class_ids = detections[:N, 4].astype(np.int32) scores = detections[:N, 5] masks = mrcnn_mask[np.arange(N), :, :, class_ids] # Compute scale and shift to translate coordinates to image domain. h_scale = image_shape[0] / (window[2] - window[0]) w_scale = image_shape[1] / (window[3] - window[1]) scale = min(h_scale, w_scale) shift = window[:2] # y, x scales = np.array([scale, scale, scale, scale]) shifts = np.array([shift[0], shift[1], shift[0], shift[1]]) # Translate bounding boxes to image domain boxes = np.multiply(boxes - shifts, scales).astype(np.int32) # Filter out detections with zero area. Often only happens in early # stages of training when the network weights are still a bit random. exclude_ix = np.where( (boxes[:, 2] - boxes[:, 0]) * (boxes[:, 3] - boxes[:, 1]) <= 0)[0] if exclude_ix.shape[0] > 0: boxes = np.delete(boxes, exclude_ix, axis=0) class_ids = np.delete(class_ids, exclude_ix, axis=0) scores = np.delete(scores, exclude_ix, axis=0) masks = np.delete(masks, exclude_ix, axis=0) N = class_ids.shape[0] # Resize masks to original image size and set boundary threshold. full_masks = [] for i in range(N): # Convert neural network mask to full size mask full_mask = utils.unmold_mask(masks[i], boxes[i], image_shape) full_masks.append(full_mask) full_masks = np.stack(full_masks, axis=-1)\ if full_masks else np.empty((0,) + masks.shape[1:3]) return boxes, class_ids, scores, full_masks def detect(self, images, verbose=0): """Runs the detection pipeline. images: List of images, potentially of different sizes. Returns a list of dicts, one dict per image. The dict contains: rois: [N, (y1, x1, y2, x2)] detection bounding boxes class_ids: [N] int class IDs scores: [N] float probability scores for the class IDs masks: [H, W, N] instance binary masks """ assert self.mode == "inference", "Create model in inference mode." assert len( images) == self.config.BATCH_SIZE, "len(images) must be equal to BATCH_SIZE" if verbose: log("Processing {} images".format(len(images))) for image in images: log("image", image) # Mold inputs to format expected by the neural network molded_images, image_metas, windows = self.mold_inputs(images) if verbose: log("molded_images", molded_images) log("image_metas", image_metas) # Run object detection detections, mrcnn_class, mrcnn_bbox, mrcnn_mask, \ rois, rpn_class, rpn_bbox =\ self.keras_model.predict([molded_images, image_metas], verbose=0) # Process detections results = [] for i, image in enumerate(images): final_rois, final_class_ids, final_scores, final_masks =\ self.unmold_detections(detections[i], mrcnn_mask[i], image.shape, windows[i]) results.append({ "rois": final_rois, "class_ids": final_class_ids, "scores": final_scores, "masks": final_masks, }) return results def ancestor(self, tensor, name, checked=None): """Finds the ancestor of a TF tensor in the computation graph. tensor: TensorFlow symbolic tensor. name: Name of ancestor tensor to find checked: For internal use. A list of tensors that were already searched to avoid loops in traversing the graph. """ checked = checked if checked is not None else [] # Put a limit on how deep we go to avoid very long loops if len(checked) > 500: return None # Convert name to a regex and allow matching a number prefix # because Keras adds them automatically if isinstance(name, str): name = re.compile(name.replace("/", r"(\_\d+)*/")) parents = tensor.op.inputs for p in parents: if p in checked: continue if bool(re.fullmatch(name, p.name)): return p checked.append(p) a = self.ancestor(p, name, checked) if a is not None: return a return None def find_trainable_layer(self, layer): """If a layer is encapsulated by another layer, this function digs through the encapsulation and returns the layer that holds the weights. """ if layer.__class__.__name__ == 'TimeDistributed': return self.find_trainable_layer(layer.layer) return layer def get_trainable_layers(self): """Returns a list of layers that have weights.""" layers = [] # Loop through all layers for l in self.keras_model.layers: # If layer is a wrapper, find inner trainable layer l = self.find_trainable_layer(l) # Include layer if it has weights if l.get_weights(): layers.append(l) return layers def run_graph(self, images, outputs): """Runs a sub-set of the computation graph that computes the given outputs. outputs: List of tuples (name, tensor) to compute. The tensors are symbolic TensorFlow tensors and the names are for easy tracking. Returns an ordered dict of results. Keys are the names received in the input and values are Numpy arrays. """ model = self.keras_model # Organize desired outputs into an ordered dict outputs = OrderedDict(outputs) for o in outputs.values(): assert o is not None # Build a Keras function to run parts of the computation graph inputs = model.inputs if model.uses_learning_phase and not isinstance(K.learning_phase(), int): inputs += [K.learning_phase()] kf = K.function(model.inputs, list(outputs.values())) # Run inference molded_images, image_metas, windows = self.mold_inputs(images) # TODO: support training mode? # if TEST_MODE == "training": # model_in = [molded_images, image_metas, # target_rpn_match, target_rpn_bbox, # gt_boxes, gt_masks] # if not config.USE_RPN_ROIS: # model_in.append(target_rois) # if model.uses_learning_phase and not isinstance(K.learning_phase(), int): # model_in.append(1.) # outputs_np = kf(model_in) # else: model_in = [molded_images, image_metas] if model.uses_learning_phase and not isinstance(K.learning_phase(), int): model_in.append(0.) outputs_np = kf(model_in) # Pack the generated Numpy arrays into a a dict and log the results. outputs_np = OrderedDict([(k, v) for k, v in zip(outputs.keys(), outputs_np)]) for k, v in outputs_np.items(): log(k, v) return outputs_npbuild函数是所有的操作细节。我们来看其中的细节,对于输入的图像我们有h,w信息(高度和宽度),我们先判断高度和宽度是否在限定范围内:
要求图像输入大小的高宽必须能被2的6次幂整除。(实际的输入图像是的)。
进行RPN网络的操作,我们设置断点看一下:
这里是
的。(没有使用C1,由于C1尺寸过大会消耗太多的显存资源)
这里是
的,
是
的,
是
的,
是
的。
随后我们自上而下的处理C5 - C2 ,得到P5 - P2:
P5 = KL.Conv2D(256, (1, 1), name='fpn_c5p5')(C5)将
连上了一层卷积层,卷积核大小是
的,卷积层数为256层。
执行后我们打断点查看
的情况:大小由
变成了
。
自上而下,将
和
融合得到
,操作如下:
P4 = KL.Add(name="fpn_p4add")([ KL.UpSampling2D(size=(2, 2), name="fpn_p5upsampled")(P5), KL.Conv2D(256, (1, 1), name='fpn_c4p4')(C4)])第三行表示将
也进行一个
的卷积操作,第二行表示将
进行一个上采样(双线性插值的操作,原来特征图尺寸是是
的,经过双线性插值后其特征图尺寸变成
,同时
进行
的卷积操作后其尺寸也变成了
)。这时他俩的尺寸完全一样.....。
最后我们对P5 - P2再进行卷积操作得到最终的RPN特征层。
最后,这里的P6只用作特征框的生成(在RPN层中),仅仅对齐进行最大池化操作。
2. 候选框的生成
2.1 根据特征图生成候选框
对每个特征图进行遍历生成大小比例不同的候选框。
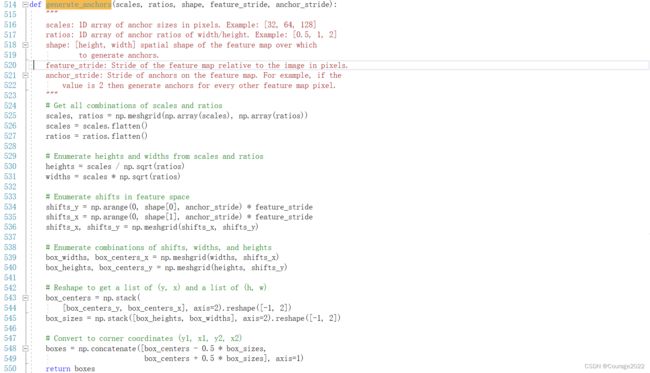
我们看generate_pyramid_anchors函数,返回的是坐标。即框体的位置坐标。
由于特征图的大小比例和原图是不一样的,有的特征图大有的特征图小,因此在不同特征图上生成候选框的时候,我们需要还原(映射)到原始图像的坐标上。
看看函数的参数:
@scales:大小,基础框(比如我们生成的基础框体的大小是
的....)
@ratios:宽度和长度的比例
@shape:输入特征层的大小
# Get all combinations of scales and ratios scales, ratios = np.meshgrid(np.array(scales), np.array(ratios)) scales = scales.flatten() ratios = ratios.flatten()这块代码的含义是对于每个scale(传入generate_anchors函数的是一个值),对每个ratios生成框体的长宽比信息并展平。比如说scale传进来是32,ratio传进来是[0.5,1,1.5]。
那么scales列表存储的是 [32,32,32],ratios列表存储的是[0.5,1,1.5]。
这块代码是根据scales和heights生成anchors的大小模板。
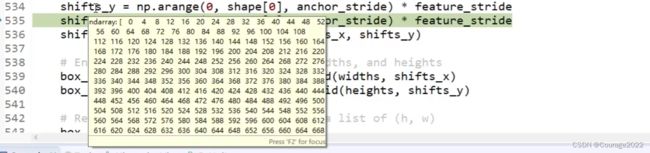
# Enumerate heights and widths from scales and ratios heights = scales / np.sqrt(ratios) widths = scales * np.sqrt(ratios)这块代码是还原操作,shape[0]是输入到generate_anchors函数中的高(
中的第一维),这里的feature_stride = 4,这里是这样子的:原始的图像大小是
的,256和1024之间差了4倍,我们生成的坐标最终不是生成在特征层上的而是原始图像上的!!!因此我们通过这步将生成的anchors还原到原图像上。
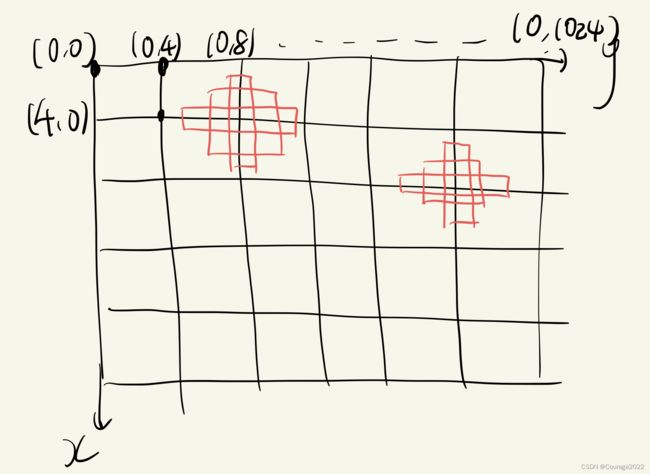
原来是0-256,现在是0-256*4即0-1024。再将x和y进行组合。现在我们得到256*256组点,如下图:
我们拿到了所有的点,我们又计算出了长宽比例以及每个框体的宽和高heights和width,我们现在对于所有的每个点,将这些框体框在每个点身上,如下图:
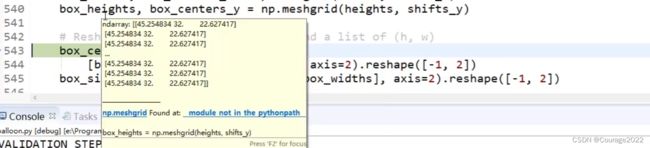
看调试结果,box_width、box_centers_x:
简而言之,生成了每个中心点的三种长宽值。
之后,拿到所有的中心点(为什么有三个:因为要生成三个框体)
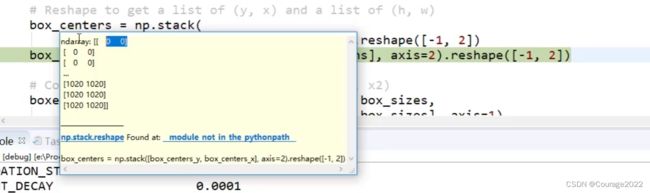
# Reshape to get a list of (y, x) and a list of (h, w) box_centers = np.stack( [box_centers_y, box_centers_x], axis=2).reshape([-1, 2]) box_sizes = np.stack([box_heights, box_widths], axis=2).reshape([-1, 2])最后我们得到实际坐标
:
# Convert to corner coordinates (y1, x1, y2, x2) boxes = np.concatenate([box_centers - 0.5 * box_sizes, box_centers + 0.5 * box_sizes], axis=1)得到了所有候选框在原图上的坐标boxes返回给上层调用:
在generate_pyramid_anchors函数的最后得到了所有特征层的框体(10000多个)。