VMD分解,matlab代码,包络线,包络谱,中心频率,峭度值,能量熵,近似熵,包络熵,希尔伯特变换,包含所有程序MATLAB代码,-西储大学数据集为例
目录
1.选取数据
2.VMD函数-matlab代码
3.采用matlab脚本导入数据并做VMD分解
4. VMD分解图
5.计算中心频率
6.画包络线
7. 画包络谱
8. 计算峭度值
9.计算能量和能量熵
10.近似熵代码
11.包络熵
12.结果展示
13.智能算法优化VMD参数
1.选取数据
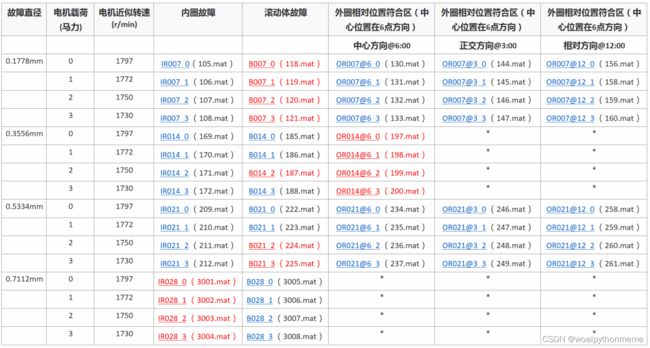
选取1797转速下的内圈故障数据,也就是105.mat,数据集可以在官网下载。下载数据文件|凯斯工程学院 |凯斯西储大学 (case.edu)![]() https://engineering.case.edu/bearingdatacenter/download-data-file
https://engineering.case.edu/bearingdatacenter/download-data-file
2.VMD函数-matlab代码
VMD函数的matlab代码实现,该代码作为函数实现,无需修改,直接使用即可。
function [u, u_hat, omega] = VMD(signal, alpha, tau, K, DC, init, tol)
% Variational Mode Decomposition
% Input and Parameters:
% ---------------------
% signal - the time domain signal (1D) to be decomposed
% alpha - the balancing parameter of the data-fidelity constraint 惩罚因子
% tau - time-step of the dual ascent ( pick 0 for noise-slack )
% K - the number of modes to be recovered 模态分量
% DC - true if the first mode is put and kept at DC (0-freq)
% init - 0 = all omegas start at 0
% 1 = all omegas start uniformly distributed
% 2 = all omegas initialized randomly
% tol - tolerance of convergence criterion; typically around 1e-6
%
% Output:
% -------
% u - the collection of decomposed modes
% u_hat - spectra of the modes
% omega - estimated mode center-frequencies
%---------- Preparations
% Period and sampling frequency of input signal
save_T = length(signal);
fs = 1/save_T;
% extend the signal by mirroring
T = save_T;
f_mirror(1:T/2) = signal(T/2:-1:1);
f_mirror(T/2+1:3*T/2) = signal;
f_mirror(3*T/2+1:2*T) = signal(T:-1:T/2+1);
f = f_mirror;
% Time Domain 0 to T (of mirrored signal)
T = length(f);
t = (1:T)/T;
% Spectral Domain discretization
freqs = t-0.5-1/T;
% Maximum number of iterations (if not converged yet, then it won't anyway)
N = 500;
% For future generalizations: individual alpha for each mode
Alpha = alpha*ones(1,K);
% Construct and center f_hat
f_hat = fftshift((fft(f)));
f_hat_plus = f_hat;
f_hat_plus(1:T/2) = 0;
% matrix keeping track of every iterant // could be discarded for mem
u_hat_plus = zeros(N, length(freqs), K);
% Initialization of omega_k
omega_plus = zeros(N, K);
switch init
case 1
for i = 1:K
omega_plus(1,i) = (0.5/K)*(i-1);
end
case 2
omega_plus(1,:) = sort(exp(log(fs) + (log(0.5)-log(fs))*rand(1,K)));
otherwise
omega_plus(1,:) = 0;
end
% if DC mode imposed, set its omega to 0
if DC
omega_plus(1,1) = 0;
end
% start with empty dual variables
lambda_hat = zeros(N, length(freqs));
% other inits
uDiff = tol+eps; % update step
n = 1; % loop counter
sum_uk = 0; % accumulator
% ----------- Main loop for iterative updates
while ( uDiff > tol && n < N ) % not converged and below iterations limit
% update first mode accumulator
k = 1;
sum_uk = u_hat_plus(n,:,K) + sum_uk - u_hat_plus(n,:,1);
% update spectrum of first mode through Wiener filter of residuals
u_hat_plus(n+1,:,k) = (f_hat_plus - sum_uk - lambda_hat(n,:)/2)./(1+Alpha(1,k)*(freqs - omega_plus(n,k)).^2);
% update first omega if not held at 0
if ~DC
omega_plus(n+1,k) = (freqs(T/2+1:T)*(abs(u_hat_plus(n+1, T/2+1:T, k)).^2)')/sum(abs(u_hat_plus(n+1,T/2+1:T,k)).^2);
end
% update of any other mode
for k=2:K
% accumulator
sum_uk = u_hat_plus(n+1,:,k-1) + sum_uk - u_hat_plus(n,:,k);
% mode spectrum
u_hat_plus(n+1,:,k) = (f_hat_plus - sum_uk - lambda_hat(n,:)/2)./(1+Alpha(1,k)*(freqs - omega_plus(n,k)).^2);
% center frequencies
omega_plus(n+1,k) = (freqs(T/2+1:T)*(abs(u_hat_plus(n+1, T/2+1:T, k)).^2)')/sum(abs(u_hat_plus(n+1,T/2+1:T,k)).^2);
end
% Dual ascent
lambda_hat(n+1,:) = lambda_hat(n,:) + tau*(sum(u_hat_plus(n+1,:,:),3) - f_hat_plus);
% loop counter
n = n+1;
% converged yet?
uDiff = eps;
for i=1:K
uDiff = uDiff + 1/T*(u_hat_plus(n,:,i)-u_hat_plus(n-1,:,i))*conj((u_hat_plus(n,:,i)-u_hat_plus(n-1,:,i)))';
end
uDiff = abs(uDiff);
end
%------ Postprocessing and cleanup
% discard empty space if converged early
N = min(N,n);
omega = omega_plus(1:N,:);
% Signal reconstruction
u_hat = zeros(T, K);
u_hat((T/2+1):T,:) = squeeze(u_hat_plus(N,(T/2+1):T,:));
u_hat((T/2+1):-1:2,:) = squeeze(conj(u_hat_plus(N,(T/2+1):T,:)));
u_hat(1,:) = conj(u_hat(end,:));
u = zeros(K,length(t));
for k = 1:K
u(k,:)=real(ifft(ifftshift(u_hat(:,k))));
end
% remove mirror part
u = u(:,T/4+1:3*T/4);
% recompute spectrum
clear u_hat;
for k = 1:K
u_hat(:,k)=fftshift(fft(u(k,:)))';
end
end3.采用matlab脚本导入数据并做VMD分解
该段代码将内圈故障数据导入,并进行了VMD分解。其中得到的u即为分解出来的IMF分量。
clc
clear
fs=12000;%采样频率
Ts=1/fs;%采样周期
L=1500;%采样点数
t=(0:L-1)*Ts;%时间序列
STA=1; %采样起始位置
%----------------导入内圈故障的数据-----------------------------------------
load 105.mat
X = X105_DE_time(1:L)'; %这里可以选取DE(驱动端加速度)、FE(风扇端加速度)、BA(基座加速度),直接更改变量名,挑选一种即可。
%--------- some sample parameters forVMD:对于VMD样品参数进行设置---------------
alpha = 2500; % moderate bandwidth constraint:适度的带宽约束/惩罚因子
tau = 0; % noise-tolerance (no strict fidelity enforcement):噪声容限(没有严格的保真度执行)
K = 8; % modes:分解的模态数,可以自行设置,这里以8为例。
DC = 0; % no DC part imposed:无直流部分
init = 1; % initialize omegas uniformly :omegas的均匀初始化
tol = 1e-7;
%--------------- Run actual VMD code:数据进行vmd分解---------------------------
[u, u_hat, omega] = VMD(X, alpha, tau, K, DC, init, tol); %其中u为分解得到的IMF分量4. VMD分解图
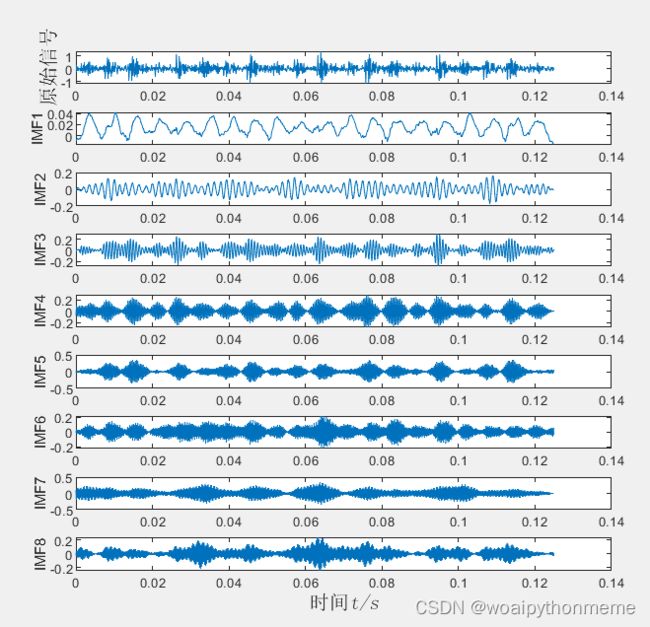
该段代码用于作图,图片可以参考下面的结果展示。
figure(1);
imfn=u;
n=size(imfn,1);
subplot(n+1,1,1);
plot(t,X); %故障信号
ylabel('原始信号','fontsize',12,'fontname','宋体');
for n1=1:n
subplot(n+1,1,n1+1);
plot(t,u(n1,:));%输出IMF分量,a(:,n)则表示矩阵a的第n列元素,u(n1,:)表示矩阵u的n1行元素
ylabel(['IMF' int2str(n1)]);%int2str(i)是将数值i四舍五入后转变成字符,y轴命名
end
xlabel('时间\itt/s','fontsize',12,'fontname','宋体');5.计算中心频率
%----------------------计算中心频率确定分解个数K-----------------------------
average=mean(omega); %对omega求平均值,即为中心频率。中心频率可以用来确定模态分量K的个数,average即为计算得出的中心频率。因为是要确定分解层数,将K设置不同的值,例如1-9,比较最后一个分量的频率。可以确定K值的依据为:一旦出现相似频率,此时的K值被确定为最佳K值。
6.画包络线
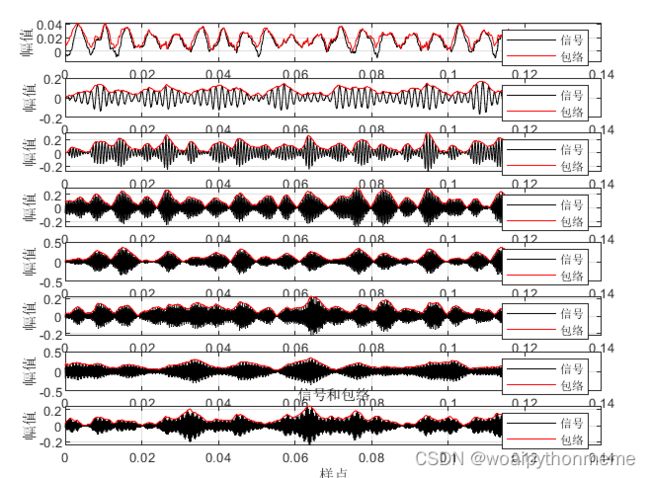
该段代码用来画包络线,图形参考下面的结果展示。
figure(2)
for i = 1:K
Hy(i,:)= abs(hilbert(u(i,:)));
subplot(K,1,i);
plot(t,u(i,:),'k',t,Hy(i,:),'r');
xlabel('样点'); ylabel('幅值')
grid; legend('信号','包络');
end
title('信号和包络');
set(gcf,'color','w');7. 画包络谱
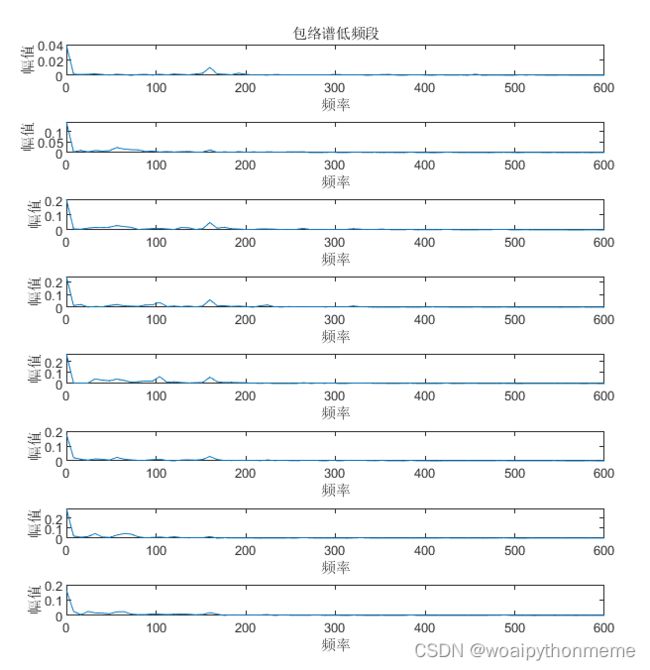
该段代码用来画包络谱,图形参考下面的结果展示。
画包络谱的时候,切记要将 “nfft” 设置为采样点数的一半。
% 画包络谱
figure('Name','包络谱','Color','white');
nfft=fix(L/2);
for i = 1:K
p=abs(fft(Hy(i,:))); %并fft,得到p,就是包络线的fft---包络谱
p = p/length(p)*2;
p = p(1: fix(length(p)/2));
subplot(K,1,i);
plot((0:nfft-1)/nfft*fs/2,p) %绘制包络谱
%xlim([0 600]) %展示包络谱低频段,这句代码可以自己根据情况选择是否注释
if i ==1
title('包络谱'); xlabel('频率'); ylabel('幅值')
else
xlabel('频率'); ylabel('幅值')
end
end
set(gcf,'color','w');8. 计算峭度值
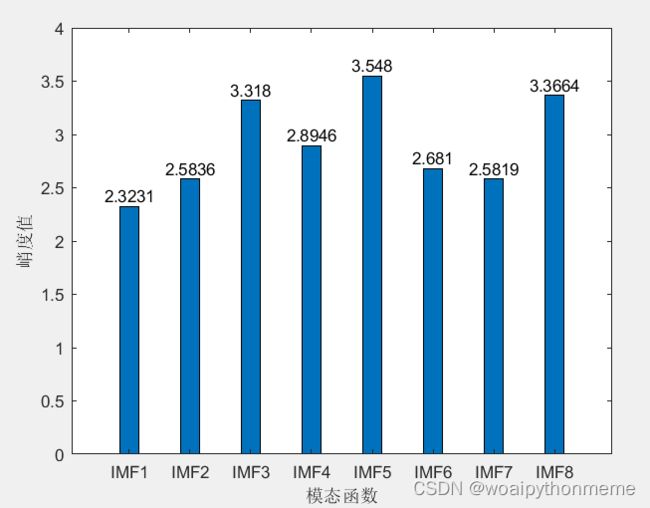
%% 计算峭度值
for i=1:K
a(i)=kurtosis(imfn(i,:));%峭度
disp(['IMF',num2str(i),'的峭度值为:',num2str(a(i))])
end
figure
b = bar(a,0.3);
xlabel('模态函数'); ylabel('峭度值')
set(gca,'xtick',1:1:K);
set(gca,'xticklabel',{'IMF1','IMF2','IMF3','IMF4','IMF5','IMF6','IMF7','IMF8'});
xtips1 = b.XEndPoints;
ytips1 = b.YEndPoints; %获取Bar对象的XEndPoints和YEndPoints属性
labels1 = string(b.YData); %获取条形末端坐标
text(xtips1, ytips1, labels1, 'HorizontalAlignment', 'center', 'VerticalAlignment', 'bottom');
%指定垂直、水平对其,让值显示在条形末端居中9.计算能量和能量熵
%% 能量熵
for i=1:K
Eimf(i) = sum(imfn(i,:).^2,2);
end
disp(['IMF分量的能量'])
disp(Eimf(1:K))
% 能量熵
E = sum(Eimf);
for j = 1:K
p(j) = Eimf(j)/E;
HE(j)=-sum(p(j).*log(p(j)));
end
disp('EMD能量熵=%.4f');
disp(HE(1:K));10.近似熵代码
近似熵函数,直接复制粘贴,不用改函数。
%近似熵函数的代码
function ApEn = kApproximateEntropy(data, dim, r)
% 计算近似熵(ApEn)
% data - 待分析数据,需要是一维数据
% dim - 模式维度
% r- 阈值大小,一船选择r=0.1-0.25,
data = data(:); %强制转化数据为列方向
N = length(data);%获取数据长度
result = zeros(1,2);%初始化参数
for j = 1:2
m = dim+j-1;
C = zeros(1,N-m+1);%C值初始化,
dataMat = zeros (m, N-m+1);%初始化
for i = 1:m
dataMat(i,:) = data(i:N-m+i); %
end
% counting similar patterns using distance calculation
for i = 1:N-m+1
tempMat = abs(dataMat - repmat (dataMat(:,i),1,N-m+1));
boolMat = any((tempMat>r),1);
C(i)=sum(~boolMat)/(N-m+1);
end
phi(j) = sum(log(C))/(N-m+1);
end
ApEn = phi(1)-phi(2);
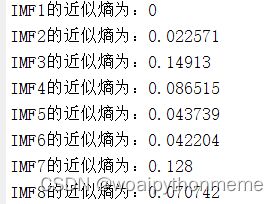
end近似熵调用:对每个IMF分量计算近似熵
for i1=1:K
imf0=imfn(i1,:);%
x=imf0';
ApEnx = kApproximateEntropy(x, 2, 0.15); %多尺度熵计算
ApEn(1,i1)= ApEnx;
disp(['IMF',num2str(i1),'的近似熵为:',num2str(ApEn(1,i1))])
end11.包络熵
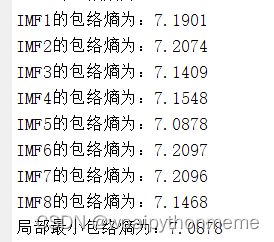
包络熵调用:对每个IMF分量计算包络熵
for i = 1:K
xx= abs(hilbert(u(i,:))); %最小包络熵计算公式!
xxx = xx/sum(xx);
ssum=0;
for ii = 1:size(xxx,2)
bb = xxx(1,ii)*log(xxx(1,ii));
ssum=ssum+bb;
end
Enen(i,:) = -ssum;%每个IMF分量的包络熵
disp(['IMF',num2str(i),'的包络熵为:',num2str(Enen(i,:))])
end
ff = min(Enen);%求取局部最小包络熵,一般用智能优化算法优化VMD,最为最小适应度函数使用
disp(['局部最小包络熵为:',num2str(ff)])12.结果展示
包络线图
包络熵低频段
包络熵计算
近似熵
13.智能算法优化VMD参数
智能算法优化VMD参数将在下一篇文章介绍!敬请关注谢谢!
(2条消息) 麻雀算法SSA,优化VMD,适应度函数为最小包络熵,包含MATLAB源代码,直接复制粘贴!_今天吃饺子的博客-CSDN博客