ACGAN 简介与代码实战
1.介绍
CGAN通过结合标签信息来提高生成数据的质量,SGAN通过重建标签信息来提高生成数据的质量,那么我们可不可以两者都用,答案是显然的,因为ACGAN就是这样干的。更加详细的内容可以参见论文:Conditional Image Synthesis with Auxiliary Classifier GANs
2.模型结构
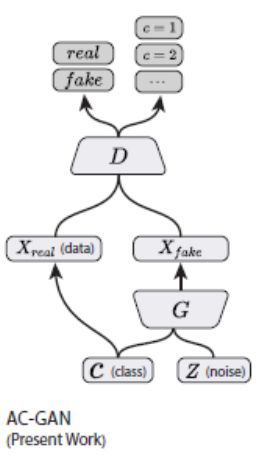
G的输入是分类标签和固定分布噪声,D的输出是真假和分类标签。
Ls为真假判断损失, Lc为分类损失,D is trained to maximize LS + LC while G is trained to maximize LC -LS.
![]()
3.模型特点
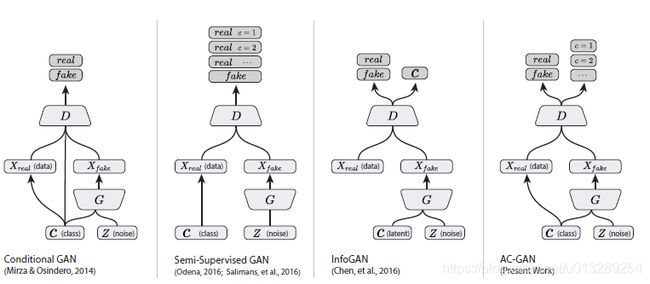
CGAN(参见CGAN 简介与代码实战),SGAN(参见SGAN 简介与代码实战),InfoGAN(参见InfoGAN 简介与代码实战),而ACGAN明显是结合了这三者的特点。
4.代码实现keras
class ACGAN():
def __init__(self):
# Input shape
self.img_rows = 28
self.img_cols = 28
self.channels = 1
self.img_shape = (self.img_rows, self.img_cols, self.channels)
self.num_classes = 10
self.latent_dim = 100
optimizer = Adam(0.0002, 0.5)
losses = ['binary_crossentropy', 'sparse_categorical_crossentropy']
# Build and compile the discriminator
self.discriminator = self.build_discriminator()
self.discriminator.compile(loss=losses,
optimizer=optimizer,
metrics=['accuracy'])
# Build the generator
self.generator = self.build_generator()
# The generator takes noise and the target label as input
# and generates the corresponding digit of that label
noise = Input(shape=(self.latent_dim,))
label = Input(shape=(1,))
img = self.generator([noise, label])
# For the combined model we will only train the generator
self.discriminator.trainable = False
# The discriminator takes generated image as input and determines validity
# and the label of that image
valid, target_label = self.discriminator(img)
# The combined model (stacked generator and discriminator)
# Trains the generator to fool the discriminator
self.combined = Model([noise, label], [valid, target_label])
self.combined.compile(loss=losses,
optimizer=optimizer)
def build_generator(self):
model = Sequential()
model.add(Dense(128 * 7 * 7, activation="relu", input_dim=self.latent_dim))
model.add(Reshape((7, 7, 128)))
model.add(BatchNormalization(momentum=0.8))
model.add(UpSampling2D())
model.add(Conv2D(128, kernel_size=3, padding="same"))
model.add(Activation("relu"))
model.add(BatchNormalization(momentum=0.8))
model.add(UpSampling2D())
model.add(Conv2D(64, kernel_size=3, padding="same"))
model.add(Activation("relu"))
model.add(BatchNormalization(momentum=0.8))
model.add(Conv2D(self.channels, kernel_size=3, padding='same'))
model.add(Activation("tanh"))
model.summary()
noise = Input(shape=(self.latent_dim,))
label = Input(shape=(1,), dtype='int32')
label_embedding = Flatten()(Embedding(self.num_classes, 100)(label))
model_input = multiply([noise, label_embedding])
img = model(model_input)
return Model([noise, label], img)
def build_discriminator(self):
model = Sequential()
model.add(Conv2D(16, kernel_size=3, strides=2, input_shape=self.img_shape, padding="same"))
model.add(LeakyReLU(alpha=0.2))
model.add(Dropout(0.25))
model.add(Conv2D(32, kernel_size=3, strides=2, padding="same"))
model.add(ZeroPadding2D(padding=((0,1),(0,1))))
model.add(LeakyReLU(alpha=0.2))
model.add(Dropout(0.25))
model.add(BatchNormalization(momentum=0.8))
model.add(Conv2D(64, kernel_size=3, strides=2, padding="same"))
model.add(LeakyReLU(alpha=0.2))
model.add(Dropout(0.25))
model.add(BatchNormalization(momentum=0.8))
model.add(Conv2D(128, kernel_size=3, strides=1, padding="same"))
model.add(LeakyReLU(alpha=0.2))
model.add(Dropout(0.25))
model.add(Flatten())
model.summary()
img = Input(shape=self.img_shape)
# Extract feature representation
features = model(img)
# Determine validity and label of the image
validity = Dense(1, activation="sigmoid")(features)
label = Dense(self.num_classes, activation="softmax")(features)
return Model(img, [validity, label])
def train(self, epochs, batch_size=128, sample_interval=50):
# Load the dataset
(X_train, y_train), (_, _) = mnist.load_data()
# Configure inputs
X_train = (X_train.astype(np.float32) - 127.5) / 127.5
X_train = np.expand_dims(X_train, axis=3)
y_train = y_train.reshape(-1, 1)
# Adversarial ground truths
valid = np.ones((batch_size, 1))
fake = np.zeros((batch_size, 1))
for epoch in range(epochs):
# ---------------------
# Train Discriminator
# ---------------------
# Select a random batch of images
idx = np.random.randint(0, X_train.shape[0], batch_size)
imgs = X_train[idx]
# Sample noise as generator input
noise = np.random.normal(0, 1, (batch_size, 100))
# The labels of the digits that the generator tries to create an
# image representation of
sampled_labels = np.random.randint(0, 10, (batch_size, 1))
# Generate a half batch of new images
gen_imgs = self.generator.predict([noise, sampled_labels])
# Image labels. 0-9
img_labels = y_train[idx]
# Train the discriminator
d_loss_real = self.discriminator.train_on_batch(imgs, [valid, img_labels])
d_loss_fake = self.discriminator.train_on_batch(gen_imgs, [fake, sampled_labels])
d_loss = 0.5 * np.add(d_loss_real, d_loss_fake)
# ---------------------
# Train Generator
# ---------------------
# Train the generator
g_loss = self.combined.train_on_batch([noise, sampled_labels], [valid, sampled_labels])
# Plot the progress
print ("%d [D loss: %f, acc.: %.2f%%, op_acc: %.2f%%] [G loss: %f]" % (epoch, d_loss[0], 100*d_loss[3], 100*d_loss[4], g_loss[0]))
# If at save interval => save generated image samples
if epoch % sample_interval == 0:
self.save_model()
self.sample_images(epoch)
def sample_images(self, epoch):
r, c = 10, 10
noise = np.random.normal(0, 1, (r * c, 100))
sampled_labels = np.array([num for _ in range(r) for num in range(c)])
gen_imgs = self.generator.predict([noise, sampled_labels])
# Rescale images 0 - 1
gen_imgs = 0.5 * gen_imgs + 0.5
fig, axs = plt.subplots(r, c)
cnt = 0
for i in range(r):
for j in range(c):
axs[i,j].imshow(gen_imgs[cnt,:,:,0], cmap='gray')
axs[i,j].axis('off')
cnt += 1
fig.savefig("images/%d.png" % epoch)
plt.close()