MySQL理论及基础命令
目录
- MySQL简介
-
- 什么是数据库?
- 什么是数据库管理系统(DBMS)
- MySQL数据库的基本概念
-
- 表(Table)
- 列(Column/Field)
- 行(Row)
- MySQL软件、数据库、表、列、行的关系
- 数据类型
-
- 数值型
- 字符串型
- 日期时间型
- 枚举类型
- MySQL的函数
-
- 聚集函数(重点)
- 日期与时间函数(重点)
- 数值处理函数
- 系统函数
- MySQL数据库操作
-
- 连接数据库:
- 查看数据库:
- 默认数据库:
- 查看数据表:
- MySQL表操作
-
- 查看表(show table)
- 创建表(create table)
- 删除表(drop,delete,truncate)
- 修改表(alter)
-
- 添加列(add)
- 删除列(drop)
- 修改列(modify,change)
- 添加主键(add primary key)
- 删除主键(drop primary key)
- 添加外键(add foreign key)
- 删除外键(drop foreign key)
- MySQL表内容操作
-
- 增(插入数据)
- 修改数据(update)
- 查询数据(select)
-
- 条件判断(where)
- 通配符(like)
- 限制(limit)
- 排序(order by)
- 分组(group by)
- 子查询
- 联表查询
-
- 内连接(inner join)
- 左连接(left join)
- 右连接(right join)
- 组合查询
- 索引Index
- 视图View
- SQL语句的分类
MySQL简介
什么是数据库?
数据库是按照数据结构来组织、存储和管理数据的仓库。
什么是数据库管理系统(DBMS)
用于管理数据库的软件称为数据库管理软件(DBMS:Database Management System)。
MySQL数据库的基本概念
表(Table)
关系数据库中的数据是保存在表里面的,存储在表中的数据是一种特定类型的数据。在数据库中,表有一个唯一的名字来标识该表,称为表名。
一个数据库可以有很多张表。
列(Column/Field)
表由列组成,列中存储着表中某部分的信息;所有表都是由一个或多个列组成的,一列也叫一个字段。
一张表可以有很多个列(字段)。
行(Row)
表中的数据是按行存储的,一行就是一条记录。
一张表中可以有多行(多条数据)。
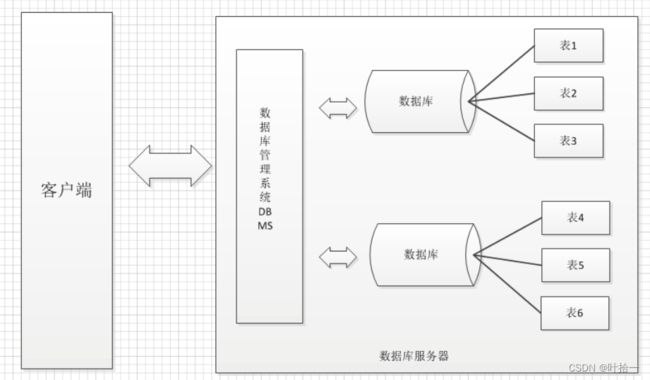
MySQL软件、数据库、表、列、行的关系
在MySQL软件系统可以创建很多个数据库,每个数据库可以有多个表,每个表可以有多个列(字段),每个表可以有多行数据。
数据类型
数值型
- 整型
- tinyint:1字节,非常小的整数,带符号:-128~127,不带符号:0~255;
- int:4字节,标准整型,带符号:-2147483648~2147483647,不带符号:0~4294967295;
- 其他类型:smallint(2字节)、mediumint(3字节)、bigint(8字节);
- 浮点型
- float:4字节,单精度浮点数;7.989999
- double:8字节,双精度浮点数;7.98999999999
- decimal(m,d):m表示整数加小数的总位数,d表示小数位数,比如decimal(4,2);7.99
- 区别:float与double存储的是近似值,decimal存储的是精确值。在数据库中涉及到钱的金额,一定要用decimal类型。
字符串型
字符串
- char(m):最多可以容纳m个字符;
- varchar(m):最多可以容纳m个字符,如果存储的字符数n少于m时,实际占用的存储空间是L+1个字节,其中L是n个字符占用的字节数,多出的1个字节是用来记录实际存储长度的;
- 其他类型:blob(longblob),text(longtext)
- char和varchar是最常用的两种字符串类型,他们的区别是:
- char是固定长度的,每个值占用相同的字符数,不够的位数MySQL会在它的右边用空格字符补足
- varchar是一种可变长度的类型,每个值占用其刚好的字符数再加上一个用来记录其长度的字节即L+1个字节
- 在使用时,char和varchar怎么选择:
- 如果数据都有相同的长度(比如手机号码),选用varchar会多占用空间,因为有一位用来存储其长度。如果数据长度不一,选用varchar能节省存储空间;
- 而char不论字符长短都需要占用相同的空间,即使是空值也不例外。
日期时间型
- year:表示年,比如2000
- date:日期型,表示一个日期格式,如2020-01-01
- time:时间型,表示一个时间格式,如22:10:15
- datetime:日期时间型,表示一个日期+时间的组合格式,如2020-01-01 22:10:15
- timestamp:时间戳型,如果某列的数据类型为timestamp且该列为not null,当插入数据时不指定该列的值,那么这个列就会自动取值为当前的日期和时间;在创建和修改数据行时,如果没有明确对timestamp数据列进行赋值,则它就会自动取值为当前的日期和时间。如果表中有多个timestamp列,只有第一个会自动取值。
枚举类型
- enum:枚举类型,当一个字段的值只能在某个范围内取值,比如性别只能取男或女,可以用enum(“男”,“女”)来表示,这个字段在插入数据时只能取男或者女或者不传值。每个枚举值都有一个索引,第一个值的索引为1。枚举类型的好处是MySQL在存储此类数据时,直接转化成数字存储而不是字符串,可以节省空间,并且在表的.frm文件中存储“数字-字符串”之间的对应关系。
MySQL的函数
聚集函数(重点)
-
聚集函数:聚集函数是在列上的运算,比如找这一列的最大、最小、平均、求和、统计行数等。
-
avg()
-
作用:返回某列的平均值
-
举例:
#计算产品的平均价格 mysql> select avg(prod_price) from products; +-----------------+ | avg(prod_price) | +-----------------+ | 16.133571 | +-----------------+ 1 row in set (0.00 sec)
-
-
count()
-
作用:返回某列的行数,注意:count统计的是某个列上非空的行的数量,如果某一行是null,就不会被统计在内,在实际使用中如果要统计表的行数,直接用count(*),只要行上有一个字段非null,就会被统计在内。
-
举例:
#统计产品的数量 mysql> select count(*) from products; +----------+ | count(*) | +----------+ | 14 | +----------+ 1 row in set (0.00 sec)
-
-
max()
-
作用:返回某列的最大值
-
举例:
#统计产品的最高价 mysql> select max(prod_price) from products; +-----------------+ | max(prod_price) | +-----------------+ | 55.00 | +-----------------+ 1 row in set (0.00 sec)
-
-
min()
-
作用:返回某列的最小值
-
举例:
#统计产品的最低价 mysql> select min(prod_price) from products; +-----------------+ | min(prod_price) | +-----------------+ | 2.50 | +-----------------+ 1 row in set (0.00 sec)
-
-
sum()
-
作用:返回某列值之和
-
举例:
#统计产品单价的总和 mysql> select sum(prod_price) from products; +-----------------+ | sum(prod_price) | +-----------------+ | 225.87 | +-----------------+ 1 row in set (0.00 sec)
-
日期与时间函数(重点)
-
curdate()
-
作用:返回系统当前日期
-
举例:
mysql> select curdate(); +------------+ | curdate() | +------------+ | 2021-07-09 | +------------+ 1 row in set (0.00 sec)
-
-
curtime()
-
作用:返回当前时间
-
举例:
mysql> select curtime(); +-----------+ | curtime() | +-----------+ | 15:03:48 | +-----------+ 1 row in set (0.00 sec)
-
-
now()
-
作用:返回当前日期和时间
-
举例:
mysql> select now(); +---------------------+ | now() | +---------------------+ | 2021-07-09 15:04:03 | +---------------------+ 1 row in set (0.00 sec)
-
-
adddate()
-
作用:增加一个日期(天、周、月、年等)
-
举例:
#计算订单下单日期之后30天的日期 mysql> select cust_id,order_num,order_date,adddate(order_date, interval 30 day) from orders; +---------+-----------+---------------------+--------------------------------------+ | cust_id | order_num | order_date | adddate(order_date, interval 30 day) | +---------+-----------+---------------------+--------------------------------------+ | 10001 | 20005 | 2005-09-01 00:00:00 | 2005-10-01 00:00:00 | | 10003 | 20006 | 2005-09-12 00:00:00 | 2005-10-12 00:00:00 | | 10004 | 20007 | 2005-09-30 00:00:00 | 2005-10-30 00:00:00 | | 10005 | 20008 | 2005-10-03 00:00:00 | 2005-11-02 00:00:00 | | 10001 | 20009 | 2005-10-08 00:00:00 | 2005-11-07 00:00:00 | | 10001 | 20010 | 2005-11-08 01:00:00 | 2005-12-08 01:00:00 | | 10002 | 20011 | 2005-11-08 00:00:00 | 2005-12-08 00:00:00 | +---------+-----------+---------------------+--------------------------------------+ 7 rows in set (0.00 sec) #计算订单下单日期之后1周的日期 mysql> select cust_id,order_num,order_date,adddate(order_date, interval 1 week) from orders; +---------+-----------+---------------------+--------------------------------------+ | cust_id | order_num | order_date | adddate(order_date, interval 1 week) | +---------+-----------+---------------------+--------------------------------------+ | 10001 | 20005 | 2005-09-01 00:00:00 | 2005-09-08 00:00:00 | | 10003 | 20006 | 2005-09-12 00:00:00 | 2005-09-19 00:00:00 | | 10004 | 20007 | 2005-09-30 00:00:00 | 2005-10-07 00:00:00 | | 10005 | 20008 | 2005-10-03 00:00:00 | 2005-10-10 00:00:00 | | 10001 | 20009 | 2005-10-08 00:00:00 | 2005-10-15 00:00:00 | | 10001 | 20010 | 2005-11-08 01:00:00 | 2005-11-15 01:00:00 | | 10002 | 20011 | 2005-11-08 00:00:00 | 2005-11-15 00:00:00 | +---------+-----------+---------------------+--------------------------------------+ 7 rows in set (0.00 sec) #计算订单下单日期之后1个月的日期 mysql> select cust_id,order_num,order_date,adddate(order_date, interval 1 month) from orders; +---------+-----------+---------------------+---------------------------------------+ | cust_id | order_num | order_date | adddate(order_date, interval 1 month) | +---------+-----------+---------------------+---------------------------------------+ | 10001 | 20005 | 2005-09-01 00:00:00 | 2005-10-01 00:00:00 | | 10003 | 20006 | 2005-09-12 00:00:00 | 2005-10-12 00:00:00 | | 10004 | 20007 | 2005-09-30 00:00:00 | 2005-10-30 00:00:00 | | 10005 | 20008 | 2005-10-03 00:00:00 | 2005-11-03 00:00:00 | | 10001 | 20009 | 2005-10-08 00:00:00 | 2005-11-08 00:00:00 | | 10001 | 20010 | 2005-11-08 01:00:00 | 2005-12-08 01:00:00 | | 10002 | 20011 | 2005-11-08 00:00:00 | 2005-12-08 00:00:00 | +---------+-----------+---------------------+---------------------------------------+ 7 rows in set (0.00 sec) #计算订单下单日期之后1年的日期 mysql> select cust_id,order_num,order_date,adddate(order_date, interval 1 year) from orders; +---------+-----------+---------------------+--------------------------------------+ | cust_id | order_num | order_date | adddate(order_date, interval 1 year) | +---------+-----------+---------------------+--------------------------------------+ | 10001 | 20005 | 2005-09-01 00:00:00 | 2006-09-01 00:00:00 | | 10003 | 20006 | 2005-09-12 00:00:00 | 2006-09-12 00:00:00 | | 10004 | 20007 | 2005-09-30 00:00:00 | 2006-09-30 00:00:00 | | 10005 | 20008 | 2005-10-03 00:00:00 | 2006-10-03 00:00:00 | | 10001 | 20009 | 2005-10-08 00:00:00 | 2006-10-08 00:00:00 | | 10001 | 20010 | 2005-11-08 01:00:00 | 2006-11-08 01:00:00 | | 10002 | 20011 | 2005-11-08 00:00:00 | 2006-11-08 00:00:00 | +---------+-----------+---------------------+--------------------------------------+ 7 rows in set (0.00 sec) #查询20006和20005两个订单之间的间隔天数 mysql> select to_days(a.order_date)-to_days(b.order_date) from (select order_date from orders where order_num=20006) as a, (selecct order_date from orders where order_num=20005) as b; +---------------------------------------+ | date(a.order_date)-date(b.order_date) | +---------------------------------------+ | 11 | +---------------------------------------+ 1 row in set (0.00 sec)
-
-
addtime()
-
作用:增加一个时间(时、分、秒等)
-
举例:
#计算订单时间之后的30分钟的时间 mysql> select *,addtime(order_date,"00:30:00") from orders; +-----------+---------------------+---------+--------------------------------+ | order_num | order_date | cust_id | addtime(order_date,"00:30:00") | +-----------+---------------------+---------+--------------------------------+ | 20005 | 2005-09-01 00:00:00 | 10001 | 2005-09-01 00:30:00 | | 20006 | 2005-09-12 00:00:00 | 10003 | 2005-09-12 00:30:00 | | 20007 | 2005-09-30 00:00:00 | 10004 | 2005-09-30 00:30:00 | | 20008 | 2005-10-03 00:00:00 | 10005 | 2005-10-03 00:30:00 | | 20009 | 2005-10-08 00:00:00 | 10001 | 2005-10-08 00:30:00 | | 20010 | 2005-11-08 01:00:00 | 10001 | 2005-11-08 01:30:00 | | 20011 | 2005-11-08 00:00:00 | 10002 | 2005-11-08 00:30:00 | +-----------+---------------------+---------+--------------------------------+ 7 rows in set (0.00 sec)
-
-
date()
-
作用:返回日期时间的日期部分
-
举例:
#查询2005-11-08号的订单信息 mysql> select * from orders where date(order_date)="2005-11-08"; +-----------+---------------------+---------+ | order_num | order_date | cust_id | +-----------+---------------------+---------+ | 20010 | 2005-11-08 01:00:00 | 10001 | | 20011 | 2005-11-08 00:00:00 | 10002 | +-----------+---------------------+---------+ 2 rows in set (0.00 sec)
-
-
year()
-
作用:返回日期时间的年的部分
-
举例:
#查询2005年的订单信息 mysql> select * from orders where year(order_date)="2005"; +-----------+---------------------+---------+ | order_num | order_date | cust_id | +-----------+---------------------+---------+ | 20005 | 2005-09-01 00:00:00 | 10001 | | 20006 | 2005-09-12 00:00:00 | 10003 | | 20007 | 2005-09-30 00:00:00 | 10004 | | 20008 | 2005-10-03 00:00:00 | 10005 | | 20009 | 2005-10-08 00:00:00 | 10001 | | 20010 | 2005-11-08 01:00:00 | 10001 | | 20011 | 2005-11-08 00:00:00 | 10002 | +-----------+---------------------+---------+ 7 rows in set (0.00 sec)
-
-
month()
-
作用:返回日期时间的月的部分
-
举例:
#查询2005年9月的订单信息 mysql> select * from orders where year(order_date)="2005" and month(order_date)=9; +-----------+---------------------+---------+ | order_num | order_date | cust_id | +-----------+---------------------+---------+ | 20005 | 2005-09-01 00:00:00 | 10001 | | 20006 | 2005-09-12 00:00:00 | 10003 | | 20007 | 2005-09-30 00:00:00 | 10004 | +-----------+---------------------+---------+ 3 rows in set (0.00 sec)
-
-
day()
-
作用:返回日期时间的天的部分
-
举例:
#查询2005年9月30号的订单信息 mysql> select * from orders where year(order_date)="2005" and month(order_date)=9 and day(order_date)=30; +-----------+---------------------+---------+ | order_num | order_date | cust_id | +-----------+---------------------+---------+ | 20007 | 2005-09-30 00:00:00 | 10004 | +-----------+---------------------+---------+ 1 row in set (0.00 sec)
-
数值处理函数
-
round(x,y)
-
作用:对x四舍五入保留y位小数
-
举例:
mysql> select prod_price,round(prod_price,1) from products; +------------+---------------------+ | prod_price | round(prod_price,1) | +------------+---------------------+ | 5.99 | 6.0 | | 9.99 | 10.0 | | 14.99 | 15.0 | | 13.00 | 13.0 | | 10.00 | 10.0 | | 2.50 | 2.5 | | 3.42 | 3.4 | | 35.00 | 35.0 | | 55.00 | 55.0 | | 8.99 | 9.0 | | 50.00 | 50.0 | | 4.49 | 4.5 | | 2.50 | 2.5 | | 10.00 | 10.0 | +------------+---------------------+ 14 rows in set (0.00 sec)
-
-
truncate(x,y)
-
作用:对x截断保留y位小数
-
举例:
mysql> select prod_price,truncate(prod_price,1) from products; +------------+------------------------+ | prod_price | truncate(prod_price,1) | +------------+------------------------+ | 5.99 | 5.9 | | 9.99 | 9.9 | | 14.99 | 14.9 | | 13.00 | 13.0 | | 10.00 | 10.0 | | 2.50 | 2.5 | | 3.42 | 3.4 | | 35.00 | 35.0 | | 55.00 | 55.0 | | 8.99 | 8.9 | | 50.00 | 50.0 | | 4.49 | 4.4 | | 2.50 | 2.5 | | 10.00 | 10.0 | +------------+------------------------+ 14 rows in set (0.00 sec)
-
-
abs(x)
-
作用:返回x的绝对值
-
举例:
mysql> select abs(-1); +---------+ | abs(-1) | +---------+ | 1 | +---------+ 1 row in set (0.00 sec)
-
-
rand()
-
作用:返回0~1内的随机值
-
举例:
mysql> select rand(); +--------------------+ | rand() | +--------------------+ | 0.3681343555153668 | +--------------------+ 1 row in set (0.00 sec)
-
系统函数
-
version()
-
作用:返回数据库版本号
-
举例:
mysql> select version(); +------------+ | version() | +------------+ | 5.6.37-log | +------------+ 1 row in set (0.00 sec)
-
-
database()
-
作用:返回当前连接的数据库
-
举例:
mysql> select database(); +-------------+ | database() | +-------------+ | crashcourse | +-------------+ 1 row in set (0.00 sec)
-
-
user()
-
作用:返回当前登录的用户
-
举例:
mysql> select user(); +----------------+ | user() | +----------------+ | root@localhost | +----------------+ 1 row in set (0.00 sec)
-
MySQL数据库操作
连接数据库:
mysql -u root -p
查看数据库:
show databases;
默认数据库:
mysql – 用户权限相关数据
test – 用于用户测试数据
information_schema – MySQL本身架构相关数据
查看数据表:
show tables;
MySQL表操作
查看表(show table)
show tables;
select * from 表名; #查询表中所有数据
创建表(create table)
create table 表名(
id int not null,
name varchar(10),
age tinyint
)engine=innodb default charset=utf8;
删除表(drop,delete,truncate)
drop table 表名; #删除表结构及数据
delete from 表名; #清空表数据
truncate table 表名; #同样清空表数据
注意:drop、delete、truncate的区别
drop是直接删除表结构以及数据以及列;
delete是只删除数据,且数据可恢复;
truncate是先删除表结构以及数据后,重新创建一个空表,且数据不可恢复。
修改表(alter)
添加列(add)
alter table 表名 add 列名 类型;
删除列(drop)
alter table 表名 drop column 列名;
修改列(modify,change)
alter table 表名 modify column 列名 类型;
alter table 表名 change 原列名 新列名 类型;
添加主键(add primary key)
alter table 表名 add primary key(列名);
删除主键(drop primary key)
alter table 表名 drop primary key;
alter table 表名 modify 列名 int,drop primary key;
添加外键(add foreign key)
alter table 从表 add constraint 外键名称
foreign 从表(外键字段)
references 主表(主键字段);
删除外键(drop foreign key)
alter table 表名 drop foreign key 外键名称;
MySQL表内容操作
增(插入数据)
insert into 表(列名,列名...) values(值,值...);
insert into 表 (列名,列名...) values (值,值,...),(值,值,值...);
insert into 表 (列名,列名...) select (列名,列名...) from 表;
修改数据(update)
update 表 set name = 'zhangyanlin' where id>1;
查询数据(select)
select * from 表名;
条件判断(where)
select * from 表 where id > 1 and name != 'aylin' and num = 12;
select * from 表 where id between 5 and 16;
select * from 表 where id in (11,22,33);
select * from 表 where id not in (11,22,33);
select * from 表 where id in (select nid from 表);
通配符(like)
select * from 表 where name like 'zhang%'; # zhang开头的所有(多个字符串)
select * from 表 where name like 'zhang_'; # zhang开头的所有(一个字符)
限制(limit)
select * from 表 limit 5; -- 前5行
select * from 表 limit 4,5; --从第4行开始的5行
select * from 表 limit 5 offset 4; -- 从第4行开始的5行
排序(order by)
select * from 表 order by 列 asc; -- 根据 “列” 从小到大排列
select * from 表 order by 列 desc; -- 根据 “列” 从大到小排列
select * from 表 order by 列1 desc,列2 asc; -- 根据 “列1” 从大到小排列,如果相同则按列2从小到大排序
分组(group by)
select num from 表 group by num;
select num,nid from 表 group by num,nid;
select num,nid from 表 where nid > 10 group by num,nid order nid desc;
select num,nid,count(*),sum(score),max(score),min(score) from 表 group by num,nid;
select num from 表 group by num having max(id) > 10;
子查询
select p.prod_name from products p where p.vend_id in
(select v.vend_id from vendors v where v.vend_name="ACME");
联表查询
inner join,left join,right join三者的区别
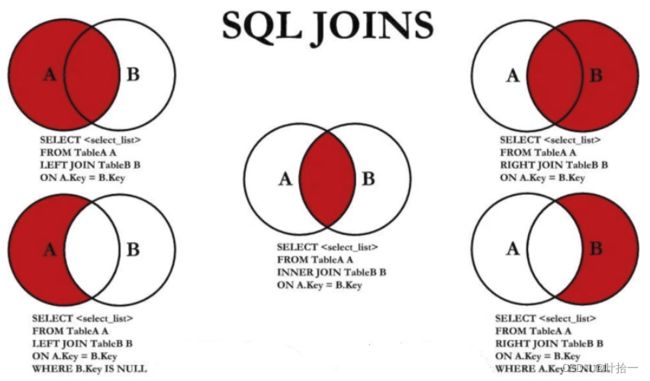
inner join的计算规则是,用左边表的每一行去匹配右边表的每一行,如果满足连接的条件,就组成一行返回,返回的行里面包括两张表的所有字段,如果不满足连接的条件,就不返回。
left join的计算规则是:以左边表为基准,用左边表的每一行去匹配右边表的每一行,如果满足连接的条件,就组成一行返回,如果连接的字段值只在左边表存在,在右边表不存在,那么在结果中就只显示左边表的字段值,右边表中的字段用空值(null)来表示。
right join的计算规则是:以右边表为基准,用右边表的每一行去匹配左边表的每一行,如果满足连接的条件,就组成一行返回,如果连接的字段值只在右边表存在,在左边表不存在,那么在结果中就只显示右边表的字段值,左边表中的字段用空值null来表示。
内连接(inner join)
select prod_name,o.order_num,quantity from products p inner join orderitems o on p.prod_id=o.prod_id;
select prod_name,vend_name,prod_price,quantity from orderitems,products,vendors where products.vend_id=vendors.vend_id and orderitems.prod_id=products.prod_id and orderitems.order_num=20005;
左连接(left join)
select customers.cust_id,cust_name,order_num from customers left join orders on customers.cust_id=orders.cust_id;
右连接(right join)
select customers.cust_id,cust_name,order_num from orders right join customers on customers.cust_id=orders.cust_id;
组合查询
-
可用union操作符来组合数条SQL查询,利用union可以将多条select语句组合起来,将它们的结果组合成单个结果集。
-
语法:
- select * from 表 where 条件 union select * from 表 where 条件;
- select * from 表 where 条件 union all select * from 表 where 条件;
- union和union all的区别:union会对结果自动去重,union all不会去重。
-
注意:两个select语句应该有相同数量的列,数据类型要相同或者可以兼容。
-
举例:
#查询价格小于等于5的产品以及供应商1001和1002生产的所有产品(不考虑价格)。
mysql> select vend_id,prod_id,prod_price from products where prod_price<=5
-> union
-> select vend_id, prod_id,prod_price from products where vend_id in (1001,1002);
+---------+---------+------------+
| VEND_ID | PROD_ID | PROD_PRICE |
+---------+---------+------------+
| 1003 | FC | 2.50 |
| 1002 | FU1 | 3.42 |
| 1003 | SLING | 4.49 |
| 1003 | TNT1 | 2.50 |
| 1001 | ANV01 | 5.99 |
| 1001 | ANV02 | 9.99 |
| 1001 | ANV03 | 14.99 |
| 1002 | OL1 | 8.99 |
+---------+---------+------------+
8 rows in set (0.01 sec)
#查询价格小于等于5的产品以及供应商1001和1002生产的所有物品(不考虑价格)。
mysql> select vend_id,prod_id,prod_price from products where prod_price<=5
-> union all
-> select vend_id, prod_id,prod_price from products where vend_id in (1001,1002);
+---------+---------+------------+
| VEND_ID | PROD_ID | PROD_PRICE |
+---------+---------+------------+
| 1003 | FC | 2.50 |
| 1002 | FU1 | 3.42 |
| 1003 | SLING | 4.49 |
| 1003 | TNT1 | 2.50 |
| 1001 | ANV01 | 5.99 |
| 1001 | ANV02 | 9.99 |
| 1001 | ANV03 | 14.99 |
| 1002 | FU1 | 3.42 |
| 1002 | OL1 | 8.99 |
+---------+---------+------------+
9 rows in set (0.01 sec)
索引Index
索引是一种数据结构,作用是可以提高查询的效率。在数据库表中,可以对某个字段创建索引,有索引的字段在查询效率上会明显比没有索引的要快。索引是针对每个字段创建的。主键和外键会自动创建索引。
举例:
#查询表有哪些索引
show index from customers;
#创建索引
create index state_index on customers(cust_state);
#删除索引
drop index state_index on customers;
但是在实际使用中,我们不会对每个字段都创建索引,一般我们会对经常被查询的字段或者是经常被用来作为连表条件的字段创建索引。
视图View
视图是一张虚拟的表,视图的数据来自于SQL语句从真正的表中查询得到,视图支持查询,但不支持增删改操作。
举例:
#创建一个视图
create view cust_name_prod_id as
select customers.`cust_name`,orderitems.`prod_id` from customers inner join orders on customers.`cust_id`=
orders.`cust_id` inner join orderitems on orders.`order_num`=orderitems.`order_num`;
#列出订购物品编号TNT2的所有客户姓名
select * from cust_name_prod_id where prod_id="TNT2";
SQL语句的分类
- DQL(数据查询语言):select (query)
- DML(数据库操纵语言):insert into/delete from/update等
- DDL(数据库描述语言):create/alter/drop等
- DCL(数据库控制语言):grant/commit/rollback等
SQL语言,所有关系型数据库的操作都是基于SQL语句来实现。