yolov3实现Kitti baseline(含评估代码:easy、moderate和hard的AP计算,fps计算)(下)
yolov3实现Kitti baseline(含评估代码:easy、moderate和hard的AP计算,fps计算)
上篇博客谈到如何训练基于kitti的yolov3模型,这篇主要讨论如何使用模型参数进行前向推理,如何实现kitti 2d目标的easy、moderate和hard计算。
1. 测试数据集的准备
前面运行train.py的代码时候,会在VOCdevkit/VOC2007/ImageSets/Main的文件夹下有一个test.txt文件,里面保存了用于测试的图片的编号,如下图所示。
1-1. 测试集图片的生成
创建一个名为kitti_test的文件夹,all_imgs里面存放所有的7841张图片(使用命令拷贝过来,参考前面两篇博客),all_labels里面存放所有的7841个txt标签信息(使用命令拷贝过来,参考前面两篇博客),test_imgs用于存放生成的测试集图片,test_labels用于存放生成的测试集txt标签信息,get_testimgs.py是一个获取测试集图片的脚本,get_testlabels.py是一个获取测试集txt标签的脚本,text.txt是上述会在VOCdevkit/VOC2007/ImageSets/Main的文件夹下存放测试集编号信息的txt文件。

运行get_testimgs.py脚本,生成test_imgs用于测试的图片,代码如下。
import shutil
# 根据txt中文件的名字批量提取对应的文件名并保存到另一个文件夹
data = []
for line in open("/home/shenchaoyao3/Desktop/kitti_test/test.txt", "r"): # 设置文件对象并读取每一行文件
data.append(line)
for a in data:
src = '/home/shenchaoyao3/Desktop/kitti_test/all_imgs/{}.jpg'.format(a[:-1])
dst = '/home/shenchaoyao3/Desktop/kitti_test/test_imgs/{}.jpg'.format(a[:-1])
shutil.copy(src, dst)
1-2. 测试集txt标签的生成
运行get_testlabels.py,获取测试集txt标签,代码如下。
import shutil
# 根据txt中文件的名字批量提取对应的文件名并保存到另一个文件夹
data = []
for line in open("/home/shenchaoyao3/Desktop/kitti_test/test.txt", "r"): # 设置文件对象并读取每一行文件
data.append(line)
for a in data:
src = '/home/shenchaoyao3/Desktop/kitti_test/all_labels/{}.txt'.format(a[:-1])
dst = '/home/shenchaoyao3/Desktop/kitti_test/test_labels/{}.txt'.format(a[:-1])
shutil.copy(src, dst)
2.前向推理预测
将获取的测试集图片拷贝到yolo3-pytorch项目库下,并创建文件夹命名test_imgs


修改predict.py的文件路径、模式,以及模型配置,yolo.py的帧率测试函数和图像检测函数,这里直接放代码,后面有疑问可以私聊解释。
yolo.py
#-----------------------------------------------------------------------#
# predict.py将单张图片预测、摄像头检测、FPS测试和目录遍历检测等功能
# 整合到了一个py文件中,通过指定mode进行模式的修改。
#-----------------------------------------------------------------------#
import time
import cv2
import numpy as np
from PIL import Image
from yolo import YOLO
if __name__ == "__main__":
yolo = YOLO()
#----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------#
# mode用于指定测试的模式:
# 'predict'表示单张图片预测,如果想对预测过程进行修改,如保存图片,截取对象等,可以先看下方详细的注释
# 'video'表示视频检测,可调用摄像头或者视频进行检测,详情查看下方注释。
# 'fps'表示测试fps,使用的图片是img里面的street.jpg,详情查看下方注释。
# 'dir_predict'表示遍历文件夹进行检测并保存。默认遍历img文件夹,保存img_out文件夹,详情查看下方注释。
#----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------#
mode = "fps"
#----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------#
# video_path用于指定视频的路径,当video_path=0时表示检测摄像头
# 想要检测视频,则设置如video_path = "xxx.mp4"即可,代表读取出根目录下的xxx.mp4文件。
# video_save_path表示视频保存的路径,当video_save_path=""时表示不保存
# 想要保存视频,则设置如video_save_path = "yyy.mp4"即可,代表保存为根目录下的yyy.mp4文件。
# video_fps用于保存的视频的fps
# video_path、video_save_path和video_fps仅在mode='video'时有效
# 保存视频时需要ctrl+c退出或者运行到最后一帧才会完成完整的保存步骤。
#----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------#
video_path = 0
video_save_path = ""
video_fps = 25.0
#-------------------------------------------------------------------------#
# test_interval用于指定测量fps的时候,图片检测的次数
# 理论上test_interval越大,fps越准确。
#-------------------------------------------------------------------------#
test_interval = 100
#-------------------------------------------------------------------------#
# dir_origin_path指定了用于检测的图片的文件夹路径
# dir_save_path指定了检测完图片的保存路径
# dir_origin_path和dir_save_path仅在mode='dir_predict','fps'时有效
#-------------------------------------------------------------------------#
dir_origin_path = "test_imgs/"
dir_save_path = "img_out/"
if mode == "predict":
'''
1、如果想要进行检测完的图片的保存,利用r_image.save("img.jpg")即可保存,直接在predict.py里进行修改即可。
2、如果想要获得预测框的坐标,可以进入yolo.detect_image函数,在绘图部分读取top,left,bottom,right这四个值。
3、如果想要利用预测框截取下目标,可以进入yolo.detect_image函数,在绘图部分利用获取到的top,left,bottom,right这四个值
在原图上利用矩阵的方式进行截取。
4、如果想要在预测图上写额外的字,比如检测到的特定目标的数量,可以进入yolo.detect_image函数,在绘图部分对predicted_class进行判断,
比如判断if predicted_class == 'car': 即可判断当前目标是否为车,然后记录数量即可。利用draw.text即可写字。
'''
while True:
img = input('Input image filename:')
number=str(img)
number=number.split('/')[1].split('.')[0]
try:
image = Image.open(img)
except:
print('Open Error! Try again!')
continue
else:
predicted_class, top, left, bottom, right, score = yolo.detect_image(image,number)
# r_image.show()
elif mode == "video":
capture = cv2.VideoCapture(video_path)
if video_save_path!="":
fourcc = cv2.VideoWriter_fourcc(*'XVID')
size = (int(capture.get(cv2.CAP_PROP_FRAME_WIDTH)), int(capture.get(cv2.CAP_PROP_FRAME_HEIGHT)))
out = cv2.VideoWriter(video_save_path, fourcc, video_fps, size)
ref, frame = capture.read()
if not ref:
raise ValueError("未能正确读取摄像头(视频),请注意是否正确安装摄像头(是否正确填写视频路径)。")
fps = 0.0
while(True):
t1 = time.time()
# 读取某一帧
ref, frame = capture.read()
if not ref:
break
# 格式转变,BGRtoRGB
frame = cv2.cvtColor(frame,cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB)
# 转变成Image
frame = Image.fromarray(np.uint8(frame))
# 进行检测
frame = np.array(yolo.detect_image(frame))
# RGBtoBGR满足opencv显示格式
frame = cv2.cvtColor(frame,cv2.COLOR_RGB2BGR)
fps = ( fps + (1./(time.time()-t1)) ) / 2
print("fps= %.2f"%(fps))
frame = cv2.putText(frame, "fps= %.2f"%(fps), (0, 40), cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 1, (0, 255, 0), 2)
cv2.imshow("video",frame)
c= cv2.waitKey(1) & 0xff
if video_save_path!="":
out.write(frame)
if c==27:
capture.release()
break
print("Video Detection Done!")
capture.release()
if video_save_path!="":
print("Save processed video to the path :" + video_save_path)
out.release()
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
elif mode == "fps":
# img = Image.open('img/000114.jpg')
# tact_time = yolo.get_FPS(img, test_interval)
# print(str(tact_time) + ' seconds, ' + str(1/tact_time) + 'FPS, @batch_size 1')
import os
from tqdm import tqdm
time_total=0
times=0
img_names = os.listdir(dir_origin_path)
for img_name in tqdm(img_names):
if img_name.lower().endswith(('.bmp', '.dib', '.png', '.jpg', '.jpeg', '.pbm', '.pgm', '.ppm', '.tif', '.tiff')):
image_path = os.path.join(dir_origin_path, img_name)
image = Image.open(image_path)
tact_time = yolo.get_FPS(image, test_interval)
time_total=time_total+tact_time
times=times+1
time_final=time_total/times
print(str(time_final) + ' seconds, ' + str(1 / time_final) + 'FPS, @batch_size 1')
elif mode == "dir_predict":
import os
from tqdm import tqdm
img_names = os.listdir(dir_origin_path)
for img_name in tqdm(img_names):
if img_name.lower().endswith(('.bmp', '.dib', '.png', '.jpg', '.jpeg', '.pbm', '.pgm', '.ppm', '.tif', '.tiff')):
image_path = os.path.join(dir_origin_path, img_name)
number = str(image_path)
number = number.split('/')[1].split('.')[0]
image = Image.open(image_path)
predicted_class, top, left, bottom, right, score = yolo.detect_image(image,number)
# if not os.path.exists(dir_save_path):
# os.makedirs(dir_save_path)
# r_image.save(os.path.join(dir_save_path, img_name))
else:
raise AssertionError("Please specify the correct mode: 'predict', 'video', 'fps' or 'dir_predict'.")
yolo.py
import colorsys
import os
import time
import numpy as np
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
from PIL import ImageDraw, ImageFont
from nets.yolo import YoloBody
from utils.utils import (cvtColor, get_anchors, get_classes, preprocess_input,
resize_image)
from utils.utils_bbox import DecodeBox
import os
os.environ["CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES"]="5"
'''
训练自己的数据集必看注释!
'''
class YOLO(object):
_defaults = {
#--------------------------------------------------------------------------#
# 使用自己训练好的模型进行预测一定要修改model_path和classes_path!
# model_path指向logs文件夹下的权值文件,classes_path指向model_data下的txt
#
# 训练好后logs文件夹下存在多个权值文件,选择验证集损失较低的即可。
# 验证集损失较低不代表mAP较高,仅代表该权值在验证集上泛化性能较好。
# 如果出现shape不匹配,同时要注意训练时的model_path和classes_path参数的修改
#--------------------------------------------------------------------------#
"model_path" : 'logs/ep100-loss2.670-val_loss4.087.pth',
"classes_path" : 'model_data/cls_classes.txt',
#---------------------------------------------------------------------#
# anchors_path代表先验框对应的txt文件,一般不修改。
# anchors_mask用于帮助代码找到对应的先验框,一般不修改。
#---------------------------------------------------------------------#
"anchors_path" : 'model_data/yolo_anchors.txt',
"anchors_mask" : [[6, 7, 8], [3, 4, 5], [0, 1, 2]],
#---------------------------------------------------------------------#
# 输入图片的大小,必须为32的倍数。
#---------------------------------------------------------------------#
"input_shape" : [416, 416],
#---------------------------------------------------------------------#
# 只有得分大于置信度的预测框会被保留下来
#---------------------------------------------------------------------#
"confidence" : 0.5,
#---------------------------------------------------------------------#
# 非极大抑制所用到的nms_iou大小
#---------------------------------------------------------------------#
"nms_iou" : 0.3,
#---------------------------------------------------------------------#
# 该变量用于控制是否使用letterbox_image对输入图像进行不失真的resize,
# 在多次测试后,发现关闭letterbox_image直接resize的效果更好
#---------------------------------------------------------------------#
"letterbox_image" : False,
#-------------------------------#
# 是否使用Cuda
# 没有GPU可以设置成False
#-------------------------------#
"cuda" : True,
}
@classmethod
def get_defaults(cls, n):
if n in cls._defaults:
return cls._defaults[n]
else:
return "Unrecognized attribute name '" + n + "'"
#---------------------------------------------------#
# 初始化YOLO
#---------------------------------------------------#
def __init__(self, **kwargs):
self.__dict__.update(self._defaults)
for name, value in kwargs.items():
setattr(self, name, value)
#---------------------------------------------------#
# 获得种类和先验框的数量
#---------------------------------------------------#
self.class_names, self.num_classes = get_classes(self.classes_path)
self.anchors, self.num_anchors = get_anchors(self.anchors_path)
self.bbox_util = DecodeBox(self.anchors, self.num_classes, (self.input_shape[0], self.input_shape[1]), self.anchors_mask)
#---------------------------------------------------#
# 画框设置不同的颜色
#---------------------------------------------------#
hsv_tuples = [(x / self.num_classes, 1., 1.) for x in range(self.num_classes)]
self.colors = list(map(lambda x: colorsys.hsv_to_rgb(*x), hsv_tuples))
self.colors = list(map(lambda x: (int(x[0] * 255), int(x[1] * 255), int(x[2] * 255)), self.colors))
self.generate()
#---------------------------------------------------#
# 生成模型
#---------------------------------------------------#
def generate(self):
#---------------------------------------------------#
# 建立yolov3模型,载入yolov3模型的权重
#---------------------------------------------------#
self.net = YoloBody(self.anchors_mask, self.num_classes)
device = torch.device('cuda' if torch.cuda.is_available() else 'cpu')
self.net.load_state_dict(torch.load(self.model_path, map_location=device))
self.net = self.net.eval()
print('{} model, anchors, and classes loaded.'.format(self.model_path))
if self.cuda:
self.net = nn.DataParallel(self.net)
self.net = self.net.cuda()
#---------------------------------------------------#
# 检测图片
#---------------------------------------------------#
def detect_image(self, image, number):
image_shape = np.array(np.shape(image)[0:2])
#---------------------------------------------------------#
# 在这里将图像转换成RGB图像,防止灰度图在预测时报错。
# 代码仅仅支持RGB图像的预测,所有其它类型的图像都会转化成RGB
#---------------------------------------------------------#
image = cvtColor(image)
#---------------------------------------------------------#
# 给图像增加灰条,实现不失真的resize
# 也可以直接resize进行识别
#---------------------------------------------------------#
image_data = resize_image(image, (self.input_shape[1],self.input_shape[0]), self.letterbox_image)
#---------------------------------------------------------#
# 添加上batch_size维度
#---------------------------------------------------------#
image_data = np.expand_dims(np.transpose(preprocess_input(np.array(image_data, dtype='float32')), (2, 0, 1)), 0)
with torch.no_grad():
images = torch.from_numpy(image_data)
if self.cuda:
images = images.cuda()
#---------------------------------------------------------#
# 将图像输入网络当中进行预测!
#---------------------------------------------------------#
outputs = self.net(images)
outputs = self.bbox_util.decode_box(outputs)
#---------------------------------------------------------#
# 将预测框进行堆叠,然后进行非极大抑制
#---------------------------------------------------------#
results = self.bbox_util.non_max_suppression(torch.cat(outputs, 1), self.num_classes, self.input_shape,
image_shape, self.letterbox_image, conf_thres = self.confidence, nms_thres = self.nms_iou)
if results[0] is None:
return image
top_label = np.array(results[0][:, 6], dtype = 'int32')
top_conf = results[0][:, 4] * results[0][:, 5]
top_boxes = results[0][:, :4]
#---------------------------------------------------------#
# 设置字体与边框厚度
#---------------------------------------------------------#
font = ImageFont.truetype(font='model_data/simhei.ttf', size=np.floor(3e-2 * image.size[1] + 0.5).astype('int32'))
thickness = int(max((image.size[0] + image.size[1]) // np.mean(self.input_shape), 1))
#---------------------------------------------------------#
# 图像绘制
#---------------------------------------------------------#
for i, c in list(enumerate(top_label)):
predicted_class = self.class_names[int(c)]
box = top_boxes[i]
score = top_conf[i]
top, left, bottom, right = box
# top = max(0, np.floor(top).astype('int32'))
# left = max(0, np.floor(left).astype('int32'))
# bottom = min(image.size[1], np.floor(bottom).astype('int32'))
# right = min(image.size[0], np.floor(right).astype('int32'))
#
# label = '{} {:.2f}'.format(predicted_class, score)
# draw = ImageDraw.Draw(image)
# label_size = draw.textsize(label, font)
# label = label.encode('utf-8')
src = 'pre_imgs/{}.txt'.format(number)
f = open(src, 'a')
f.write("{} {:.2f} {:.2f} {:.2f} {:.2f} {:.2f}".format(predicted_class, left, top, right, bottom, score))
f.write('\n')
# print(label, top, left, bottom, right)
#
# if top - label_size[1] >= 0:
# text_origin = np.array([left, top - label_size[1]])
# else:
# text_origin = np.array([left, top + 1])
#
# for i in range(thickness):
# draw.rectangle([left + i, top + i, right - i, bottom - i], outline=self.colors[c])
# draw.rectangle([tuple(text_origin), tuple(text_origin + label_size)], fill=self.colors[c])
# draw.text(text_origin, str(label,'UTF-8'), fill=(0, 0, 0), font=font)
# del draw
f.close()
# return image
return predicted_class,top,left,bottom,right,score
def get_FPS(self, image, test_interval):
image_shape = np.array(np.shape(image)[0:2])
#---------------------------------------------------------#
# 在这里将图像转换成RGB图像,防止灰度图在预测时报错。
# 代码仅仅支持RGB图像的预测,所有其它类型的图像都会转化成RGB
#---------------------------------------------------------#
image = cvtColor(image)
#---------------------------------------------------------#
# 给图像增加灰条,实现不失真的resize
# 也可以直接resize进行识别
#---------------------------------------------------------#
image_data = resize_image(image, (self.input_shape[1],self.input_shape[0]), self.letterbox_image)
#---------------------------------------------------------#
# 添加上batch_size维度
#---------------------------------------------------------#
image_data = np.expand_dims(np.transpose(preprocess_input(np.array(image_data, dtype='float32')), (2, 0, 1)), 0)
with torch.no_grad():
images = torch.from_numpy(image_data)
if self.cuda:
images = images.cuda()
#---------------------------------------------------------#
# 将图像输入网络当中进行预测!
#---------------------------------------------------------#
outputs = self.net(images)
outputs = self.bbox_util.decode_box(outputs)
#---------------------------------------------------------#
# 将预测框进行堆叠,然后进行非极大抑制
#---------------------------------------------------------#
results = self.bbox_util.non_max_suppression(torch.cat(outputs, 1), self.num_classes, self.input_shape,
image_shape, self.letterbox_image, conf_thres=self.confidence, nms_thres=self.nms_iou)
t1 = time.time()
for _ in range(test_interval):
with torch.no_grad():
#---------------------------------------------------------#
# 将图像输入网络当中进行预测!
#---------------------------------------------------------#
outputs = self.net(images)
outputs = self.bbox_util.decode_box(outputs)
#---------------------------------------------------------#
# 将预测框进行堆叠,然后进行非极大抑制
#---------------------------------------------------------#
results = self.bbox_util.non_max_suppression(torch.cat(outputs, 1), self.num_classes, self.input_shape,
image_shape, self.letterbox_image, conf_thres=self.confidence, nms_thres=self.nms_iou)
t2 = time.time()
tact_time = (t2 - t1) / test_interval
return tact_time
def get_map_txt(self, image_id, image, class_names, map_out_path):
f = open(os.path.join(map_out_path, "detection-results/"+image_id+".txt"),"w")
image_shape = np.array(np.shape(image)[0:2])
#---------------------------------------------------------#
# 在这里将图像转换成RGB图像,防止灰度图在预测时报错。
# 代码仅仅支持RGB图像的预测,所有其它类型的图像都会转化成RGB
#---------------------------------------------------------#
image = cvtColor(image)
#---------------------------------------------------------#
# 给图像增加灰条,实现不失真的resize
# 也可以直接resize进行识别
#---------------------------------------------------------#
image_data = resize_image(image, (self.input_shape[1],self.input_shape[0]), self.letterbox_image)
#---------------------------------------------------------#
# 添加上batch_size维度
#---------------------------------------------------------#
image_data = np.expand_dims(np.transpose(preprocess_input(np.array(image_data, dtype='float32')), (2, 0, 1)), 0)
with torch.no_grad():
images = torch.from_numpy(image_data)
if self.cuda:
images = images.cuda()
#---------------------------------------------------------#
# 将图像输入网络当中进行预测!
#---------------------------------------------------------#
outputs = self.net(images)
outputs = self.bbox_util.decode_box(outputs)
#---------------------------------------------------------#
# 将预测框进行堆叠,然后进行非极大抑制
#---------------------------------------------------------#
results = self.bbox_util.non_max_suppression(torch.cat(outputs, 1), self.num_classes, self.input_shape,
image_shape, self.letterbox_image, conf_thres = self.confidence, nms_thres = self.nms_iou)
if results[0] is None:
return
top_label = np.array(results[0][:, 6], dtype = 'int32')
top_conf = results[0][:, 4] * results[0][:, 5]
top_boxes = results[0][:, :4]
for i, c in list(enumerate(top_label)):
predicted_class = self.class_names[int(c)]
box = top_boxes[i]
score = str(top_conf[i])
top, left, bottom, right = box
if predicted_class not in class_names:
continue
f.write("%s %s %s %s %s %s\n" % (predicted_class, score[:6], str(int(left)), str(int(top)), str(int(right)),str(int(bottom))))
f.close()
return
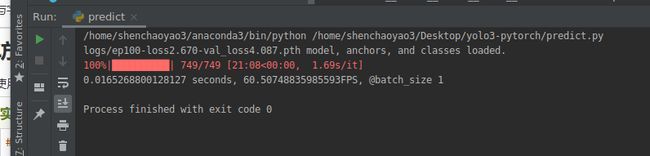
运行predict.py,模式为dir_predict会在pre_imgs文件夹下生成预测的txt标签信息,至此就有预测标签和争取标签信息的对比文件,接下来编写脚本,对比两个文件信息,计算相应难度的AP;而模式为fps的话就会计算test_imgs文件夹内的所有图片的帧率。
3. 评估——easy、moderate和hard的AP计算
创建kitti_evaluation_for_2d_detection文件夹,并在其内创建pre_labels存放之前pre_imgs文件夹下的预测txt标签信息,test_labels文件夹下存放真实的txt标签信息。
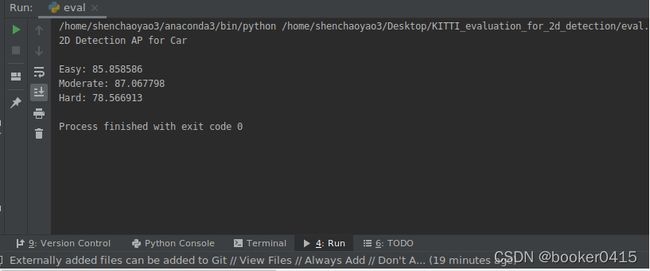
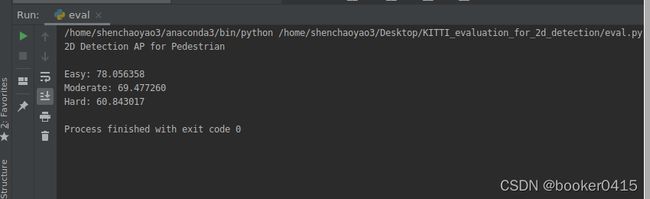
运行以下代码eval.py,生成Car和Pedestrain三个难度的预测信息。
import numpy as np
import os
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# VALID_CLASSES = ['Car', 'Van', 'Pedestrian', 'Person_sitting', 'Cyclist', 'DontCare']
VALID_CLASSES = ['Car', 'Pedestrian', 'Cyclist']
CLS_DICT = {'Car':0, 'Pedestrian':1, 'Cyclist':2}
MIN_HEIGHT = [40, 25, 25]
MAX_OCCLUSION = [0, 1, 2]
MAX_TRUNCATION = [0.15, 0.3, 0.5]
MIN_OVERLAP = {'Car':0.7,'Pedestrian':0.5,'Cyclist': 0.5}
N_SAMPLE_PTS = 41
def load_gt(filename):
f = open(filename, 'r')
lines = f.readlines()
f.close()
record_list = []
for line in lines:
line = line.strip().split(' ')
if len(line) == 0:
continue
if line[0] not in VALID_CLASSES:
continue
record = {}
record['class'] = line[0]
record['trunc'] = float(line[1])
record['occ'] = float(line[2])
record['box'] = [float(c) for c in line[4:8]]
record_list.append(record)
return record_list
def load_pred(filename):
f = open(filename, 'r')
lines = f.readlines()
f.close()
record_list = []
for line in lines:
line = line.strip().split(' ')
if len(line) == 0:
continue
if line[0] not in VALID_CLASSES:
continue
record = {}
record['class'] = line[0]
record['box'] = [float(c) for c in line[1:5]]
record['score'] = float(line[-1])
record_list.append(record)
return record_list
def get_thresholds(v, n_groundTruth):
v = np.array(v)
sort_ind_desc = np.argsort(v * -1)
vs = v[sort_ind_desc]
t = []
current_recall = 0
for i in range(vs.shape[0]):
l_recall = (i+1)/n_groundTruth
if i < vs.shape[0] - 1:
r_recall = (i+2)/n_groundTruth
else:
r_recall = l_recall
if (r_recall - current_recall) < (current_recall - l_recall) and i < (vs.shape[0] - 1):
continue
t.append(vs[i])
current_recall += 1.0 / (N_SAMPLE_PTS - 1.0)
return t
def get_iou(gt, pred, union=True):
gxmin, gymin, gxmax, gymax = gt['box']
pxmin, pymin, pxmax, pymax = pred['box']
ixmin = np.maximum(gxmin, pxmin)
iymin = np.maximum(gymin, pymin)
ixmax = np.minimum(gxmax, pxmax)
iymax = np.minimum(gymax, pymax)
ih = np.maximum(0., iymax - iymin)
iw = np.maximum(0., ixmax - ixmin)
gvol = (gxmax - gxmin) * (gymax - gymin)
pvol = (pxmax - pxmin) * (pymax - pymin)
ivol = iw * ih
if union:
iou = ivol / (gvol + pvol - ivol)
else:
iou = ivol / pvol
return iou
def clean_data(gts, preds, cls, diff):
ignore_gt = []
ignore_pred = []
dontcare = []
n_gt = 0
#clean ground truth
for gt in gts:
#set ignore
if cls == gt['class']:
valid_class = 1
else:
if gt['class'] == 'Van' and cls == 'Car':
valid_class = 0
elif gt['class'] == 'Person_sitting' and cls == 'Pedestrian':
valid_class = 0
else:
valid_class = -1
height = gt['box'][3] - gt['box'][1]
if gt['occ'] > MAX_OCCLUSION[diff] or gt['trunc'] > MAX_TRUNCATION[diff] or height < MIN_HEIGHT[diff]:
ignore = True
else:
ignore = False
if valid_class == 1 and not ignore:
n_gt += 1
ignore_gt.append(0)
elif valid_class == 0 or (ignore and valid_class == 1):
ignore_gt.append(1)
else:
ignore_gt.append(-1)
#set Don't care
if gt['class'] == 'DontCare':
dontcare.append(True)
else:
dontcare.append(False)
#clean predictions
for pred in preds:
if pred['class'] == cls:
valid_class = 1
else:
valid_class = 0
height = pred['box'][3] - pred['box'][1]
if height < MIN_HEIGHT[diff]:
ignore_pred.append(1)
elif valid_class == 1:
ignore_pred.append(0)
else:
ignore_pred.append(-1)
return ignore_gt, dontcare, ignore_pred, n_gt
def compute_statistics(gts, preds, dontcare, ignore_gt, ignore_pred, compute_fp, threshold, cls, diff):
n_gt = len(gts)
n_pred = len(preds)
assigned_detection = [False for _ in range(n_pred)]
TP, FP, FN = 0, 0, 0
vs = []
ignore_threshold = []
if compute_fp:
for pred in preds:
if pred['score'] < threshold:
ignore_threshold.append(True)
else:
ignore_threshold.append(False)
else:
for pred in preds:
ignore_threshold.append(False)
for i in range(n_gt):
if ignore_gt[i] == -1:
continue
det_idx = -1
valid_detection = -1
max_iou = 0.
assigned_ignored_det = False
for j in range(n_pred):
if ignore_pred[j] == -1:
continue
if assigned_detection[j]:
continue
if ignore_threshold[j]:
continue
iou = get_iou(gts[i], preds[j])
if not compute_fp and iou > MIN_OVERLAP[cls] and preds[j]['score'] > threshold:
det_idx = j
valid_detection = preds[j]['score']
elif compute_fp and iou > MIN_OVERLAP[cls] and (iou > max_iou or assigned_ignored_det) and ignore_pred[j] == 0:
max_iou = iou
det_idx = j
valid_detection = 1
assigned_ignored_det = False
elif compute_fp and iou > MIN_OVERLAP[cls] and valid_detection == -1. and ignore_pred[j] == 1:
det_idx = j
valid_detection = 1
assigned_ignored_det = True
if valid_detection == -1 and ignore_gt[i] == 0:
FN += 1
elif valid_detection != -1 and (ignore_gt[i] == 1 or ignore_pred[det_idx]==1):
assigned_detection[det_idx] = True
elif valid_detection != -1:
TP += 1
vs.append(preds[det_idx]['score'])
assigned_detection[det_idx] = True
if compute_fp:
for i in range(n_pred):
if not (assigned_detection[i] or ignore_pred[i]==-1 or ignore_pred[i]==1 or ignore_threshold[i]):
FP += 1
n_stuff = 0
for i in range(n_gt):
if not dontcare[i]:
continue
for j in range(n_pred):
if assigned_detection[j]:
continue
if ignore_pred[j] == -1 or ignore_pred[j] == 1:
continue
if ignore_threshold[j]:
continue
iou = get_iou(preds[j], gts[i], union=False)
if iou > MIN_OVERLAP[cls]:
assigned_detection[j] = True
n_stuff += 1
FP -= n_stuff
return TP, FP, FN, vs
def eval_class(gt_list, pred_list, cls, diff):
ignore_gt_list = []
ignore_pred_list = []
dontcare_list = []
total_gt_num = 0
#clean data
vs = []
for i in range(len(gt_list)):
ignore_gt, dontcare, ignore_pred, n_gt_ = clean_data(gt_list[i], pred_list[i], cls, diff)
ignore_gt_list.append(ignore_gt)
ignore_pred_list.append(ignore_pred)
dontcare_list.append(dontcare)
total_gt_num += n_gt_
_, _, _, vs_ = compute_statistics(gt_list[i], pred_list[i], dontcare, ignore_gt, ignore_pred, False, 0, cls, diff)
vs = vs + vs_
thresholds = get_thresholds(vs, total_gt_num)
len_th = len(thresholds)
TPs = [0.] * len_th
FPs = [0.] * len_th
FNs = [0.] * len_th
for i in range(len(gt_list)):
for t, th in enumerate(thresholds):
TP, FP, FN, _, = compute_statistics(gt_list[i], pred_list[i], dontcare_list[i], ignore_gt_list[i], ignore_pred_list[i], True, th, cls, diff)
TPs[t] += TP
FPs[t] += FP
FNs[t] += FN
precisions = [0.] * N_SAMPLE_PTS
recalls = []
for t, th in enumerate(thresholds):
r = TPs[t] / (TPs[t] + FNs[t])
recalls.append(r)
precisions[t] = TPs[t] / (TPs[t] + FPs[t])
for t, th in enumerate(thresholds):
precisions[t] = np.max(precisions[t:])
return precisions, recalls
def plot_and_compute(precisions,cls, plot):
if plot:
Xs = np.arange(0., 1., 1./len(precisions[0]))
l_easy = plt.plot(Xs, precisions[0], c='green')[0]
l_moderate = plt.plot(Xs, precisions[1], c='blue')[0]
l_hard = plt.plot(Xs, precisions[2], c='red')[0]
labels = ['Easy','Moderate','Hard']
plt.legend(handles=[l_easy,l_moderate,l_hard],labels=labels,loc='best')
plt.xlabel('Recall')
plt.ylabel('Precision')
plt.title(cls)
plt.ylim((0,1.0))
plt.grid()
plt.savefig('2d_result.png')
plt.show()
plt.close()
val_easy, val_moderate, val_hard = 0., 0., 0.
for i in range(0, N_SAMPLE_PTS,4):
val_easy += precisions[0][i]
val_moderate += precisions[1][i]
val_hard += precisions[2][i]
ap_easy = 100. * val_easy / 11.
ap_moderate = 100. * val_moderate / 11.
ap_hard = 100. * val_hard / 11.
print('2D Detection AP for %s\n'%cls)
print('Easy: %f'%ap_easy)
print('Moderate: %f'%ap_moderate)
print('Hard: %f'%ap_hard)
def eval(gt_dir, pred_dir, cls):
gt_list = []
pred_list = []
for f in os.listdir(pred_dir):
record_pred = load_pred(os.path.join(pred_dir, f))
record_gt = load_gt(os.path.join(gt_dir, f))
pred_list.append(record_pred)
gt_list.append(record_gt)
recall_all_diff = []
precision_all_diff = []
for diff in range(3):
precisions, recalls = eval_class(gt_list, pred_list, cls, diff)
precision_all_diff.append(precisions)
recall_all_diff.append(recalls)
plot_and_compute(precision_all_diff, cls, plot=True)
if __name__ == '__main__':
gt_dir = '/home/shenchaoyao3/Desktop/KITTI_evaluation_for_2d_detection/test_labels/'
pred_dir = '/home/shenchaoyao3/Desktop/KITTI_evaluation_for_2d_detection/pre_labels/'
#Car, Pedestrian, Cyclist
cls = 'Pedestrian'
eval(gt_dir, pred_dir, cls)