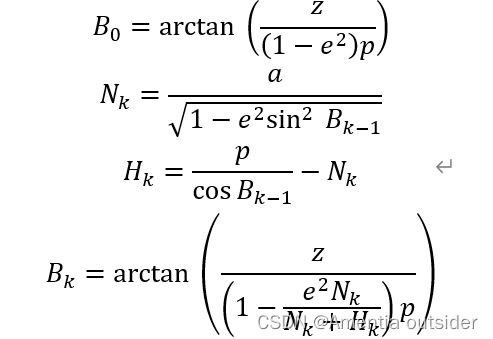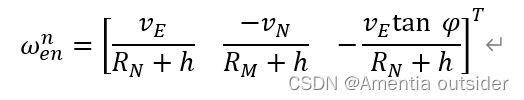GNSS-INS组合导航:KF-GINS(二)
Earth.h文件
基于Eigen库矩阵计算。
1、WGS84确定椭球模型参数
const double WGS84_WIE = 7.2921151467E-5; /* 地球自转角速度*/
const double WGS84_F = 0.0033528106647474805; /* 扁率 */
const double WGS84_RA = 6378137.0000000000; /* 长半轴a */
const double WGS84_RB = 6356752.3142451793; /* 短半轴b */
const double WGS84_GM0 = 398600441800000.00; /* 地球引力常数 */
const double WGS84_E1 = 0.0066943799901413156; /* 第一偏心率平方 */
const double WGS84_E2 = 0.0067394967422764341; /* 第二偏心率平方 */2、计算重力
class Earth {
public:
/* 正常重力计算 */
static double gravity(const Vector3d &blh) {
double sin2 = sin(blh[0]);
sin2 *= sin2;
return 9.7803267715 * (1 + 0.0052790414 * sin2 + 0.0000232718 * sin2 * sin2) +
blh[2] * (0.0000000043977311 * sin2 - 0.0000030876910891) + 0.0000000000007211 * blh[2] * blh[2];
}与严老师PSINS中的代码相近
eth.g = eth.g0*(1+5.27094e-3*eth.sl2+2.32718e-5*sl4)-3.086e-6*pos(3); % grs803、计算子午圈半径
/* 计算子午圈半径和卯酉圈半径 */
static Eigen::Vector2d meridianPrimeVerticalRadius(double lat) {
double tmp, sqrttmp;
tmp = sin(lat);
tmp *= tmp;
tmp = 1 - WGS84_E1 * tmp;
sqrttmp = sqrt(tmp);
return {WGS84_RA * (1 - WGS84_E1) / (sqrttmp * tmp), WGS84_RA / sqrttmp};
}4、计算卯酉圈半径
static double RN(double lat) {
double sinlat = sin(lat);
return WGS84_RA / sqrt(1.0 - WGS84_E1 * sinlat * sinlat);
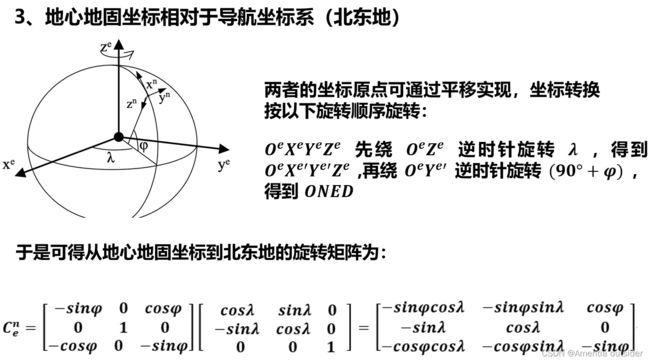
}5、n系到e系转换矩阵
static Matrix3d cne(const Vector3d &blh) {
double coslon, sinlon, coslat, sinlat;
sinlat = sin(blh[0]);
sinlon = sin(blh[1]);
coslat = cos(blh[0]);
coslon = cos(blh[1]);
Matrix3d dcm;
dcm(0, 0) = -sinlat * coslon;
dcm(0, 1) = -sinlon;
dcm(0, 2) = -coslat * coslon;
dcm(1, 0) = -sinlat * sinlon;
dcm(1, 1) = coslon;
dcm(1, 2) = -coslat * sinlon;
dcm(2, 0) = coslat;
dcm(2, 1) = 0;
dcm(2, 2) = -sinlat;
return dcm;
}
6、n系到e系转换四元数
static Quaterniond qne(const Vector3d &blh) {
Quaterniond quat;
double coslon, sinlon, coslat, sinlat;
coslon = cos(blh[1] * 0.5);
sinlon = sin(blh[1] * 0.5);
coslat = cos(-M_PI * 0.25 - blh[0] * 0.5);
sinlat = sin(-M_PI * 0.25 - blh[0] * 0.5);
quat.w() = coslat * coslon;
quat.x() = -sinlat * sinlon;
quat.y() = sinlat * coslon;
quat.z() = coslat * sinlon;
return quat;
}7、从n系到e系转换四元数得到经纬度
static Vector3d blh(const Quaterniond &qne, double height) {
return {-2 * atan(qne.y() / qne.w()) - M_PI * 0.5, 2 * atan2(qne.z(), qne.w()), height};
}8、地理坐标转地心地固坐标
/* 大地坐标(纬度、经度和高程)转地心地固坐标 */
static Vector3d blh2ecef(const Vector3d &blh) {
double coslat, sinlat, coslon, sinlon;
double rnh, rn;
coslat = cos(blh[0]);
sinlat = sin(blh[0]);
coslon = cos(blh[1]);
sinlon = sin(blh[1]);
rn = RN(blh[0]);
rnh = rn + blh[2];
return {rnh * coslat * coslon, rnh * coslat * sinlon, (rnh - rn * WGS84_E1) * sinlat};
}9、地心地固坐标系转地理坐标
tatic Vector3d ecef2blh(const Vector3d &ecef) {
double p = sqrt(ecef[0] * ecef[0] + ecef[1] * ecef[1]);
double rn;
double lat, lon;
double h = 0, h2;
// 初始状态
lat = atan(ecef[2] / (p * (1.0 - WGS84_E1)));
lon = 2.0 * atan2(ecef[1], ecef[0] + p);
do {
h2 = h;
rn = RN(lat);
h = p / cos(lat) - rn;
lat = atan(ecef[2] / (p * (1.0 - WGS84_E1 * rn / (rn + h))));
} while (fabs(h - h2) > 1.0e-4);
return {lat, lon, h};
}这里有许多公式,知乎上有一位北大遥感的大佬对此部分做过详细的总结。
10、n系相对位置转地理坐标相对位置、地理坐标相对位置转n系相对位置
/* n系相对位置转大地坐标相对位置 */
static Matrix3d DRi(const Vector3d &blh) {
Matrix3d dri = Matrix3d::Zero();
Eigen::Vector2d rmn = meridianPrimeVerticalRadius(blh[0]);
dri(0, 0) = 1.0 / (rmn[0] + blh[2]);
dri(1, 1) = 1.0 / ((rmn[1] + blh[2]) * cos(blh[0]));
dri(2, 2) = -1;
return dri;
}
/* 大地坐标相对位置转n系相对位置 */
static Matrix3d DR(const Vector3d &blh) {
Matrix3d dr = Matrix3d::Zero();
Eigen::Vector2d rmn = meridianPrimeVerticalRadius(blh[0]);
dr(0, 0) = rmn[0] + blh[2];
dr(1, 1) = (rmn[1] + blh[2]) * cos(blh[0]);
dr(2, 2) = -1;
return dr;
}
11、地球自转角速度投影到e系
/* 地球自转角速度投影到e系 */
static Vector3d iewe() {
return {0, 0, WGS84_WIE};
}12、地球自转角速度投影到n系
/* 地球自转角速度投影到n系 */
static Vector3d iewn(double lat) {
return {WGS84_WIE * cos(lat), 0, -WGS84_WIE * sin(lat)};
}
static Vector3d iewn(const Vector3d &origin, const Vector3d &local) {
Vector3d global = local2global(origin, local);
return iewn(global[0]);
}13、n系相对于e系转动角速度投影到n系
/* n系相对于e系转动角速度投影到n系 */
static Vector3d enwn(const Eigen::Vector2d &rmn, const Vector3d &blh, const Vector3d &vel) {
return {vel[1] / (rmn[1] + blh[2]), -vel[0] / (rmn[0] + blh[2]), -vel[1] * tan(blh[0]) / (rmn[1] + blh[2])};
}
static Vector3d enwn(const Vector3d &origin, const Vector3d &local, const Vector3d &vel) {
Vector3d global = local2global(origin, local);
Eigen::Vector2d rmn = meridianPrimeVerticalRadius(global[0]);
return enwn(rmn, global, vel);
}感谢武汉大学卫星导航定位技术研究中心多源智能导航实验室(i2Nav)牛小骥教授团队开源的KF-GINS软件平台。