开始第一个例子: Hello World
新建Java工程,设置maven依赖
新建maven工程,设置项目编译级别为Java8及以上,引入fluent mybatis依赖包。
```xml
```
### 新建演示用的数据库结构
```mysql
create schema fluent_mybatis_tutorial;
create table hello_world
(
id bigint unsigned auto_increment primary key,
say_hello varchar(100) null,
your_name varchar(100) null,
gmt_create datetime DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '创建时间',
gmt_modified datetime DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '更新时间',
is_deleted tinyint(2) DEFAULT 0 COMMENT '是否逻辑删除'
) ENGINE = InnoDB
CHARACTER SET = utf8 comment '简单演示表';
```
创建数据库表对应的Entity类
创建数据库表对应的Entity类: HelloWorldEntity, 你只需要简单的做3个动作:
1. 根据驼峰命名规则命名Entity类和字段
2. HelloWorldEntity继承IEntity接口类
3. 在HelloWorldEntity类上加注解 @FluentMybatis
```java
@FluentMybatis
public class HelloWorldEntity implements IEntity {
private Long id;
private String sayHello;
private String yourName;
private Date gmtCreate;
private Date gmtModified;
private Boolean isDeleted;
// get, set, toString 方法
}
```
很简单吧,在这里,你即不需要配置任何mybatis xml文件, 也不需要写任何Mapper接口, 但你已经拥有了强大的增删改查的功能,并且是Fluent API,让我们写一个测试来见证一下Fluent Mybatis的魔法力量!
### 运行测试来见证Fluent Mybatis的神奇
为了运行测试, 我们还需要进行JUnit和Spring Test相关配置。
#### 配置spring bean定义
1. 数据源DataSource配置
2. mybatis的mapper扫描路径
3. mybatis的SqlSessionFactoryBean
```java
@ComponentScan(basePackages = "cn.org.atool.fluent.mybatis.demo1")
@MapperScan("cn.org.atool.fluent.mybatis.demo1.entity.mapper")
@Configuration
public class HelloWorldConfig {
/**
* 设置dataSource属性
*
* @return
*/
@Bean
public DataSource dataSource() {
BasicDataSource dataSource = new BasicDataSource();
dataSource.setDriverClassName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
dataSource.setUrl("jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/fluent_mybatis_tutorial?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf8");
dataSource.setUsername("root");
dataSource.setPassword("password");
return dataSource;
}
/**
* 定义mybatis的SqlSessionFactoryBean
*
* @param dataSource
* @return
*/
@Bean
public SqlSessionFactoryBean sqlSessionFactoryBean(DataSource dataSource) {
SqlSessionFactoryBean bean = new SqlSessionFactoryBean();
bean.setDataSource(dataSource);
return bean;
}
}
```
#### 使用Junit4和Spring-test来执行测试
1. 使用spring-test初始化spring容器
2. 注入HelloWorldEntity对应的Mapper类: HelloWorldMapper, 这个类是fluent mybatis编译时生成的。
3. 使用HelloWorldMapper进行删除、插入、查询、修改操作。
```java
@RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class)
@ContextConfiguration(classes = HelloWorldConfig.class)
public class HelloWorldTest {
/**
* fluent mybatis编译时生成的Mapper类
*/
@Autowired
HelloWorldMapper mapper;
@Test
public void testHelloWorld() {
/**
* 为了演示方便,先删除数据
*/
mapper.delete(mapper.query()
.where.id().eq(1L).end());
/**
* 插入数据
*/
HelloWorldEntity entity = new HelloWorldEntity();
entity.setId(1L);
entity.setSayHello("hello world");
entity.setYourName("fluent mybatis");
entity.setIsDeleted(false);
mapper.insert(entity);
/**
* 查询 id = 1 的数据
*/
HelloWorldEntity result1 = mapper.findOne(mapper.query()
.where.id().eq(1L).end());
/**
* 控制台直接打印出查询结果
*/
System.out.println("1. HelloWorldEntity:" + result1.toString());
/**
* 更新id = 1的记录
*/
mapper.updateBy(mapper.updater()
.update.sayHello().is("say hello, say hello!")
.set.yourName().is("fluent mybatis is powerful!").end()
.where.id().eq(1L).end()
);
/**
* 查询 id = 1 的数据
*/
HelloWorldEntity result2 = mapper.findOne(mapper.query()
.where.sayHello().like("hello")
.and.isDeleted().eq(false).end());
/**
* 控制台直接打印出查询结果
*/
System.out.println("2. HelloWorldEntity:" + result2.toString());
}
}
```
执行Junit4测试方法,控制台输出
```text
1. HelloWorldEntity:HelloWorldEntity{id=1, sayHello='hello world', yourName='fluent mybatis', gmtCreate=null, gmtModified=null, isDeleted=false}
2. HelloWorldEntity:HelloWorldEntity{id=1, sayHello='say hello, say hello!', yourName='fluent mybatis is powerful!', gmtCreate=null, gmtModified=null, isDeleted=false}
```
神奇吧! 我们再到数据库中查看一下结果
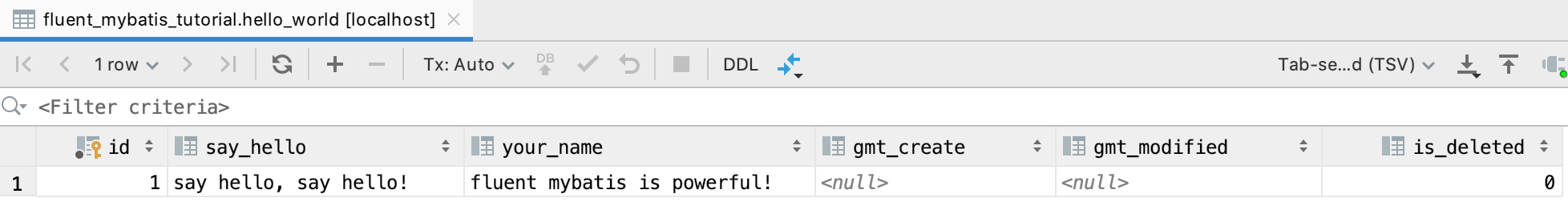
现在,我们已经通过一个简单例子演示了fluent mybatis的强大功能,
在进一步介绍fluent mybatis更强大功能前,我们揭示一下为啥我们只写了一个数据表对应的Entity类,
却拥有了一系列增删改查的数据库操作方法。
fluent mybatis根据Entity类上@FluentMybatis注解在编译时,
会在target目录class目录下自动编译生成一系列文件:
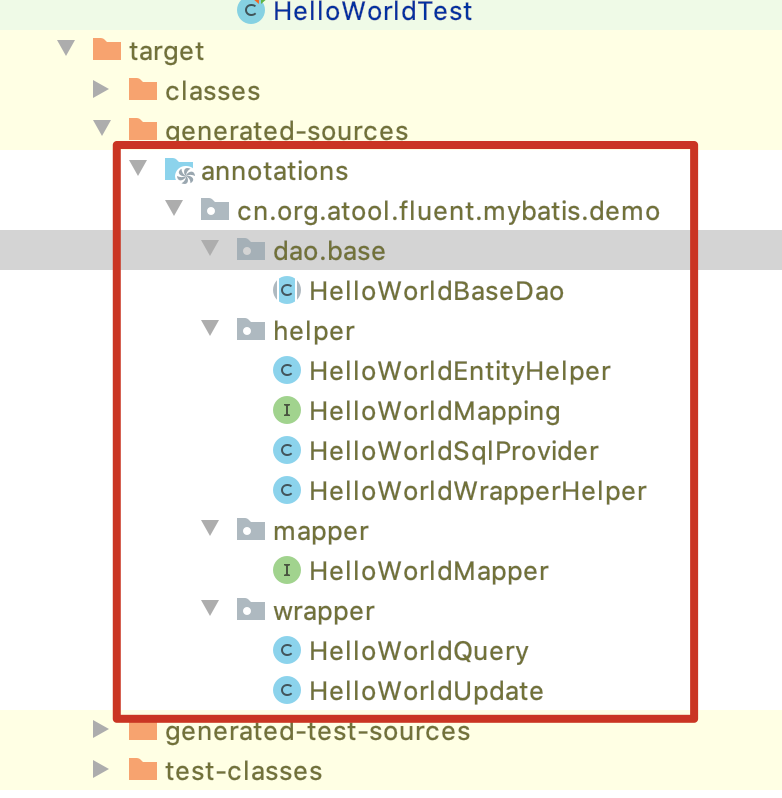
- 核心接口类, 使用时需要了解
1. mapper/*Mapper: mybatis的Mapper定义接口, 定义了一系列通用的数据操作接口方法。
2. dao/*BaseDao: Dao实现基类, 所有的DaoImpl都继承各自基类
根据分层编码的原则,我们不会在Service类中直接使用Mapper类,而是引用Dao类。我们在Dao实现类中根据条件实现具体的数据操作方法。
3. wrapper/*Query: fluent mybatis核心类, 用来进行动态sql的构造, 进行条件查询。
4. wrapper/*Updater: fluent mybatis核心类, 用来动态构造update语句。
5. *EntityHelper: Entity帮助类, 实现了Entity和Map的转换方法
- 辅助实现时, 实现fluent mybatis动态sql拼装和fluent api时内部用到的类,使用时无需了解
在使用上,我们主要会接触到上述5个生成的java类。Fluent Mybatis为了实现动态拼接和Fluent API功能,还生成了一系列辅助类。
1. helper/*Mapping: 表字段和Entity属性映射定义类
2. helper/*SqlProviderP: Mapper接口动态sql提供者
3. helper/*WrapperHelper: Query和Updater具体功能实现, 包含几个实现:select, where, group by, having by, order by, limit
[Fluent Mybatis源码, gitee](https://gitee.com/fluent-mybatis/fluent-mybatis)
[Fluent Mybatis文档&示例](https://gitee.com/fluent-mybatis/fluent-mybatis-docs)
[Fluent Mybatis源码, github](https://github.com/atool/fluent-mybatis)