P、V操作与c++代码实现爸爸放苹果,妈妈放桔子,两个儿子专吃盘子中桔子,两个女儿专吃盘子中苹果问题
二、吃水果综合设计
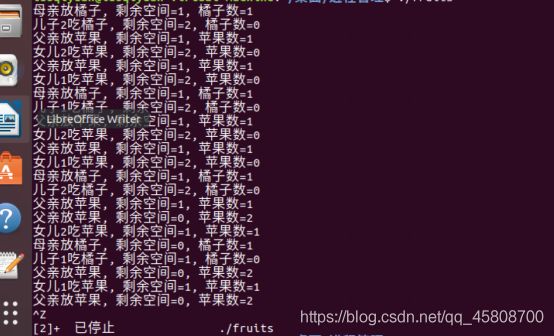
桌子上有一只盘子,最多可容纳两个水果,每次只能放入或取出一个水果。爸爸专向盘子放苹果(apple),妈妈专向盘子中放桔子(orange);两个儿子专等吃盘子中的桔子,两个女儿专等吃盘子中的苹果。请用P、V操作来实现爸爸、妈妈、儿子、女儿之间的同步与互斥关系。
【设计要求】
了解信号量机制,了解并掌握进程同步和互斥机制,熟悉信号量的操作函数,利用信号量实现对共享资源的控制。编程模拟实现这一问题的程序控制,分析处理过程。
1. 1.pv操作代码
semaphore empty=2,mutex=1,apple=0,orange=0;
void father(){
do{
P(empty); //等待盘子为空
P(metux); //等待获取对盘子的操作
爸爸向盘中放一个苹果;
V(mutex); //释放对盘子的操作
V(apple); //通知女儿可以来盘子中取苹果
}while(TRUE);
}
void mather(){
do{
P(empty); //等待盘子为空
P(metux); //等待获取对盘子的操作
妈妈向盘中放一个桔子;
V(mutex); //释放对盘子的操作
V(orange); //通知儿子可以来盘子中取橘子
}while(TRUE);
}
void son1(){
do{
P(orange); //判断盘子中是否有桔子
P(metux); //等待获取对盘子的操作
儿子1取出盘中的桔子;
V(mutex); //释放对盘子的操作
V(empty); //盘子空了,可以继续放水果了
}while(TRUE);
}
void son2(){
do{
P(orange); //判断盘子中是否有桔子
P(metux); //等待获取对盘子的操作
儿子2取出盘中的桔子;
V(mutex); //释放对盘子的操作
V(empty); //盘子空了,可以继续放水果了
}while(TRUE);
}
void daugther1(){
do{
P(apple); //判断盘子中是否有苹果
P(metux); //等待获取对盘子的操作
女儿1取出盘中的苹果;
V(mutex); //释放对盘子的操作
V(empty); //盘子空了,可以继续放水果了
}while(TRUE);
}
void daugther2(){
do{
P(apple); //判断盘子中是否有苹果
P(metux); //等待获取对盘子的操作
女儿2取出盘中的苹果;
V(mutex); //释放对盘子的操作
V(empty); //盘子空了,可以继续放水果了
}while(TRUE);
}
void main() { //四个并发进程的同步执行
cobegin
father(); mather(); son();son();daugther();daugther();
coend
}
2.c++程序代码
#include