Pytorch损失函数解析
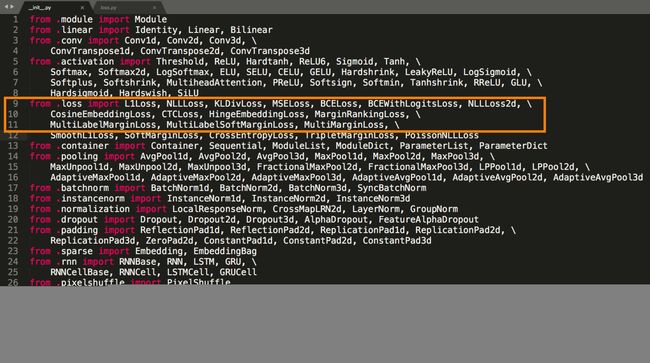
本文根据pytorch里面的源码解析各个损失函数,各个损失函数的python接口定义于包torch.nn.modules中的loss.py,在包modules的初始化__init__.py中关于损失函数的导入:
1.损失函数的base类
1.1 Loss的三个参数
从函数代码中可以看出,__init__函数有三个参数size_average, reduce, reduction,这三个参数的关系如下图所示;可以很明显看出,reduce参数控制返回的是Tensor还是scalar,size_average控制在一个batch里面的计算结果,根据需求可以自己设置,一般是(loss.mean())

2.1 weight
weight普遍用于分类任务,是一个长度和类别数目一样的Tensor,用于计算损失时针对不同类别进行加权,如下是数字识别不同数字损失的加权例子;

2.各个损失函数汇总
2.1 MAE(L1 Loss)
y是模型的预测输出,t是ground truth,两者都是长度为n的tensor,损失计算如下:
L ( y , t ) = 1 n ∑ i n ∣ y i − t i ∣ L(\bold{y},\bold{t})=\frac{1}{n}\sum_{i}^{n}|y_{i}-t_{i}| L(y,t)=n1i∑n∣yi−ti∣
2.2 MSE(L2 Loss)
y是模型的预测输出,t是ground truth,两者都是长度为n的tensor,损失计算如下:
L ( y , t ) = 1 n ∑ i n ∣ y i − t i ∣ 2 L(\bold{y},\bold{t})=\frac{1}{n}\sum_{i}^{n}|y_{i}-t_{i}|^{2} L(y,t)=n1i∑n∣yi−ti∣2
2.3 BCELoss & BCEWithLogitsLoss
BCELoss是常用于二分类的损失函数,y是模型的预测输出(sigmoid的概率值),t是ground truth标签(非0即1),损失计算如下:
L ( y , t ) = − 1 n ∑ i n ( t i ⋅ log y i + ( 1 − t i ) ⋅ log ( 1 − y i ) ) L(\bold{y},\bold{t})=-\frac{1}{n}\sum_{i}^{n}(t_{i}\cdot \log{y_{i}}+(1-t_{i})\cdot\log{(1-y_{i})}) L(y,t)=−n1i∑n(ti⋅logyi+(1−ti)⋅log(1−yi))
BCEWithLogitsLoss=Sigmoid+BCELoss,不需要在模型输出添加sigmoid层,因为这部分已经被包含在损失函数内部;
2.4 NLLLoss
分类损失:LogSoftmax + NLLLoss = CrossEntropyLoss
y是模型的预测输出(LogSoftmax的值(-∞,0)),t是ground truth标签,损失计算如下:
L ( y , t ) = − 1 n ∑ i n y i [ t i ] L(\bold{y},\bold{t})=-\frac{1}{n}\sum_{i}^{n}y_{i}[t_{i}] L(y,t)=−n1i∑nyi[ti]
举个例子,比如经过LogSoftmax的输出Tensor为[-1.233, -2.657,-0.534],label为2,则损失为0.534。
2.5 CrossEntropyLoss
y是模型的预测输出,是长度为类别数量n的tensor,t是ground truth标签,损失计算如下:
L ( y , t ) = − log ( e x p ( y t ) ∑ j e x p ( y j ) ) L(\bold{y},\bold{t})=-\log(\frac{exp(y_{\bold{t}})}{\sum_{j}exp(y_{j})}) L(y,t)=−log(∑jexp(yj)exp(yt))
2.6 MultiLabelMarginLoss
y是模型的预测输出,是长度为类别数量n的tensor,t是ground truth标签(one-hot编码),损失计算如下:
L ( y , t ) = ∑ i j m a x ( 0 , 1 − ( t [ y [ j ] ] − y [ i ] ) ) y . s i z e ( 0 ) L(\bold{y},\bold{t})=\sum_{ij}\frac{max(0, 1-(t[y[j]]-y[i]))}{y.size(0)} L(y,t)=ij∑y.size(0)max(0,1−(t[y[j]]−y[i]))
2.7 MultiLabelSoftMarginLoss
y是模型的预测输出,是长度为类别数量n的tensor,t是ground truth标签(one-hot编码),损失计算如下:
L ( y , t ) = − ∑ i ( t [ i ] ∗ log ( 1 + e x p ( − y [ i ] ) ) − 1 + ( 1 − t [ i ] ) ∗ log ( e x p ( − y [ i ] ) ( 1 + e x p ( − y [ i ] ) ) ) L(\bold{y},\bold{t})=-\sum_{i}(t[i]*\log(1+exp(-y[i]))^{-1}+(1-t[i])*\log(\frac{exp(-y[i])}{(1+exp(-y[i])})) L(y,t)=−i∑(t[i]∗log(1+exp(−y[i]))−1+(1−t[i])∗log((1+exp(−y[i])exp(−y[i])))
2.8 MultiMarginLoss
y是模型的预测输出,是长度为类别数量n的tensor,t是ground truth标签(one-hot编码),损失计算如下:
L ( y , t ) = ∑ i m a x ( 0 , w [ t ] ∗ ( m a r g i n − y [ t ] + y [ i ] ) p ) y . s i z e ( 0 ) L(\bold{y},\bold{t})=\frac{\sum_{i}max(0,w[t] * (margin-y[t]+y[i])^p)}{y.size(0)} L(y,t)=y.size(0)∑imax(0,w[t]∗(margin−y[t]+y[i])p)
2.9 SoftMarginLoss
y是模型的预测输出,是长度为类别数量n的tensor,t是ground truth标签(二分类,-1或1),损失计算如下:
L ( y , t ) = ∑ i log ( 1 + e x p ( − t [ i ] ∗ y [ i ] ) ) y . n e l e m e n t ( ) L(\bold{y},\bold{t})=\sum_{i}\frac{\log(1+exp(-t[i]*y[i]))}{y.nelement()} L(y,t)=i∑y.nelement()log(1+exp(−t[i]∗y[i]))
2.10 SmoothL1Loss
Huber Loss常用于回归问题,对离群点,噪声不敏感,y是模型的预测输出,t是ground truth,两者都是长度为n的tensor,损失函数如下,
L δ ( y i , t i ) = { 1 2 ( y i − t i ) 2 ∣ y i − t i ∣ < δ δ ∣ y i − t i ∣ − 1 2 δ 2 o t h e r w i s e L_{\delta}(\bold{y_{i}},\bold{t_{i}})=\begin{cases} \frac{1}{2}(\bold{y_{i}}-\bold{t_{i}})^{2} & |\bold{y_{i}}-\bold{t_{i}}| < \delta \\ \delta|\bold{y_{i}}-\bold{t_{i}}| - \frac{1}{2}\delta^{2} & otherwise \end{cases} Lδ(yi,ti)={21(yi−ti)2δ∣yi−ti∣−21δ2∣yi−ti∣<δotherwise
L δ ( y , t ) = 1 n ∑ i = 1 n L δ ( y i , t i ) L_{\delta}(\bold{y},\bold{t})=\frac{1}{n}\sum_{i=1}^{n}L_{\delta}(\bold{y_{i}}, \bold{t_{i}}) Lδ(y,t)=n1i=1∑nLδ(yi,ti)
SmoothL1Loss是Huber Loss函数特殊化,\delta=1时,
L s m o o t h l 1 ( y i , t i ) = { 1 2 ( y i − t i ) 2 ∣ y i − t i ∣ < 1 ∣ y i − t i ∣ − 1 2 o t h e r w i s e L_{smoothl1}(\bold{y_{i}},\bold{t_{i}})=\begin{cases} \frac{1}{2}(\bold{y_{i}}-\bold{t_{i}})^{2} & |\bold{y_{i}}-\bold{t_{i}}| < 1 \\ |\bold{y_{i}}-\bold{t_{i}}| - \frac{1}{2} & otherwise \end{cases} Lsmoothl1(yi,ti)={21(yi−ti)2∣yi−ti∣−21∣yi−ti∣<1otherwise
L s m o o t h l 1 ( y , t ) = 1 n ∑ i = 1 n L s m o o t h l 1 ( y i , t i ) L_{smoothl1}(\bold{y},\bold{t})=\frac{1}{n}\sum_{i=1}^{n}L_{smoothl1}(\bold{y_{i}}, \bold{t_{i}}) Lsmoothl1(y,t)=n1i=1∑nLsmoothl1(yi,ti)
2.11 KLDivLoss
K-L源于信息论,信息量的度量单位是熵,一般用H来表示,分布的熵的公式如下:
H = − ∑ i = 1 N p ( x i ) log p ( x i ) H=-\sum_{i=1}^{N}p(x_{i})\log{p(x_i)} H=−i=1∑Np(xi)logp(xi)
只需要改进一下H的公式,就能得到k-L散度的计算公式,设p为观察得到的概率分布,q是另一分布来近似p,则p,q之间的K-L散度为:
D ( p i ∣ ∣ q i ) = ∑ i = 1 n p ( x i ) ⋅ ( log p ( x i ) − log q ( x i ) ) = ∑ i = 1 n p ( x i ) log ( p ( x i ) q ( x i ) ) D(p_{i}||q_{i})=\sum_{i=1}^{n}p(x_{i}) \cdot (\log{p(x_{i})}-\log{q(x_{i})})= \sum_{i=1}^{n}p(x_{i})\log(\frac{p(x_{i})}{q(x_i)}) D(pi∣∣qi)=i=1∑np(xi)⋅(logp(xi)−logq(xi))=i=1∑np(xi)log(q(xi)p(xi))
需要注意的是,K-L散度并不是不同分布之间距离的度量,因为从计算公式来看,是不满足对称性!
2.12 MarginRankingLoss
计算两个张量的相似度,输入是三个参数,x1,x2以及y是长度相同的Tensor,y取值为-1或者1,
L ( x 1 , x 2 , y ) = m a x ( 0 , − y ∗ ( x 1 − x 2 ) + m a r g i n ) = { m a x ( 0 , − ( x 1 − x 2 ) + m a r g i n ) y = 1 m a x ( 0 , ( x 1 − x 2 ) + m a r g i n ) y = − 1 L(x_{1},x_{2},y)=max(0, -y * (x_{1} - x_{2})+ margin)=\begin{cases} max(0, -(x_{1}-x_{2})+margin) & y=1 \\ max(0, (x_{1}-x_{2})+margin) & y=-1 \end{cases} L(x1,x2,y)=max(0,−y∗(x1−x2)+margin)={max(0,−(x1−x2)+margin)max(0,(x1−x2)+margin)y=1y=−1
2.13 CosineEmbeddingLoss
余弦损失函数,计算两个向量的相似性,两个向量的余弦值越高,则相似性越高,输入是三个参数,x1,x2以及y是长度相同的Tensor,y取值为-1或者1,
L ( x 1 , x 2 , y ) = { 1 − c o s ( x 1 , x 2 ) y = 1 m a x ( 0 , c o s ( x 1 − x 2 ) − m a r g i n ) y = − 1 L(x_{1},x_{2},y)=\begin{cases} 1-cos(x_{1}, x_{2}) & y=1 \\ max(0, cos(x_{1}-x_{2})-margin) & y=-1 \end{cases} L(x1,x2,y)={1−cos(x1,x2)max(0,cos(x1−x2)−margin)y=1y=−1
1.当y=1时,直接用-cos(x1,x2)的平移函数作为损失函数;
2.当y=-1时,在cos(x1,x2)=margin处做了分割,用于衡量两个向量的不相似性;
2.14 HingeEmbeddingLoss
输入是两个参数,x与y是长度相同的Tensor,y取值为-1或者1,
l o s s ( x , y ) = 1 n ∑ i = 1 n { x i y i = 1 m a x ( 0 , m a r g i n − x i ) y i = − 1 loss(x,y)=\frac{1}{n}\sum_{i=1}^{n}\begin{cases} x_{i} & y_i=1 \\ max(0, margin-x_{i}) & y_{i}=-1 \end{cases} loss(x,y)=n1i=1∑n{ximax(0,margin−xi)yi=1yi=−1
margin默认为1,
1.当y=-1的时候,loss=max(0,1-x),如果x>1(margin),则loss=0;如果x<1,则loss=1-x;
2.当y=1,loss=x。
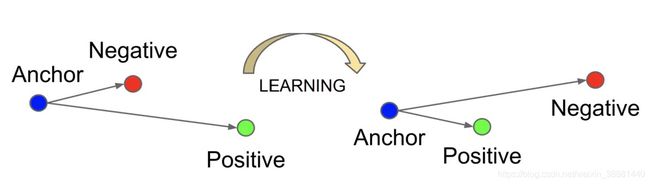
2.15 TripletMarginLoss
Triplet Loss是用来训练差异性较小的样本,如人脸等,数据选择包括三项Anchor示例,Positive示例,Negative示例,通过优化Anchor示例与正示例的距离小于Anchor示例与负示例的距离,来实现样本的相似性的计算,如下图所示:
损失函数如下:
L ( a , p , n ) = 1 n ∑ i = 1 n m a x { d ( a i , p i ) − d ( a i , n i ) + m a r g i n , 0 } L(a,p,n)=\frac{1}{n}\sum_{i=1}^{n}max\{d(a_{i},p_{i})-d(a_{i},n_{i})+margin,0\} L(a,p,n)=n1i=1∑nmax{d(ai,pi)−d(ai,ni)+margin,0}
d ( x i , y i ) = ∣ ∣ x i − y i ∣ ∣ p d(x_{i}, y_{i})=||x_{i}-y_{i}||_{p} d(xi,yi)=∣∣xi−yi∣∣p
3.参考说明:
本文是作者在实践过程中总结出来的激活函数说明,后续有补充会及时更新,如有不正确之处,欢迎各位大佬批评指正!!!
1.https://www.jianshu.com/p/43318a3dc715;
2.https://juejin.cn/post/6844903949124763656;
3.https://www.jianshu.com/p/46c6f68264a1;
4.https://my.oschina.net/u/4584682/blog/4481019