python 爬虫教程(九):pyspider 使用
大家好,今天介绍pyspider使用的相关内容。
目录
一、简介
二、安装
三、快速上手
1.创建项目
2. 爬虫实现
3.数据存储
一、简介
pyspider 是一个支持任务监控、项目管理、多种数据库,具有 WebUI 的爬虫框架,它采用 Python 语言编写,分布式架构。详细特性如下:
-
拥有 Web 脚本编辑界面,任务监控器,项目管理器和结构查看器;
-
数据库支持 MySQL、MongoDB、Redis、SQLite、Elasticsearch、PostgreSQL、SQLAlchemy;
-
队列服务支持 RabbitMQ、Beanstalk、Redis、Kombu;
-
支持抓取 JavaScript 的页面;
-
组件可替换,支持单机、分布式部署,支持 Docker 部署;
-
强大的调度控制,支持超时重爬及优先级设置;
-
支持 Python2&3。
pyspider 主要分为 Scheduler(调度器)、 Fetcher(抓取器)、 Processer(处理器)三个部分,整个过程受到 Monitor(监控器)的监控,抓取的结果被 Result Worker(结果处理器)处理。基本流程为:Scheduler 发起任务调度,Fetcher 抓取网页内容,Processer 解析网页内容,再将新生成的 Request 发给 Scheduler 进行调度,将生成的提取结果输出保存。
-
pyspider 拥有 WebUI,爬虫的编写、调试可在 WebUI 中进行;Scrapy 采用采用代码、命令行操作,实现可视化需对接 Portia。
-
pyspider 支持使用 PhantomJS 对 JavaScript 渲染页面的采集 ;Scrapy 需对接 Scrapy-Splash 组件。
-
pyspider 内置了 PyQuery(Python 爬虫(五):PyQuery 框架) 作为选择器;Scrapy 对接了 XPath、CSS 选择器、正则匹配。
-
pyspider 扩展性弱;Scrapy 模块之间耦合度低,扩展性强,如:对接 Middleware、 Pipeline 等组件实现更强功能。
总的来说,pyspider 更加便捷,Scrapy 扩展性更强,如果要快速实现爬取优选 pyspider,如果爬取规模较大、反爬机制较强,优选 scrapy。
二、安装
方式一
pip install pyspider
这种方式比较简单,不过在 Windows 系统上可能会出现错误:Command "python setup.py egg_info" failed with error ...,我在自己的 Windows 系统上安装时就遇到了该问题,因此,选择了下面第二种方式进行了安装。
方式二
使用 wheel 方式安装。步骤如下:
执行以上安装步骤后,我们在控制台输入 pyspider,如图所示:
-
pip install wheel安装wheel; -
打开网址 https://www.lfd.uci.edu/~gohlke/pythonlibs/,使用
Ctrl + F搜索pycurl,根据自己安装的 Python 版本,选择合适的版本下载,比如:我用的Python3.6,就选择带有cp36标识的版本。如下图红框所示:
-
使用 pip 安装下载文件,如:
pip install E:\pycurl-7.43.0.3-cp36-cp36m-win_amd64.whl; -
最后还是使用
pip install pyspider安装。
出现上述结果说明启动成功,如果启动时一直卡在 result_worker starting...,我们可以再打开一个控制台窗口,同样输入 pyspider 进行启动,启动成功后关掉之前的窗口即可。
启动成功后,我们再验证一下,打开浏览器,输入 http://localhost:5000 访问,如图所示:
我们发现确实启动成功了。
三、快速上手
1.创建项目
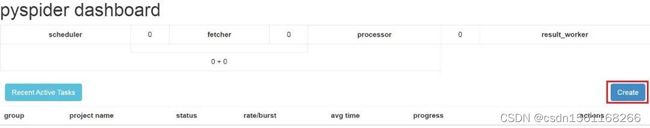
首先,我们点击图形界面中的 Create 按钮开始创建项目,如图中红框所示:
然后会跳出信息填写窗口,如图所示:
我们需要填写 Project Name 和 Start URL(s),这里以链家网二手房信息为例:https://hz.lianjia.com/ershoufang,填写完成后点击 Create 按钮。结果如图所示:
-
roject Name:项目名
-
Start URL(s):爬取链接地址
2. 爬虫实现
pyspider 访问 https 协议的网站时会提示证书问题(通常为 HTTP 599),因此我们需要在 crawl 方法中添加参数 validate_cert=False 来屏蔽证书验证。如图所示:
我们计划获取房子的单价(unit_price)、描述标题(title)、卖点信息(sell_point),编写具体实现如下所示:
from pyspider.libs.base_handler import *
class Handler(BaseHandler):
crawl_config = {
}
@every(minutes=24 * 60)
def on_start(self):
self.crawl('https://hz.lianjia.com/ershoufang/', callback=self.index_page,validate_cert=False)
@config(age=10 * 24 * 60 * 60)
def index_page(self, response):
for each in response.doc('.title').items():
self.crawl(each.attr.href, callback=self.detail_page,validate_cert=False)
@config(priority=2)
def detail_page(self, response):
yield {
'unit_price':response.doc('.unitPrice').text(),
'title': response.doc('.main').text(),
'sell_point': response.doc('.baseattribute > .content').text()
}-
@every(minutes=24 * 60):通知 Scheduler 每天运行一次。
-
@config(age=10 * 24 * 60 * 60):设置任务的有效期限。
-
@config(priority=2):设定任务优先级
-
on_start(self):程序的入口。
-
self.crawl(url, callback):主方法,用于创建一个爬取任务。
-
index_page(self, response):用来抓取返回的 html 文档中对应标签的数据。
-
detail_page(self, response):返回一个 dict 对象作为结果。
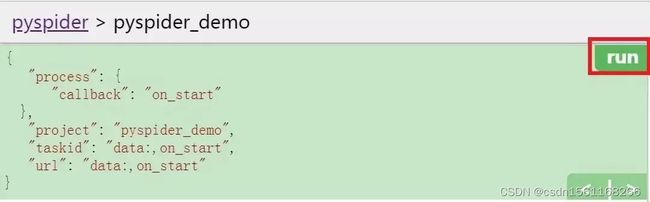
我们点击运行按钮,如图所示:
点击之后,我们发现 follows 按钮处出现了提示信息,如图所示:
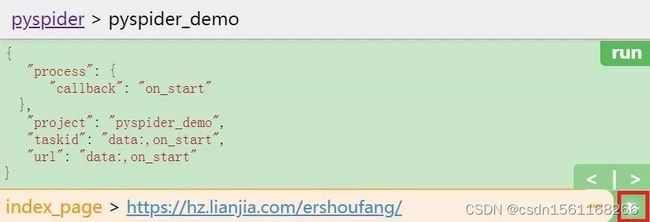
点击上图中红框圈起来的三角号按钮,结果如图所示:
我们随意选一条 detail_page,点击其右侧三角号按钮,结果如图所示:
从结果来看,已经可以爬取到我们需要的信息了。
3.数据存储
获取到信息之后,需要将信息存储起来,我们计划将数据存储到 MySQL 数据库。
首先,安装 pymysql,命令如下:
pip install pymysql
接着添加保存代码,完整代码如下:
from pyspider.libs.base_handler import *
import pymysql
class Handler(BaseHandler):
crawl_config = {
}
def __init__(self):
# 下面参数修改成自己对应的 MySQL 信息
self.db = MySQLdb.connect(ip, username, password, db, charset='utf8')
def add_Mysql(self, title, unit_price, sell_point):
try:
cursor = self.db.cursor()
sql = 'insert into house(title, unit_price, sell_point) values ("%s","%s","%s")' % (title[0],unit_price[0],sell_point);
print(sql)
cursor.execute(sql)
self.db.commit()
except Exception as e:
print(e)
self.db.rollback()
@every(minutes=24 * 60)
def on_start(self):
self.crawl('https://hz.lianjia.com/ershoufang/', callback=self.index_page,validate_cert=False)
@config(age=10 * 24 * 60 * 60)
def index_page(self, response):
for each in response.doc('.title').items():
self.crawl(each.attr.href, callback=self.detail_page,validate_cert=False)
@config(priority=2)
def detail_page(self, response):
title = response.doc('.main').text(),
unit_price = response.doc('.unitPrice').text(),
sell_point = response.doc('.baseattribute > .content').text()
self.add_Mysql(title, unit_price, sell_point)
yield {
'title': response.doc('.main').text(),
'unit_price':response.doc('.unitPrice').text(),
'sell_point': response.doc('.baseattribute > .content').text()
}
先测试一下是否能将数据保存到 MySQL 中,还是选一条 detail_page,如图所示:
点击其右侧三角号按钮,结果如图所示:
从输出结果来看是执行了保存操作,我们再到 MySQL 中看一下,如图所示:
数据已经存到了 MySQL 中了。
上面我们是手动操作保存的数据,接下来看一下如何通过设置任务保存。
点击当前页左上角的 pyspider 按钮,如图所示:
返回 dashboard 界面,如图所示:
我们点击 status 下方红框圈住的位置,将状态修改为 RUNNING 或 DEBUG,然后点击 actions 下方的 run 按钮即可。
参考:
http://docs.pyspider.org/en/latest/