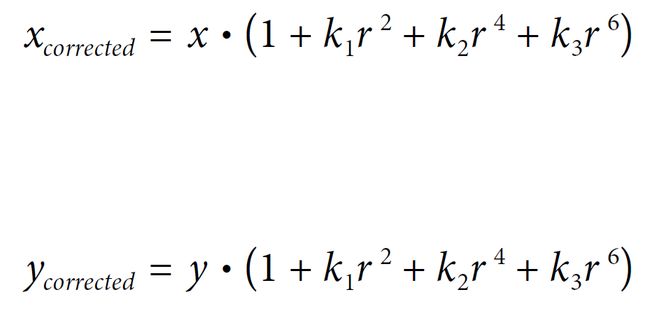相机标定与3D重建(3)使用OpenCV对摄像机进行标定
相机已经存在很长很长时间了。然而,随着20世纪末廉价针孔相机的出现,针孔相机在我们的日常生活中司空见惯。不幸的是,这种廉价是有代价的:严重的扭曲。幸运的是,这些都是常量,通过标定和一些重新映射,我们可以纠正这一点。此外,通过标定,还可以确定相机的自然单位(像素)和现实单位(例如毫米)之间的关系。
1.理论
对于畸变,OpenCV考虑了径向和切向畸变。
对于径向畸变,采用以下公式:
x d i s t o r t e d = x ( 1 + k 1 r 2 + k 2 r 4 + k 3 r 6 ) y d i s t o r t e d = y ( 1 + k 1 r 2 + k 2 r 4 + k 3 r 6 ) x_{distorted}=x(1+k_1r^2+k_2r^4+k_3r^6) \\ y_{distorted}=y(1+k_1r^2+k_2r^4+k_3r^6) xdistorted=x(1+k1r2+k2r4+k3r6)ydistorted=y(1+k1r2+k2r4+k3r6)
因此,对于一个未扭曲的像素点(x,y),它在扭曲图像上的位置将是( x d i s t o r t e d , x d i s t o r t e d x_{distorted}, x_{distorted} xdistorted,xdistorted)。径向畸变的存在表现为“桶”或“鱼眼”效应。
切向畸变的发生是由于透镜与成像平面并非完全平行。它可以用公式表示:
x d i s t o r t e d = x + [ 2 p 1 x y + p 2 ( r 2 + 2 x 2 ) y d i s t o r t e d = y + [ 2 p 2 x y + p 2 ( r 2 + 2 y 2 ) x_{distorted}=x + [2p_1xy + p_2(r^2+2x^2) \\ y_{distorted}=y + [2p_2xy + p_2(r^2+2y^2) xdistorted=x+[2p1xy+p2(r2+2x2)ydistorted=y+[2p2xy+p2(r2+2y2)
所以我们有5个畸变参数,在OpenCV中表现为一个5列的行矩阵:distortion_coefficients=(k1 k2 p1 p2 k3)
现在,对于单位转换,我们使用以下公式:
[ x y w ] = [ f x 0 c x 0 f y c y 0 0 1 ] [ X Y Z ] \left[ \begin{matrix} x \\ y \\ w \end{matrix} \right] = \left[ \begin{matrix} f_x & 0 & c_x\\ 0 & f_y & c_y \\ 0 & 0 & 1\end{matrix} \right]\left[ \begin{matrix} X \\ Y \\ Z \end{matrix} \right] xyw = fx000fy0cxcy1 XYZ
这里 w w w的存在是用单应性坐标系( w = Z w=Z w=Z)来解释的。未知的参数是 f x f_x fx和 f y f_y fy(相机焦距)和 ( c x , c y ) (c_x,c_y) (cx,cy),它们是用像素坐标表示的光学中心。如果两个轴都有一个共同的焦距和一个给定的纵横比(通常是1),那么 f y = f x ∗ a f_y=f_x∗a fy=fx∗a,在上面的公式中,我们将有一个单一的焦距 f f f。包含这四个参数的矩阵称为摄像机矩阵。尽管无论使用何种相机分辨率,失真系数都是相同的,但这些系数应与标定分辨率的当前分辨率一起缩放。
确定这两个矩阵的过程就是标定。这些参数的计算是通过基本几何方程来完成的。所用的方程取决于所选择的标定对象。目前OpenCV支持三种(不止三种)类型的对象进行标定:
- 经典的黑白棋盘
- 对称圆形图案
- 不对称圆形图案
基本上,你需要用你的相机拍下这些标定模式的快照,然后让OpenCV找到它们。每一个发现的模式都会产生一个新的等式。要解这个方程,至少需要预定数量的模式快照来形成一个适定的方程系统。这个数字在棋盘图案中更高,在圆形图案中更低。例如,理论上棋盘图案需要至少两次快照。然而,在实际操作中,我们的输入图像中存在大量的噪声,因此为了获得好的结果,您可能需要至少10个输入模式的良好快照。
2.目标
示例应用程序将:
- 确定失真矩阵
- 确定摄像机矩阵
- 从相机,视频和图像文件列表中获取输入
- 从XML/YAML文件读取配置
- 将结果保存到XML/YAML文件中
- 计算重投影误差
3.源代码
你也可以在OpenCV源代码库的samples/cpp/tutorial_code/calib3d/camera_calibration/文件夹中找到源代码,或者从这里下载。对于程序的使用,请使用-h参数运行它。程序有一个基本的参数:它的配置文件的名称。如果没有给出,那么它将尝试打开名为“default.xml”的文件。下面是一个XML格式的配置文件示例。在配置文件中,您可以选择使用相机,视频文件或图像列表作为输入。如果选择最后一个,则需要创建一个枚举的配置文件,如文件所示。需要记住的是,需要使用应用程序工作目录中的绝对路径或相对路径指定图像地址。您可以在上面提到的samples目录中找到所有这些内容。
应用程序启动时从配置文件读取设置。虽然,这是一个重要的部分,它与本教程的主题无关:相机标定。因此,我选择不在这里发布该部分的代码。关于如何做到这一点的技术背景,可以在使用XML和YAML文件的文件输入和输出教程中找到。
#include 4.源码解释
4.1读取配置文件
配置文件in_VID5.xml的内容如下,可以根据需要自己修改
<?xml version="1.0"?>
>
>
<!-- Number of inner corners per a item row and column. (square, circle) -->
9
6
<!-- The size of a square in some user defined metric system (pixel, millimeter)-->
50
0
<!-- Time delay between frames in case of camera. -->
100
<!-- How many frames to use, for calibration. -->
25
1
1
<!-- The name of the output log file. -->
"out_camera_data.xml"
1
1
1
1
0
0
0
0
1
1
>
>
下面是读取in_VID5.xml文件的代码:
Settings s;
const string inputSettingsFile = parser.get<string>(0);
FileStorage fs(inputSettingsFile, FileStorage::READ); // Read the settings
if (!fs.isOpened())
{
cout << "Could not open the configuration file: \"" << inputSettingsFile << "\"" << endl;
parser.printMessage();
return -1;
}
fs["Settings"] >> s;
fs.release();
为此,我使用了简单的OpenCV类输入操作。在读取文件之后,我有一个额外的后处理函数来检查输入的有效性。只有当所有的输入都是好的输入变量才为真。
4.2得到下一个输入,如果它失败或我们有足够的参数-标定
在这之后,我们有一个大的循环,我们在其中执行以下操作:从图像列表、摄像机或视频文件中获取下一个图像。如果这失败或我们有足够的图像,然后我们运行标定过程。在图像的情况下,我们跳出循环,否则通过从检测模式更改为标定模式,剩余的帧将被用作去畸变(如果设置了该选项)。
for(;;)
{
Mat view;
bool blinkOutput = false;
view = s.nextImage();
//----- If no more image, or got enough, then stop calibration and show result -------------
if( mode == CAPTURING && imagePoints.size() >= (size_t)s.nrFrames )
{
if(runCalibrationAndSave(s, imageSize, cameraMatrix, distCoeffs, imagePoints, grid_width, release_object))
mode = CALIBRATED;
else
mode = DETECTION;
}
if(view.empty()) // If there are no more images stop the loop
{
// if calibration threshold was not reached yet, calibrate now
if( mode != CALIBRATED && !imagePoints.empty() )
runCalibrationAndSave(s, imageSize, cameraMatrix, distCoeffs, imagePoints, grid_width,
release_object);
break;
}
对于一些相机,我们可能需要翻转输入图像。在这里我们也这样做。
4.3 在当前输入中找到模式
我上面提到的方程式的形成是为了寻找输入中的主要模式:在棋盘中,这些模式是正方形的角,而对于圆形,也就是圆形本身。这些位置将形成被写入pointBuf向量的结果。
vector<Point2f> pointBuf;
bool found;
int chessBoardFlags = CALIB_CB_ADAPTIVE_THRESH | CALIB_CB_NORMALIZE_IMAGE;
if(!s.useFisheye) {
// fast check erroneously fails with high distortions like fisheye
chessBoardFlags |= CALIB_CB_FAST_CHECK;
}
switch( s.calibrationPattern ) // Find feature points on the input format
{
case Settings::CHESSBOARD:
found = findChessboardCorners( view, s.boardSize, pointBuf, chessBoardFlags);
break;
case Settings::CIRCLES_GRID:
found = findCirclesGrid( view, s.boardSize, pointBuf );
break;
case Settings::ASYMMETRIC_CIRCLES_GRID:
found = findCirclesGrid( view, s.boardSize, pointBuf, CALIB_CB_ASYMMETRIC_GRID );
break;
default:
found = false;
break;
}
根据输入模式的类型,您可以使用cv::findChessboardCorners或cv::findCirclesGrid函数。对于这两个,你传递当前图像和标定板的大小,你就会得到图案的位置。此外,它们还返回一个布尔变量,表示是否在输入中找到了模式(我们只需要考虑那些为真的图像!)
在相机的情况下,我们只在经过一个输入延迟时间时拍摄相机图像。这样做是为了让用户移动棋盘,并获得不同的图像。相似的图像会产生相似的方程,在标定步骤上相似的方程会形成不适定问题,因此标定会失败。对于正方形图像,角的位置只是近似的。我们可以通过调用cv::cornerSubPix函数来改进这一点。winSize用于控制搜索窗口的边长。默认值为11。winSize可以通过命令行参数--winSize=来更改。它将产生更好的标定结果。在这之后,我们向imagePoints向量添加一个有效的输入结果,以将所有等式收集到一个容器中。最后,为了可视化结果,我们将使用cv::findChessboardCorners函数在输入图像上绘制发现的点。
if ( found) // If done with success,
{
// improve the found corners' coordinate accuracy for chessboard
if( s.calibrationPattern == Settings::CHESSBOARD)
{
Mat viewGray;
cvtColor(view, viewGray, COLOR_BGR2GRAY);
cornerSubPix( viewGray, pointBuf, Size(winSize,winSize),
Size(-1,-1), TermCriteria( TermCriteria::EPS+TermCriteria::COUNT, 30, 0.0001 ));
}
if( mode == CAPTURING && // For camera only take new samples after delay time
(!s.inputCapture.isOpened() || clock() - prevTimestamp > s.delay*1e-3*CLOCKS_PER_SEC) )
{
imagePoints.push_back(pointBuf);
prevTimestamp = clock();
blinkOutput = s.inputCapture.isOpened();
}
// Draw the corners.
drawChessboardCorners( view, s.boardSize, Mat(pointBuf), found );
}
4.4向用户显示状态和结果,加上应用程序的命令行控制
这部分在图像上显示文本输出。
string msg = (mode == CAPTURING) ? "100/100" :
mode == CALIBRATED ? "Calibrated" : "Press 'g' to start";
int baseLine = 0;
Size textSize = getTextSize(msg, 1, 1, 1, &baseLine);
Point textOrigin(view.cols - 2*textSize.width - 10, view.rows - 2*baseLine - 10);
if( mode == CAPTURING )
{
if(s.showUndistorted)
msg = cv::format( "%d/%d Undist", (int)imagePoints.size(), s.nrFrames );
else
msg = cv::format( "%d/%d", (int)imagePoints.size(), s.nrFrames );
}
putText( view, msg, textOrigin, 1, 1, mode == CALIBRATED ? GREEN : RED);
if( blinkOutput )
bitwise_not(view, view);
如果我们运行标定并得到带有失真系数的相机矩阵,我们可能想要使用cv:: undistortion函数来校正图像:
if( mode == CALIBRATED && s.showUndistorted )
{
Mat temp = view.clone();
if (s.useFisheye)
{
Mat newCamMat;
fisheye::estimateNewCameraMatrixForUndistortRectify(cameraMatrix, distCoeffs, imageSize,
Matx33d::eye(), newCamMat, 1);
cv::fisheye::undistortImage(temp, view, cameraMatrix, distCoeffs, newCamMat);
}
else
undistort(temp, view, cameraMatrix, distCoeffs);
}
然后我们显示图像并等待输入键,如果这是u,我们切换失真消除,如果是g,我们再次开始检测过程,最后为ESC键,我们退出应用:
imshow("Image View", view);
char key = (char)waitKey(s.inputCapture.isOpened() ? 50 : s.delay);
if( key == ESC_KEY )
break;
if( key == 'u' && mode == CALIBRATED )
s.showUndistorted = !s.showUndistorted;
if( s.inputCapture.isOpened() && key == 'g' )
{
mode = CAPTURING;
imagePoints.clear();
}
4.5显示失真消除图像
当您使用图像列表时,不可能在循环中消除失真。因此,必须在循环之后执行此操作。利用这一点,我现在扩展cv::undistort函数,它实际上首先调用 cv::initUndistortRectifyMap来查找变换矩阵,然后使用cv::remap函数执行变换。因为,标定成功后,只需计算一次映射,通过使用这个扩展的形式,您可以加快您的应用程序:
if( s.inputType == Settings::IMAGE_LIST && s.showUndistorted && !cameraMatrix.empty())
{
Mat view, rview, map1, map2;
if (s.useFisheye)
{
Mat newCamMat;
fisheye::estimateNewCameraMatrixForUndistortRectify(cameraMatrix, distCoeffs, imageSize,
Matx33d::eye(), newCamMat, 1);
fisheye::initUndistortRectifyMap(cameraMatrix, distCoeffs, Matx33d::eye(), newCamMat, imageSize,
CV_16SC2, map1, map2);
}
else
{
initUndistortRectifyMap(
cameraMatrix, distCoeffs, Mat(),
getOptimalNewCameraMatrix(cameraMatrix, distCoeffs, imageSize, 1, imageSize, 0), imageSize,
CV_16SC2, map1, map2);
}
for(size_t i = 0; i < s.imageList.size(); i++ )
{
view = imread(s.imageList[i], IMREAD_COLOR);
if(view.empty())
continue;
remap(view, rview, map1, map2, INTER_LINEAR);
imshow("Image View", rview);
char c = (char)waitKey();
if( c == ESC_KEY || c == 'q' || c == 'Q' )
break;
}
}
4.6标定与保存
因为每台相机只需要进行一次标定,所以在成功标定后保存它是有意义的。这样,以后您就可以将这些值加载到您的程序中。因此,我们首先进行标定,如果标定成功,我们将结果保存到OpenCV样式的XML或YAML文件中,这取决于您在配置文件中给出的扩展名。
因此在第一个函数中我们把这两个过程分开。因为我们想要保存许多标定变量,所以我们将在这里创建这些变量,并将它们传递给标定和保存函数。同样,我不会显示保存部分,因为它与标定没有什么共同之处。
bool runCalibrationAndSave(Settings& s, Size imageSize, Mat& cameraMatrix, Mat& distCoeffs,
vector<vector<Point2f> > imagePoints, float grid_width, bool release_object)
{
vector<Mat> rvecs, tvecs;
vector<float> reprojErrs;
double totalAvgErr = 0;
vector<Point3f> newObjPoints;
bool ok = runCalibration(s, imageSize, cameraMatrix, distCoeffs, imagePoints, rvecs, tvecs, reprojErrs,
totalAvgErr, newObjPoints, grid_width, release_object);
cout << (ok ? "Calibration succeeded" : "Calibration failed")
<< ". avg re projection error = " << totalAvgErr << endl;
if (ok)
saveCameraParams(s, imageSize, cameraMatrix, distCoeffs, rvecs, tvecs, reprojErrs, imagePoints,
totalAvgErr, newObjPoints);
return ok;
}
我们借助cv::calibrateCameraRO函数进行标定。它有以下参数:
- The object points目标点:
vector向量,对于每个输入图像,它描述了模式的外观。如果我们有一个平面模式(如棋盘),那么我们可以简单地将所有Z坐标设为零。这是这些重要点的集合。因为,我们对所有输入图像使用单一模式,我们只需计算一次,然后将其乘以所有其他输入视图。我们用calcBoardCornerPositions函数计算角点:
static void calcBoardCornerPositions(Size boardSize, float squareSize, vector<Point3f>& corners,
Settings::Pattern patternType /*= Settings::CHESSBOARD*/)
{
corners.clear();
switch(patternType)
{
case Settings::CHESSBOARD:
case Settings::CIRCLES_GRID:
for( int i = 0; i < boardSize.height; ++i )
for( int j = 0; j < boardSize.width; ++j )
corners.push_back(Point3f(j*squareSize, i*squareSize, 0));
break;
case Settings::ASYMMETRIC_CIRCLES_GRID:
for( int i = 0; i < boardSize.height; i++ )
for( int j = 0; j < boardSize.width; j++ )
corners.push_back(Point3f((2*j + i % 2)*squareSize, i*squareSize, 0));
break;
default:
break;
}
}
然后把它乘以:
vector<vector<Point3f> > objectPoints(1);
calcBoardCornerPositions(s.boardSize, s.squareSize, objectPoints[0], s.calibrationPattern);
objectPoints[0][s.boardSize.width - 1].x = objectPoints[0][0].x + grid_width;
newObjPoints = objectPoints[0];
objectPoints.resize(imagePoints.size(),objectPoints[0]);
请注意:
如果你的标定板是不准确的、未测量的、大致平面的目标(使用现成打印机的纸上的棋盘图案是最方便的标定目标,但大多数都不够精确),可以利用一种方法来显著提高估计相机内部参数的精度。如果提供了命令行参数-d=,将调用这个新的标定方法。在上面的代码片段中,grid_width实际上是由-d=设置的值。它是左上(0,0,0)和右上(s.squareSize*(s.boardSize.width-1), 0, 0)之间的测量距离。应该用尺子或游标卡尺精确测量。标定后,newObjPoints将更新为精确的三维物体点坐标。
- The image points图像点:
vector对于每个输入图像包含重要点的坐标(棋盘的角和圆图案的圆心)。我们已经从cv::findChessboardCorners或cv::findCirclesGrid函数中收集了这个。我们只需要把它传下去。 - 从相机、视频文件或图像中获得的图像的大小。
- 固定对象的索引点。我们将其设置为-1以要求标准标定方法。如果要使用新的对象释放方法,则将其设置为标定板网格右上角点的索引。详细说明见
cv::calibrateCameraRO。
int iFixedPoint = -1;
if (release_object)
iFixedPoint = s.boardSize.width - 1;
- The camera matrix:如果我们使用固定长宽比选项,我们需要设置
f_x:
cameraMatrix = Mat::eye(3, 3, CV_64F);
if( !s.useFisheye && s.flag & CALIB_FIX_ASPECT_RATIO )
cameraMatrix.at<double>(0,0) = s.aspectRatio;
- The distortion coefficient matrix:初始化为零
distCoeffs = Mat::zeros(8, 1, CV_64F);
- 对于所有视图,该函数将计算旋转和平移向量,将目标点(在世界坐标空间中给出)转换为图像点(在模型坐标空间中给出)。第7和第8个参数是矩阵的输出向量,其中第i个位置包含第i个物体点到第i个图像点的旋转和平移向量。
- 标定模式点的更新输出向量。标准标定方法忽略此参数。
- 最后一个参数是flag。你需要在这里指定一些选项,比如固定焦距的长宽比,假设切向失真为零,或者固定主点。这里我们使用
CALIB_USE_LU来获得更快的标定速度。
rms = calibrateCameraRO(objectPoints, imagePoints, imageSize, iFixedPoint,
cameraMatrix, distCoeffs, rvecs, tvecs, newObjPoints,
s.flag | CALIB_USE_LU);
- 该函数返回平均重投影误差。这个数字对所找到的参数的精度给出了很好的估计。这应该尽可能接近于零。考虑到内参、畸变参数、旋转和平移矩阵,我们可以通过使用
cv::projectPoints来计算一个视图的误差,首先将物体点转换为图像点。然后我们计算通过变换得到的结果与角/圆查找算法之间的绝对范数。为了找到平均误差,我们计算所有标定图像的计算误差的算术平均值。
static double computeReprojectionErrors( const vector<vector<Point3f> >& objectPoints,
const vector<vector<Point2f> >& imagePoints,
const vector<Mat>& rvecs, const vector<Mat>& tvecs,
const Mat& cameraMatrix , const Mat& distCoeffs,
vector<float>& perViewErrors, bool fisheye)
{
vector<Point2f> imagePoints2;
size_t totalPoints = 0;
double totalErr = 0, err;
perViewErrors.resize(objectPoints.size());
for(size_t i = 0; i < objectPoints.size(); ++i )
{
if (fisheye)
{
fisheye::projectPoints(objectPoints[i], imagePoints2, rvecs[i], tvecs[i], cameraMatrix,
distCoeffs);
}
else
{
projectPoints(objectPoints[i], rvecs[i], tvecs[i], cameraMatrix, distCoeffs, imagePoints2);
}
err = norm(imagePoints[i], imagePoints2, NORM_L2);
size_t n = objectPoints[i].size();
perViewErrors[i] = (float) std::sqrt(err*err/n);
totalErr += err*err;
totalPoints += n;
}
return std::sqrt(totalErr/totalPoints);
}
4.7结果
假设有一个输入棋盘图案,大小为9 X 6。我使用AXIS IP摄像机创建了标定板的两个快照,并将其保存到VID5目录中。我把它放在我工作目录的images/ camercalibration文件夹中,并创建了下面的VID5.XML文件来描述使用哪些图像:
<opencv_storage>
<images>
images/CameraCalibration/VID5/xx1.jpg
images/CameraCalibration/VID5/xx2.jpg
images/CameraCalibration/VID5/xx3.jpg
images/CameraCalibration/VID5/xx4.jpg
images/CameraCalibration/VID5/xx5.jpg
images/CameraCalibration/VID5/xx6.jpg
images/CameraCalibration/VID5/xx7.jpg
images/CameraCalibration/VID5/xx8.jpg
images>
opencv_storage>
如何生成上面的xml文件呢?
// genImageXML.cpp
#include 然后传递images/ camercalibration /VID5/VID5. xml作为配置文件的输入。下面是在应用程序运行时发现的一个棋盘模式:

应用失真去除后,我们得到:
同样的方法也适用于这个不对称的圆形图案,设置输入宽度为4,高度为11。这一次,我通过为输入指定ID(“1”)来使用一个实时摄像机输入。以下是检测到的模式的样子:

在这两种情况下,在指定的输出XML/YAML文件中,你会发现相机和畸变系数矩阵:
<camera_matrix type_id="opencv-matrix">
<rows>3rows>
<cols>3cols>
<dt>ddt>
<data>
6.5746697944293521e+002 0. 3.1950000000000000e+002 0.
6.5746697944293521e+002 2.3950000000000000e+002 0. 0. 1.data>camera_matrix>
<distortion_coefficients type_id="opencv-matrix">
<rows>5rows>
<cols>1cols>
<dt>ddt>
<data>
-4.1802327176423804e-001 5.0715244063187526e-001 0. 0.
-5.7843597214487474e-001data>distortion_coefficients>
将这些值作为常量添加到你的程序中,调用cv::initUndistortRectifyMap和cv::remap函数来消除失真,为廉价和低质量的相机享受无失真输入。
BONUS
我们现在将使用 OpenCV 执行标定过程。为了确定 9 个参数(4 个相机内在系数和 5 个失真系数),我们需要一些失真的棋盘图像——建议使用至少 10 个图像的数据集,使用要标定的相机拍摄。

我们首先进行导入并设置数据以供以后在标定过程中使用。 OpenCV 的cornerSubPix() 函数需要一个终止标准,该函数执行高精度搜索棋盘图像中的角点。需要一组对象点来告诉 OpenCV 我们正在使用 8 x 8 棋盘作为标定目标。
import cv2
import numpy as np
import glob
# 设置cornerSubPix() 的终止标准
criteria = (cv2.TERM_CRITERIA_EPS + cv2.TERM_CRITERIA_MAX_ITER, 30, 0.001)
# 为 8x8 棋盘创建和填充对象点
objp = np.zeros((7 * 7, 3), np.float32)
objp[:,:2] = np.mgrid[0:7, 0:7].T.reshape(-1, 2)
# 为对象点和图像点创建数组
objpoints = [] # 现实世界空间中的 3d 点
imgpoints = [] # 图像平面中的 2d点
设置好初始变量后,我们可以遍历失真棋盘图像的标定数据集,并应用 OpenCV 的 findChessboardCorners() 函数来定位棋盘图像中的角。
# 收集文件夹中图像的文件名
images = glob.glob('calibration*.png')
# 遍历文件夹中的图像并创建棋盘角
for fname in images:
print(fname)
image = cv2.imread(fname)
gray = cv2.split(image)[0]
ret, corners = cv2.findChessboardCorners(gray, (7, 7), None)
if ret == True:
objpoints.append(objp)
corners_SubPix = cv2.cornerSubPix(gray, corners, (11, 11), (-1, -1), criteria)
imgpoints.append(corners_SubPix)
print("Return value: ", ret)
img = cv2.drawChessboardCorners(gray, (7, 7), corners_SubPix, ret)
cv2.imshow("Corners", img)
cv2.waitKey(500)
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
下图显示了 findChessboardCorners() 函数的示例输出——OpenCV 已成功检测到失真棋盘图像的所有内角,随后可用于执行标定。

以下代码使用 OpenCV 的 calibrateCamera() 函数来确定相机内在矩阵和失真系数。文件存储 API 用于将参数保存到 XML 文件中。
# 相机标定: cameraMatrix = 3x3 相机内参; 畸变系数distCoeffs = 5x1 向量
# gray.shape[::-1] 将单通道图像值从 h、w 交换为 w、h(numpy 到 OpenCV 格式)
retval, cameraMatrix, distCoeffs, rvecs, tvecs = cv2.calibrateCamera(objpoints, imgpoints, gray.shape[::-1], None, None)
# 保存相机内参和畸变系数
fs = cv2.FileStorage("intrinsics.xml", cv2.FileStorage_WRITE)
fs.write("image_width", gray.shape[1])
fs.write("image_height", gray.shape[0])
fs.write("camera_matrix", cameraMatrix)
fs.write("distortion_coefficients", distCoeffs)
fs.release()
在文本编辑器中检查XML文件后,确定4个值的相机内在系数和5个失真系数。

成功获得我们的参数后,我们可以导入一个新的失真图像并应用 OpenCV 的非失真函数来拉直图像。使用的图像取自厨房台面样本,在应用视觉检查功能之前需要对其进行失真处理——桶形失真在原始图像中非常明显。

下面的代码为要处理的图像细化摄像机矩阵,然后计算和应用转换。
# 输入失真图像,保留为 3 通道
image_dist = cv2.imread('./sample.png')
print("Distorted image shape: ", image_dist.shape)
cv2.imshow("Distorted Image", image_dist)
cv2.waitKey(0)
# 根据比例因子返回相应的新的相机内参矩阵,并得到有效的ROI
h, w = image_dist.shape[:2]
cameraMatrixNew, roi = cv2.getOptimalNewCameraMatrix(cameraMatrix, distCoeffs, (w, h), 1, (w, h))
# 计算原始图像和矫正图像之间的转换关系,将结果以映射的形式表达,映射关系存储在map1和map2中
map1, map2 = cv2.initUndistortRectifyMap(cameraMatrix, distCoeffs, None, cameraMatrixNew, (w, h), cv2.CV_32FC1)
# 把原始图像中某位置的像素映射到矫正后的图像指定位置,
# 这里的map1和map2就是上面cv::initUndistortRectifyMap()计算出来的结果。
image_undist = cv2.remap(image_dist, map1, map2, cv2.INTER_LINEAR)
cv2.imshow("Undistorted Image Full", image_undist)
cv2.waitKey(0)
也可以使用undistort函数,因为undistort函数内部调用了initUndistortRectifyMap函数和remap函数。
下图是变换后的未失真输出。边缘处的黑色斑块是重新映射过程的副产品,因为像素被重新定位以获得直线度。

OpenCV的重映射函数识别出了上面图像边缘的黑色斑块,提供了一个有效的ROI(感兴趣区域),在变换之后给出了可能的最大的矩形图像。
# crop undistorted image to valid ROI
print("Valid ROI: ", roi)
x, y, w, h = roi
image_undist = image_undist[y:y+h, x:x+w]
cv2.imshow("Undistorted Image Valid ROI", image_undist)
cv2.waitKey(0)
生成的图像是裁剪后的有效 ROI,随后可用作视觉检测算法的输入。
参考目录
https://docs.opencv.org/4.x/d4/d94/tutorial_camera_calibration.html