java ee配置数据库_Java EE 学习(7):IDEA + maven + spring 搭建 web(3)- 配置数据库...
参考: https://my.oschina.net/gaussik/blog/513444
注:在阅读本文前,请先阅读:
5 数据库配置
下面,就要通过一个简单的例子,来介绍 SpringMVC 如何集成 Spring Data JPA(由 Hibernate JPA 提供),来进行强大的数据库访问,并通过本章节的讲解,更加深刻地认识Controller 是如何进行请求处理的,看完这一章节,你就可以开始你的开发工作了。
准备工作:
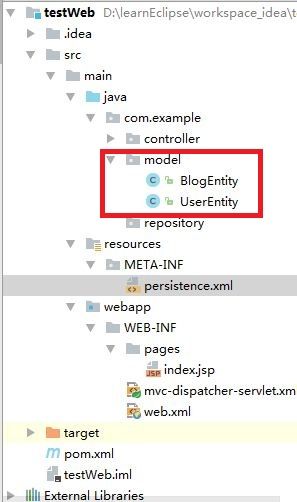
在src\main\java中新建两个包:com.example.model、com.example.repository,将在后面用上,如下图所示:
(1)、创建Mysql数据库
本文的讲解使用Mysql数据库,如果使用其它数据库的读者,可以去网上参考其他的配置教程,在此不做太多的叙述。数据库是一个底层的东西,底层的细节对上层的抽象并没有太大的影响,因此,只要配置好数据库,本章的内容仍然是适用于所有数据库的(貌似如此)。
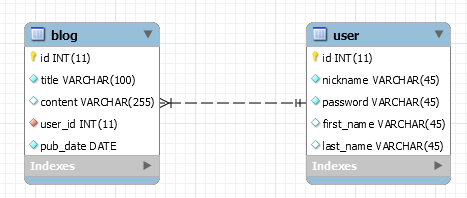
假设我们现在要建立一个小小的博客系统,其数据库ER图如下所示(当然这只是一个小小的例子,真实的博客系统比这要复杂的多):
新建一个数据库springdemo,在数据库中,有两张表:
(1)用户表user:用户登录信息,主键 id 设为自增;
(2)博文表blog:储存用户发表的博文,主键 id 设为自增,其中有一个外键 user_id 链接到 user 表。
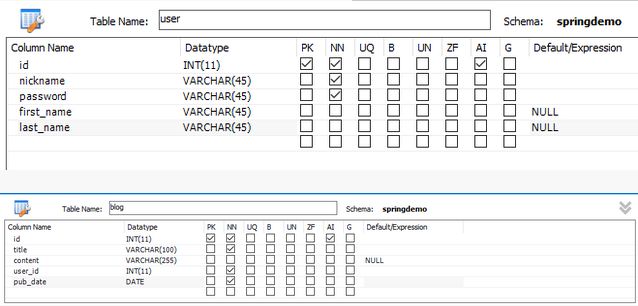
详细表结构如下图所示:
使用MySQL Workbench添加外键流程:
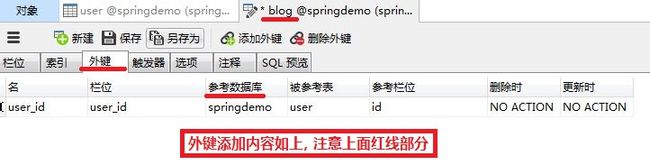
注意:在添加外键时,应该根据需求设置,例如右边红框中的 Foreign Key Options,默认在 Delete 时是 NO ACTION,说明在删除一个用户时,如果数据库中存在该用户的文章,那么就无法删除该用户,也无法删除该用户的所有文章,而如果将该选项改为 CASCADE,那么删除该用户,就会同时删除该用户所有的文章。通常后者是不太可取的,因为如果发生了删除用户的误操作,很有可能该用户的内容被连带删除,且不可逆,这也是实现真实系统时需要考虑的原因之一。
以下是使用 Navicat for MySql 创建的过程:
user 表:
blog 表:
添加外键:
(2)、IntelliJ IDEA导入数据库
对于此前所接触的一些常用的框架中,一张数据表往往对应一个Java Bean。在 SpringMVC 中,这个Java Bean 相当于 model。那么,这个类是否需要自己来写呢?不需要,利用 IntelliJ IDEA 可以帮我们自动的生成这些 JavaBean。
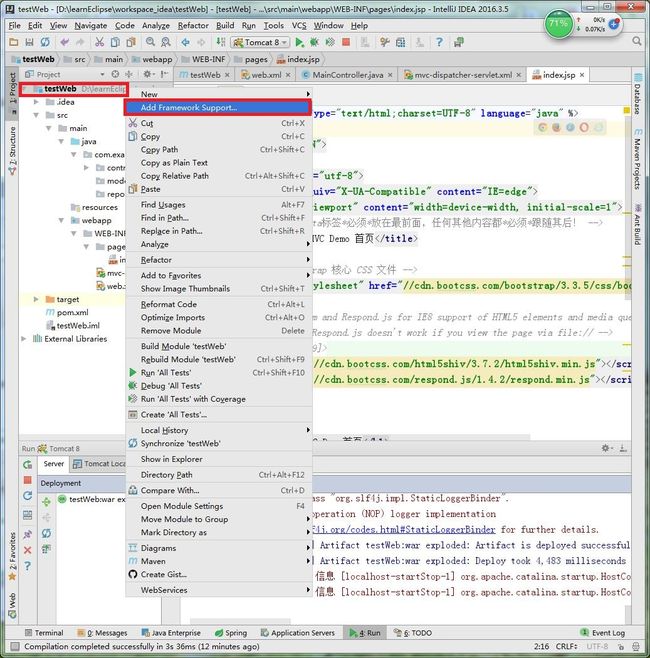
首先,右键项目,选择 Add Framework Support:
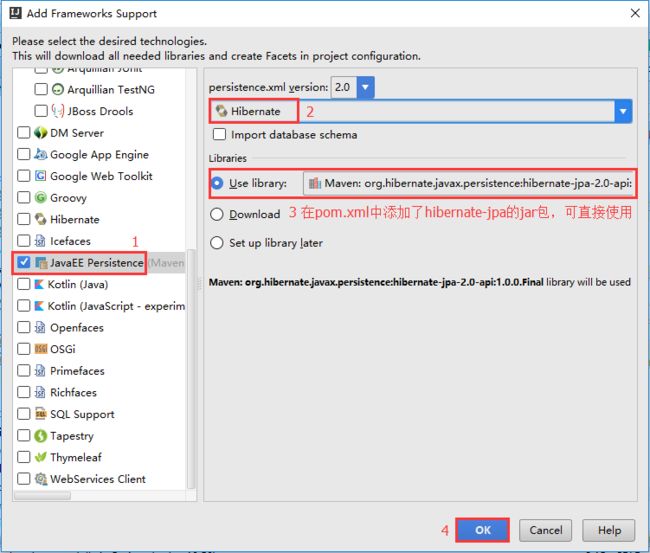
下拉选择 JavaEE Persistence,右边 provider 选择 Hibernate:
注:这一部分有一点过时,更新的项目中直接把数据库的配置放在了mvc-dispatcher-servlet.xml 中,但依然要做这一步的操作,为了这一步可以使用 Persistence 的工具。
关于新的配置,可以翻到博客底部。
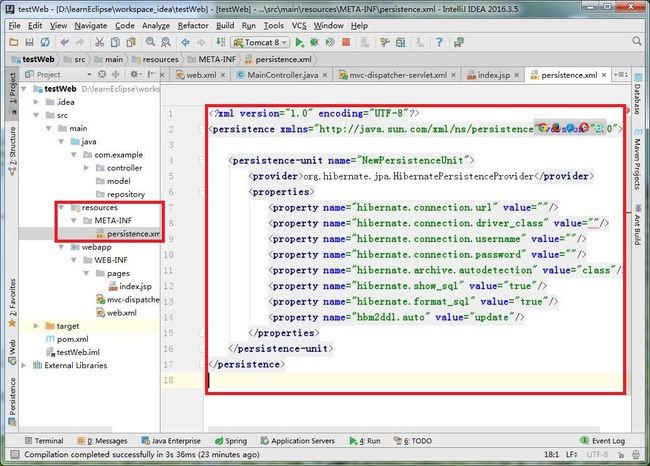
在这一步结束后,我们可以发现,在 resources 里面生成了persistence.xml配置文件,左边栏出现了一个 Persistence 标题(若没有请点击左下角那个灰框):
persistemce.xml 具体如下:
org.hibernate.jpa.HibernatePersistenceProvider
我们先不着急填写这个配置文件。点开左边栏的 Persistence,显示如下图所示:
右键项目名,选择Generate Persistence Mapping,再选择By Database Schema:
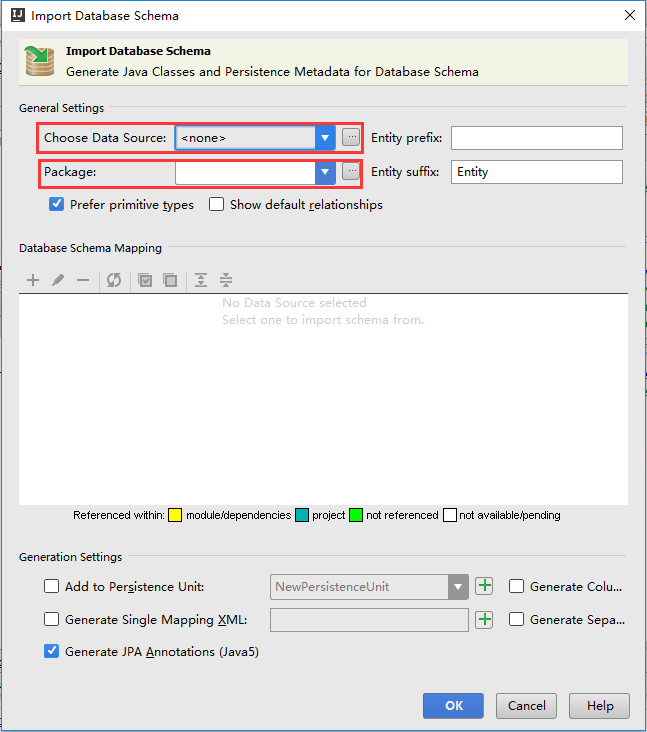
出现如下界面,其主要需要配置的地方如下图红框所示:
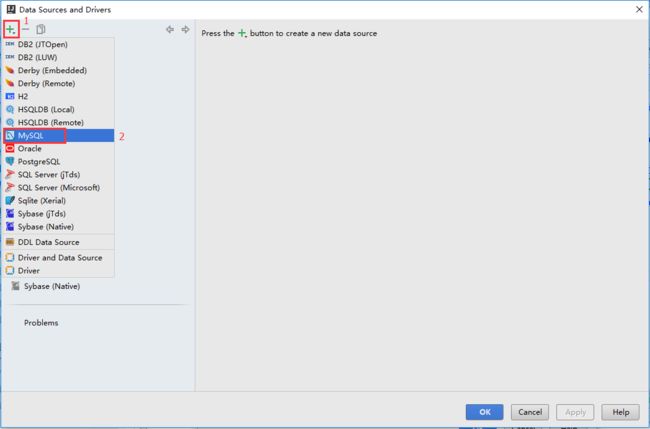
点击 Choose Data Source 右边的三个点选择数据源,在弹出的界面左上角选择 “+”,选择 Mysql:
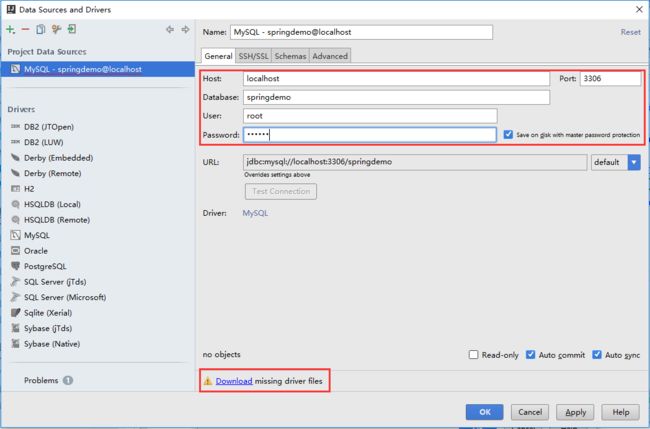
在如下界面填写主机、端口号、数据库名、用户名、密码,如果驱动丢失点击下面的 Download 可以下载驱动,点击 Test Connection可以测试数据库是否连接成功:
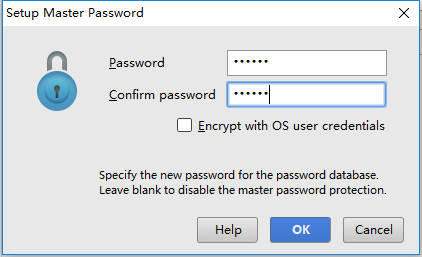
在以上界面配置完成后,点OK,第一次使用需要 Setup Master Password:
回到如下页面:
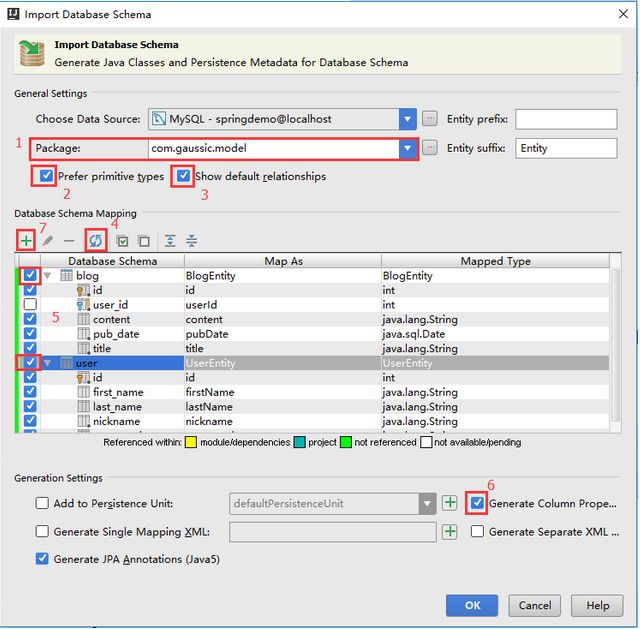
(1)package 填写 model 包;
(2) 勾选 Prefer primitive type 使用原始数据类型;
(3) 勾选 Show default relationships 以显示所有数据库关系;
(4)再点击刷新按钮,将会找到数据库中的两个表
(5)勾选两个数据表;
(6) 再勾选 Generate Column Defination 以生成每一列的描述信息。
(7)选中 blog 表然后点击“+”号按钮,添加外键关系(若已经添加过外键,此步则可以跳过)。
添加外键(若已经添加过,此不可忽略)
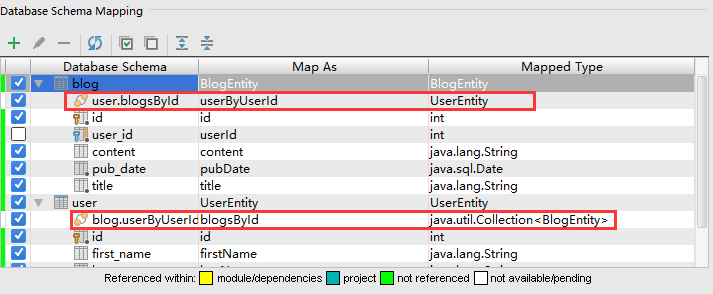
点击OK后,在Database Schema Mapping中可以发现多出了两个关系,如图所示:
再点击OK,稍后,打开model包,可以看到生成了两个Java Bean,在SpringMVC中称为两个实体,它们对应了数据库的两张表:
BlogEntity 如下所示(注意把java.sql.Date改为java.util.Date):
package com.example.model; # 注意自己的包名import javax.persistence.*;import java.util.Date; # change: 更改导入包
/**
* Created by dzkanon 2016/3/8.*/@Entity
@Table(name = "blog", schema = "springdemo", catalog = "")public class BlogEntity {
private int id;private String title;private String content;privateDate pubDate;private UserEntity userByUserId; @Id
@Column(name = "id", nullable = false)public int getId(){return id;}
public void setId(int id){
this.id = id;}
@Basic
@Column(name = "title", nullable = false, length = 100)public String getTitle(){return title;}
public void setTitle(String title){
this.title = title;}
@Basic
@Column(name = "content", nullable = true, length = 255)public String getContent(){return content;}
public void setContent(String content){
this.content = content;}
@Basic
@Column(name = "pub_date", nullable = false)publicDate getPubDate(){return pubDate;}
public void setPubDate(Date pubDate){
this.pubDate = pubDate;}
@Override
public boolean equals(Object o){if (this == o) return true;
if (o == null || getClass() != o.getClass()) return false;BlogEntity that= (BlogEntity) o;
if (id != that.id) return false;
if (title != null ? !title.equals(that.title) : that.title != null) return false;
if (content != null ? !content.equals(that.content) : that.content != null) return false;
if (pubDate != null ? !pubDate.equals(that.pubDate) : that.pubDate != null) return false;
return true;}
@Override
public int hashCode(){
int result= id;result= 31 * result + (title != null ? title.hashCode() : 0);result= 31 * result + (content != null ? content.hashCode() : 0);result= 31 * result + (pubDate != null ? pubDate.hashCode() : 0);
return result;}
@ManyToOne
@JoinColumn(name = "user_id", referencedColumnName = "id", nullable = false)public UserEntity getUserByUserId(){return userByUserId;}
public void setUserByUserId(UserEntity userByUserId){
this.userByUserId = userByUserId;}
}
# 此处,注意,对于 “blog” , “springdemo” 之类的标红,不用管,是 IDEA 自身问题,不影响项目运行
再看UserEntity:
package com.example.model; # 使用自己的包import javax.persistence.*;import java.util.Collection;
/**
* Created by dzkanon 2016/3/8.*/@Entity
@Table(name = "user", schema = "springdemo", catalog = "")public class UserEntity {
private int id;private String nickname;private String password;private String firstName;private String lastName;private Collection blogsById; @Id
@Column(name = "id", nullable = false)public int getId(){return id;}
public void setId(int id){
this.id = id;}
@Basic
@Column(name = "nickname", nullable = false, length = 45)public String getNickname(){return nickname;}
public void setNickname(String nickname){
this.nickname = nickname;}
@Basic
@Column(name = "password", nullable = false, length = 45)public String getPassword(){return password;}
public void setPassword(String password){
this.password = password;}
@Basic
@Column(name = "first_name", nullable = true, length = 45)public String getFirstName(){return firstName;}
public void setFirstName(String firstName){
this.firstName = firstName;}
@Basic
@Column(name = "last_name", nullable = true, length = 45)public String getLastName(){return lastName;}
public void setLastName(String lastName){
this.lastName = lastName;}
@Override
public boolean equals(Object o){if (this == o) return true;
if (o == null || getClass() != o.getClass()) return false;UserEntity that= (UserEntity) o;
if (id != that.id) return false;
if (nickname != null ? !nickname.equals(that.nickname) : that.nickname != null) return false;
if (password != null ? !password.equals(that.password) : that.password != null) return false;
if (firstName != null ? !firstName.equals(that.firstName) : that.firstName != null) return false;
if (lastName != null ? !lastName.equals(that.lastName) : that.lastName != null) return false;
return true;}
@Override
public int hashCode(){
int result= id;result= 31 * result + (nickname != null ? nickname.hashCode() : 0);result= 31 * result + (password != null ? password.hashCode() : 0);result= 31 * result + (firstName != null ? firstName.hashCode() : 0);result= 31 * result + (lastName != null ? lastName.hashCode() : 0);
return result;}
@OneToMany(mappedBy = "userByUserId")public Collection getBlogsById(){return blogsById;}
public void setBlogsById(Collection blogsById){
this.blogsById = blogsById;}
}
(3)、配置数据库
既然数据库已经导入了,那么前期准备工作基本完成,还需要进行最终的配置。
首先,打开mvc-dispatcher-servlet.xml,添加下列配置(如果某些地方报错,请选中并按 Alt + Insert 补全配置):
# 注意自己的包名
讲解:
(1) jpa:repositories:这一部分涉及到数据库的接口,将在后面详解;
(2)entityManagerFactory:实体管理器工厂,读取 persistence.xml 配置;
(3)transactionManager:事务管理器,利用 entityManager 进行事务管理;
(4)tx:annotation-driven:打开事务管理器的注解驱动,可以使用注解的方法操纵数据库。
整体如下所示:
http://www.springframework.org/schema/contexthttp://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvchttp://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc/spring-mvc.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/data/jpahttp://www.springframework.org/schema/data/jpa/spring-jpa.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/txhttp://www.springframework.org/schema/tx/spring-tx.xsd"> # 此处同样要更改,改为 黄色部分
# 另,此文件 配置正确,无任何错误!!
下面,填充 persistence.xml,将 persistence-unit 的 name改为 defaultPersistenceUnit。在下面的文件中,我添加了一些更为详细的配置:
org.hibernate.jpa.HibernatePersistenceProvider
现在,重新启动 tomcat,如果没有报错,说明数据库已经配置完成了,接下来就要讲解数据库的相关开发工作,另开一文:
更新(未尝试):
阅读评论发现许多同学的persistence.xml出现了问题,因为出现问题的原因可能有很多,如果没有完全的报错以及代码的话,我这边很难解决问题,一个办法就是在GitHub Issues上面提问并贴出代码,我这边尽量解答。另一个办法就是下载最新的代码运行看有没有什么问题。
最后一个办法,尝试另外一种配置方法,无需 persistence.xml,直接在 mvc-dispatcher-servlet.xml 中配置数据库,如下所示:
com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/springdemo?useSSL=false
root
111111
false
true
UTF-8
true
true
update
true
org.hibernate.dialect.MySQL5Dialect
true
true
true
org.hibernate.service.jdbc.connections.internal.C3P0ConnectionProvider
5
600
1800
50
SELECT 1;
true
3000
删除persistence.xml,直接修改entityManagerFactory bean为如上图所示。这个方法可以摆脱persistence.xml的困扰,但是有一个小小的问题,如果之前没有添加Java EE Persistence这个框架的,文中的Persistence工具栏将不会显示。一个解决办法就是,先修改mvc-dispatcher-servlet,然后再添加Java EE Persistence框架,等能够看到Persistence工具栏后,删除persistence.xml,余下的步骤可以继续操作。