SpringBoot(6)--配置文件的值注入问题探讨
主要内容:
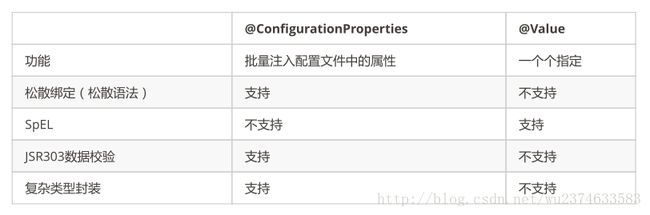
(1)@Value获取值和@ConfigurationProperties获取值比较
(2)配置文件注入值数据校验
(3)@PropertySource&@ImportResource&@Bean
1 @Value和@ConfigurationProperties
案例1:
application.yml
#注释
person:
lastname: 吴凯
age: 24
date: 2017/07/07
maps: {k1: v1,k2: v2}
lists: [l1,l2,l3]
dog: {name: jack,age: 3 }Person.java
public class Person {
/*
* @value 相当于
*
*
*
*/
@Value("${person.lastname}")
private String lastname;
@Value("#{12*2}")
private Integer age;
private Date date;
private Map maps;
private List 输出结果:
Person [lastname=吴凯, age=24, date=null, maps=null, lists=null, dog=null]注意:#和$的区别
配置文件yml还是properties他们都能获取到值;
总结:
如果说,我们只是在某个业务逻辑中需要获取一下配置文件中的某项值,使用@Value;
如果说,我们专门编写了一个javaBean来和配置文件进行映射,我们就直接使用@ConfigurationProperties;
2 配置文件注入值数据校验
package com.wuk.helloworld.entity;
import java.util.Date;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
import javax.validation.constraints.Email;
import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.ConfigurationProperties;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import org.springframework.validation.annotation.Validated;
@Component
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix="person")
@Validated
public class Person {
@Email
private String lastname;
private Integer age;
private Date date;
private Map maps;
private List @Validated和@Email注解
注意:
只有 @ConfigurationProperties支持JSR303进行配置文件值校验;
3 @PropertySource&@ImportResource&@Bean
@PropertySource
作用:加载指定的配置文件。
给bean指定配置文件,注意不要带任何空格。
@PropertySource(value= {"classpath:person.properties"})
@Component
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix="person")
public class Person {
private String lastname;
private Integer age;
private Date date;
private Map maps;
private List 注意:这里所指的类路径指的是如下文件夹里面:
@ImportResource
作用:导入Spring的配置文件,让配置文件里面的内容生效。
Spring Boot里面没有Spring的配置xml文件,而且我们自己编写的配置文件,也不能自动识别。想让Spring的配置文件生效,加载进来;@ImportResource标注在一个配置类上。
案例:
首先我们写一个类 HelloService.java
package com.wuk.helloworld.service;
public class HelloService {
}然后写一个配置类beans.xml
<beans>
<bean id="helloService" class="com.wuk.helloworld.service.HelloService">
bean>
beans>然后我们进行测试
//容器ioc
@Autowired
private ApplicationContext ioc;
@Test
public void testHelloService() {
System.out.println(ioc.containsBean("helloService"));
}结果:
false也就是说,没有容器里面并没有该实体对象,也就是说没有加载我们写的配置类。
做法如下:
找一个配置类,比如主配置类HelloworldApplication.java
采用@ImportResource进行加载。
@ImportResource(locations= {"classpath:beans.xml"})
@SpringBootApplication
public class HelloworldApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(HelloworldApplication.class, args);
}
}这时候运行结果是true。
SpringBoot推荐给容器中添加组件的方式;推荐使用全注解的方式
1、配置类@Configuration——>Spring配置文件
2、使用@Bean给容器中添加组件
写一个类
package com.wuk.helloworld.config;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import com.wuk.helloworld.service.HelloService;
/*
* @Configuration:指明当前类是一个配置类;就是来替代之前的Spring配置文件
* 在配置文件中用测试:
//容器
@Autowired
private ApplicationContext ioc;
@Test
public void testHelloService() {
System.out.println(ioc.containsBean("helloService"));
}结果:
配置类@bean给容器添加组件。。。
true