MyBatis的二级缓存讲解
1、二级缓存的定义
二级缓存也称作是应用级缓存,与一级缓存不同的是它的作用范围是整个应用,而且可以跨线程使用。所以二级缓存有更高的命中率,适合缓存一些修改比较少的数据。
2、二级缓存扩展性需求
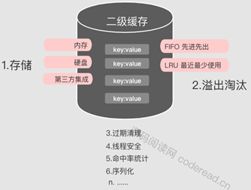
二级缓存的生命周期是整个应用,所以必须限制二级缓存的容量,在这里mybatis使用的是溢出淘汰机制。而一级缓存是会话级的生命周期非常短暂是没有必要实现这些功能的。相比较之下,二级缓存机制更加完善。
3、二级缓存的结构
二级缓存在结构设计上采用装饰器+责任链模式

1)二级缓存是如何组装这些装饰器的呢?
这里我们先介绍一下CacheBuilder类顾名思义这是一个缓存构建类。该类就是二级缓存的构建类里面定义了一些上图装饰器类型的属性,以及构建组合这些装饰器的行为。
源码分析:
public Cache build() {
this.setDefaultImplementations();
Cache cache = this.newBaseCacheInstance(this.implementation, this.id);
this.setCacheProperties((Cache)cache);
if (PerpetualCache.class.equals(cache.getClass())) {
Iterator var2 = this.decorators.iterator();
while(var2.hasNext()) {
Class<? extends Cache> decorator = (Class)var2.next();
cache = this.newCacheDecoratorInstance(decorator, (Cache)cache);
this.setCacheProperties((Cache)cache);
}
cache = this.setStandardDecorators((Cache)cache);
} else if (!LoggingCache.class.isAssignableFrom(cache.getClass())) {
cache = new LoggingCache((Cache)cache);
}
return (Cache)cache;
}
private void setDefaultImplementations() {
if (this.implementation == null) {
this.implementation = PerpetualCache.class;
if (this.decorators.isEmpty()) {
this.decorators.add(LruCache.class);
}
}
}
private Cache setStandardDecorators(Cache cache) {
try {
MetaObject metaCache = SystemMetaObject.forObject(cache);
if (this.size != null && metaCache.hasSetter("size")) {
metaCache.setValue("size", this.size);
}
if (this.clearInterval != null) {
cache = new ScheduledCache((Cache)cache);
((ScheduledCache)cache).setClearInterval(this.clearInterval);
}
if (this.readWrite) {
cache = new SerializedCache((Cache)cache);
}
Cache cache = new LoggingCache((Cache)cache);
cache = new SynchronizedCache(cache);
if (this.blocking) {
cache = new BlockingCache((Cache)cache);
}
return (Cache)cache;
} catch (Exception var3) {
throw new CacheException("Error building standard cache decorators. Cause: " + var3, var3);
}
}
4、BlockingCache防穿透缓存区
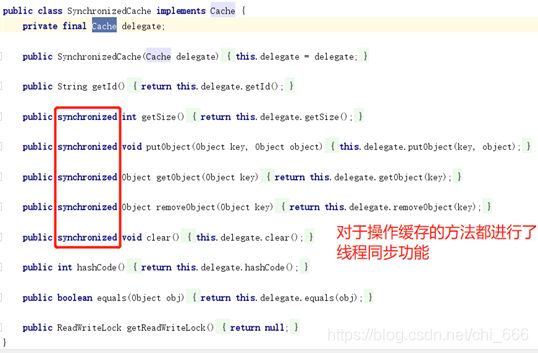
5、SynchronizedCache线程同步缓存区
实现线程同步功能,与序列化缓存区共同保证二级缓存线程安全。若blocking=false关闭则SynchronizedCache位于责任链的最前端,否则就位于BlockingCache后面而BlockingCache位于责任链的最前端,从而保证了整条责任链是线程同步的。
源码分析:只是对于操作缓存的方法进行了线程同步功能
6、LoggingCache统计命中率以及打印日志
统计二级缓存命中率并输出打印,由以下源码可知:日志中出现了“Cache Hit Ratio”便表示命中了二级缓存。
源码分析:
public class LoggingCache implements Cache {
private final Log log;
private final Cache delegate;
protected int requests = 0;
protected int hits = 0;
public LoggingCache(Cache delegate) {
this.delegate = delegate;
this.log = LogFactory.getLog(this.getId());
}
public Object getObject(Object key) {
++this.requests;//执行一次查询加一次
Object value = this.delegate.getObject(key);//查询缓存中是否已经存在
if (value != null) {
++this.hits;//命中一次加一次
}
if (this.log.isDebugEnabled()) {//开启debug日志
this.log.debug("Cache Hit Ratio [" + this.getId() + "]: " + this.getHitRatio());
}
return value;
}
private double getHitRatio() {//计算命中率
return (double)this.hits / (double)this.requests;//命中次数:查询次数
}
}
7、ScheduledCache过期清理缓存区
@CacheNamespace(flushInterval=100L)设置过期清理时间默认1个小时,
若设置flushInterval为0代表永远不进行清除。
源码分析:操作缓存时都会进行检查缓存是否过期
public class ScheduledCache implements Cache {
private final Cache delegate;
protected long clearInterval;
protected long lastClear;
public ScheduledCache(Cache delegate) {
this.delegate = delegate;
this.clearInterval = 3600000L;
this.lastClear = System.currentTimeMillis();
}
public void clear() {
this.lastClear = System.currentTimeMillis();
this.delegate.clear();
}
private boolean clearWhenStale() {
//判断当前时间与上次清理时间差是否大于设置的过期清理时间
if (System.currentTimeMillis() - this.lastClear > this.clearInterval) {
this.clear();//一旦进行清理便是清理全部缓存
return true;
} else {
return false;
}
}
}
8、LruCache(最近最少使用)防溢出缓存区
内部使用链表(增删比较快)实现最近最少使用防溢出机制
源码分析:
public void setSize(final int size) {
this.keyMap = new LinkedHashMap<Object, Object>(size, 0.75F, true) {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 4267176411845948333L;
protected boolean removeEldestEntry(Entry<Object, Object> eldest) {
boolean tooBig = this.size() > size;
if (tooBig) {
LruCache.this.eldestKey = eldest.getKey();
}
return tooBig;
}
};
}
//每次访问都会遍历一次key进行重新排序,将访问元素放到链表尾部。
public Object getObject(Object key) {
this.keyMap.get(key);
return this.delegate.getObject(key);
}
9、FifoCache(先进先出)防溢出缓存区
源码分析:内部使用队列存储key实现先进先出防溢出机制。
public class FifoCache implements Cache {
private final Cache delegate;
private final Deque<Object> keyList;
private int size;
public FifoCache(Cache delegate) {
this.delegate = delegate;
this.keyList = new LinkedList();
this.size = 1024;
}
public void putObject(Object key, Object value) {
this.cycleKeyList(key);
this.delegate.putObject(key, value);
}
public Object getObject(Object key) {
return this.delegate.getObject(key);
}
private void cycleKeyList(Object key) {
this.keyList.addLast(key);
if (this.keyList.size() > this.size) {//比较当前队列元素个数是否大于设定值
Object oldestKey = this.keyList.removeFirst();//移除队列头元素
this.delegate.removeObject(oldestKey);//根据移除元素的key移除缓存区中的对应元素
}
}
}
10、二级缓存的使用(命中条件)
1)会话提交后
2)sql语句、参数相同
3)相同的statementID
4)RowBounds相同
注意:设置为自动提交事务并不会命中二级缓存。
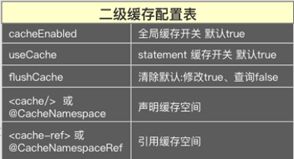
11、二级缓存的配置
12、二级缓存为什么要提交之后才能命中缓存?

会话一与会话二原本是两条隔离的事务,但由于二级缓存的存在导致彼此可见会发生脏读。若会话二的修改直接填充到二级缓存,会话一查询时缓存中存在即直接返回数据,此时会话二回滚会话一读到的数据就是脏数据。为了解决这一问题mybatis二级缓存机制就引入了事务管理器(暂存区),所有变动的数据都会暂时存放到事务管理器的暂存区中,只有执行提交动作后才会真正的将数据从暂存区中填充到二级缓存中。
1)会话:事务缓存管理器:暂存区=1:1:N
2)暂存区:缓存区=1:1(一个暂存区对应唯一一个缓存区)
3)会话关闭,事务缓存管理器也会关闭,暂存区也会被清空
4)一个事务缓存管理器管理多个暂存区
5)有多少个暂存区取决于你访问了多少个Mapper文件(缓存的key是Mapper文件全路径ID)
13、二级缓存执行流程

1)查询是实时查询缓存区的。
2)所有对二级缓存的实时变动都是通过暂存区来实现的。
3)暂存区清理完会进行标识,但此时二级缓存中数据并未清理,只有执行commit后才会真正清理二级缓存中的数据。
4)查询会实时查询缓存区,若暂存区清理标识为true就算从缓存区中查询到数据也会返回一个null,重新查询数据库(暂存区清理标识为true也会返回null是为了防止脏读,一旦提交清空掉二级缓存中的数据此时读取到的就是脏数据,因此返回null重新查询数据库得到的才是正确数据)。
源码分析:
a1、若开启二级缓存进行查询方法的时候会走到类CachingExecutor中的query方法
public <E> List<E> query(MappedStatement ms, Object parameterObject, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, CacheKey key, BoundSql boundSql) throws SQLException {
Cache cache = ms.getCache();//获得Cache
if (cache != null) {
this.flushCacheIfRequired(ms);//判断是否配置了flushCache=true,若配置了清空暂存区
if (ms.isUseCache() && resultHandler == null) {
this.ensureNoOutParams(ms, boundSql);
List<E> list = (List)this.tcm.getObject(cache, key);//获得缓存
if (list == null) {//若为空查询数据库并将数据填充到暂存区
list = this.delegate.query(ms, parameterObject, rowBounds, resultHandler, key, boundSql);
this.tcm.putObject(cache, key, list);
}
return list;
}
}
return this.delegate.query(ms, parameterObject, rowBounds, resultHandler, key, boundSql);
}
a2、根据上一步中的tcm.getObject(cache, key)方法查询二级缓存
public Object getObject(Object key) {
Object object = this.delegate.getObject(key);//查询二级缓存
if (object == null) {//为空也是为了先设置一个值防止缓存穿透
this.entriesMissedInCache.add(key);
}
//判断暂存区清空标识是否为true,若为true直接返回null重新查询数据库防止脏读
return this.clearOnCommit ? null : object;
}