Spring Boot项目连接数据库的方式有哪些?
一、准备工作:
1、建一个简单的数据库,名为springboot_db,在其下建一个表,名为t_author,脚本如下:
CREATE DATABASE /*!32312 IF NOT EXISTS*/`springboot_db` /*!40100 DEFAULT CHARACTER SET utf8 */;
USE `springboot_db`;
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS `t_author`;
CREATE TABLE `t_author` (
`id` bigint(20) unsigned NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT COMMENT '用户ID',
`real_name` varchar(32) NOT NULL COMMENT '用户名称',
`nick_name` varchar(32) NOT NULL COMMENT '用户匿名',
PRIMARY KEY (`id`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB AUTO_INCREMENT=1 DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8;
2、添加配置文件,可用使用yaml配置,即application.yml(与application.properties配置文件,没什么太大的区别)连接池的配置如下:
spring:
datasource:
url: jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/springboot_db?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=UTF-8&useSSL=false
driverClassName: com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
username: root
password: root
type: com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource
3、需要建立与数据库对应的POJO类,代码如下:
public class Author {
private Long id;
private String realName;
private String nickName;
// SET和GET方法略
}
二、方式一:与JdbcTemplate集成
通过JdbcTemplate来访问数据库,Spring boot提供了如下的starter来支撑:
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-jdbc
再引入Junit测试Starter:
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-test
test
DAO接口:
package com.guxf.dao;
import java.util.List;
import com.guxf.domain.Author;
public interface AuthorDao {
int add(Author author);
int update(Author author);
int delete(Long id);
Author findAuthor(Long id);
List findAuthorList();
}
实现Dao接口代码(此处只写Add,其他方法略):
package com.guxf.impl;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.jdbc.core.namedparam.NamedParameterJdbcTemplate;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Repository;
import com.guxf.dao.AuthorDao;
import com.guxf.domain.Author;
@Repository
public class AuthorDaoJdbcTemplateImpl implements AuthorDao{
@Autowired
private NamedParameterJdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate;
@Override
public int add(Author author) {
String sql = "insert into t_author(id,real_name,nick_name) " +
"values(:id,:realName,:nickName)";
Map param = new HashMap<>();
param.put("id",author.getId());
param.put("realName", author.getRealName());
param.put("nickName", author.getNickName());
return (int) jdbcTemplate.update(sql, param);
}
@Override
public int update(Author author) {
return 0;
}
@Override
public int delete(Long id) {
return 0;
}
@Override
public Author findAuthor(Long id) {
return null;
}
@Override
public List findAuthorList() {
return null;
}
}
通过JUnit来测试上面的代码(需根据自己的实际Application名稍作修改):
package com.guxf.boot;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.junit.runner.RunWith;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
import org.springframework.test.context.junit4.SpringJUnit4ClassRunner;
import com.guxf.BootApplication;
import com.guxf.dao.AuthorDao;
import com.guxf.domain.Author;
@RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class)
@SpringBootTest(classes = BootApplication.class)
public class AuthorDaoTest {
@Autowired
private AuthorDao authorDao;
@Test
public void testInsert() {
Author author = new Author();
author.setId(1L);
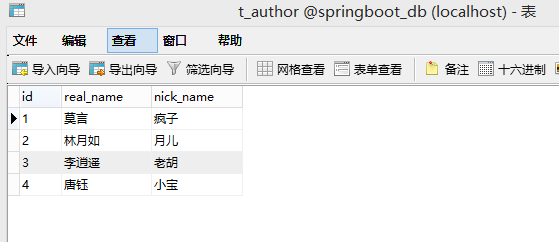
author.setRealName("莫言");
author.setNickName("疯子");
authorDao.add(author);
System.out.println("插入成功!");
}
}
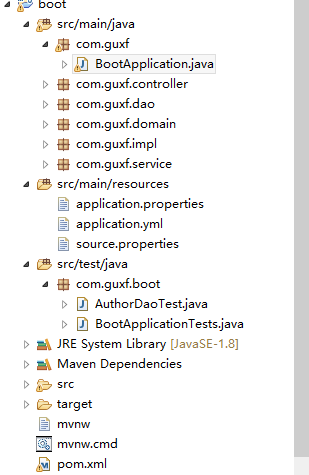
PS:需要注意的是,Application类所在的包必须是其他包的父包,@SpringBootApplication这个注解继承了@ComponentScan,其默认情况下只会扫描Application类所在的包及子包,结构图:
Application代码示例:
package com.guxf;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
@SpringBootApplication
public class BootApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(BootApplication.class, args);
}
}
三、方式二:与JPA集成
引入Starter:
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-data-jpa
对POJO类增加Entity的注解,并指定表名(如果不指定,默认的表名为author),然后指定ID的及其生成策略,这些都是JPA的知识,与Spring boot无关,代码:
package com.guxf.domain;
import javax.persistence.Entity;
import javax.persistence.GeneratedValue;
import javax.persistence.Id;
@Entity(name = "t_author")
public class Author {
@Id
@GeneratedValue
private Long id;
private String realName;
private String nickName;
// SET和GET方法略
}
需要继承JpaRepository这个类,这里我们实现了两个查询方法,第一个是符合JPA命名规范的查询,JPA会自动帮我们完成查询语句的生成,另一种方式是我们自己实现JPQL(JPA支持的一种类SQL的查询):
package com.guxf.service;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Optional;
import org.springframework.data.jpa.repository.JpaRepository;
import org.springframework.data.jpa.repository.Query;
import org.springframework.data.repository.query.Param;
import com.guxf.domain.Author;
public interface AuthorRepository extends JpaRepository {
public Optional findById(Long userId);
@Query("select au from com.guxf.domain.Author au where nick_name=:nickName")
public List queryByNickName(@Param("nickName") String nickName);
}
测试代码:
package com.guxf.boot;
import static org.junit.Assert.*;
import java.util.List;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.junit.runner.RunWith;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
import org.springframework.test.context.junit4.SpringJUnit4ClassRunner;
import com.guxf.BootApplication;
import com.guxf.domain.Author;
import com.guxf.service.AuthorRepository;
@RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class)
@SpringBootTest(classes = BootApplication.class)
public class AuthorDaoTestJPA {
@Autowired
private AuthorRepository authorRepository;
@Test
public void testQuery() {
List authorList = authorRepository.queryByNickName("疯子");
assertTrue(authorList.size() > 0);
System.out.println("成功!");
}
}
四、方式三:与MyBatis集成
引入starter:
org.mybatis.spring.boot
mybatis-spring-boot-starter
1.1.1
MyBatis一般可以通过XML或者注解的方式来指定操作数据库的SQL,首先,我们需要配置mapper的目录。我们在application.yml中进行配置:
spring:
datasource:
url: jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/springboot_db?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=UTF-8&useSSL=false
driverClassName: com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
username: root
password: root
type: com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource
mybatis:
#config-locations: mybatis/mybatis-config.xml
mapper-locations: com/guxf/mapper/*.xml
type-aliases-package: com.guxf.mapper.AuthorMapper
编写mapper对应的接口:
package com.guxf.mapper;
import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.Mapper;
import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.mapper.BaseMapper;
import com.guxf.domain.Author;
@Mapper
public interface AuthorMapper extends BaseMapper {
public Long insertAuthor(Author author);
public void updateAuthor(Author author);
public Author queryById(Long id);
}
配置Mapper的XML文件:
id,real_name,nick_name
INSERT INTO
t_author(
UPDATE t_author
real_name = #{realName},
nick_name = #{nickName},
WHERE id = #{id}
测试类代码:
package com.guxf;
import static org.junit.Assert.*;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.junit.runner.RunWith;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
import org.springframework.test.context.junit4.SpringJUnit4ClassRunner;
import com.guxf.BootApplication;
import com.guxf.domain.Author;
import com.guxf.mapper.AuthorMapper;
@RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class)
@SpringBootTest(classes = BootApplication.class)
public class AuthorDaoTestMybatis {
@Autowired
private AuthorMapper mapper;
@Test
public void testInsert() {
Author author = new Author();
author.setId(4L);
author.setRealName("唐钰");
author.setNickName("小宝");
mapper.insertAuthor(author);
System.out.println("成功!");
}
@Test
public void testMybatisQuery() {
Author author = mapper.queryById(1L);
assertNotNull(author);
System.out.println(author);
}
@Test
public void testUpdate() {
Author author = mapper.queryById(2L);
author.setNickName("月儿");
author.setRealName("林月如");
mapper.updateAuthor(author);
}
}
配置扫描,需要根据自己项目结构实际修改,下面贴上我的项目结构图: