Java多线程--深入浅出Java多线程
#深入浅出Java多线程
慕课网对应课程 – 深入浅出Java多线程
Java多线程基础概念
进程
程序(任务)的执行过程 动态性
持有资源(共享内存,共享文件)和线程
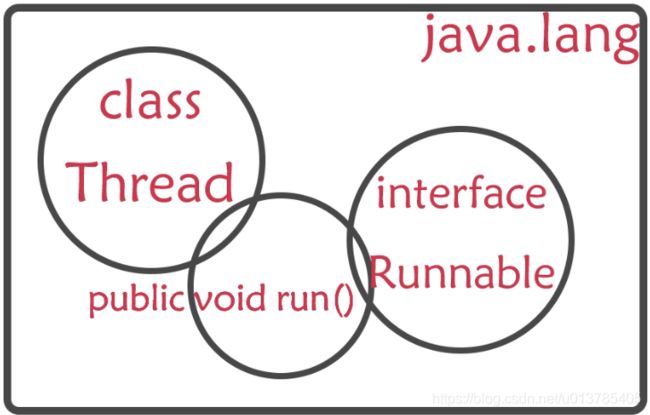
线程
线程是系统中最小的执行单元,同一进程中有多个线程,线程共享进程的资源
线程的交互
互斥 同步
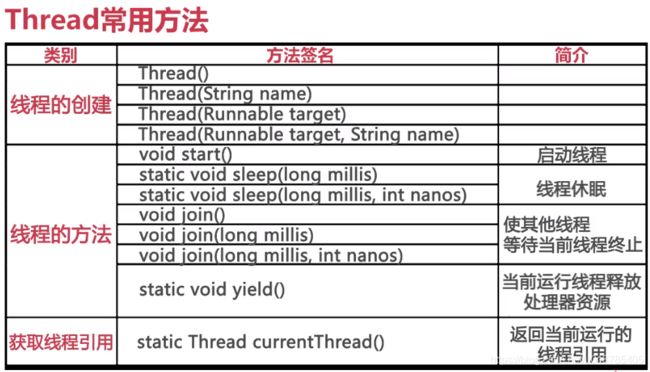
Java线程的常用方法
演员程序
package com.mooc.actor;
public class Actor extends Thread{
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println(getName()+"is an Actor");
int count = 0;
boolean keepRunning = true;
while (keepRunning){
System.out.println(getName()+" is on stage "+ (++count));
if (count==100){
keepRunning = false;
}
if (count%10 ==0){
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
System.out.println(getName()+" end Shows!");
}
public static void main(String[] args){
Actor actor = new Actor();
actor.setName("Mr.Thread");
actor.start();
Thread actress = new Thread(new Actress(),"Ms.Runnable");
actress.start();
}
}
class Actress implements Runnable{
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"is an Actor");
int count = 0;
boolean keepRunning = true;
while (keepRunning){
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+" is on stage "+ (++count));
if (count==100){
keepRunning = false;
}
if (count%10 ==0){
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+" end Shows!");
}
}
军队:ArmyRunnable
英雄人物:KeyPersonThread
舞台: Stage
ArmyRunnable
package com.mooc.concorrent;
public class ArmyRunnable implements Runnable{
// volatile 保证了线程可以正确的读取其他线程写入的值
// 可见性 ref JMM, happens-before原则
volatile boolean keepRunning = true;
@Override
public void run() {
while(keepRunning){
// 发动5连击
for (int i=0;i<5;i++){
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"进攻对方["+i+"]");
//让出处理器的时间,下次该谁进攻还不一定
Thread.yield();
}
}
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"结束了战斗");
}
}
KeyPersonThread
package com.mooc.concorrent;
public class KeyPersonThread extends Thread {
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"开始了战斗!!");
for (int i=0;i<10;i++){
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"左突右杀,攻击隋军...");
}
System.out.println(getName()+"结束了战斗!");
}
}
Stage
package com.mooc.concorrent;
/**
* 隋唐演义的大戏舞台
*/
public class Stage extends Thread {
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println("欢迎观看隋唐演义");
try {
Thread.sleep(5000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("大幕徐徐拉开!");
try {
Thread.sleep(5000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("话说隋朝末年,隋军与农名起义军杀得昏天地暗...");
ArmyRunnable armyTaskOfSuiDynasty = new ArmyRunnable();
ArmyRunnable armyTaskOfRevolt = new ArmyRunnable();
//使用Runnable结口创建新程
Thread armyOfSuiDynasty = new Thread(armyTaskOfSuiDynasty,"隋军");
Thread armyOfRevolt = new Thread(armyTaskOfRevolt,"农民起义军");
// 启动线程,军队开始作战
armyOfSuiDynasty.start();
armyOfRevolt.start();
// 舞台休眠,专心看军队厮杀
try {
Thread.sleep(50);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("正当双方激战正酣,半路杀出了程咬金");
KeyPersonThread mrCheng = new KeyPersonThread();
mrCheng.setName("程咬金");
System.out.println("程咬金的理想就是结束战争,使百姓安居乐业!");
armyTaskOfSuiDynasty.keepRunning = false;
armyTaskOfRevolt.keepRunning = false;
try {
Thread.sleep(2000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
/**
* 历史大戏留给关键人物
*/
mrCheng.start();
// 万众瞩目,所有线程等待程先生完成历史使命
try {
mrCheng.join();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("战争结束。人民安居乐业,程先生实现了积极地人生梦想,为人民做出了贡献!!");
System.out.println("谢谢观看隋唐演义,再见!!");
// try {
// armyOfRevolt.join();
// } catch (InterruptedException e) {
// e.printStackTrace();
// }
}
public static void main(String[] args ){
new Stage().start();
// Thread stage = new Stage();
// stage.start();
}
}
jion 方法的作用;
Java线程的正确停止
Java线程停止的错误方法stop()
not stop()方法
stop()方法会让线程戛然而止,我们不知道那些工作还没有做,也不知道现在已经完成了什么,无法开展清理工作
Java线程停止的正确方法-设置退出flag
public void run() {
while(keepRunning){
// 发动5连击
for (int i=0;i<5;i++){
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"进攻对方["+i+"]");
//让出处理器的时间,下次该谁进攻还不一定
Thread.yield();
}
}
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"结束了战斗");
}
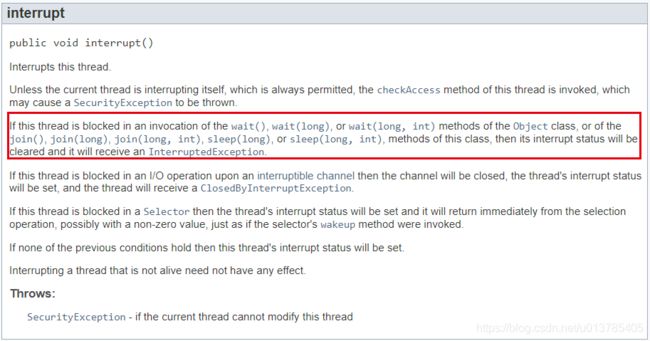
Java 线程停止广为流传的错误方法–interrupt()
interruput()方法的初衷并不是用于停止线程
try {
Thread.sleep(50);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
try {
Thread.sleep(2000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
package com.mooc.concorrent;
public class WrongWayStopThread extends Thread{
@Override
public void run() {
// while (true){
while (!this.isInterrupted()){
System.out.println("Thread is running...");
long time = System.currentTimeMillis();
while ((System.currentTimeMillis()-time)<1000){
//减少屏幕输出的空循环
}
/**
* 不能使用sleep,会清空interrupt 状态,抛出interruptException
*/
// try {
// Thread.sleep(1000);
// } catch (InterruptedException e) {
// e.printStackTrace();
// }
}
}
public static void main(String[] args){
WrongWayStopThread thread = new WrongWayStopThread();
System.out.println("Starting thread...");
thread.start();
try {
Thread.sleep(3000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("Interrupting thread...");
thread.interrupt();
try {
Thread.sleep(3000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("Stoping application...");
}
}
线程交互
争用条件
Race Condition
当多个线程同时共享访问同一数据(内存区域)时,每个线程都尝试操作该数据,从而导致数据被破坏(corrupted),这种现象称为争用条件。
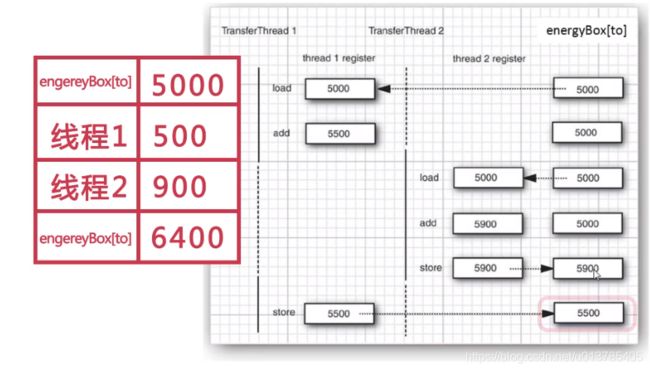
线程的交互: 互斥与同步
- 互斥
- 同步 通信机制