【数据结构与算法】图的深度优先和广度优先遍历
作者简介 : 大家好,我是南瓜籽,一个在校大二学生,我将会持续分享Java相关知识。
个人主页 : 南瓜籽的主页
✨✨座右铭✨✨ : 坚持到底,决不放弃,是成功的保证,只要你不放弃,你就有机会,只要放弃的人,他肯定是不会成功的人。
图的基本介绍
图的常用概念
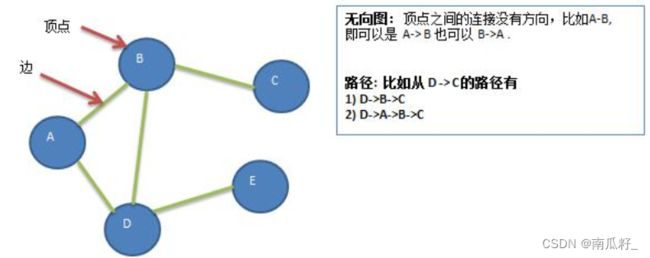
1)顶点(vertex)
2) 边(edge)
3) 路径
4) 无向图
5) 有向图
6) 带权图
图的表示方式
图的表示方式有两种:二维数组表示(邻接矩阵);链表表示(邻接表)
图的深度优先遍历
深度优先遍历基本思想
图的深度优先搜索(DepthFirstSearch)。
- 深度优先遍历,从初始访问结点出发,初始访问结点可能有多个邻接结点,深度优先遍历的策略就是首先访问第一个邻接结点,然后再以这个被访问的邻接结点作为初始结点,访问它的第一个邻接结点,可以这样理解:每次都在访问完当前结点后首先访问当前结点的第一个邻接结点。
- 我们可以看到,这样的访问策略是优先往纵向挖掘深入,而不是对一个结点的所有邻接结点进行横向访问。
- 显然,深度优先搜索是一个递归的过程
深度优先遍历算法步骤
- 访问初始结点v,并标记结点v为已访问。
- 查找结点v的第一个邻接结点w。
- 若w存在,则继续执行4,如果w不存在,则回到第1步,将从v的下一个结点继续。
- 若w未被访问,对w进行深度优先遍历递归(即把w当做另一个v,然后进行步骤123)。
- 查找结点v的w邻接结点的下一个邻接结点,转到步骤3。
深度优先算法代码实现
/**
* 深度优先遍历
* @param isVisited
* @param i
*/
public void dfs(boolean[] isVisited,int i){
// 1.输出节点
System.out.print(getVertex(i) + "->");
// 2.将该节点设置为已访问
isVisited[i] = true;
// 3.找到该节点下一个邻接节点的下标
int w = getFirstNeighbor(i);
while (w != -1){ // 说明有下一个邻接节点
if (!isVisited[w]){
// 如果该节点没有被访问
dfs(isVisited,w);
}else {
// 如果该节点被访问过
w = getNextNeighbor(i,w);
}
}
}
/**
* 方法重载,遍历所有节点,并进行dfs
*/
public void dfs(){
for (int i = 0; i < getNumOfVertex(); i++) {
if (!isVisited[i]){
// 没有被访问过的节点
dfs(isVisited,i);
}
}
}
图的广度优先遍历
广度优先遍历基本思想
- 图的广度优先搜索(BroadFirstSearch)。
- 类似于一个分层搜索的过程,广度优先遍历需要使用一个队列以保持访问过的结点的顺序,以便按这个顺序来访问这些结点的邻接结点
广度优先遍历算法步骤
- 访问初始结点v并标记结点v为已访问。
- 结点v入队列。
- 当队列非空时,继续执行,否则算法结束。
- 出队列,取得队头结点top。
- 查找结点top的第一个邻接结点next。
- 若结点top的邻接结点next不存在,则转到步骤3;否则循环执行以下三个步骤:
6.1若结点next尚未被访问,则访问结点next并标记为已访问。
6.2结点next入队列
6.3查找结点top的继next邻接结点后的下一个邻接结点next,转到步骤6。
广度优先算法代码实现
/**
* 对一个节点进行广度优先遍历
*/
public void bfs(boolean[] isVisited,int i){
int top; // 头节点下标
int next; // 邻接节点下标
// 1.输出该节点
System.out.print(getVertex(i) + "->");
// 2.将当前节点标志为已访问
isVisited[i] = true;
// 3.节点入队列
Queue queue = new Queue(vertexList.size());
queue.inQueue(i);
// 4.遍历队列
while (!queue.isEmpty()){
// 4.1取出队头节点下标
top = queue.outQueue();
// 4.2得到第一个邻接节点的下标
next = getFirstNeighbor(top);
while (next != -1){
// 4.3找到了第一个邻接节点的下标
if (!isVisited[next]){
// 4.3.1没有被访问过,输出该节点
System.out.print(getVertex(next) + "->");
// 4.3.2将该节点标志为已访问
isVisited[next] = true;
// 4.3.3节点入队列
queue.inQueue(next);
}else {
// 4.4如果已经访问过了,得到下一个邻接节点的下标
next = getNextNeighbor(top,next); // 广度优先
}
}
}
}
/**
* 方法重载,对所有节点进行广度优先遍历
*/
public void bfs(){
for (int i = 0; i < getNumOfVertex(); i++) {
if (!isVisited[i]){
bfs(isVisited,i);
}
}
}
图的属性和其他方法定义
public class Graph {
private List<String> vertexList; // 存储顶点集合
private int[][] edges;// 存储图对应的邻接矩阵
private int numOfEdges; // 表示边的数目
private boolean[] isVisited; // 记录某个顶点是否被访问过
/**
* 构造器初始化
* @param n
*/
public Graph(int n) {
this.vertexList = new ArrayList<>(n);
this.edges = new int[n][n];
this.isVisited = new boolean[n];
this.numOfEdges = 0;
}
/**
*
* @param index
* @return 得到第一个邻接节点的下标
*/
public int getFirstNeighbor(int index){
for (int i = 0; i < vertexList.size(); i++) {
if (edges[index][i] > 0){
return i;
}
}
return -1;
}
/**
* 根据前一个邻接节点下标找到下一个邻接节点
* @param v1
* @param v2
* @return 找到了返回下标,否则返回 -1
*/
public int getNextNeighbor(int v1,int v2){
for (int i = v2 + 1; i < vertexList.size(); i++) {
if (edges[v1][i] > 0){
return i;
}
}
return -1;
}
/**
*
* @return 得到图中节点的个数
*/
public int getNumOfVertex(){
return vertexList.size();
}
/**
*
* @return 得到边的个数
*/
public int getNumOfEdges(){
return numOfEdges;
}
/**
*
* @param index 下标
* @return 返回节点对应的值
*/
public String getVertex(int index){
return vertexList.get(index);
}
/**
*
* @param v1
* @param v2
* @return 返回v1和v2对应的权值
*/
public int getWeight(int v1,int v2){
return edges[v1][v2];
}
/**
* 插入节点
* @param vertex
*/
public void insertVertex(String vertex){
vertexList.add(vertex);
}
/**
* 插入边
* @param v1 点的下标
* @param v2 点的下标
* @param weight 权值
*/
public void insertEdge(int v1,int v2,int weight){
// 无向图,需要两边都存储
edges[v1][v2] = weight;
edges[v2][v1] = weight;
numOfEdges++;// 边的数目增加
}
/**
* 显示图对应的矩阵
*/
public void showGraph(){
for (int[] edge : edges) {
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(edge));
}
}
}
队列
class Queue {
private int maxSize; // 数组的最大容量
private int front;// 队列头
private int rear;// 队列尾
private int[] arr;// 该数组用于存放数据, 模拟队列
public Queue(int maxSize){// 初始化队列
this.maxSize = maxSize;
this.front = -1;// 指向队列头部
this.rear = -1;// 指向队列尾部
arr = new int[maxSize];// 初始化数组
}
/**
* 判断队列是否已满
* @return true 为满 false为未满
*/
public boolean isFull(){
return this.rear == this.maxSize - 1;
}
/**
* 判断队列是否为空
* @return true为空 false已经有了数据
*/
public boolean isEmpty(){
return this.rear == this.front;
}
/**
* 添加数据到队列中
* @param n
*/
public void inQueue(int n){
// 1.判断队列是否已满
if (isFull()){
System.out.printf("队列已满,%d无法存入队列中\n",n);
return;
}
this.rear++;
this.arr[rear] = n;
}
/**
* 出队列
* @return
*/
public int outQueue(){
// 1.判断是否为空
if (isEmpty()){
throw new RuntimeException("队列为空,不能出队列");
}
this.front++;
// 返回数据
return this.arr[front];
}
/**
* 显示队列所有数据
*/
public void listQueue(){
// 1.判断是否为空
if (isEmpty()){
throw new RuntimeException("队列为空");
}
System.out.println("--------队列数据显示-------");
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
System.out.printf("arr[%d]=%d\n",i,arr[i]);
}
System.out.println();
}
/**
* 得到队头数据
* @return
*/
public int getHeadQueue(){
// 1.判断是否为空
if (isEmpty()){
throw new RuntimeException("队列为空~~~");
}
// 2.返回
return this.arr[this.front + 1];
}
}
测试
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 初始化图和邻接矩阵
Graph graph = new Graph(5);
graph.insertVertex("A");
graph.insertVertex("B");
graph.insertVertex("C");
graph.insertVertex("D");
graph.insertVertex("E");
graph.insertEdge(0,1,1);
graph.insertEdge(0,2,1);
graph.insertEdge(1,2,1);
graph.insertEdge(1,3,1);
graph.insertEdge(1,4,1);
// 图的遍历
graph.showGraph();
// 深度优先遍历
System.out.println("------------深度优先遍历");
graph.dfs();
// 广度优先遍历
System.out.println("------------广度优先遍历");
graph.bfs();
}
结果:
[0, 1, 1, 0, 0]
[1, 0, 1, 1, 1]
[1, 1, 0, 0, 0]
[0, 1, 0, 0, 0]
[0, 1, 0, 0, 0]
------------深度优先遍历
A->B->C->D->E->
------------广度优先遍历
A->B->C->D->E->