java 包装类 万字详解(通俗易懂)
前言
简介和溯源
拆装箱
String类和基本类型的相互转化
String类和包装类型的相互转化
八大包装类的常用方法汇总(含代码演示)
一、前言 :
本节内容是我们《API-常用类》专题的最后一节了。本节内容主要讲包装类, 内容包括但不限于 包装类的诞生 , 包装类的类图 , 拆装箱 , String类和基本类型/包装类型间的相互转化 ,以及 八大包装类常用方法 的演示。up希望能通过IDEA类图,Debug,代码演示等多种方式,帮助大家快速上手并理解java包装类。 注意 : ① 代码中的注释也很重要; ② 不要眼高手低,自己敲一遍才能知道怎么用。 ③ 点击侧边栏目录可以跳转。良工不示人以朴,所有文章都会适时改进。 感谢阅读!
二、简介和溯源
1.简介 :
基本数据类型不是对象,不能使用类的方法;因此, java针对基本类型提供了它们对应的包装类,八大基本数据类型,对应了八种包装类,以对象的形式来调用。包装类有了类的特点,使我们可以调用包装类中的方法。
包装类属于java.base模块,java.lang包下,如下图所示 :
可以看到,在形式上除了Integer和Character这两个包装类外,其他六个包装类的类名均是对应的基本类型首字母大写后得到的。
当然,形式上的东西再咋滴也没有那么重要,那么这些个包装类在类与类的关系上有什么不同呢?下面我们来看看这些个包装类分别是什么来头。
2.溯源 :
IDEA最常用的17个快捷键中, Ctrl + h/H 快捷键可以快速当前类的继承关系,并且在 IDEA中,还可以继而查看当前类继承关系的图表表示。
先来看一下Integer类的继承关系图表 :
可以看到,Integer类继承了Number类,并且实现了若干接口。
现在,利用Ctrl + Alt + b/B 的快捷键,将其他七大包装类分别添加进入该图标,如下GIF所示 :
最后的效果图如下所示 :
哈哈,是不是感觉自己被耍了,这**是什么玩意儿?乱七八糟的! 欸,别急,仔细观察这张图,你只需要记住一个结论:除了Boolean和Character这两个包装类外,其他六大包装类都继承自Number类,并且它们都实现了一些接口。
那么,Boolean类和Character类的类关系图又是个什么情况呢?
Boolean类的类关系图如下 :
Character类的关系图如下 :
可以看到,Boolean类和Character类都没有继承Number类,它们都实现了一些接口,并且实现的接口还不尽相同。当然,你只需要记住Boolean类和Character类与其他六大包装类的区别就行,你也不需要去背它们的关系图,因为背了也没个儿用。
三、装箱和拆箱
1.介绍
装箱 : 基本类型 ——> 包装类型(或者叫对象类型,引用类型)
拆箱 : 包装类型 ——> 基本类型
2.手动拆装箱 :
JDK5.0之前,拆装箱均是手动完成的。
手动装箱,可以使用包装类的构造器来完成,也可以使用 valueOf() 方法。
手动拆箱,以Integer类为例,需要用到 intValue() 方法。
演示 :
以Integer包装类为例,以Intro类为演示类。
代码如下 :
package csdn.knowledge.api.Integer;
public class Intro {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//JDK5.0之前,拆装箱都是手动完成。
int temp = 19;
//手动装箱(基本类型 ————> 包装/引用类型)
Integer integer_0 = new Integer(temp); //划线表示该构造方法已过时
Integer integer_1 = new Integer(11);
Integer integer_2 = Integer.valueOf(temp);
//手动拆箱(包装/引用类型 ————> 基本类型)
int tempI_0 = integer_0.intValue(); /**该方法的接收类型为int类型*/
System.out.println("integer_0的值 = " + integer_0);
System.out.println("integer_1的值 = " + integer_1);
System.out.println("integer_2的值 = " + integer_2);
System.out.println("tempI_0 = " + tempI_0);
System.out.println("----------------------------------");
}
}运行结果 :
3.自动拆装箱 :
JDK5.0开始,java提供了自动拆装箱的机制。(不需要手动调用构造器或者方法了)
自动拆箱 : 实际上 底层仍然调用了valueOf() 方法。
自动装箱 : 实际上 底层仍然调用了intValue() 方法(以Integer包装类为例)
演示 :
以Integer包装类为例,以Intro类为演示类。
代码如下 :
package csdn.knowledge.api.Integer;
public class Intro {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//JDK5.0以后,java提供了自动拆装箱
Integer integer_3 = 199; //(自动)装箱——其实底层调用的仍然是valueOf方法(可Debug)
int tempI_1 = integer_3; //(自动)拆箱——其实底层调用的仍然是intValue方法
System.out.println("integer_3的值 = " + integer_3);
System.out.println("tempI_1 = " + integer_3);
System.out.println("----------------------------------");
}
}运行结果 :
我们可以通过Debug来验证自动拆装箱实际在底层调用了手动拆装箱时用到的方法。如下GIF图 :
可以看到,明明是自动装箱,可我们选择强制跳入方法时,依然跳入了valueOf() 方法;又明明是自动拆箱,可我们选择强制跳入方法时,依然跳入了intValue() 方法。
这里还要再强调一点,关于valueOf() 方法,Integer类中的valueOf() 方法源码如下 :
@IntrinsicCandidate
public static Integer valueOf(int i) {
if (i >= IntegerCache.low && i <= IntegerCache.high)
return IntegerCache.cache[i + (-IntegerCache.low)];
return new Integer(i);
}注意看,这里的valueOf方法中又一个if条件语句的判断,它的意思是,如果传入的int基本类型的值在这个范围内,我就不new新的Integer对象,而是调用底层的缓冲数组。通过追溯源码,我们可以得知这里的low和high 的实际范围是-128 ~ 127,如下图所示 :
并且,我们依然可以再次通过Debug来看看底层的缓冲数组是否真实存在,如下GIF所示 :
四、关于String类型的转化问题 :
1.String类型和基本类型的相互转化 :
①String类 ——> 基本类型
static 基本类型 parseXxx(String) :
包装类中的该方法可以将字符串类型的数据转换成对应的基本类型,需要用相应的基本类型来作接收。需要注意的是,在将字符串类型转为其他类型前,一定要确认字符串里面的内容能否正常转换,比方说,如果你想把”jdlsajflsajfl“这段字符串转换为int类型,那tm能行吗?这时候IDEA会报数字格式异常,如下图所示 :
演示 :
以Method类为演示类,代码如下 :
package csdn.knowledge.api.Integer;
public class Method {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//parseXxx(String),以对应的基本类型作接收
byte temp_byte = Byte.parseByte("11");
short temp_short = Short.parseShort("141");
int temp_int = Integer.parseInt("430");
long temp_long = Long.parseLong("11211");
float temp_float = Float.parseFloat("66.66F");
double temp_double = Double.parseDouble("666.666");
boolean temp_boolean = Boolean.parseBoolean("true");
System.out.println("temp_byte = " + temp_byte);
System.out.println("temp_short = " + temp_short);
System.out.println("temp_int = " + temp_int);
System.out.println("temp_long = " + temp_long);
System.out.println("temp_float = " + temp_float);
System.out.println("temp_double = " + temp_double);
System.out.println("temp_boolean = " + temp_boolean);
}
}
运行结果 :
这时候,可能有眼尖的小伙伴儿发现了——这咋没有Character包装类捏?
这是因为在八大包装类中,除了Character类外,其他的7种包装类中都有parseXxx() 方法。如果你想将字符串类型的数据转换成char类型的数据,你可以通过String类中的toCharArray() 方法和 charAt() 方法来做到。还记得我们在String类中讲到的这俩方法吗?
回顾一下 :
转换功能的方法 —— char[] toCharArray() : 将字符串转换成字符数组
获取功能的方法 —— char charAt(int index) : 获取指定索引位置的字符
以StringDemo类为演示类,代码如下 :
package csdn.knowledge.api.Integer;
public class StringDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//定义一个字符串
String string = "CSDN_yyds";
//利用toCharArray() 方法将字符串转换为字符数组
char[] charArray = string.toCharArray();
System.out.println("string字符串一共有" + charArray.length + "个字符.");
for (int i = 0; i < charArray.length; i++) {
System.out.println("第" + (i + 1) + "个字符是:" + charArray[i]);
}
System.out.println("---------------------------------------");
//利用charAt方法来直接获取字符串中的每一个字符元素
char temp_char_0 = string.charAt(0);
char temp_char_1 = string.charAt(1);
char temp_char_2 = string.charAt(2);
char temp_char_3 = string.charAt(3);
char temp_char_4 = string.charAt(4);
char temp_char_5 = string.charAt(5);
char temp_char_6 = string.charAt(6);
char temp_char_7 = string.charAt(7);
char temp_char_8 = string.charAt(8);
System.out.println("string字符串第一个元素为:" + temp_char_0);
System.out.println("string字符串第二个元素为:" + temp_char_1);
System.out.println("string字符串第三个元素为:" + temp_char_2);
System.out.println("string字符串第四个元素为:" + temp_char_3);
System.out.println("string字符串第五个元素为:" + temp_char_4);
System.out.println("string字符串第六个元素为:" + temp_char_5);
System.out.println("string字符串第七个元素为:" + temp_char_6);
System.out.println("string字符串第八个元素为:" + temp_char_7);
System.out.println("string字符串第九个元素为:" + temp_char_8);
}
}
运行结果:
②基本类型 ——> String类
基本类型要转字符串那就太简单了,最常见的两种方式——①直接与空字符串进行拼接,②String类的valueOf方法。
回顾一下 :
转换功能的方法 —— static String valueOf(...) : 将指定类型数据转换成字符串
演示 :
以StringDemo_1作为演示类,代码如下 :
package csdn.knowledge.api.Integer;
public class StringDemo_1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//方法一 : 以空字符串拼接的形式
//byte --> String
byte temp_byte = 127;
String temp_string_0 = 127 + "";
//short --> String
short temp_short = 141;
String temp_string_1 = temp_short + "";
//int --> String
int temp_int = 428;
String temp_string_2 = temp_int + "";
//long --> String
long temp_long = 11211;
String temp_string_3 = temp_long + "";
//float --> String
float temp_float = 135.0F;
String temp_string_4 = temp_float + "";
//double --> String
double temp_double = 433.0;
String temp_string_5 = temp_double + "";
//char --> String
char temp_char = 'A';
String temp_string_6 = temp_char + "";
//boolean --> String
boolean temp_boolean = true;
String temp_string_7 = temp_boolean + "";
System.out.println("temp_string_0 = " + temp_string_0);
System.out.println("temp_string_1 = " + temp_string_1);
System.out.println("temp_string_2 = " + temp_string_2);
System.out.println("temp_string_3 = " + temp_string_3);
System.out.println("temp_string_4 = " + temp_string_4);
System.out.println("temp_string_5 = " + temp_string_5);
System.out.println("temp_string_6 = " + temp_string_6);
System.out.println("temp_string_7 = " + temp_string_7);
System.out.println("========================================");
//方法二 : 利用String类的valueOf方法
temp_string_0 = String.valueOf(temp_byte) + "_EX";
temp_string_1 = String.valueOf(temp_short) + "_EX";
temp_string_2 = String.valueOf(temp_int) + "_EX";
temp_string_3 = String.valueOf(temp_long) + "_EX";
temp_string_4 = String.valueOf(temp_float) + "_EX";
temp_string_5 = String.valueOf(temp_double) + "_EX";
temp_string_6 = String.valueOf(temp_char) + "_EX";
temp_string_7 = String.valueOf(temp_boolean) + "_EX";
System.out.println("temp_string_0 = " + temp_string_0);
System.out.println("temp_string_1 = " + temp_string_1);
System.out.println("temp_string_2 = " + temp_string_2);
System.out.println("temp_string_3 = " + temp_string_3);
System.out.println("temp_string_4 = " + temp_string_4);
System.out.println("temp_string_5 = " + temp_string_5);
System.out.println("temp_string_6 = " + temp_string_6);
System.out.println("temp_string_7 = " + temp_string_7);
}
}
运行结果 :
2.String类型和包装类的相互转化 :
①String类 ——> 包装类
有两种方式,如下 :
方式一 : Integer integer_0 = Integer.parseInt(字符串类型变量);
方式二 : 利用包装类的构造器,例如 : Integer integer_1 = new Integer(字符串类型变量);
方式一中用到了parseInt方法,注意,我们在上文String类型转基本类型时就用到了parseInt方法,但我们当时是用int类型变量来作接收的。当然,parseInt方法的返回值类型本来就是int类型,如下图所示 :
因此,这里的方式一实际上应用了自动装箱,把等号右边返回的int类型的值,在底层又调用valueOf方法装箱成了Integer包装类。
演示 :
以StringDemo_为演示类,代码如下 :
package csdn.knowledge.api.Integer;
public class StringDemo_ {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//演示 : String类型 ————> 包装类型
String string_0 = "141";
Integer integer_0 = Integer.parseInt(string_0);
String string_1 = "133";
Integer integer_1 = new Integer(string_1);
System.out.println("integer_0的值 = " + integer_0);
System.out.println("integer_1的值 = " + integer_1);
}
}
运行结果 :
②包装类 ——> String类
有三种方式,如下 :
方式一 : String xxx = 包装类变量名 + "";
方式二 : String xxx = 包装类类名.toString();
方式三 : String xxx = String.valueOf(...);
方式一和我们上文中提到的基本类型转String类型的方式一回事儿;方式二体现出包装类相对于基本类型的优势,可以直接调用包装类中的方法;方式三也和我们上文中提到的基本类型转String类型的方式一回事儿。因此,这里就不重点演示了,仅以Integer类为例。
以StringDemo_2为演示类,代码如下 :
package csdn.knowledge.api.Integer;
public class StringDemo_2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//演示 : 包装类 ————> String类
//方式一 :
Integer integer_0 = 141; //自动装箱
String string_0 = integer_0 + "";
//方式二 :
Integer integer_1 = 135;
String string_1 = Integer.toString(integer_1) + " hello";
//方式三 :
Integer integer_2 = 431;
String string_2 = String.valueOf(integer_2) + " world";
System.out.println("string_0 = " + string_0);
System.out.println("string_1 = " + string_1);
System.out.println("string_2 = " + string_2);
}
}
运行结果 :
五、八大包装类的常用成员方法
0.前言 :
是否还记得我们在开篇中引入的包装类的类图,即下图 :
如果你觉得看这个已经够难受了,那你就错了。IDEA提供了功能,可以将类的方法在类图中直接显示出来。到时候你会头大的,如下GIF所示 :
可以看到,类图的转场效果还是比较nice的。但是,这么多方法,就算up真的要一一演示的话,不说我能不能撑住,我猜你是肯定撑不住。你不信?那好,1h内背完这张图里的所有方法,私信up领取1万块钱(bushi)。所以,up决定把每个包装类中比较典型的几个方法给提出来,再给大家演示演示,咱们都节省时间,你说对不对捏。当然,开个玩笑哈。我们已经学习了API,那么之后如果有用到新的方法直接去API里查看就行,方便地很。
up会在代码中直接标出注释,注明该方法的具体功能以及该方法如何使用。所以,大家结合注释,直接看代码即可。
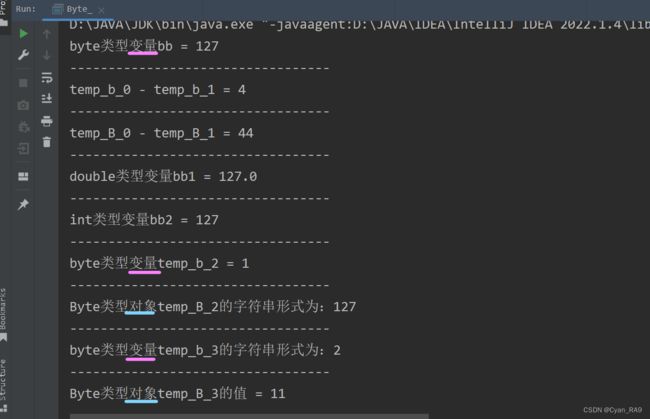
1.Byte类常用方法汇总 :
以Byte_类为演示类,代码如下 :
package csdn.knowledge.api.Integer.Eight;
public class Byte_ {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//演示 : Byte类常用方法
//1 —— byte byteValue() : 返回当前Byte类对象对应的值,以byte类型作接收。
Byte b = 127; //自动装箱
byte bb = b.byteValue();
System.out.println("byte类型变量bb = " + bb);
System.out.println("----------------------------------");
//2 —— static int compare(byte x, byte y) : 比较两个byte变量的值, 返回值为前面byte变量的值减去后面byte变量的值。
byte temp_b_0 = 5;
byte temp_b_1 = 1;
int i = Byte.compare(temp_b_0, temp_b_1);
System.out.println("temp_b_0 - temp_b_1 = " + i);
System.out.println("----------------------------------");
//3 —— int compareTo(Byte anotherByte) : 比较两个Byte类对象的值,返回值同方法2
Byte temp_B_0 = 55;
Byte temp_B_1 = 11;
int i1 = temp_B_0.compareTo(temp_B_1);
System.out.println("temp_B_0 - temp_B_1 = " + i1);
System.out.println("----------------------------------");
//4 —— double doubleValue() : 与方法1同理
double bb1 = b.doubleValue();
System.out.println("double类型变量bb1 = " + bb1);
System.out.println("----------------------------------");
//5 —— int intValue() : 与方法1同理
int bb2 = b.intValue();
System.out.println("int类型变量bb2 = " + bb2);
System.out.println("----------------------------------");
//6 —— static int parseByte(String xxx) : 字符串类型 ——> byte类型
byte temp_b_2 = Byte.parseByte("1");
System.out.println("byte类型变量temp_b_2 = " + temp_b_2);
System.out.println("----------------------------------");
//7 —— String toString() : 将当前Byte对象的值转换为String类型
Byte temp_B_2 = 127;
String string_0 = temp_B_2.toString();
System.out.println("Byte类型对象temp_B_2的字符串形式为:" + string_0);
System.out.println("----------------------------------");
//8 —— static String toString(byte b) : 将指定的byte值转换为String对象
byte temp_b_3 = 2;
String string_1 = Byte.toString(temp_b_3);
System.out.println("byte类型变量temp_b_3的字符串形式为:" + string_1);
System.out.println("----------------------------------");
//9 —— static Byte valueOf(...) : 字符串类型 ——> Byte类型
Byte temp_B_3 = Byte.valueOf("11");
System.out.println("Byte类型对象temp_B_3的值 = " + temp_B_3);
}
}运行结果 :
2.Short类常用方法汇总 :
以Short_类为演示类,代码如下 :
package csdn.knowledge.api.Integer.Eight;
public class Short_ {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//演示Short类常用方法
//1 —— short shortValue() : 返回当前Short对象的值,以short基本类型作接收。
Short temp_S_0 = 128; //自动装箱
short temp_s_0 = temp_S_0.shortValue();
System.out.println("short类型变量temp_s_0 = " + temp_s_0);
System.out.println("------------------------------------");
//1_EX —— int intValue()
//1_EX —— double doubleValue()
//......等等同方法1格式一样的方法。用法原理与方法1相同。
//2 —— static int compare(short x, short y) : 比较两个short变量的值, 返回值为前面short变量的值减去后面short变量的值。
short temp_s_1 = 6;
short temp_s_2 = 3;
int i = Short.compare(temp_s_1, temp_s_2);
System.out.println("temp_s_1 - temp_s_2 = " + i);
System.out.println("------------------------------------");
//3 —— int compareTo(Short anotherShort) : 比较两个Short类对象的值,返回值同方法2
Short temp_S_1 = 66;
Short temp_S_2 = 33;
int i1 = temp_S_1.compareTo(temp_S_2);
System.out.println("temp_S_1 - temp_S_2 = " + i1);
System.out.println("------------------------------------");
//4 —— static int parseShort(String xxx) : 字符串类型 ——> short基本类型
short temp_s_3 = Short.parseShort("128");
System.out.println("short类型变量temp_s_3 = " + temp_s_3);
System.out.println("------------------------------------");
//5 —— String toString() : 将当前Short对象的值转换为String类型
Short temp_S_3 = 1277;
String string_0 = temp_S_3.toString();
System.out.println("Short类型对象temp_S_3的字符串形式为:" + string_0);
System.out.println("------------------------------------");
//6 —— static String toString(short s) : 将指定的short值转换为String对象
short temp_s_4 = 2;
String string_1 = Short.toString(temp_s_4);
System.out.println("short类型变量temp_s_4的字符串形式为:" + string_1);
System.out.println("----------------------------------");
//7 —— static Short valueOf(...) : 字符串类型 ——> Short类型
Short temp_S_4 = Short.valueOf("1111");
System.out.println("Short类型对象temp_S_4的值 = " + temp_S_4);
}
}
运行结果 :
3.Integer类常用方法汇总 :
以Integer_类为演示类,代码如下 :
package csdn.knowledge.api.Integer.Eight;
public class Integer_ {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//演示Integer类常用方法
//1 —— int intValue() : 返回当前Integer对象的值,以int基本类型作接收。
Integer temp_I_0 = 1280; //自动装箱
int temp_i_0 = temp_I_0.intValue();
System.out.println("int类型变量temp_i_0 = " + temp_i_0);
System.out.println("------------------------------------");
/*
1_EX —— int intValue()
1_EX —— double doubleValue()
......等等同方法1格式一样的方法。用法原理与方法1相同。
*/
//2 —— static int compare(int x, int y) : 比较两个int变量的值。如果前一个数大,返回1;如果前一个数小,返回-1;相等则返回0。
int temp_i_1 = 7;
int temp_i_2 = 11;
int i = Integer.compare(temp_i_1, temp_i_2);
System.out.println("temp_i_1和temp_i_2,如果前一个数大,返回1;如果前一个数小,返回-1;相等则返回0 : " + i);
System.out.println("------------------------------------");
//3 —— int compareTo(Integer anotherInteger) : 比较两个Integer类对象的值,返回值同方法2
Integer temp_I_1 = 77;
Integer temp_I_2 = 11;
int i1 = temp_I_1.compareTo(temp_I_2);
System.out.println("temp_I_1和temp_I_2,如果前一个数大,返回1;如果前一个数小,返回-1;相等则返回0 : " + i1);
System.out.println("------------------------------------");
//4 —— static int parseInt(String xxx) : 字符串类型 ——> int基本类型
int temp_i_3 = Integer.parseInt("4444");
System.out.println("int类型变量temp_i_3 = " + temp_i_3);
System.out.println("------------------------------------");
//5 —— String toString() : 将当前Integer对象的值转换为String类型
Integer temp_I_3 = 11217;
String string_0 = temp_I_3.toString();
System.out.println("Integer类型对象temp_I_3的字符串形式为:" + string_0);
System.out.println("------------------------------------");
//6 —— static String toString(int s) : 将指定的int值转换为String对象
int temp_i_4 = 111111;
String string_1 = Integer.toString(temp_i_4);
System.out.println("int类型变量temp_i_4的字符串形式为:" + string_1);
System.out.println("----------------------------------");
//7 —— static Integer valueOf(...) : 字符串类型 ——> Integer类型
Integer temp_I_4 = Integer.valueOf("1111");
System.out.println("Integer类型对象temp_I_4的值 = " + temp_I_4);
System.out.println("----------------------------------");
//8 —— static int max(int x, int y) 和 min(int x, int y) : 获取两个数中的最大值和最小值
System.out.println("100和101哪个数更大?" + Integer.max(100, 101));
System.out.println("200和201哪个数更小?" + Integer.min(200, 201));
System.out.println("----------------------------------");
//9 —— static int sum(int x, int y) : 返回(x + y)的值
System.out.println("100 + 201 = " + Integer.sum(100 ,201));
}
}运行结果:
4.Long类常用方法汇总 :
以Long_类为演示类,代码如下 :
package csdn.knowledge.api.Integer.Eight;
public class Long_ {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//演示Long类常用方法
//1 —— long longValue() : 返回当前Long对象的值,以long基本类型作接收。
Long temp_L_0 = 2224L; //自动装箱
long temp_l_0 = temp_L_0.longValue();
System.out.println("long类型变量temp_l_0 = " + temp_l_0);
System.out.println("------------------------------------");
/*
1_EX —— int intValue()
1_EX —— double doubleValue()
......等等同方法1格式一样的方法。用法原理与方法1相同。
*/
//2 —— static int compare(long x, long y) : 比较两个long变量的值. 如果前一个数大,返回1;如果前一个数小,返回-1;相等则返回0。
long temp_l_1 = 222L;
long temp_l_2 = 111L;
int i = Long.compare(temp_l_1, temp_l_2);
System.out.println("temp_l_1和temp_l_2,如果前一个数大,返回1;如果前一个数小,返回-1;相等则返回0 : " + i);
System.out.println("------------------------------------");
//3 —— int compareTo(Long anotherLong) : 比较两个Long类对象的值,返回值同方法2
Long temp_L_1 = 773L;
Long temp_L_2 = 113L;
int i1 = temp_L_1.compareTo(temp_L_2);
System.out.println("temp_L_1和temp_L_2,如果前一个数大,返回1;如果前一个数小,返回-1;相等则返回0 : " + i1);
System.out.println("------------------------------------");
//4 —— static long parseLong(String xxx) : 字符串类型 ——> long基本类型
long temp_l_3 = Long.parseLong("35252");
System.out.println("long类型变量temp_l_3 = " + temp_l_3);
System.out.println("------------------------------------");
//5 —— String toString() : 将当前Long对象的值转换为String类型
Long temp_L_3 = 11217L;
String string_0 = temp_L_3.toString();
System.out.println("Long类型对象temp_L_3的字符串形式为:" + string_0);
System.out.println("------------------------------------");
//6 —— static String toString(long l) : 将指定的long值转换为String对象
long temp_l_4 = 222222;
String string_1 = Long.toString(temp_l_4);
System.out.println("long类型变量temp_l_4的字符串形式为:" + string_1);
System.out.println("----------------------------------");
//7 —— static Long valueOf(...) : 字符串类型 ——> Long类型
Long temp_L_4 = Long.valueOf("111241");
System.out.println("Long类型对象temp_L_4的值 = " + temp_L_4);
System.out.println("----------------------------------");
//8 —— static long max(long x, long y) 和 min(long x, long y) : 获取两个数中的最大值和最小值
System.out.println("10000和10100哪个数更大?" + Long.max(10000, 10100));
System.out.println("20000和20100哪个数更小?" + Long.min(20000, 20100));
System.out.println("----------------------------------");
//9 —— static long sum(long x, long y) : 返回(x + y)的值
System.out.println("11111111 + 8888889 = " + Long.sum(11111111 ,8888889));
}
}运行结果 :
5.Character类常用方法汇总 :
以Character_类为演示类,代码如下 :
package csdn.knowledge.api.Integer.Eight;
public class Character_ {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//演示 : Character类常用方法
//1 —— 装箱拆箱 : valueOf() 和 charValue()
Character character_0 = Character.valueOf('S');
char char_0 = character_0.charValue();
System.out.println("Character类对象character_0的字符是:" + character_0);
System.out.println("char基本类型变量char_0 = " + char_0);
System.out.println("----------------------------------");
//2 —— static int compare(char x, char y) : 返回前面字符ASCII码值 - 后面字符ASCII值的int类型
int i1 = Character.compare('A', 'F');
System.out.println("ASCII码值'A' - 'F' = " + i1);
System.out.println("----------------------------------");
//3 —— int compareTo(Character anotherCharacter) : 比较两个Character类对象的字符,返回值同方法2
Character character_1 = 'a'; //自动装箱
Character character_2 = 'd';
int i2 = character_1.compareTo(character_2);
System.out.println("character_1 - character_2 = " + i2);
System.out.println("----------------------------------");
//4 —— static boolean isDigit(char c1) : 判断该字符是不是数字
//5 —— static boolean isLetter(char c2) : 判断该字符是不是字母
//6 —— static boolean isUpperCase(char c3) : 判断该字符是不是大写形式
//7 —— static boolean isLowerCase(char c4) : 判断该字符是不是小写形式
//8 —— static boolean isWhitespace(char c5) : 判断该字符是不是空格
System.out.println("\'A\'是不是数字 : " + Character.isDigit('A'));
System.out.println("\'A\'是不是字母 : " + Character.isLetter('A'));
System.out.println("\'A\'是不是大写形式 : " + Character.isUpperCase('A'));
System.out.println("\'A\'是不是小写形式 : " + Character.isLowerCase('A'));
System.out.println("\'A\'是不是空格 : " + Character.isWhitespace('A'));
System.out.println("----------------------------------");
//9 —— static char toUpperCase(char c) : 将该字符转换为大写形式,以char类型作接收
//10 —— static char toLowerCase(char c) : 将该字符转换为小写形式,以char类型作接收
char c1 = Character.toUpperCase('n');
char c2 = Character.toLowerCase('B');
System.out.println("\'n\'字符的大写形式为:" + c1);
System.out.println("\'B\'字符的小写形式为:" + c2);
}
}
运行结果 :
6.Float类常用方法汇总 :
以Float_类为演示类,代码如下 :
package csdn.knowledge.api.Integer.Eight;
public class Float_ {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//演示 : Float类常用方法
//1 —— float floatValue() : 返回当前Float对象的值,以float基本类型作接收。
Float temp_F_0 = 1024.11F; //自动装箱
float temp_f_0 = temp_F_0.floatValue();
System.out.println("float类型变量temp_f_0 = " + temp_f_0);
System.out.println("------------------------------------");
/*
1_EX —— int intValue()
1_EX —— double doubleValue()
......等等同方法1格式一样的方法。用法原理与方法1相同。
*/
//2 —— static int compare(float x, float y) : 比较两个float变量的值, 如果前一个数大,返回1;如果前一个数小,返回-1;相等则返回0。
float temp_f_1 = 222.11F;
float temp_f_2 = 222.11F;
int i = Float.compare(temp_f_1, temp_f_2);
System.out.println("temp_f_1和temp_f_2,如果前一个数大,返回1;如果前一个数小,返回-1;相等则返回0 : " + i);
System.out.println("------------------------------------");
//3 —— int compareTo(Float anotherFloat) : 比较两个Float类对象的值,返回值同方法2
Float temp_F_1 = 222.11F;
Float temp_F_2 = 123.11F;
int i1 = temp_F_1.compareTo(temp_F_2);
System.out.println("temp_F_1和temp_F_2,如果前一个数大,返回1;如果前一个数小,返回-1;相等则返回0 : " + i1);
System.out.println("------------------------------------");
//4 —— static float parseFloat(String xxx) : 字符串类型 ——> float基本类型
float temp_f_3 = Float.parseFloat("35252.11125");
System.out.println("float类型变量temp_f_3 = " + temp_f_3);
System.out.println("------------------------------------");
//5 —— String toString() : 将当前Float对象的值转换为String类型
Float temp_F_3 = 12144217.12F;
String string_0 = temp_F_3.toString();
System.out.println("Float类型对象temp_F_3的字符串形式为:" + string_0);
System.out.println("------------------------------------");
//6 —— static String toString(float f) : 将指定的float值转换为String对象
float temp_f_4 = 222222.11F;
String string_1 = Float.toString(temp_f_4);
System.out.println("float类型变量temp_f_4的字符串形式为:" + string_1);
System.out.println("----------------------------------");
//7 —— static float valueOf(...) : 字符串类型 ——> float类型
Float temp_F_4 = Float.valueOf("111241.1235");
System.out.println("Float类型对象temp_F_4的值 = " + temp_F_4);
System.out.println("----------------------------------");
//8 —— static float max(float x, float y) 和 min(float x, float y) : 获取两个数中的最大值和最小值
System.out.println("10000.00 和 10100.11, 哪个数更大?" + Float.max(10000.00F, 10100.11F));
System.out.println("200.00 和 201.88, 哪个数更小?" + Float.min(200.00F, 201.88F));
System.out.println("----------------------------------");
//9 —— static float sum(float x, float y) : 返回(x + y)的值
System.out.println("11111.11 + 8889.022 = " + Float.sum(11111.11F,8889.022F));
}
}运行结果 :
7.Double类常用方法汇总 :
以Double_类为演示类,代码如下 :
package csdn.knowledge.api.Integer.Eight;
public class Double_ {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//演示 : Double类常用方法
//1 —— double doubleValue() : 返回当前Double对象的值,以double基本类型作接收。
Double temp_D_0 = 1024.5; //自动装箱
double temp_d_0 = temp_D_0.doubleValue();
System.out.println("double类型变量temp_d_0 = " + temp_d_0);
System.out.println("------------------------------------");
/*
1_EX —— int intValue()
1_EX —— double doubleValue()
......等等同方法1格式一样的方法。用法原理与方法1相同。
*/
//2 —— static int compare(double x, double y) : 比较两个double变量的值, 如果前一个数大,返回1;如果前一个数小,返回-1;相等则返回0。
double temp_d_1 = 888.88;
double temp_d_2 = 888.88;
int i = Double.compare(temp_d_1, temp_d_2);
System.out.println("temp_d_1和temp_d_2,如果前一个数大,返回1;如果前一个数小,返回-1;相等则返回0 : " + i);
System.out.println("------------------------------------");
//3 —— int compareTo(Double anotherDouble) : 比较两个Double类对象的值,返回值同方法2
Double temp_D_1 = 123.1234;
Double temp_D_2 = 1234.123;
int i1 = temp_D_1.compareTo(temp_D_2);
System.out.println("temp_D_1和temp_D_2,如果前一个数大,返回1;如果前一个数小,返回-1;相等则返回0 : " + i1);
System.out.println("------------------------------------");
//4 —— static double parseDouble(String xxx) : 字符串类型 ——> double基本类型
double temp_d_3 = Double.parseDouble("35252.11125");
System.out.println("double类型变量temp_d_3 = " + temp_d_3);
System.out.println("------------------------------------");
//5 —— String toString() : 将当前Float对象的值转换为String类型
Double temp_D_3 = 3333144217.12;
String string_0 = temp_D_3.toString();
System.out.println("Double类型对象temp_D_3的字符串形式为:" + string_0);
System.out.println("------------------------------------");
//6 —— static String toString(double f) : 将指定的double值转换为String对象
double temp_d_4 = 233.333333333;
String string_1 = Double.toString(temp_d_4);
System.out.println("double类型变量temp_d_4的字符串形式为:" + string_1);
System.out.println("----------------------------------");
//7 —— static double valueOf(...) : 字符串类型 ——> double类型
Double temp_D_4 = Double.valueOf("66666.1235");
System.out.println("Double类型对象temp_D_4的值 = " + temp_D_4);
System.out.println("----------------------------------");
//8 —— static double max(double x, double y) 和 min(double x, double y) : 获取两个数中的最大值和最小值
System.out.println("134.23 和 111.11, 哪个数更大?" + Double.max(134.23, 111.11));
System.out.println("222.111 和 111.222, 哪个数更小?" + Double.min(222.111, 111.222));
System.out.println("----------------------------------");
//9 —— static double sum(double x, double y) : 返回(x + y)的值
System.out.println("11111.11 + 8889.022 = " + Double.sum(11111.11,8889.022));
}
}运行结果 :
8.Boolean类常用方法汇总 :
以Boolean_类为演示类,代码如下 :
package csdn.knowledge.api.Integer.Eight;
public class Boolean_ {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//演示 : Boolean类常用方法
//1 —— boolean booleanValue() : 返回当前Boolean对象的值,以boolean基本类型作接收。
Boolean temp_B_0 = true; //自动装箱
boolean temp_b_0 = temp_B_0.booleanValue();
System.out.println("boolean类型变量temp_b_0 = " + temp_b_0);
System.out.println("------------------------------------");
//2 —— static int compare(boolean x, boolean y) : 比较两个boolean变量的值,两个变量真值相同返回0。否则返回值取决于传入第一个boolean变量的真值,true返回1,false返回-1.
boolean temp_b_1 = false;
boolean temp_b_2 = true;
int i = Boolean.compare(temp_b_1, temp_b_2);
int ii = Boolean.compare(temp_b_2, temp_b_1);
int iii = Boolean.compare(temp_b_2, temp_b_2);
System.out.println("temp_b_1和temp_b_2, 两个真值相同返回1。否则返回值取决于传入第一个boolean变量的真值,true返回1,false返回-1 : " + i);
System.out.println("temp_b_2和temp_b_1, 两个真值相同返回1。否则返回值取决于传入第一个boolean变量的真值,true返回1,false返回-1 : " + ii);
System.out.println("temp_b_2和temp_b_2, 两个真值相同返回1。否则返回值取决于传入第一个boolean变量的真值,true返回1,false返回-1 : " + iii);
System.out.println("------------------------------------");
//3 —— int compareTo(Boolean anotherBoolean) : 比较两个Boolean类对象的值,返回值同方法2
Boolean temp_B_1 = false;
Boolean temp_B_2 = false;
int i1 = temp_B_1.compareTo(temp_B_2);
System.out.println("temp_B_1和temp_B_2的真值情况是 : " + i1);
System.out.println("------------------------------------");
//4 —— static int parseBoolean(String xxx) : 字符串类型 ——> boolean基本类型
boolean temp_b_3 = Boolean.parseBoolean("666");
System.out.println("boolean类型变量temp_b_3 = " + temp_b_3);
System.out.println("------------------------------------");
//5 —— String toString() : 将当前Boolean对象的值转换为String类型
Boolean temp_B_3 = false;
String string_0 = temp_B_3.toString();
System.out.println("Boolean类型对象temp_B_3的字符串形式为:" + string_0);
System.out.println("------------------------------------");
//6 —— static String toString(boolean s) : 将指定的boolean值转换为String对象
boolean temp_b_4 = true;
String string_1 = Boolean.toString(temp_b_4);
System.out.println("boolean类型变量temp_b_4的字符串形式为:" + string_1);
System.out.println("----------------------------------");
//7 —— static Short valueOf(...) : 字符串类型 ——> Boolean类型
Boolean temp_B_4 = Boolean.valueOf("false");
System.out.println("Boolean类型对象temp_B_4的值 = " + temp_B_4);
}
}运行结果 :
六、包装类总结 :
,以上就是我们包装类的全部内容了。重点在于String类与基本类型/包装类型之间的相互转化。如何进行的转化,使用了什么方法,大家一定要烂熟于心。对于八大包装类的常用方法,虽然说肯定有遗漏的,没有举出例子的方法,而且up也并没有把各个方法的源码放出来,给大家仔细讲解源码。但是毕竟是基础阶段,委实不适合如此干。当然up自己是看过源码才知道这些个方法是咋用的,大家如果有兴趣,也很简单,直接Ctrl + b/B 追进去看看,或者Debug一下就懂了。至于这些个方法的用法,我觉得已经标注的挺清楚了。 感谢阅读!
System.out.println("END--------------------------------------------------");