睿智的目标检测——YoloV7-Tiny-OBB旋转目标检测算法部署
YoloV7-OBB旋转目标检测算法部署
-
- 学习前言
- 源码下载
- 安装TensorRT
-
- 1.TensorRT简介
- 2.下载TensorRT
- 3.TensorRT安装
- 安装torch2trt
-
- 1.torch2trt简介
- 2.torch2trt安装
- 模型转换
- 结果比对
学习前言
本文将借助torch2trt工具实现Yolov7-Tiny-OBB算法的TensorRT快速推理。
源码下载
https://github.com/Egrt/yolov7-tiny-obb
喜欢的可以点个star噢。
安装TensorRT
1.TensorRT简介
官网链接:https://developer.nvidia.com/tensorrt
NVIDIA® TensorRT™ is an SDK for optimizing trained deep learning models to enable high-performance inference. TensorRT contains a deep learning inference optimizer for trained deep learning models, and a runtime for execution. After you have trained your deep learning model in a framework of your choice, TensorRT enables you to run it with higher throughput and lower latency.
根据官方对于TensorRT的介绍可知,TensorRT是一个针对已训练好模型的SDK,通过该SDK能够在NVIDIA的设备上进行高性能的推理。那么TensorRT具体会对我们训练好的模型做哪些优化呢,可以参考TensorRT官网中的一幅图,如下图所示:

总结下来主要有以下6点:
Reduced Precision:将模型量化成INT8或者FP16的数据类型(在保证精度不变或略微降低的前提下),以提升模型的推理速度。Layer and Tensor Fusion:通过将多个层结构进行融合(包括横向和纵向)来优化GPU的显存以及带宽。Kernel Auto-Tuning:根据当前使用的GPU平台选择最佳的数据层和算法。Dynamic Tensor Memory:最小化内存占用并高效地重用张量的内存。Multi-Stream Execution:使用可扩展设计并行处理多个输入流。Time Fusion:使用动态生成的核去优化随时间步长变化的RNN网络。
2.下载TensorRT
进入官方网站:https://developer.nvidia.com/nvidia-tensorrt-8x-download
寻找自己对应的版本,我这里选择为:
下载得到 zip 压缩包,解压。
3.TensorRT安装
任意顺序完成以下几步:
- 复制TensorRT-8.4.3.1\bin中内容到C:\Program Files\NVIDIA GPU Computing Toolkit\CUDA\v11.3\bin
- 复制TensorRT的include文件夹到CUDA的include文件夹
- 复制TensorRT-8.4.3.1\lib文件夹中的lib文件到CUDA的lib文件夹,dll文件到CUDA的bin文件夹
- 使用pip install xxx.whl安装TensorRT-8.4.3.1文件夹中的

如下图所示:

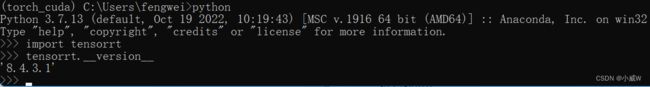
使用python检查是否安装成功。
安装torch2trt
1.torch2trt简介

torch2trt是一个PyTorch模型到TensorRT模型的转换器,它基于TensorRT Python API开发,具有以下特征
易于使用- 通过单个函数调用转换模块torch2trt易于扩展- 用 Python 编写自己的层转换器并注册@tensorrt_converter
2.torch2trt安装
直接使用以下命令进行下载与安装:
git clone https://github.com/NVIDIA-AI-IOT/torch2trt
cd torch2trt
python setup.py install
在安装好TensorRT与torch2trt库之后就可以开始进行Yolov7-Tiny-OBB模型的转换了。
模型转换
首先构建我们的Yolov7-Tiny-OBB模型,并使用cuda推理:
class YOLO(object):
_defaults = {
#--------------------------------------------------------------------------#
# 使用自己训练好的模型进行预测一定要修改model_path和classes_path!
# model_path指向logs文件夹下的权值文件,classes_path指向model_data下的txt
#
# 训练好后logs文件夹下存在多个权值文件,选择验证集损失较低的即可。
# 验证集损失较低不代表mAP较高,仅代表该权值在验证集上泛化性能较好。
# 如果出现shape不匹配,同时要注意训练时的model_path和classes_path参数的修改
#--------------------------------------------------------------------------#
"model_path" : 'model_data/yolov7_obb_ssdd.pth',
"classes_path" : 'model_data/ssdd_classes.txt',
#---------------------------------------------------------------------#
# anchors_path代表先验框对应的txt文件,一般不修改。
# anchors_mask用于帮助代码找到对应的先验框,一般不修改。
#---------------------------------------------------------------------#
"anchors_path" : 'model_data/yolo_anchors.txt',
"anchors_mask" : [[6, 7, 8], [3, 4, 5], [0, 1, 2]],
}
@classmethod
def get_defaults(cls, n):
if n in cls._defaults:
return cls._defaults[n]
else:
return "Unrecognized attribute name '" + n + "'"
#---------------------------------------------------#
# 初始化YOLO
#---------------------------------------------------#
def __init__(self, **kwargs):
self.__dict__.update(self._defaults)
for name, value in kwargs.items():
setattr(self, name, value)
self._defaults[name] = value
#---------------------------------------------------#
# 获得种类和先验框的数量
#---------------------------------------------------#
self.class_names, self.num_classes = get_classes(self.classes_path)
self.anchors, self.num_anchors = get_anchors(self.anchors_path)
self.generate()
show_config(**self._defaults)
#---------------------------------------------------#
# 生成模型
#---------------------------------------------------#
def generate(self):
#---------------------------------------------------#
# 建立yolo模型,载入yolo模型的权重
#---------------------------------------------------#
self.net = YoloBody(self.anchors_mask, self.num_classes)
device = torch.device('cuda' if torch.cuda.is_available() else 'cpu')
self.net.load_state_dict(torch.load(self.model_path, map_location=device))
self.net = self.net.eval().cuda()
print('{} model, and classes loaded.'.format(self.model_path))
获取Yolov7-Tiny-OBB模型:
# create some regular pytorch model...
model = YOLO().net
创建一个输入张量,由于Yolov7-Tiny-OBB的输入图像大小(640,640):
# create example data
x = torch.ones((1, 3, 640, 640)).cuda()
接下来使用torch2trt将torch转换为TensorRT模型。
# convert to TensorRT feeding sample data as input
model_trt = torch2trt(model, [x])
y = model(x)
y_trt = model_trt(x)
最后将转换后的模型保存在model_data文件夹中:
# save the TensorRT model
torch.save(model_trt.state_dict(), 'model_data/yolov7_tiny_obb_trt.pth')
完整的代码如下:
'''
Author: [egrt]
Date: 2023-02-18 21:57:23
LastEditors: [egrt]
LastEditTime: 2023-02-18 22:08:39
Description:
'''
import torch
from torch2trt import torch2trt
from nets.yolo import YoloBody
from utils.utils import (cvtColor, get_anchors, get_classes, preprocess_input,
resize_image, show_config)
class YOLO(object):
_defaults = {
#--------------------------------------------------------------------------#
# 使用自己训练好的模型进行预测一定要修改model_path和classes_path!
# model_path指向logs文件夹下的权值文件,classes_path指向model_data下的txt
#
# 训练好后logs文件夹下存在多个权值文件,选择验证集损失较低的即可。
# 验证集损失较低不代表mAP较高,仅代表该权值在验证集上泛化性能较好。
# 如果出现shape不匹配,同时要注意训练时的model_path和classes_path参数的修改
#--------------------------------------------------------------------------#
"model_path" : 'model_data/yolov7_obb_ssdd.pth',
"classes_path" : 'model_data/ssdd_classes.txt',
#---------------------------------------------------------------------#
# anchors_path代表先验框对应的txt文件,一般不修改。
# anchors_mask用于帮助代码找到对应的先验框,一般不修改。
#---------------------------------------------------------------------#
"anchors_path" : 'model_data/yolo_anchors.txt',
"anchors_mask" : [[6, 7, 8], [3, 4, 5], [0, 1, 2]],
}
@classmethod
def get_defaults(cls, n):
if n in cls._defaults:
return cls._defaults[n]
else:
return "Unrecognized attribute name '" + n + "'"
#---------------------------------------------------#
# 初始化YOLO
#---------------------------------------------------#
def __init__(self, **kwargs):
self.__dict__.update(self._defaults)
for name, value in kwargs.items():
setattr(self, name, value)
self._defaults[name] = value
#---------------------------------------------------#
# 获得种类和先验框的数量
#---------------------------------------------------#
self.class_names, self.num_classes = get_classes(self.classes_path)
self.anchors, self.num_anchors = get_anchors(self.anchors_path)
self.generate()
show_config(**self._defaults)
#---------------------------------------------------#
# 生成模型
#---------------------------------------------------#
def generate(self):
#---------------------------------------------------#
# 建立yolo模型,载入yolo模型的权重
#---------------------------------------------------#
self.net = YoloBody(self.anchors_mask, self.num_classes)
device = torch.device('cuda' if torch.cuda.is_available() else 'cpu')
self.net.load_state_dict(torch.load(self.model_path, map_location=device))
self.net = self.net.eval().cuda()
print('{} model, and classes loaded.'.format(self.model_path))
# create some regular pytorch model...
model = YOLO().net
# create example data
x = torch.ones((1, 3, 640, 640)).cuda()
# convert to TensorRT feeding sample data as input
model_trt = torch2trt(model, [x])
y = model(x)
y_trt = model_trt(x)
# save the TensorRT model
torch.save(model_trt.state_dict(), 'model_data/yolov7_tiny_obb_trt.pth')
结果比对
在模型的推理流程中,修改yolo.py文件中模型的加载方式:
#---------------------------------------------------#
# 生成模型
#---------------------------------------------------#
def generate(self, onnx=False, trt=True):
#---------------------------------------------------#
# 建立yolo模型,载入yolo模型的权重
#---------------------------------------------------#
self.net = YoloBody(self.anchors_mask, self.num_classes)
device = torch.device('cuda' if torch.cuda.is_available() else 'cpu')
self.net.load_state_dict(torch.load(self.model_path, map_location=device))
self.net = self.net.fuse().eval()
print('{} model, and classes loaded.'.format(self.model_path))
if not onnx:
if self.cuda:
self.net = nn.DataParallel(self.net)
self.net = self.net.cuda()
if trt:
from torch2trt import TRTModule
model_trt = TRTModule()
model_trt.load_state_dict(torch.load('model_data/yolov7_tiny_obb_trt.pth'))
self.net = model_trt
最终模型的推理速度对如比下:
转换前fps为53,转换后的fps为120。速度的提升非常显著;mAP从98%降低到了 97.75%,影响不大。
| 模型名称 | 训练集 | 测试集 | fps | mAP |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Yolov7-Tiny-OBB | UAV-ROD train | UAV-ROD val | 53 | 98.00% |
| Yolov7-Tiny-OBB-TRT | UAV-ROD train | UAV-ROD val | 120 | 97.75% |

