树莓派Pico使用MicroPython实现0.96OLED显示
1、首先要下载pico支持的microPython的包MicroPython固件
2、下载Pycharm安装配置好记得也需要Python的环境(教程太多自行百度食用)
3、下载插件
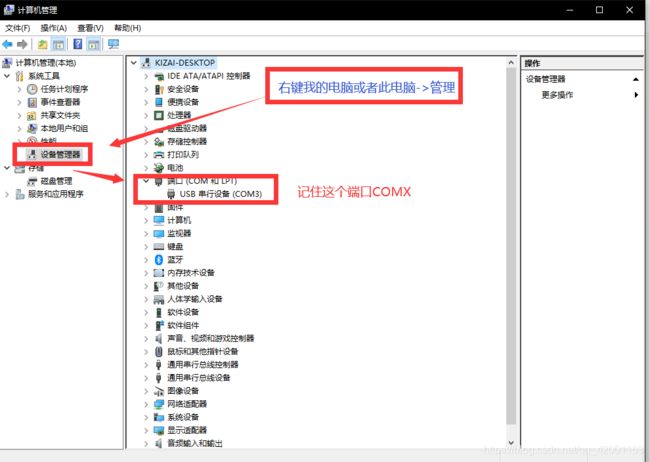
4、配置端口设置
5、新建工程>导包>新建pythonfile>代码
# _*_ coding utf-8 _*_
# 作者:KiZai
# 开发时间: 2021/3/10 17:59
# 文件名: main .py
# 开发工具: PyCharm
# MicroPython SSD1306 i2c OLED driver and example application
from micropython import const
import framebuf
from machine import I2C, Pin
import utime
# register definitions
SET_CONTRAST = const(0x81)
SET_ENTIRE_ON = const(0xA4)
SET_NORM_INV = const(0xA6)
SET_DISP = const(0xAE)
SET_MEM_ADDR = const(0x20)
SET_COL_ADDR = const(0x21)
SET_PAGE_ADDR = const(0x22)
SET_DISP_START_LINE = const(0x40)
SET_SEG_REMAP = const(0xA0)
SET_MUX_RATIO = const(0xA8)
SET_COM_OUT_DIR = const(0xC0)
SET_DISP_OFFSET = const(0xD3)
SET_COM_PIN_CFG = const(0xDA)
SET_DISP_CLK_DIV = const(0xD5)
SET_PRECHARGE = const(0xD9)
SET_VCOM_DESEL = const(0xDB)
SET_CHARGE_PUMP = const(0x8D)
# Subclassing FrameBuffer provides support for graphics primitives 子类化FrameBuffer支持图形原语
# http://docs.micropython.org/en/latest/pyboard/library/framebuf.html
# buffer is set to width (128) x pages = 64/8 = 8 => buffer = 1024
class SSD1306(framebuf.FrameBuffer):
def __init__(self, width, height, external_vcc):
self.width = width
self.height = height
self.external_vcc = external_vcc
self.pages = self.height // 8 # Height = 64 => pages = 8
self.buffer = bytearray(self.pages * self.width)
super().__init__(self.buffer, self.width, self.height, framebuf.MONO_VLSB)
self.init_display()
def init_display(self):
for cmd in (
SET_DISP | 0x00, # off
# address setting
SET_MEM_ADDR,
0x00, # horizontal
# resolution and layout
SET_DISP_START_LINE | 0x00,
SET_SEG_REMAP | 0x01, # column addr 127 mapped to SEG0
SET_MUX_RATIO,
self.height - 1,
SET_COM_OUT_DIR | 0x08, # scan from COM[N] to COM0
SET_DISP_OFFSET,
0x00,
SET_COM_PIN_CFG,
0x02 if self.width > 2 * self.height else 0x12,
# timing and driving scheme
SET_DISP_CLK_DIV,
0x80,
SET_PRECHARGE,
0x22 if self.external_vcc else 0xF1,
SET_VCOM_DESEL,
0x30, # 0.83*Vcc
# display
SET_CONTRAST,
0xFF, # maximum
SET_ENTIRE_ON, # output follows RAM contents
SET_NORM_INV, # not inverted
# charge pump
SET_CHARGE_PUMP,
0x10 if self.external_vcc else 0x14,
SET_DISP | 0x01,
): # on
self.write_cmd(cmd)
self.fill(0)
self.show()
def poweroff(self):
self.write_cmd(SET_DISP | 0x00)
def poweron(self):
self.write_cmd(SET_DISP | 0x01)
def contrast(self, contrast):
self.write_cmd(SET_CONTRAST)
self.write_cmd(contrast)
def invert(self, invert):
self.write_cmd(SET_NORM_INV | (invert & 1))
def show(self):
x0 = 0
x1 = self.width - 1
if self.width == 64:
# displays with width of 64 pixels are shifted by 32
x0 += 32
x1 += 32
self.write_cmd(SET_COL_ADDR)
self.write_cmd(x0)
self.write_cmd(x1)
self.write_cmd(SET_PAGE_ADDR)
self.write_cmd(0)
self.write_cmd(self.pages - 1)
self.write_data(self.buffer)
class SSD1306_I2C(SSD1306):
def __init__(self, width, height, i2c, addr=0x3C, external_vcc=False):
self.i2c = i2c
self.addr = addr
self.temp = bytearray(2)
self.write_list = [b"\x40", None] # Co=0, D/C#=1
super().__init__(width, height, external_vcc)
def write_cmd(self, cmd):
self.temp[0] = 0x80 # Co=1, D/C#=0
self.temp[1] = cmd
self.i2c.writeto(self.addr, self.temp)
def write_data(self, buf):
self.write_list[1] = buf
self.i2c.writevto(self.addr, self.write_list)
led1 = Pin(25,Pin.OUT)
led2 = Pin(16,Pin.OUT)
key1 = Pin(18,Pin.IN)
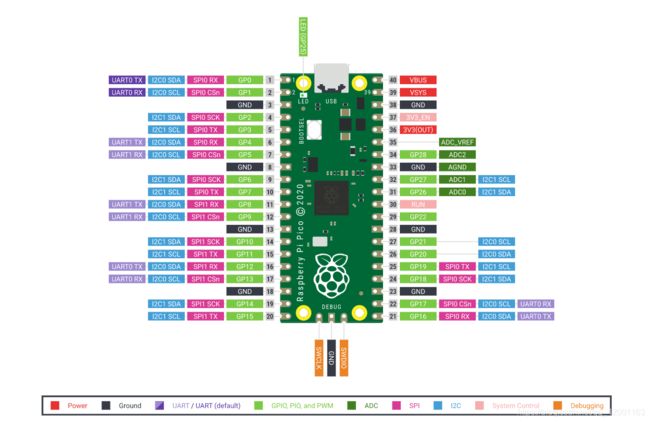
sda = Pin(4) # physical pin 6
scl = Pin(5) # physical pin 7
i2c = I2C(id=0, sda=sda, scl=scl, freq=100000)
ssd = SSD1306_I2C(128, 64, i2c)
ssd.fill(0)
# FrameBuffer.text(s, x, y[, c]) c = colour(optional) x,y = coordinates
# characters always 8x8 => 128/8 => 16 chars
# 1234567890123456
ssd.text("RaspberryPi Pico", 0, 10, 1)
ssd.text("2021-3-10", 0, 30, 1)
ssd.text("kizai", 0, 50, 2)
ssd.show()
utime.sleep(2.5)
count = 0
led1(1)
led2(1)
while True:
if(key1.value()==0):
led1(0)
utime.sleep(1)
led1(1)
txt = str(count)
print(txt)
ssd.fill(0)
ssd.text(txt, 0, 20, 1)
ssd.show()
count += 1
utime.sleep(1.5)
print("Oops done?")
6、管脚图与实现效果
觉得可以麻烦一键三连喔!!!!