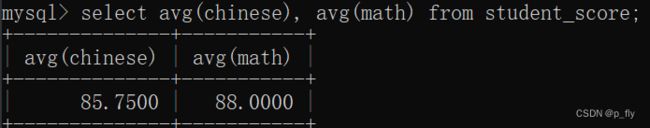【MySQL】聚合查询+联合查询
目录
聚合查询
聚合函数
分组查询
联合查询
内连接
外连接
自连接
子查询
合并查询
聚合查询
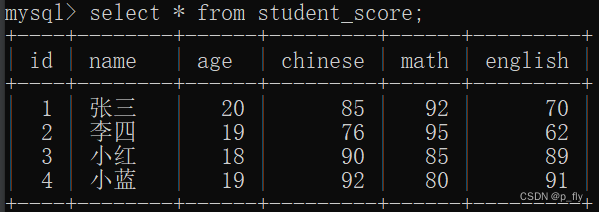
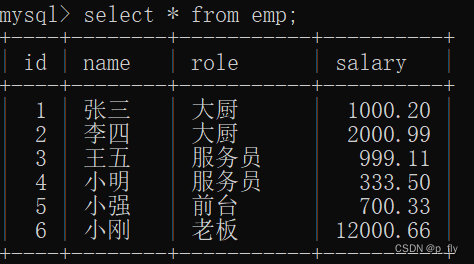
聚合查询就是在一个表里通过聚合函数进行查询操作,通常是求和,求平均值等操作。
聚合函数
常见的聚合函数。
| 函数 | 说明 |
| count(*/表达式/列名) from 表名 | 返回查询到数据的数量 |
| sum(列名) from 表名 | 返回查询到数据的总和,不是数字没有意义 |
| avg(列名) from 表名 | 返回查询到数据的平均值,同上 |
| max(同上) from 表名 |
返回查询到数据的最大值,同上 |
| min(同上) from 表名 | 返回查询到数据的最小值,同上 |
演示
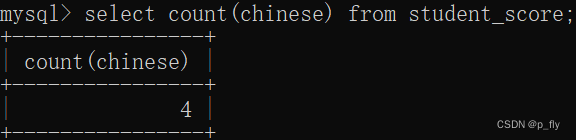
count()
select count(*) from student_score;select count(chinese) from student_score;
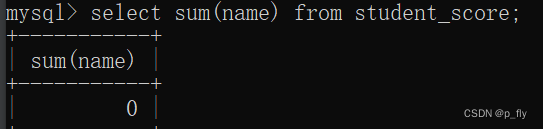
sum()
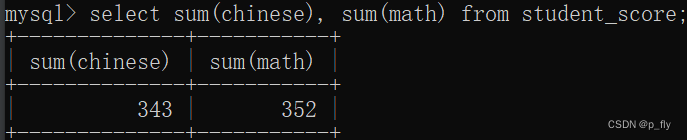
select sum(name) from student_score;
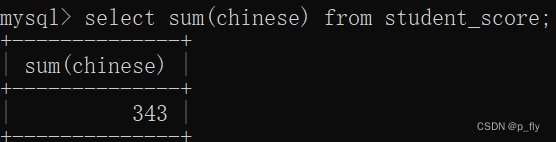
-- 非数字的相加返回的是 0select sum(chinese) from student_score;
select sum(chinese), sum(math) from student_score;
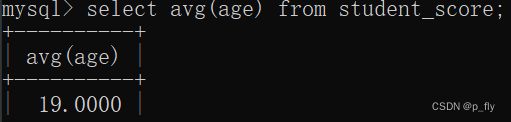
avg()
select avg(age) from student_score;
-- 默认保留四位小数select avg(chinese), avg(math) from student_score;
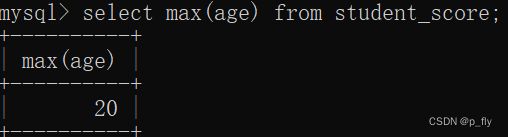
max()
select max(age) from student_score;
select max(chinese), max(math) from student_score;
分组查询
group by子句
在查询中可以使用该子句对指定列进行分组查询。
要求:select 列名/聚合函数 其他形式不可以
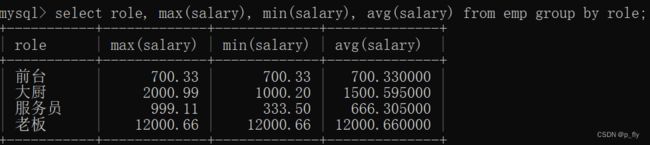
select 列名/聚合函数 from 表名 group by 列名;select role, max(salary), min(salary), avg(salary) from emp group by role;
-- 查询出每个职务的最高工资,最低工资和平均工资having子句
该子句出现在group by子句后。如果想对group by子句再加一些条件,就只能用having子句,而不能使用where子句。可以理解为where操作原表,having操作select出的临时表
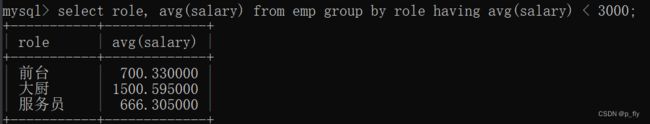
select ... from ... group by ... having 条件;select role, avg(salary) from emp group by role having avg(salary) < 3000;
-- 找出平均工资小于3000的职务联合查询
上述的聚合查询只针对同一张表进行查询操作,接下来的联合查询是对多表进行查询。
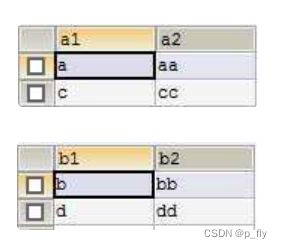
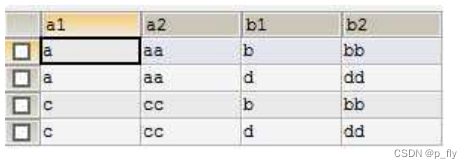
多张表的联合查询是对多张表的数据取 笛卡尔积 的操作。
笛卡尔积
两张表
进行笛卡尔积后
其实就是一张表的每一行与另一张表的每一行分别相连。
班级信息表
学生信息表
课程信息表
学生成绩表
内连接
内连接通常匹配的是表于表之间有关联的,然后去重,得到一张新表。
select 列名 from 表1 (别名1) (inner) join 表2 (别名2) on 连接条件 (inner) join 表3 (别名) on 连接条件 and 其他条件;
-- 上述相当于与 先把表1与表2进行笛卡尔积,再与表3进行笛卡尔积,n张表类似
select 列名 from 表1 (别名1),表2 (别名2), 表3 (别名3) where 连接条件 and 其他条件;
-- 上面两种语法都可以
-- 别名可有可无
-- inner可以忽略
-- 第二种写起来简便一些在多张表中联合找目标值的时候
1. 先观察这几张表有没有什么可以连接的地方,就是有没有相同意义的列
2.进行笛卡尔积,加上where 条件,条件通过观察可得,筛选掉无意义数据
3.进一步根据要求查找目标缩小范围,增加条件
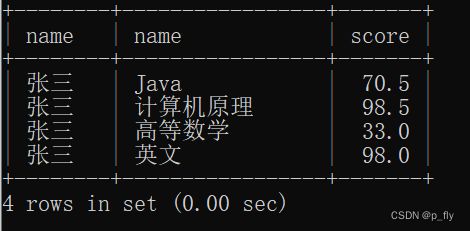
例1:查询张三的各科成绩
写法1:
select student.name, course.name, score.score from student, course, score
where score.student_id = student.id and score.course_id = course.id and student.name = '张三';写法2:
select student.name, course.name, score.score from student join score on score.student_id = student.id
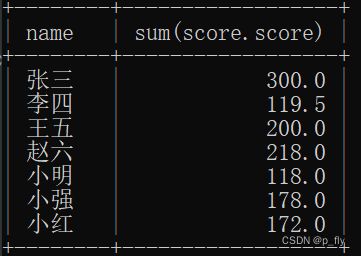
join course on score.course_id = course.id and student.name = '张三';例2:查询所有同学的总成绩
写法1:
select student.name, sum(score.score) from student, course, score
where score.student_id = student.id and score.course_id = course.id
group by student.id;写法2:
select student.name, sum(score.score) from student join score on score.student_id = student.id
join course on score.course_id = course.id
group by student.id;外连接
外连接返回一组记录(或行),其中包括内连接将返回的内容,但也包括在其他表中找不到对应匹配项的其他行。外连接分为左连接和右连接:联合查询时,左(右)侧的表完全显示我们就说是左(右)外连接,对应不上用null表示。
-- 左连接 表1全部显示
select 列名 from 表1 left join 表2 on 连接条件;
-- 右连接 表2全部显示
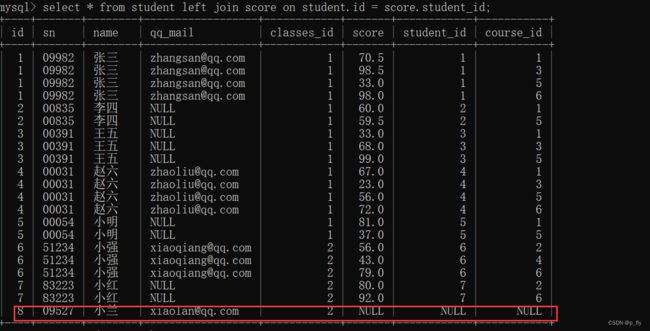
select 列名 from 表1 right join 表2 on 连接条件;上面的几张表中,小兰同学没有成绩,但是我们也要将小兰同学信息显示出来(左连接)
自连接
自连接是一张表与自己进行连接,即自己与自己进行笛卡尔积。通常为了解决列于列之间的比较。
select 列名 from 表名 别名1, 表名 别名2 where 连接条件;
select 列名 from 表名 别名1 (inner) join 表名 别名2 on 连接条件;
-- 必须用别名,否则会出现表名不唯一的错误查询计算机原理比Java成绩高的同学
方法1:
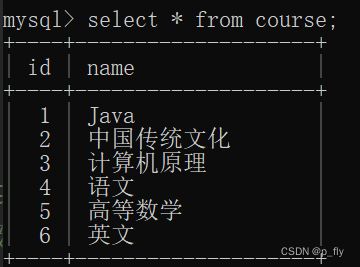
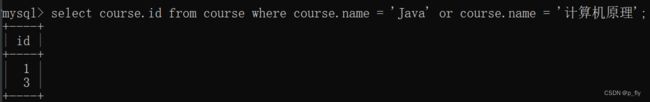
-- 1.先查询计算机原理和Java的course_id, 因为course中只用course_id, 而没有学科名字
select course.id from course where course.name = 'Java' or course.name = '计算机原理';
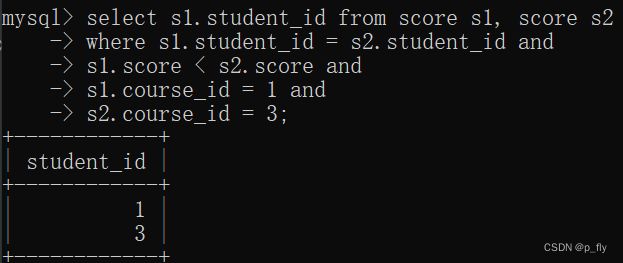
-- 2.course表自连接后,通过观察把无意项去掉,然后加上条件比较,最后找到符合学生的id
select s1.student_id from score s1, score s2
where s1.student_id = s2.student_id and
s1.score < s2.score and
s1.course_id = 1 and
s2.course_id = 3;方法2:
-- 该方法把学生所有信息都显示出来了
-- 先把score自连接后去除无意义数据,接着与student表连接同时去除无意义数据
-- 然后与course与score连接同时去除无意义数据
-- 最后在找分数符合的人
select stu.*, s1.score Java, s2.score 计算机原理 from
score s1 join score s2 on s1.student_id = s2.student_id
join student stu on s1.student_id = stu.id
join course c1 on s1.course_id = c1.id
join course c2 on s2.course_id = c2.id
and s1.score < s2.score
and c1.NAME = 'Java'
and c2.NAME = '计算机原理';子查询
子查询本质上就是套娃,在查询语句中嵌套查询语句,也叫嵌套查询。
-- 单行子查询 返回一行记录
select 列名 from 表名 where 条件中出现select查询;
-- 多行子查询 返回多行记录
select 列名 from 表名 where 条件中出现 (not) in 关键字与select查询搭配使用;
select 列名 from 表名 where 条件中出现 (not) exists 关键字与select查询搭配使用;例1:
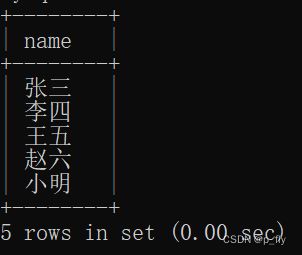
查询与张三同班的同学
select student.name from student where classes_id = (select id from student where name = '张三');
例2:
查询Java或计算机组成 课程的成绩信息
select * from score where
course_id in (select id from course where name = '计算机原理' or name = 'Java');
-- in的用法就是子句查询发回后的值是否包含于外面
-- in后面的select还可以查询多列,只要与外面的一一对应上即可
-- exists用法与in一样合并查询
合并查询就是把多个select出来的临时表进行合并,这些表中字段必须一致才可以。
通常使用集合操作符union,union all进行连接。
union:合并临时表时会去掉重复行
例1:查询课程id小于3,或者课程名为Java的课程信息
select * from course where id < 3
union
select * from course where name = 'Java';
-- 等价于
select * from course where id < 3 or name = 'Java';union all:合并临时表时不会去掉重复行
例2:
查询课程id小于3,或者课程名为Java的课程信息
select * from course where id < 3
union all
select * from course where name = 'Java';有什么错误评论区指出,希望可以帮到你。