【SSM】Spring系列——Spring集成MyBatis
文章目录
- 04 Spring集成MyBatis
-
- 4.1 Spring的事务管理
- 4.2 Spring中事务的五大隔离级别
- 4.3 不同数据库的隔离级别(面试点)
- 4.4 Spring事务的传播特性
- 4.5 @Transactional的参数讲解
- 4.6 MyBatis框架与Hibernate框架使用的事务管理器(面试点)
-
- 4.6.1 Spring+MyBatis的事务管理器配置
- 4.6.2 Spring+ Hibernate的事务管理器配置
- 4.7Spring中事务的实现
-
- 4.7.1 基于xml方式的实现
-
- (1) 导入相关依赖
- (2) 引入aop名称空间
- (3) 引入tx名称空间
- (4) 配置事务
- 4.7.2 基于注解方式实现
-
- (1)导入相关依赖(同xml方式)
- (2)配置注解驱动
- (3)@Transactional设置传播特性
- 4.7.3 Spring+MyBatis整合案例
- 4.8 Spring Bean的生命周期
-
- 4.8.1 Spring Bean的生命周期图示
- 4.8.2 Spring Bean的生命周期中各种方法分类
04 Spring集成MyBatis
将 MyBatis 与 Spring 进行整合,主要解决的问题就是将 SqlSessionFactory 对象交由 Spring 来管理。所以,该整合只需要将 SqlSessionFactory 的对象生成器 SqlSessionFactoryBean 注册在 Spring 容器中,再将其注入给 Dao 的实现类即可完成整合。
实现 Spring 与 MyBatis 的整合。常用的方式:扫描的 Mapper 动态代理。Spring 像插线板一样,mybatis 框架是插头,可以容易的组合到一起。插线板 spring 插上 mybatis,两个框架就是一个整体。
4.1 Spring的事务管理
事务原本是数据库中的概念,在实际项目的开发中,进行事务的处理一般是在业务逻辑层, 即 Service 层。这样做是为了能够使用事务的特性来管理关联操作的业务。
在 Spring 中通常可以通过以下两种方式来实现对事务的管理:
(1)使用 Spring 的事务注解管理事务
(2)使用 AspectJ 的 AOP 配置管理事务(声明式事务管理)
4.2 Spring中事务的五大隔离级别
- 读未提交(Read Uncommitted):允许脏读,也就是可能读取到其他会话中未提交事务修改的数据
- 读已提交(Read Committed):只能读取到已经提交的数据。Oracle等多数数据库默认都是该级别 (不重复读)
- 可重复读(Repeated Read):可重复读。在同一个事务内的查询都是事务开始时刻一致的,InnoDB默认级别。在SQL标准中,该隔离级别消除了不可重复读,但是还存在幻象读,但是innoDB解决了幻读
- 串行读(Serializable):完全串行化的读,每次读都需要获得表级共享锁,读写相互都会阻塞
4.3 不同数据库的隔离级别(面试点)
MySQL:mysql默认的事务处理级别是’REPEATABLE-READ’,也就是可重复读
Oracle:oracle数据库支持READ COMMITTED 和 SERIALIZABLE这两种事务隔离级别。
默认系统事务隔离级别是READ COMMITTED,也就是读已提交
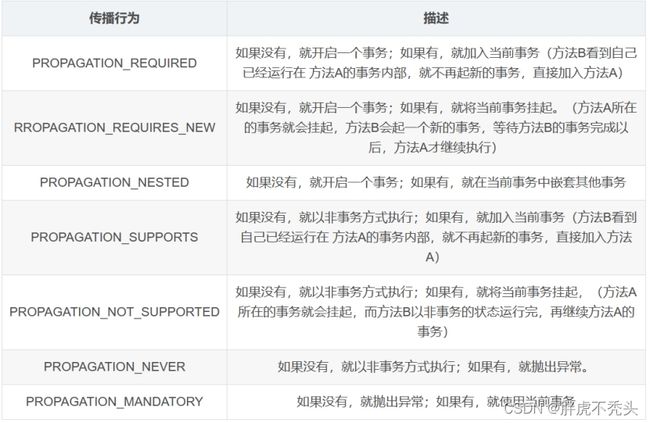
4.4 Spring事务的传播特性
总结:
常用
- PROPAGATION_REQUIRED:必被包含事务
- PROPAGATION_REQUIRES_NEW:自己新开事务,不管之前是否有事务
- PROPAGATION_SUPPORTS:支持事务,如果加入的方法有事务,则支持事务,如果没有,不单开事务
- PROPAGATION_NEVER:不能运行中事务中,如果包在事务中,抛异常
- PROPAGATION_NOT_SUPPORTED:不支持事务,运行在非事务的环境
不常用
- PROPAGATION_MANDATORY:必须包在事务中,没有事务则抛异常
- PROPAGATION_NESTED:嵌套事务
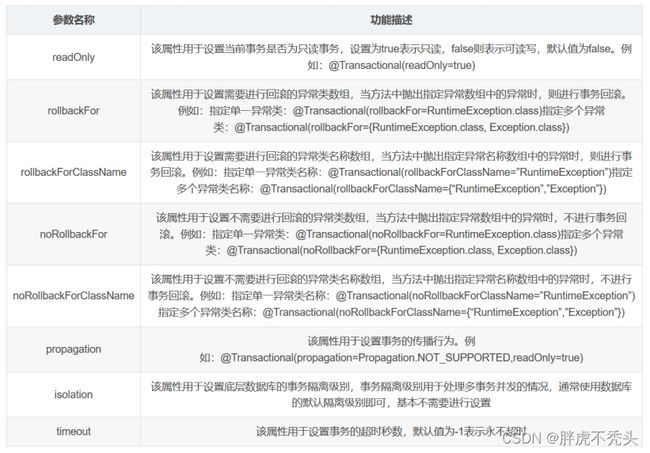
4.5 @Transactional的参数讲解
示例:
@Transactional(readOnly = false, // 读写事务
timeout = -1, // 事务的超时时间不限制(数据库有异常或没有连接上,等待的时间,但还是要看连接的数据库是如何设置的。
//noRollbackFor = ArithmeticException.class, // noRollbackFor设置遇到指定的错误不用回滚。此处是遇到数学异常不回滚
isolation = Isolation.DEFAULT, // 事务的隔离级别,数据库的默认
propagation = Propagation.REQUIRED // 事务的传播行为,此处是指当前的方法要在事务中去执行。
)
@Transactional有几点需要注意
- 只能声明在public的method。原因是spring是通过JDK代理或者CGLIB代理的,生成的代理类,只能处理public方法,注解放在类名称上面,这样你配置的这个@Transactional 对这个类中的所有public方法都起作用,@Transactional 在方法名上,只对这个方法有作用,同样必须是public的方法。
- 不能被类内部方法调用。还是因为代理的原因,类内部自调用,不会经过代理类,所以@Transactional不会生效
4.6 MyBatis框架与Hibernate框架使用的事务管理器(面试点)
4.6.1 Spring+MyBatis的事务管理器配置
<bean id="transactionManager" class="**org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager**">
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource" />
bean>
<tx:annotation-driven transaction-manager="transactionManager" />
4.6.2 Spring+ Hibernate的事务管理器配置
<bean id="transactionManager" class="**org.springframework.orm.hibernate3.HibernateTransactionManager**">
<property name="sessionFactory" ref="sessionFactory" />
bean>
<tx:annotation-driven transaction-manager="transactionManager" proxy-target-class="true" />
4.7Spring中事务的实现
Spring中事务的实现有两种方式,一种是基于xml文件的实现,一种是基于注解方式实现。在SSM的开发中,多使用注解方式实现事务的处理。
4.7.1 基于xml方式的实现
实现步骤:
(1) 导入相关依赖
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>junitgroupId>
<artifactId>junitartifactId>
<version>4.11version>
<scope>testscope>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframeworkgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-aspectsartifactId>
<version>5.2.5.RELEASEversion>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframeworkgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-contextartifactId>
<version>5.2.5.RELEASEversion>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframeworkgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-txartifactId>
<version>5.2.5.RELEASEversion>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframeworkgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-jdbcartifactId>
<version>5.2.5.RELEASEversion>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.mybatisgroupId>
<artifactId>mybatisartifactId>
<version>3.5.1version>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.mybatisgroupId>
<artifactId>mybatis-springartifactId>
<version>1.3.1version>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>mysqlgroupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-javaartifactId>
<version>8.0.22version>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibabagroupId>
<artifactId>druidartifactId>
<version>1.1.12version>
dependency> dependencies><build>
<resources>
<resource>
<directory>src/main/javadirectory>
<includes>
<include>**/*.propertiesinclude>
<include>**/*.xmlinclude>
includes>
<filtering>falsefiltering>
resource>
<resource>
<directory>src/main/resourcesdirectory>
<includes>
<include>**/*.propertiesinclude>
<include>**/*.xmlinclude>
includes>
<filtering>falsefiltering>
resource>
resources>
build>
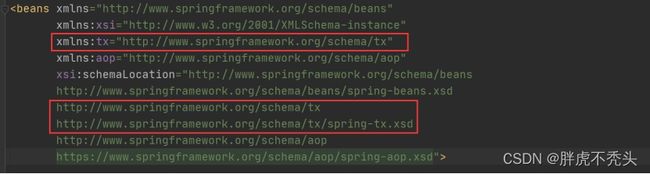
(2) 引入aop名称空间
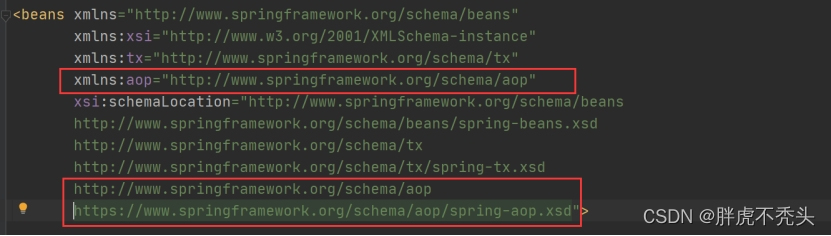
(3) 引入tx名称空间
(4) 配置事务
<bean id="transactionManager" class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager">
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource">property>
bean>
<tx:advice id="txAdvice" transaction-manager="transactionManager">
<tx:attributes>
<tx:method name="*get*" read-only="true"/>
<tx:method name="*select*" read-only="true"/>
<tx:method name="*find*" read-only="true"/>
<tx:method name="*search*" read-only="true"/>
<tx:method name="*add*" propagation="REQUIRED" />
<tx:method name="*save*" propagation="REQUIRED" no-rollback-for="ArithmeticException"/>
<tx:method name="*insert*" propagation="REQUIRED" no-rollback-for="ArithmeticException"/>
<tx:method name="*delete*" propagation="REQUIRED"/>
<tx:method name="*remove*" propagation="REQUIRED"/>
<tx:method name="*clean*" propagation="REQUIRED"/>
<tx:method name="*update*" propagation="REQUIRED"/>
<tx:method name="*modify*" propagation="REQUIRED"/>
<tx:method name="*set*" propagation="REQUIRED"/>
<tx:method name="*change*" propagation="REQUIRED"/>
<tx:method name="*" propagation="SUPPORTS"/>
tx:attributes>
tx:advice>
<aop:config >
<aop:pointcut id="pointcat" expression="execution(* com.bjpowernode.service.*.*(..))">aop:pointcut>
<aop:advisor advice-ref="txAdvice" pointcut-ref="pointcat">aop:advisor>
aop:config>
4.7.2 基于注解方式实现
(1)导入相关依赖(同xml方式)
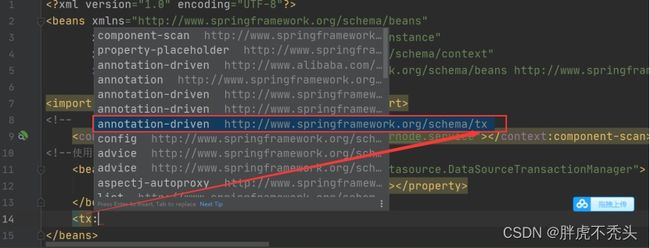
(2)配置注解驱动
<bean id="transactionManager" class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager">
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource">property>
bean>
<tx:annotation-driven>tx:annotation-driven>
(3)@Transactional设置传播特性
@Service
//交给Spring接管,进行对象的创建,并且自动注入mapper
@Transactional( propagation = Propagation.*REQUIRED*
//必须添加事务
,readOnly = true
//只读事务(用于查询操作)
,timeout = -1 //设置连接永不超时
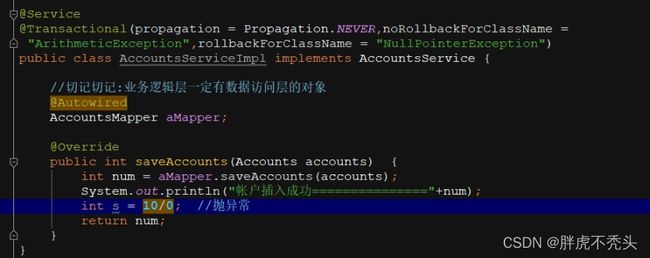
,noRollbackForClassName = "ArithmeticException"
//遇到这个异常不回滚事务
,isolation = Isolation.*DEFAULT*
//使用数据库的隔离级别
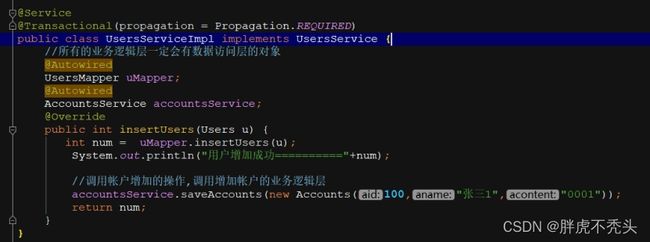
) public class UsersServiceImpl implements UsersService {
4.7.3 Spring+MyBatis整合案例
整合实现步骤:
1.新建maven工程,添加各种依赖
2.修改目录结构
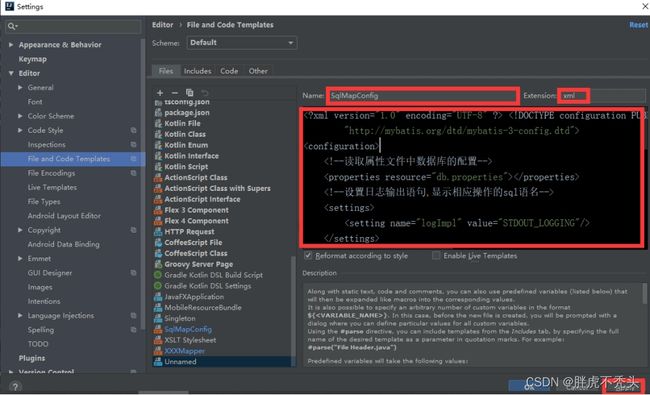
3.添加SqlMapConfig.xml和XXXMapper.xml模板
4.添加db.properties文件
5.添加SqlMapConfig.xml文件
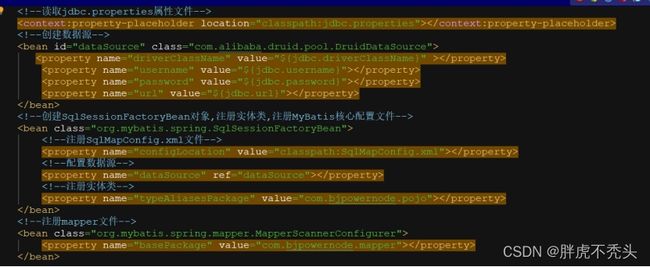
6.添加applicationContext_dao.xml文件并实现功能
7.添加applicationContext_service.xml文件并实现功能(注解驱动)
8.添加applicationContext_trans.xml文件(xml配置文件方式)
<import resource="classpath:applicationContext_dao.xml">import>
<context:component-scan base-package="com.bjpowernode.service">context:component-scan>
<bean id="transactionManager" class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager">
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource">property>
bean>
<tx:advice id="txAdvice" transaction-manager="transactionManager">
<tx:attributes>
<tx:method name="get*" read-only="true" />
<tx:method name="select*" read-only="true"/>
<tx:method name="find*" read-only="true"/>
<tx:method name="search*" read-only="true"/>
<tx:method name="insert*" propagation="REQUIRED">tx:method>
<tx:method name="add*" propagation="REQUIRED">tx:method>
<tx:method name="save*" propagation="REQUIRED" no-rollback-for="ArithmeticException">tx:method>
<tx:method name="set*" propagation="REQUIRED">tx:method>
<tx:method name="update*" propagation="REQUIRED">tx:method>
<tx:method name="modify*" propagation="REQUIRED">tx:method>
<tx:method name="change*" propagation="REQUIRED">tx:method>
<tx:method name="delete*" propagation="REQUIRED">tx:method>
<tx:method name="remove*" propagation="REQUIRED">tx:method>
<tx:method name="clear*" propagation="REQUIRED">tx:method>
<tx:method name="empty*" propagation="REQUIRED">tx:method>
<tx:method name="*" propagation="SUPPORTS">tx:method>
tx:attributes>
tx:advice>
<aop:config>
<aop:pointcut id="pointcut" expression="execution(* com.bjpowernode.service.*.*(..))"/>
<aop:advisor advice-ref="txAdvice" pointcut-ref="pointcut">aop:advisor> aop:config>
9.新建库springuser,新建表users,accounts
10.新建实体类Users,Accounts
11.新建mapper包下的接口和.xml文件
12.新建service包下的接口和接口实现类
13.新建测试类,完成功能测试
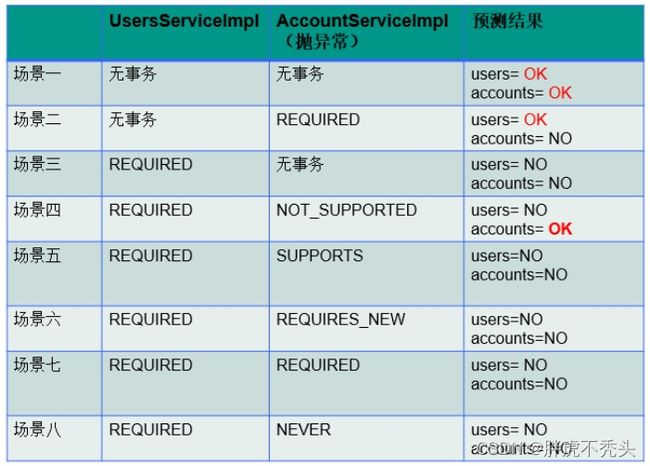
测试结果总结如下:
4.8 Spring Bean的生命周期
4.8.1 Spring Bean的生命周期图示
- Spring作为当前Java最流行、最强大的轻量级框架,受到了程序员的热烈欢迎。
- 准确的了解Spring Bean的生命周期是非常必要的。
- 我们通常使用ApplicationContext作为Spring容器,这里我们讲的也是 ApplicationContext中Bean的生命周期。
4.8.2 Spring Bean的生命周期中各种方法分类
Bean的完整生命周期经历了各种方法调用,这些方法可以划分为以下几类:
1、Bean自身的方法:这个包括了Bean本身调用的方法和通过配置文件中的init-method和destroy-method指定的方法
2、Bean级生命周期接口方法:这个包括了BeanNameAware、BeanFactoryAware、InitializingBean和DiposableBean这些接口的方法
3、容器级生命周期接口方法:这个包括了InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor 和 BeanPostProcessor 这两个接口实现,一般称它们的实现类为“后处理器”。
4、工厂后处理器接口方法:这个包括了AspectJWeavingEnabler, ConfigurationClassPostProcessor, CustomAutowireConfigurer等等非常有用的工厂后处理器 接口的方法。工厂后处理器也是容器级的。在应用上下文装配配置文件之后立即调用。
总结:class(UsersService)-实例化-对象属性填充(AccountsService)-初始化(DefaultUsers)AOP-代理对象-bean.
@Service
//交给Spring去创建对象
IOC@Transactional =èAOP处理
public class UsersServiceImpl implements UsersService {
//切记切记:一定有数据访问层的对象
@Autowired
UsersMapper usersMapper;
//由Spring负责依赖注入
IOCDefaultUsers users;=è初始化处理的对象
@Override
public int insert(Users users) {
int num = usersMapper.insert(users)***\*;
System.out.println("用户增加成功!num="+num);
System.out.println(1);
return num;
}
}
4.9 Spring中用到的设计模式总结
Spring框架中用到了很多的设计模式,总结如下:
- 工厂模式:Spring通过工厂模式BeanFactory,ApplicationContext创建Bean对象。
- 代理设计模式:SpringAOP的实现,底层使用了动态代理模式。
- 单例模式:Spring中的Bean默认都是单例的。
- 模板方法模式:Spring中jdbcTemplate,hibernateTemplate等以Template结尾的类都用到了模板模式。
- 装饰模式:我们的项目需要连接多个数据库,而不同的客户在访问时可能会访问不同的数据库,这种模式可以让我们根据用户的需求动态的切换数据库。
- 观察者模式:Spring的事件驱动是观察者模式的应用。
- 适配器模式:SpringAOP的增强功能使用到了适配器模式。