目录
- 一、构造函数
- 二、继承与重写
- 三、泛型
- 四、反射
-
- 1 - 反射的基本概念
- 2 - 反射的基础数据类型
- 3 - 反射API
-
-
- a - 获取Type类型
- b - 获取struct成员变量的信息
- c - 获取struct成员方法的信息
- d - 获取函数的信息
- e - 判断类型是否实现了某接口
- 五、reflect.Value
-
-
-
- a - 空value判断
- b - 获取Value
- c - 指针Value和非指针Value互相转换
- d - 获取Value对应的原始数据
- e - 通过Value修改原始数据的值
- f - 通过Value修改slice
- g - 通过Value修改map
- 六、反射创建对象
- 七、反射调用函数和成员方法
一、构造函数
type User struct {
Name string
Age int
Sex byte
}
func main() {
u := User{}
up := new(User)
}
func NewDefaultUser() *User {
return &User{
Name: "",
Age: -1,
Sex: 3,
}
}
func NewUser(name string, age int, sex byte) *User {
return &User{
Name: name,
Age: age,
Sex: sex,
}
}
- 单例模式:确保在并发的情况下,整个进程里只会创建struct的一个实例
type User struct {
Name string
Age int
Sex byte
}
func NewDefaultUser() *User {
return &User{
Name: "",
Age: -1,
Sex: 3,
}
}
var (
sUser *User
uOnce sync.Once
)
func GetUserInstance() *User {
uOnce.Do(func() {
if sUser == nil {
sUser = NewDefaultUser()
}
})
return sUser
}
func main() {
su1 := GetUserInstance()
su2 := GetUserInstance()
fmt.Println(su1.Age, su2.Age)
su1.Age = 20
fmt.Println(su2.Age)
}
二、继承与重写
- 继承的实现:通过嵌入匿名结构体,变相实现“继承”的功能,因为访问匿名成员时可以跳过成员名直接访问它的内部成员
type Plane struct {
color string
}
type Bird struct {
Plane
}
func main() {
bird := Bird{}
bird.Plane.color = "red"
fmt.Println(bird.color)
}
type Plane struct {
color string
}
func (pl Plane) fly() {
fmt.Println("plane fly")
}
type Bird struct {
Plane
}
func (bd Bird) fly() {
fmt.Println("bird fly")
}
func main() {
bird := Bird{}
bird.Plane.color = "red"
fmt.Println(bird.Plane.color)
fmt.Println(bird.color)
bird.Plane.fly()
bird.fly()
}
- 组合:严格意义上来说Go语言并不支持继承,它只是支持组合
type Plane struct{}
type Car struct{}
type Bird struct {
Plane
Car
}
三、泛型
- 使用泛型之前:在有泛型之前,同样的功能需要为不同的参数类型单独实现一个函数
func add4int(a, b int) int {
return a + b
}
func add4float32(a, b float32) float32 {
return a + b
}
func add4string(a, b string) string {
return a + b
}
type Addable interface {
int | string
}
func add[T Addable](a, b T) T {
return a + b
}
func main() {
fmt.Println(add(1, 2))
fmt.Println(add("hello", "world"))
}
四、反射
1 - 反射的基本概念
- 什么是反射:反射就是在运行期间(不是编译期间)探知对象的类型信息和内存结构、更新变量、调用它们的方法
- 反射的使用场景
- 函数的参数类型是interface{},需要在运行时对原始类型进行判断,针对不同的类型采取不同的处理方式。比如json.Marshal(v interface{})
- 在运行时根据某些条件动态决定调用哪个函数,比如根据配置文件执行相应的算子函数
- 反射的弊端
- 代码难以阅读,难以维护
- 编译期间不能发现类型错误,覆盖测试难度很大,有些bug需要到线上运行很长时间才能发现,可能会造成严重用后
- 反射性能很差,通常比正常代码慢一到两个数量级。在对性能要求很高,或大量反复调用的代码块里建议不要使用反射
2 - 反射的基础数据类型
- 反射的基础数据类型
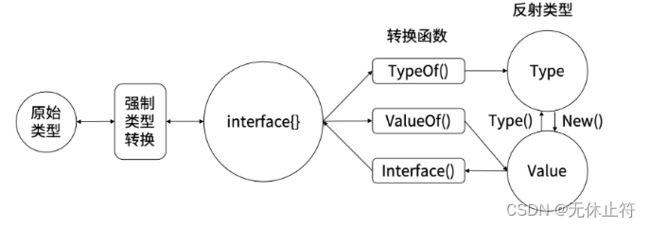
- reflect.Type用于获取类型相关的信息
type Type interface {
Method(int) Method
MethodByName(string) (Method, bool)
NumMethod() int
Name() string
PkgPath() string
Size() uintptr
String() string
Kind() Kind
Implements(u Type) bool
AssignableTo(u Type) bool
ConvertibleTo(u Type) bool
Elem() Type
Field(i int) StructField
FieldByIndex(index []int) StructField
FieldByName(name string) (StructField, bool)
FieldByNameFunc(match func(string) bool) (StructField, bool)
Len() int
NumIn() int
NumOut() int
}
- reflect.Value用于修改原始数据类型里的值
type Value struct {
typ *rtype
ptr unsafe.Pointer
}
3 - 反射API
a - 获取Type类型
type User struct {
age int64
Gender bool `json:"sex"`
uint8
}
type Student struct {
User
}
func get_type() {
typeI := reflect.TypeOf(2)
typeS := reflect.TypeOf("abc")
fmt.Println(typeI)
fmt.Printf("%s %T\n", typeI, typeI)
fmt.Println(typeI.String())
fmt.Println(typeS)
fmt.Println(typeI.Kind() == reflect.Int)
fmt.Println(typeS.Kind() == reflect.String)
fmt.Println("-------------------")
user := &User{}
typeUser := reflect.TypeOf(user)
fmt.Println(typeUser)
fmt.Println(typeUser.Elem())
fmt.Println(typeUser.Elem().Name())
fmt.Println(typeUser.Kind() == reflect.Ptr)
fmt.Println(typeUser.Elem().Kind() == reflect.Struct)
fmt.Println("-------------------")
user2 := &User{}
typeUser2 := reflect.TypeOf(user2)
fmt.Println(typeUser2.Size())
fmt.Println(typeUser2.PkgPath())
}
b - 获取struct成员变量的信息
type User struct {
age int64
Gender bool `json:"sex"`
uint8
}
type Student struct {
Name string
user User
}
func get_field() {
typeUser := reflect.TypeOf(User{})
fieldNum := typeUser.NumField()
for i := 0; i < fieldNum; i++ {
field := typeUser.Field(i)
fmt.Println(field.Name)
fmt.Println(field.Offset)
fmt.Println(field.Anonymous)
fmt.Println(field.Type)
fmt.Println(field.IsExported())
fmt.Println(field.Tag.Get("json"))
fmt.Println("------------------")
}
if field, ok := typeUser.FieldByName("Gender"); ok {
fmt.Println(field.Name)
fmt.Println(field.Offset)
fmt.Println(field.Anonymous)
fmt.Println(field.Type)
fmt.Println(field.IsExported())
fmt.Println(field.Tag.Get("json"))
fmt.Println("------------------")
} else {
fmt.Println("结构体中没有名为Gender的成员变量")
}
field := typeUser.FieldByIndex([]int{0})
fmt.Println(field.Name)
fmt.Println(field.Offset)
fmt.Println(field.Anonymous)
fmt.Println(field.Type)
fmt.Println(field.IsExported())
fmt.Println(field.Tag.Get("json"))
fmt.Println("------------------")
typeStudent := reflect.TypeOf(Student{})
fieldUser := typeStudent.FieldByIndex([]int{1, 0})
fmt.Println(fieldUser.Name)
}
c - 获取struct成员方法的信息
type User struct {
age int64
Gender bool `json:"sex"`
uint8
}
type Student struct {
Name string
user User
}
func (*Student) Examine1(a int, b float32) (byte, string) {
return byte(3), "abc"
}
func (Student) Examine2(a int, b float32) (byte, string) {
return byte(3), "abc"
}
func get_method_info() {
typeStudent := reflect.TypeOf(Student{})
foreachMethod(typeStudent)
ptypeStudent := reflect.TypeOf(&Student{})
foreachMethod(ptypeStudent)
if method, ok := typeStudent.MethodByName("Examine2"); ok {
fmt.Println(method.Name)
fmt.Println(method.Type)
fmt.Println(method.IsExported())
fmt.Println(method.Type.NumIn())
fmt.Println(method.Type.NumOut())
}
}
func foreachMethod(rt reflect.Type) {
methodNum := rt.NumMethod()
for i := 0; i < methodNum; i++ {
method := rt.Method(i)
fmt.Println(method.Name)
fmt.Println(method.Type)
fmt.Println(method.IsExported())
fmt.Println(method.Type.NumIn())
fmt.Println(method.Type.NumOut())
fmt.Println("-------------")
}
}
d - 获取函数的信息
func Add(a, b int) int {
return a + b
}
func main() {
addType := reflect.TypeOf(Add)
fmt.Printf("is function type %t\n", addType.Kind() == reflect.Func)
argInNum := addType.NumIn()
argOutNum := addType.NumOut()
for i := 0; i < argInNum; i++ {
argTyp := addType.In(i)
fmt.Printf("第%d个输入参数的类型%s\n", i, argTyp)
}
for i := 0; i < argOutNum; i++ {
argTyp := addType.Out(i)
fmt.Printf("第%d个输出参数的类型%s\n", i, argTyp)
}
}
e - 判断类型是否实现了某接口
type People interface {
Examine1(a int, b float32) (byte, string)
}
type User struct {
age int64
Gender bool `json:"sex"`
uint8
}
type Student struct {
Name string
user User
}
func (*Student) Examine1(a int, b float32) (byte, string) {
return byte(3), "abc"
}
func convert() {
userType := reflect.TypeOf(User{})
studentType := reflect.TypeOf(Student{})
fmt.Println(userType.AssignableTo(studentType))
fmt.Println(studentType.AssignableTo(userType))
fmt.Println(userType.ConvertibleTo(studentType))
fmt.Println(studentType.ConvertibleTo(userType))
userType2 := reflect.TypeOf(User{})
fmt.Println(userType.AssignableTo(userType2))
fmt.Println(userType2.ConvertibleTo(userType))
}
func impl() {
peopleType := reflect.TypeOf((*People)(nil)).Elem()
userType := reflect.TypeOf(User{})
studentType := reflect.TypeOf(Student{})
pstudentType := reflect.TypeOf(&Student{})
fmt.Println(userType.Implements(peopleType))
fmt.Println(studentType.Implements(peopleType))
fmt.Println(pstudentType.Implements(peopleType))
}
五、reflect.Value
a - 空value判断
func is_empty() {
var i interface{}
vl := reflect.ValueOf(i)
fmt.Println(vl)
fmt.Println(vl.IsValid())
var user *User
vl = reflect.ValueOf(user)
fmt.Println(vl)
if vl.IsValid() {
fmt.Println(vl.IsNil())
}
var u User
vl = reflect.ValueOf(u)
fmt.Println(vl)
if vl.IsValid() {
fmt.Println(vl.IsZero())
}
}
b - 获取Value
type User struct {
age int64
Gender bool `json:"sex"`
uint8
}
func main() {
iValue := reflect.ValueOf(1)
sValue := reflect.ValueOf("hello")
fmt.Println(iValue)
fmt.Println(sValue)
fmt.Println(iValue.Kind() == reflect.Int)
fmt.Println(sValue.Kind() == reflect.String)
iType := iValue.Type()
sType := sValue.Type()
fmt.Println(iType.Kind() == reflect.Int)
fmt.Println(sType.Kind() == reflect.String)
}
c - 指针Value和非指针Value互相转换
type User struct {
age int64
Gender bool `json:"sex"`
uint8
}
func main() {
userPtrValue := reflect.ValueOf(&User{3, true, 6})
userValue := userPtrValue.Elem()
fmt.Println(userValue.Kind(), userPtrValue.Kind())
userPtrValue2 := userValue.Addr()
fmt.Println(userValue.Kind(), userPtrValue2.Kind())
}
d - 获取Value对应的原始数据
- 通过Interface()函数把Value转为interface{},再从interface{}强制类型转换,转为原始数据类型
- 在Value上直接调用Int()、String()等
type User struct {
age int64
Gender bool `json:"sex"`
uint8
}
func main() {
iValue := reflect.ValueOf(1)
sValue := reflect.ValueOf("hello")
fmt.Printf("origin value iValue is %d %d\n", iValue.Interface().(int), iValue.Int())
fmt.Printf("origin value sValue is %s %s\n", sValue.Interface().(string), sValue.String())
userValue := reflect.ValueOf(User{3, true, 6})
user := userValue.Interface().(User)
fmt.Printf("age=%d gender=%t uint=%d\n", user.age, user.Gender, user.uint8)
userPtrValue := reflect.ValueOf(&User{2, false, 5})
user2 := userPtrValue.Interface().(*User)
fmt.Printf("age=%d gender=%t uint=%d\n", user2.age, user2.Gender, user2.uint8)
}
e - 通过Value修改原始数据的值
- 通过反射修改原始数据的值:
- 要想修改原始数据的值,给ValueOf传的必须是指针,而指针Value不能调用Set和FieldByName方法,所以得先通过Elem()转为非指针Value
- 未导出成员的值不能通过反射进行修改,所以在修改前需要先进行CanSet判断
func main() {
var i int = 18
iValue := reflect.ValueOf(&i)
iValue.Elem().SetInt(28)
fmt.Println(i)
user := User{10, true, 3}
userValue := reflect.ValueOf(&user)
fieldGenderValue := userValue.Elem().FieldByName("Gender")
fieldGenderValue.SetBool(false)
fmt.Println(user.Gender)
fieldAgeValue := userValue.Elem().FieldByName("age")
if fieldAgeValue.CanSet() {
fieldAgeValue.SetInt(8)
} else {
fmt.Println("age成员未导出,不可以set")
}
}
f - 通过Value修改slice
type User struct {
age int64
Gender bool `json:"sex"`
uint8
}
func main() {
users := make([]*User, 1, 5)
users[0] = &User{18, true, 8}
sliceValue := reflect.ValueOf(&users)
if sliceValue.Elem().Len() > 0 {
sliceValue.Elem().Index(0).Elem().FieldByName("Gender").SetBool(false)
fmt.Printf("1st user Gender change to %t\n", users[0].Gender)
}
sliceValue.Elem().SetLen(2)
sliceValue.Elem().Index(1).Set(reflect.ValueOf(&User{10, false, 3}))
fmt.Printf("2nd user age %d\n", users[1].age)
fmt.Printf("slice old cap is %d\n", cap(users))
sliceValue.Elem().SetCap(3)
fmt.Printf("slice new cap is %d\n", cap(users))
}
g - 通过Value修改map
- 反射修改map
- Value.SetMapIndex()函数:往map里添加一个key-value对
- Value.MapIndex()函数: 根据Key取出对应的map
type User struct {
age int64
Gender bool `json:"sex"`
uint8
}
func main() {
u1 := &User{1, true, 2}
u2 := &User{3, true, 5}
userMap := make(map[int]*User, 5)
userMap[0] = u1
mapValue := reflect.ValueOf(&userMap)
mapValue.Elem().SetMapIndex(reflect.ValueOf(1), reflect.ValueOf(u2))
for k, user := range userMap {
fmt.Printf("key = %d, user age = %d\n", k, user.age)
}
mapValue.Elem().MapIndex(reflect.ValueOf(0)).Elem().FieldByName("Gender").SetBool(false)
fmt.Println("u1 Gender = ", u1.Gender)
}
六、反射创建对象
type User struct {
age int64
Gender bool `json:"sex"`
uint8
}
func main() {
userType := reflect.TypeOf(User{1, false, 2})
value := reflect.New(userType)
value.Elem().FieldByName("Gender").SetBool(true)
if userOrign, ok := value.Interface().(*User); ok {
fmt.Println(userOrign.Gender)
}
}
type User struct {
age int64
Gender bool `json:"sex"`
uint8
}
func main() {
sliceType := reflect.TypeOf([]User{})
sliceValue := reflect.MakeSlice(sliceType, 2, 3)
sliceValue.Index(0).Set(reflect.ValueOf(User{1, false, 2}))
sliceValue.Index(1).Set(reflect.ValueOf(User{3, true, 5}))
users := sliceValue.Interface().([]User)
fmt.Printf("1st user age %d\n", users[0].age)
fmt.Printf("2st user Gender %t\n", users[1].Gender)
}
type User struct {
Id int
age int64
Gender bool `json:"sex"`
Name string
}
func main() {
var userMap map[int]*User
mapType := reflect.TypeOf(userMap)
mapValue := reflect.MakeMapWithSize(mapType, 10)
user := &User{1, 1, false, "Jack"}
key := reflect.ValueOf(user.Id)
mapValue.SetMapIndex(key, reflect.ValueOf(user))
mapValue.MapIndex(key).Elem().FieldByName("Name").SetString("Tom")
userMap = mapValue.Interface().(map[int]*User)
fmt.Printf("user name %s %s\n", userMap[1].Name, user.Name)
}
七、反射调用函数和成员方法
func Add(a, b int) int {
return a + b
}
func main() {
valueFunc := reflect.ValueOf(Add)
typeFunc := reflect.TypeOf(Add)
argNum := typeFunc.NumIn()
args := make([]reflect.Value, argNum)
for i := 0; i < argNum; i++ {
if typeFunc.In(i).Kind() == reflect.Int {
args[i] = reflect.ValueOf(3)
}
}
sumValue := valueFunc.Call(args)
if typeFunc.Out(0).Kind() == reflect.Int {
sum := sumValue[0].Interface().(int)
fmt.Printf("sum=%d\n", sum)
}
sumValue = valueFunc.Call([]reflect.Value{reflect.ValueOf(3), reflect.ValueOf(4)})
if typeFunc.Out(0).Kind() == reflect.Int {
sum := sumValue[0].Interface().(int)
fmt.Printf("sum=%d\n", sum)
}
}
type User struct {
Id int
age int64
Gender bool `json:"sex"`
Name string
}
func (u *User) GetAge() int64 {
return u.age
}
func (u User) Think() {
fmt.Printf("%s is in Think\n", u.Name)
}
func main() {
user := &User{7, 18, false, "jack"}
valueUser := reflect.ValueOf(user)
bmiMethod := valueUser.MethodByName("GetAge")
resultValue := bmiMethod.Call([]reflect.Value{})
result := resultValue[0].Interface().(int64)
fmt.Printf("GetAge=%d\n", result)
thinkMethod := valueUser.MethodByName("Think")
thinkMethod.Call([]reflect.Value{})
valueUser2 := reflect.ValueOf(user)
thinkMethod = valueUser2.MethodByName("Think")
thinkMethod.Call([]reflect.Value{})
}
