Springboot框架自动装配原理之@Import注解作用
1. 简介
在平时看源码或者很多配置类上面都会出现@Import注解,功能就是和Spring XML 里面 的 一样. @Import注解是用来导入配置类或者一些需要前置加载的类.,springboot框架实现自动装配的原理之一正是利用这一特性解决了spring框架中重量级的xml配置
2. 源码解析
@Import注解源码以及源码描述的翻译
/**
- Indicates one or more component classes to import — typically
- {@link Configuration @Configuration} classes.
表示要导入的一个或多个组件类 通常@Configuration 类。
-
- Provides functionality equivalent to the {@code
{@code @Bean} definitions declared in imported {@code @Configuration} classes should be
- accessed by using {@link org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired @Autowired}
- injection. Either the bean itself can be autowired, or the configuration class instance
- declaring the bean can be autowired. The latter approach allows for explicit, IDE-friendly
- navigation between {@code @Configuration} class methods.
在导入的 @Configuration 类中声明的 @Bean 定义应该是
通过使用 @Autowired访问注射。 bean 本身可以自动装配,或者配置类实例
声明 bean 可以自动装配。 后一种方法允许显式的、IDE 友好的
@Configuration 类方法之间的导航。
-
May be declared at the class level or as a meta-annotation.
- 16.
If XML or other non-{@code @Configuration} bean definition resources need to be
- imported, use the {@link ImportResource @ImportResource} annotation instead.
- */
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
public @interface Import {
/**
* {@link Configuration @Configuration}, {@link ImportSelector},
* {@link ImportBeanDefinitionRegistrar}, or regular component classes to import.
*/
Class<?>[] value();
通过源码的描述翻译可以总结出@Import可以通过以下四种方式导入一个bean(其实只有三种):
- 导入普通类(4.2 版本之前只可以导入配置类,4.2版本之后 也可以导入 普通类)
- 导入@Configuration配置类(@Configuration配置类已经是被注册为bean了,因此再用Import导入没什么意义
- 导入ImportSelector实现类
- 导入ImportBeanDefinitionRegistrar实现类
3. 测试例子
3.1 导入普通类测试
配置类ImportConfig
package com.eureka.config;
import com.eureka.register.SelfImportBeanDefinitionRegistrar;
import com.eureka.selector.SelfImportSelector;
import com.eureka.service.TestA;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Import;
@Configuration
@Import({TestA.class})
public class ImportConfig {
}
普通类TestA
public class TestA {
public void printName() {
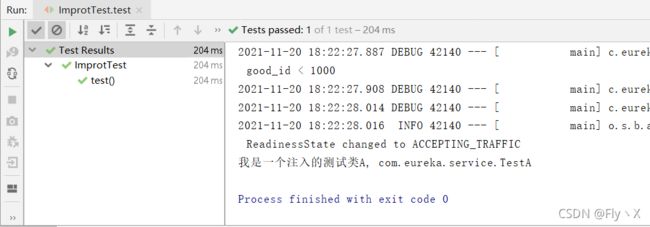
System.out.println("我是一个注入的测试类A, " + TestA.class.getName());
}
}
测试:
@SpringBootTest
public class ImprotTest {
@Autowired
private TestA testA;
@Test
public void test() {
testA.printName();
}
}
3.2 导入ImportSelector实现类测试
ImportSelector实现类如何导入bean,我们来分析下ImportSelector的源码
public interface ImportSelector {
/**
* Select and return the names of which class(es) should be imported based on
* the {@link AnnotationMetadata} of the importing @{@link Configuration} class.
* @return the class names, or an empty array if none
* 查询基于import导入Configuration 类的 AnnotationMetadata中需要导入的所有类的类全名
* 并返回这些类。
*/
String[] selectImports(AnnotationMetadata importingClassMetadata);
/**
* Return a predicate for excluding classes from the import candidates, to be
* transitively applied to all classes found through this selector's imports.
* If this predicate returns {@code true} for a given fully-qualified
* class name, said class will not be considered as an imported configuration
* class, bypassing class file loading as well as metadata introspection.
* @return the filter predicate for fully-qualified candidate class names
* of transitively imported configuration classes, or {@code null} if none
* @since 5.2.4
* 返回用于从导入候选中排除类的谓词,为传递地应用于通过此选择器的导入找到的所有类。
* 如果此谓词为给定的完全限定条件返回true,表示类不会被视为导入的配置类,绕过类文件
* 加载以及元数据内省。
*/
@Nullable
default Predicate<String> getExclusionFilter() {
return null;
}
}
通过ImportSelector 源码的描述翻译可以得知ImportSelector 类的通过 selectImports方法返回的一个类全名的数组,spring容器根据这些类全名查找这些类并注册为bean;如果需要还可以通过getExclusionFilter方法过滤 selectImports返回的不需要注册为bean的类全名
下面分别创建TestB和TestC以及ImportSelector实现类:
/**
* 测试类B
*/
public class TestB {
public void printInfo() {
System.out.println("我是一个注入的测试类B, " + TestA.class.getName());
}
}
/**
* 测试类C
*/
public class TestC {
public void printInfo() {
System.out.println("我是一个注入的测试类C, " + TestC.class.getName());
}
}
/**
* ImportSelector实现类
*/
public class SelfImportSelector implements ImportSelector {
@Override
public String[] selectImports(AnnotationMetadata annotationMetadata) {
return new String[]{"com.eureka.service.TestC","com.eureka.service.TestB"};
}
}
/**
* ImportConfig 配置类
*/
@Configuration
@Import({SelfImportSelector.class})
public class ImportConfig {
}
测试:
@SpringBootTest
public class ImprotTest {
@Autowired
private TestB testB;
@Autowired
private TestC testC;
@Test
public void test1() {
testB.printInfo();
testC.printInfo();
}
}
3.3 导入ImportBeanDefinitionRegistrar实现类
ImportBeanDefinitionRegistrar实现类如何导入bean,我们来分析ImportBeanDefinitionRegistrar的源码
public interface ImportBeanDefinitionRegistrar {
/**
* Register bean definitions as necessary based on the given annotation metadata of
* the importing {@code @Configuration} class.
* Note that {@link BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor} types may not be
* registered here, due to lifecycle constraints related to {@code @Configuration}
* class processing.
*
The default implementation delegates to
* {@link #registerBeanDefinitions(AnnotationMetadata, BeanDefinitionRegistry)}.
* @param importingClassMetadata annotation metadata of the importing class
* @param registry current bean definition registry
* @param importBeanNameGenerator the bean name generator strategy for imported beans:
* {@link ConfigurationClassPostProcessor#IMPORT_BEAN_NAME_GENERATOR} by default, or a
* user-provided one if {@link ConfigurationClassPostProcessor#setBeanNameGenerator}
* has been set. In the latter case, the passed-in strategy will be the same used for
* component scanning in the containing application context (otherwise, the default
* component-scan naming strategy is {@link AnnotationBeanNameGenerator#INSTANCE}).
* @since 5.2
* @see ConfigurationClassPostProcessor#IMPORT_BEAN_NAME_GENERATOR
* @see ConfigurationClassPostProcessor#setBeanNameGenerator
*/
default void registerBeanDefinitions(AnnotationMetadata importingClassMetadata, BeanDefinitionRegistry registry,
BeanNameGenerator importBeanNameGenerator) {
registerBeanDefinitions(importingClassMetadata, registry);
}
/**
* Register bean definitions as necessary based on the given annotation metadata of
* the importing {@code @Configuration} class.
* Note that {@link BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor} types may not be
* registered here, due to lifecycle constraints related to {@code @Configuration}
* class processing.
*
The default implementation is empty.
* @param importingClassMetadata annotation metadata of the importing class
* @param registry current bean definition registry
*/
default void registerBeanDefinitions(AnnotationMetadata importingClassMetadata, BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) {
}
}
根据源码可知 registerBeanDefinitions(AnnotationMetadata importingClassMetadata, BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) 方法的参数BeanDefinitionRegistry 来注册一个bean对象,我们可以通过将需要注册为bean的类封装成一个BeanDefinition对象交由BeanDefinitionRegistry对象来处理,同时还可以为该类配置相应的属性,此操作相当于spring xml中的bean标签内的所有配置
下面分别创建 DefaultTestService类 和 ImportTestService类 以及 ImportBeanDefinitionRegistrar 实现类 SelfImportBeanDefinitionRegistrar
/**
* TestService接口类
*/
public interface TestService {
void printInfo();
}
/**
* TestService实现类DefaultTestService
*/
public class DefaultTestService implements TestService {
private String beanName;
private String beanType;
private Integer beanTime;
@Override
public void printInfo() {
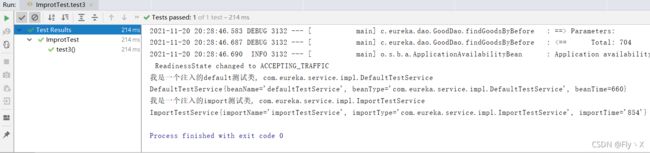
System.out.println("我是一个注入的default测试类, " + DefaultTestService.class.getName());
}
...getter setter略...
@Override
public String toString() {
return "DefaultTestService{" +
"beanName='" + beanName + '\'' +
", beanType='" + beanType + '\'' +
", beanTime=" + beanTime +
'}';
}
}
/**
* TestService实现类ImportTestService
*/
public class ImportTestService implements TestService {
private String importName;
private String importType;
private String importTime;
@Override
public void printInfo() {
System.out.println("我是一个注入的import测试类, " + ImportTestService.class.getName());
}
...getter setter略...
@Override
public String toString() {
return "ImportTestService{" +
"importName='" + importName + '\'' +
", importType='" + importType + '\'' +
", importTime='" + importTime + '\'' +
'}';
}
}
public class SelfImportBeanDefinitionRegistrar implements ImportBeanDefinitionRegistrar {
@Override
public void registerBeanDefinitions(AnnotationMetadata importingClassMetadata, BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) {
// 创建DefaultTestService类的BeanDefinition对象
RootBeanDefinition root = new RootBeanDefinition(DefaultTestService.class);
MutablePropertyValues mpv = root.getPropertyValues();
// 给DefaultTestService类设置属性
mpv.addPropertyValue("beanName", "defaultTestService");
mpv.addPropertyValue("beanType", DefaultTestService.class.getTypeName());
mpv.addPropertyValue("beanTime", (int)(Math.random()*1000 + 200));
// 创建ImportTestService类的BeanDefinition对象
RootBeanDefinition root1 = new RootBeanDefinition(ImportTestService.class);
MutablePropertyValues mpv1 = root1.getPropertyValues();
// 给ImportTestService类设置属性
mpv1.addPropertyValue("importName", "importTestService");
mpv1.addPropertyValue("importType", ImportTestService.class.getTypeName());
mpv1.addPropertyValue("importTime", (int)(Math.random()*1000 + 200));
registry.registerBeanDefinition("defaultTestService", root);
registry.registerBeanDefinition("importTestService", root1);
}
}
/**
* ImportConfig 配置类
*/
@Configuration
@Import({SelfImportBeanDefinitionRegistrar.class})
public class ImportConfig {
}
测试类:
@SpringBootTest
public class ImprotTest {
@Resource(name = "defaultTestService")
private TestService defaultTestService;
@Resource(name = "importTestService")
private TestService importTestService;
@Test
public void test3() {
defaultTestService.printInfo();
System.out.println(defaultTestService.toString());
importTestService.printInfo();
System.out.println(importTestService.toString());
}
}