【Python入门第二十九天】Python RegEx
RegEx 或正则表达式是形成搜索模式的字符序列。
RegEx 可用于检查字符串是否包含指定的搜索模式。
RegEx 模块
Python 提供名为 re 的内置包,可用于处理正则表达式。
导入 re 模块:
import re
Python 中的 RegEx
导入 re 模块后,就可以开始使用正则表达式了:
实例
检索字符串以查看它是否以 “China” 开头并以 “country” 结尾:
import re
txt = "China is a great country"
x = re.search("^China.*country$", txt)
运行实例
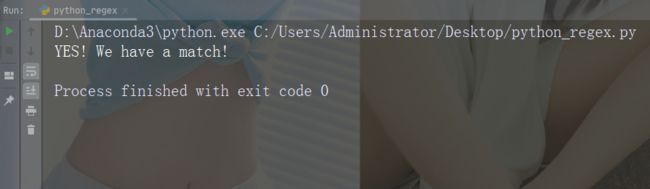
import re
txt = "China is a great country"
x = re.search("^China.*country$", txt)
if (x):
print("YES! We have a match!")
else:
print("No match")
RegEx 函数
re 模块提供了一组函数,允许我们检索字符串以进行匹配:
元字符
元字符是具有特殊含义的字符
字符:[]
描述:一组字符
示例:“[a-m]”
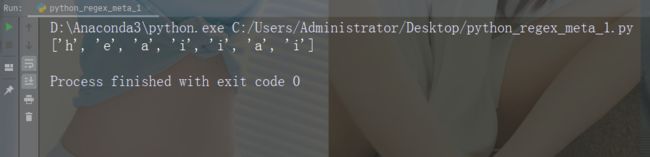
import re
str = "The rain in Spain"
#Find all lower case characters alphabetically between "a" and "m":
x = re.findall("[a-m]", str)
print(x)
运行示例
字符:
描述:示意特殊序列(也可用于转义特殊字符)
示例:“\d”
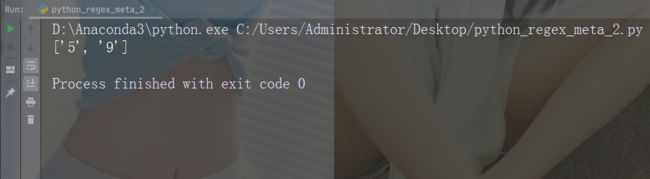
import re
str = "That will be 59 dollars"
#Find all digit characters:
x = re.findall("\d", str)
print(x)
运行示例
字符:.
描述:任何字符(换行符除外)
示例: “he…o”
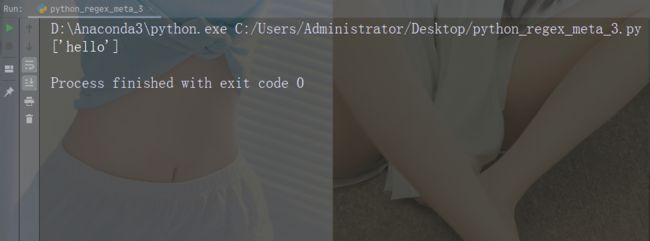
import re
str = "hello world"
#Search for a sequence that starts with "he", followed by two (any) characters, and an "o":
x = re.findall("he..o", str)
print(x)
运行示例
字符:^
描述:起始于
示例: “^hello”
import re
str = "hello world"
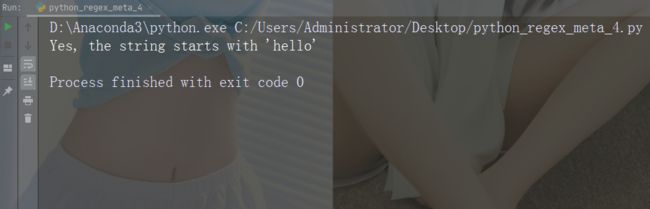
#Check if the string starts with 'hello':
x = re.findall("^hello", str)
if (x):
print("Yes, the string starts with 'hello'")
else:
print("No match")
运行示例
字符:$
描述:结束于
示例:“world$”
import re
str = "hello world"
#Check if the string ends with 'world':
x = re.findall("world$", str)
if (x):
print("Yes, the string ends with 'world'")
else:
print("No match")
运行示例
字符:*
描述:零次或多次出现
示例:“aix*”
import re
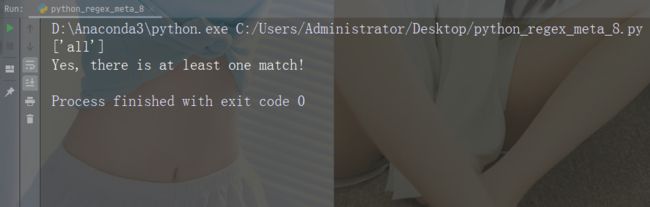
str = "The rain in Spain falls mainly in the plain!"
#Check if the string contains "ai" followed by 0 or more "x" characters:
x = re.findall("aix*", str)
print(x)
if (x):
print("Yes, there is at least one match!")
else:
print("No match")
运行示例
字符:+
描述:一次或多次出现
示例: “aix+”
import re
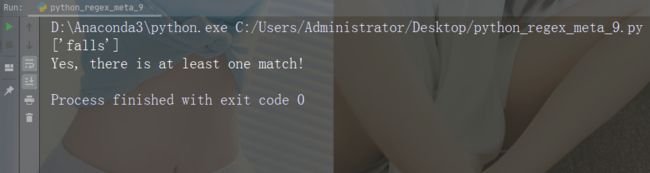
str = "The rain in Spain falls mainly in the plain!"
#Check if the string contains "ai" followed by 1 or more "x" characters:
x = re.findall("aix+", str)
print(x)
if (x):
print("Yes, there is at least one match!")
else:
print("No match")
运行示例
字符:{}
描述: 确切地指定的出现次数
示例:“al{2}”
import re
str = "The rain in Spain falls mainly in the plain!"
#Check if the string contains "a" followed by exactly two "l" characters:
x = re.findall("al{2}", str)
print(x)
if (x):
print("Yes, there is at least one match!")
else:
print("No match")
运行示例
字符:|
描述:两者任一
示例:“falls|stays”
import re
str = "The rain in Spain falls mainly in the plain!"
#Check if the string contains either "falls" or "stays":
x = re.findall("falls|stays", str)
print(x)
if (x):
print("Yes, there is at least one match!")
else:
print("No match")
运行示例
字符:()
描述:捕获和分组
特殊序列
特殊序列指的是 \ 后跟下表中的某个字符,拥有特殊含义。
字符:\A
描述:如果指定的字符位于字符串的开头,则返回匹配项
示例:“\AThe”
import re
str = "The rain in Spain"
#Check if the string starts with "The":
x = re.findall("\AThe", str)
print(x)
if (x):
print("Yes, there is a match!")
else:
print("No match")
运行示例
字符:\b
描述:返回指定字符位于单词的开头或末尾的匹配项
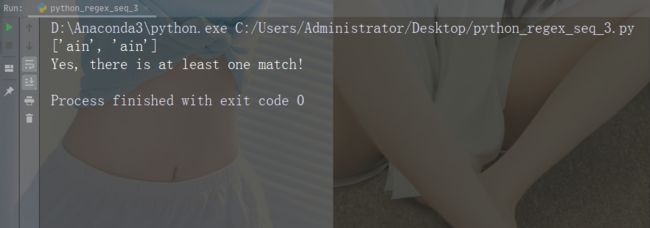
示例:r"\bain"
import re
str = "The rain in Spain"
#Check if "ain" is present at the beginning of a WORD:
x = re.findall(r"\bain", str)
print(x)
if (x):
print("Yes, there is at least one match!")
else:
print("No match")
运行示例
import re
str = "The rain in Spain"
#Check if "ain" is present at the end of a WORD:
x = re.findall(r"ain\b", str)
print(x)
if (x):
print("Yes, there is at least one match!")
else:
print("No match")
运行示例
字符:\B
描述:返回指定字符存在的匹配项,但不在单词的开头(或结尾处)
示例:r"\Bain"
import re
str = "The rain in Spain"
#Check if "ain" is present, but NOT at the beginning of a word:
x = re.findall(r"\Bain", str)
print(x)
if (x):
print("Yes, there is at least one match!")
else:
print("No match")
运行示例
示例:r"ain\B"
import re
str = "The rain in Spain"
#Check if "ain" is present, but NOT at the end of a word:
x = re.findall(r"ain\B", str)
print(x)
if (x):
print("Yes, there is at least one match!")
else:
print("No match")
运行示例
字符:\d
描述:返回字符串包含数字的匹配项(数字 0-9)
示例:“\d”
import re
str = "The rain in Spain"
#Check if the string contains any digits (numbers from 0-9):
x = re.findall("\d", str)
print(x)
if (x):
print("Yes, there is at least one match!")
else:
print("No match")
运行示例
字符:\D
描述:返回字符串不包含数字的匹配项
示例:“\D”
import re
str = "The rain in Spain"
#Return a match at every no-digit character:
x = re.findall("\D", str)
print(x)
if (x):
print("Yes, there is at least one match!")
else:
print("No match")
运行示例
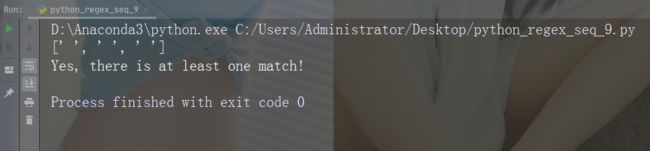
字符:\s
描述:返回字符串包含空白字符的匹配项
示例:“\s”
import re
str = "The rain in Spain"
#Return a match at every white-space character:
x = re.findall("\s", str)
print(x)
if (x):
print("Yes, there is at least one match!")
else:
print("No match")
运行示例
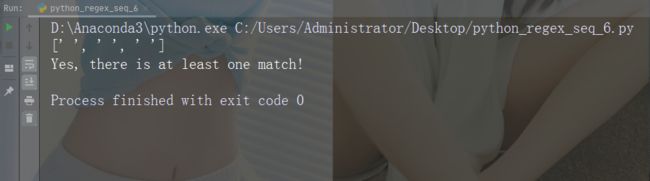
字符:\S
描述:返回字符串不包含空白字符的匹配项
示例:“\S”
import re
str = "The rain in Spain"
#Return a match at every NON white-space character:
x = re.findall("\S", str)
print(x)
if (x):
print("Yes, there is at least one match!")
else:
print("No match")
运行示例
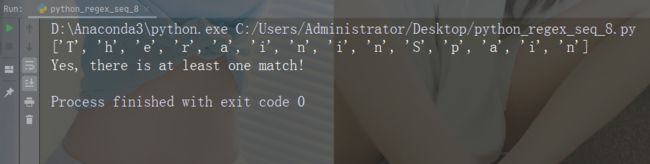
字符:\w
描述: 返回一个匹配项,其中字符串包含任何单词字符
(从 a 到 Z 的字符,从 0 到 9 的数字和下划线 _ 字符)
示例:“\w”
import re
str = "The rain in Spain"
#Return a match at every word character (characters from a to Z, digits from 0-9, and the underscore _ character):
x = re.findall("\w", str)
print(x)
if (x):
print("Yes, there is at least one match!")
else:
print("No match")
运行示例
字符:\W
描述:返回一个匹配项,其中字符串不包含任何单词字符
示例:“\W”
import re
str = "The rain in Spain"
#Return a match at every NON word character (characters NOT between a and Z. Like "!", "?" white-space etc.):
x = re.findall("\W", str)
print(x)
if (x):
print("Yes, there is at least one match!")
else:
print("No match")
运行示例
字符:\Z
描述:如果指定的字符位于字符串的末尾,则返回匹配项 。
示例:“Spain\Z”
import re
str = "The rain in Spain"
#Check if the string ends with "Spain":
x = re.findall("Spain\Z", str)
print(x)
if (x):
print("Yes, there is a match!")
else:
print("No match")
运行示例
集合(Set)
集合(Set)是一对方括号 [] 内的一组字符,具有特殊含义。
字符:[arn]
描述:返回一个匹配项,其中存在指定字符(a,r 或 n)之一
示例
import re
str = "The rain in Spain"
#Check if the string has any a, r, or n characters:
x = re.findall("[arn]", str)
print(x)
if (x):
print("Yes, there is at least one match!")
else:
print("No match")
运行示例
字符:[a-n]
描述:返回字母顺序 a 和 n 之间的任意小写字符匹配项
示例
import re
str = "The rain in Spain"
#Check if the string has any characters between a and n:
x = re.findall("[a-n]", str)
print(x)
if (x):
print("Yes, there is at least one match!")
else:
print("No match")
运行示例
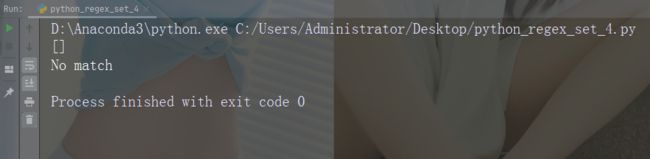
字符:[^arn]
描述:返回除 a、r 和 n 之外的任意字符的匹配项
示例
import re
str = "The rain in Spain"
#Check if the string has other characters than a, r, or n:
x = re.findall("[^arn]", str)
print(x)
if (x):
print("Yes, there is at least one match!")
else:
print("No match")
运行示例
字符:[0123]
描述:返回存在任何指定数字(0、1、2 或 3)的匹配项
示例
import re
str = "The rain in Spain"
#Check if the string has any 0, 1, 2, or 3 digits:
x = re.findall("[0123]", str)
print(x)
if (x):
print("Yes, there is at least one match!")
else:
print("No match")
运行示例
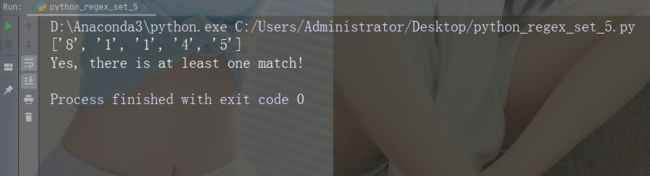
字符:[0-9]
描述:返回 0 与 9 之间任意数字的匹配
示例
import re
str = "8 times before 11:45 AM"
#Check if the string has any digits:
x = re.findall("[0-9]", str)
print(x)
if (x):
print("Yes, there is at least one match!")
else:
print("No match")
运行示例
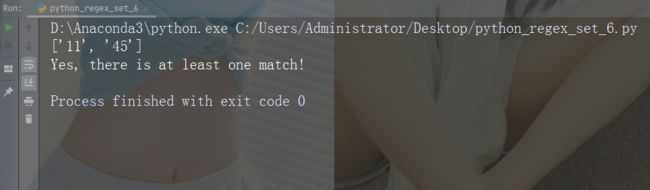
字符:[0-5][0-9]
描述:返回介于 0 到 9 之间的任何数字的匹配项
示例
import re
str = "8 times before 11:45 AM"
#Check if the string has any two-digit numbers, from 00 to 59:
x = re.findall("[0-5][0-9]", str)
print(x)
if (x):
print("Yes, there is at least one match!")
else:
print("No match")
运行示例
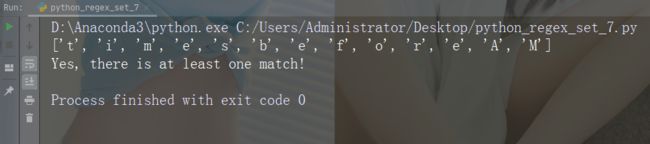
字符:[a-zA-Z]
描述:返回字母顺序 a 和 z 之间的任何字符的匹配,小写或大写
示例
import re
str = "8 times before 11:45 AM"
#Check if the string has any characters from a to z lower case, and A to Z upper case:
x = re.findall("[a-zA-Z]", str)
print(x)
if (x):
print("Yes, there is at least one match!")
else:
print("No match")
运行示例
字符:[+]
描述:在集合中,+、*、.、|、()、$、{} 没有特殊含义,因此 [+] 表示:返回字符串中任何 + 字符的匹配项。
示例
import re
str = "8 times before 11:45 AM"
#Check if the string has any + characters:
x = re.findall("[+]", str)
print(x)
if (x):
print("Yes, there is at least one match!")
else:
print("No match")
运行示例
findall() 函数
findall() 函数返回包含所有匹配项的列表。
实例
打印所有匹配的列表
import re
str = "China is a great country"
x = re.findall("a", str)
print(x)
运行实例
这个列表以被找到的顺序包含匹配项。
如果未找到匹配项,则返回空列表。
实例
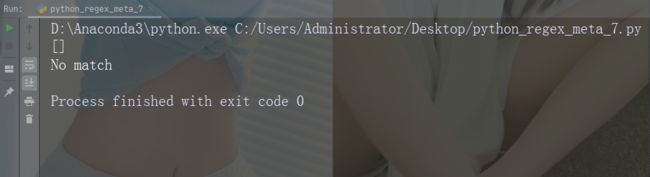
如果未找到匹配,则返回空列表:
import re
str = "China is a great country"
x = re.findall("USA", str)
print(x)
运行实例
search() 函数
search() 函数搜索字符串中的匹配项,如果存在匹配则返回 Match 对象。
如果有多个匹配,则仅返回首个匹配项。
实例
在字符串中搜索第一个空白字符
import re
str = "China is a great country"
x = re.search("\s", str)
print("The first white-space character is located in position:", x.start())
运行实例
如果未找到匹配,则返回值 None:
实例
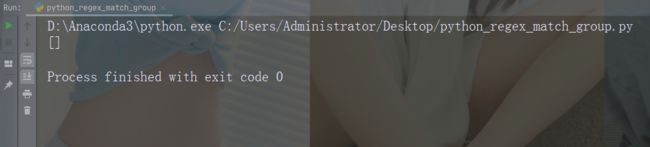
进行不返回匹配的检索
import re
str = "China is a great country"
x = re.search("USA", str)
print(x)
运行实例
split() 函数
split() 函数返回一个列表,其中字符串在每次匹配时被拆分。
实例
在每个空白字符处进行拆分
import re
str = "China is a great country"
x = re.split("\s", str)
print(x)
运行实例
可以通过指定 maxsplit 参数来控制出现次数:
实例
仅在首次出现时拆分字符串:
import re
str = "China is a great country"
x = re.split("\s", str, 1)
print(x)
运行实例
sub() 函数
sub() 函数把匹配替换为您选择的文本
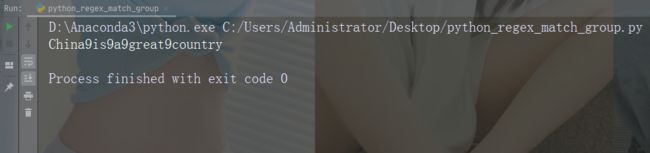
实例
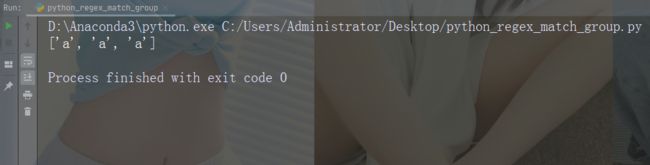
用数字 9 替换每个空白字符
import re
str = "China is a great country"
x = re.sub("\s", "9", str)
print(x)
运行实例
可以通过指定 count 参数来控制替换次数:
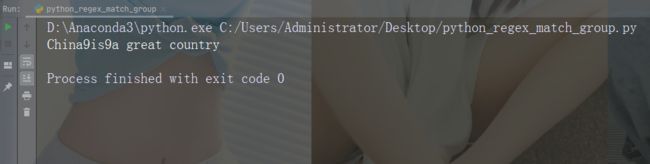
实例
替换前两次出现
import re
str = "China is a great country"
x = re.sub("\s", "9", str, 2)
print(x)
运行实例
Match 对象
Match 对象是包含有关搜索和结果信息的对象。
注释:如果没有匹配,则返回值 None,而不是 Match 对象。
实例
执行会返回 Match 对象的搜索:
import re
str = "China is a great country"
x = re.search("a", str)
print(x) # 将打印一个对象
运行实例
Match 对象提供了用于取回有关搜索及结果信息的属性和方法:
span()返回的元组包含了匹配的开始和结束位置.string返回传入函数的字符串group()返回匹配的字符串部分
实例
打印首个匹配出现的位置(开始和结束位置)。
正则表达式查找以大写 “C” 开头的任何单词:
import re
str = "China is a great country"
x = re.search(r"\bC\w+", str)
print(x.span())
运行实例
实例
打印传入函数的字符串
import re
str = "China is a great country"
x = re.search(r"\bC\w+", str)
print(x.string)
运行实例
实例
打印匹配的字符串部分
正则表达式查找以大写 “C” 开头的任何单词:
import re
str = "China is a great country"
x = re.search(r"\bC\w+", str)
print(x.group())
运行实例
注释:如果没有匹配项,则返回值 None,而不是 Match 对象。
文章不理解?我还录制了专门的Python基础全套视频讲解,直接在下方名片领取。