第17章Linux 音频设备驱动之Linux ALSA 音频设备驱动(一)
17.4 Linux ALSA 音频设备驱动
17.4.1 ALSA 的组成
虽然 OSS 已经非常成熟,但OSS是一个没有完全开放源代码的商业产品,而且目前基本上在 Linux mainline 中失去了更新。 ALSA (Advanced Linux Sound Architecture)恰好弥补这一空白,ALSA符合 GPL,是在 Linux 下进行音频编程时另一种可供选择的声卡驱动体系结构。ALSA 除了像 OSS 提供一组内核驱动程序模块之外,还专门为简化应用程序的编写提供相应的函数库,与 OSS 提供的基于 ioctl 的原始编程接口相比,ALSA 函
数库使用起来更加方便。ALSA 的主要特点如下。
1)支持多种声卡设备
2)模块化的内核驱动程序
3)支持 SMP 和多线程
4)提供应用开发函数库(alsa-lib)以简化应用程序开发
5)支持 OSS API,兼容 OSS 应用程序
ALSA 具友好的编程接口,并且完全兼容OSS,对应用程序员来讲是一个更佳的选择。ALSA 系统包括驱动包 alsa-driver、开发包 alsa-libs、开发包插件 alsa-libplugins、设置管理工具包 alsa-utils、其他声音相关处理小程序包 alsa-tools、特殊音频固件支持包 alsa- firmware、OSS 接口兼容模拟层工具 alsa-oss 共 7 个子项目,其中只有驱动包是必需的。
alsa-driver 指内核驱动程序,包括硬件相关的代码和一些公共代码,非常庞大,代码总量达数十万行;alsa-libs 指用户空间的函数库,提供给应用程序使用,应用程序应包含头文件asoundlib.h,并使用共享库 libasound.so;alsa-utils 包含一些基于 ALSA 的用于控制声卡的应用程序,如 alsaconf(侦测系统中声卡并写一个适合的 ALSA 配置文件)、alsactl(控制 ALSA 声卡驱动的高级设置)、alsamixer (基于窗口菜单 ncurses 的混音器程序)、amidi (用于读写 ALSA RawMIDI)、amixer(ALSA 声卡混音器的命令行控制)、aplay(基于命令行的声音文件播放)、arecord(基于命令行的声音文件录制)等。
目前 ALSA 内核提供给用户空间的接口有:
信息接口(Information Interface,/proc/asound)
控制接口(Control Interface,/dev/snd/controlCX)
混音器接口(Mixer Interface,/dev/snd/mixerCXDX)
PCM 接口(PCM Interface,/dev/snd/pcmCXDX)
Raw 迷笛接口(Raw MIDI Interface,/dev/snd/midiCXDX)
音序器接口(Sequencer Interface,/dev/snd/seq)
定时器接口(Timer Interface,/dev/snd/timer)
和 OSS 类似,上述接口也以文件的方式被提供,不同的是这些接口被提供给 alsa-lib 使用,不是直接给应用程序使用的。应用程序最好使用 alsa-lib,或者更高级的接口,比如 jack 提供的接口。
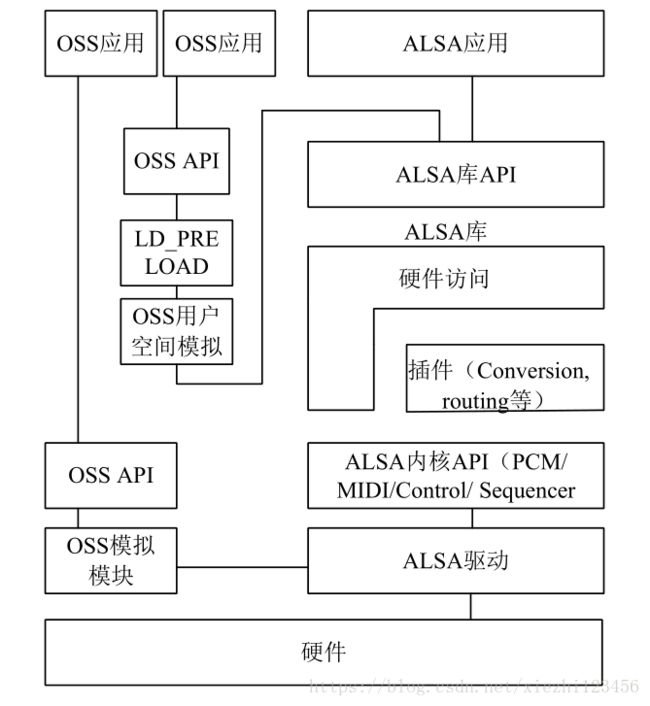
图17.6所示为ALSA声卡驱动与用户空间体系结构的简图,从中可以看出 ALSA 内核驱动与用户空间库及 OSS 之间的关系。
17.6 ALSA 体系结构
17.4.2 card 和组件
对于每个声卡,必须创建一个 card 实例。card 是声卡的“总部”,它管理这个声卡上的所有设备(组件),如 PCM、mixers、MIDI、synthesizer(合成器) 等。因此,card 和组件是 ALSA 声卡驱动中的主要组成元素。
1.创建 card
struct snd_card *snd_card_new(int idx, const char *xid, struct module *module, int extra_size);
idx :card 索引号
xid :标识字符串
module: 一般为 THIS_MODULE
extra_size :要分配的额外数据的大小,分配的 extra_size 大小的内存将作为 card->private_data
2.创建组件
int snd_device_new(struct snd_card *card, snd_device_type_t type, void *device_data,
struct snd_device_ops *ops);
当 card 被创建后,设备(组件)能够被创建并关联于该 card。
第 1 个参数card是 snd_card_new()创建的 card 指针
第 2 个参数 type 指的是 device-level 即设备类型,形式为 SNDRV_DEV_XXX,包括 SNDRV_DEV_CODEC、SNDRV_DEV_CONTROL、SNDRV_DEV_PCM、SNDRV_DEV_RAWMIDI 等,用户自定义设备的 device-level 是 SNDRV_DEV_LOWLEVEL,ops 参数是 1 个函数集(定义为 snd_device_ops 结构体)的指针,device_data 是设备数据指针,注意函数 snd_device_new()本身不会分配设备数据的内存,因此应事先分配。
3.组件释放
每个ALSA 预定义的组件在构造时需调用创建组件snd_device_new()函数,而每个组件的析构方法则在函数集中被包含。对于PCM、AC97 此类预定义组件,不需关心它们的析构,而对于自定义的组件,则需要填充 snd_device_ops 中的析构函数指针 dev_free,这样,当 snd_card_free()被调用时,组件将自动被释放。
4.芯片特定的数据(Chip-Specific Data)
芯片特定的数据一般以 struct xxxchip 结构体形式组织,这个结构体中包含芯片相关的 I/O 端口地址、资源指针、中断号等,其意义等同于字符设备驱动中的 file->private_data。
定义芯片特定的数据主要有两种方法,一种方法是将sizeof(struct xxxchip)传入snd_card_new()作为 extra_size 参数,它将自动成为 snd_card 的 private_data 成员,如代码清单 17.5 所示。
代码清单 17.5 创建芯片特定的数据方法 1
/* 芯片特定的数据结构体 */
struct xxxchip {
...
};
/* 创建声卡并申请 xxxchip 内存作为 card-> private_data */
card = snd_card_new(index, id, THIS_MODULE, sizeof(struct xxxchip));
struct xxxchip *chip = card->private_data;
另一种方法是在 snd_card_new()传入给 extra_size 参数 0,再分配 sizeof(struct xxxchip)的内存,将分配内
存的地址传入 snd_device_new()的 device_data 的参数,如代码清单 17.6 所示。
代码清单 17.6 创建芯片特定的数据方法 2
struct snd_card *card;
struct xxxchip *chip;
/* 使用 0 作为第 4 个参数,并动态分配 xxx_chip 的内存*/
card = snd_card__new(index[dev], id[dev], THIS_MODULE, 0);
...
chip = kzalloc(sizeof(*chip), GFP_KERNEL);
/* 在 xxxchip 结构体中,应该包括声卡指针*/
struct xxxchip {
struct snd_card *card;
...
};
/* 并将其 card 成员赋值为 snd_card_new()创建的 card 指针*/
chip->card = card;
static struct snd_device_ops ops = {
. dev_free = snd_xxx_chip_dev_free, /* 组件析构*/
};
...
/* 创建自定义组件*/
snd_device_new(card, SNDRV_DEV_LOWLEVEL, chip, &ops);
/* 在析构函数中释放 xxxchip 内存*/
static int snd_xxx_chip_dev_free(struct snd_device *device)
{
return snd_xxx_chip_free(device->device_data); /* 释放*/
}
5.注册/释放声卡
当 snd_card 被准备好以后,可使用 snd_card_register()函数注册这个声卡,如下所示:
int snd_card_register(struct snd_card *card);
对应的 snd_card_free()完成相反的功能,如下所示:
int snd_card_free(struct snd_card *card);
17.4.3 PCM 设备
每个声卡最多可以有 4 个 PCM(脉冲编码调制) 实例,一个 PCM 实例对应一个设备文件。PCM 实例由 PCM播放和录音流组成,而每个 PCM 流又由一个或多个 PCM 子流组成。有的声卡支持多重播放功能。
1.PCM 实例构造
int snd_pcm_new(struct snd_card *card, char *id, int device, int playback_count, int capture_count,
struct snd_pcm ** rpcm);
第 1 个参数是 card 指针,第 2 个是标识字符串,第 3 个是 PCM 设备索引(0 表示第 1 个 PCM设备),第 4 和第 5 个分别为播放和录音设备的子流数。当存在多个子流时,需要恰当地处理 open()、close()和其他函数。在每个回调函数中,可以通过 snd_pcm_substream 的 number 成员得知目前操作的是哪个子流,如下所示:
struct snd_pcm_substream *substream;
int index = substream->number;
一种习惯的做法是在驱动中定义一个 PCM“构造函数”,负责 PCM 实例的创建,如代码清单 17.7所示。
代码清单 17.7 PCM 设备的“构造函数”
static int _ _devinit snd_xxxchip_new_pcm(struct xxxchip *chip)
{
struct snd_pcm *pcm;
int err;
/* 创建 PCM 实例 */
if ((err = snd_pcm_new(chip->card, "xxx Chip", 0, 1, 1, &pcm)) < 0)
return err;
/* 置 pcm->private_data 为芯片特定数据*/
strcpy(pcm->name, "xxx Chip");
chip->pcm = pcm;
...
return 0;
}
2.设置 PCM 操作
include/sound/pcm.h
void snd_pcm_set_ops(struct snd_pcm *pcm, int direction, struct snd_pcm_ops *ops);
sound/core/pcm_lib.c
/**
* snd_pcm_set_ops - set the PCM operators
* @pcm: the pcm instance
* @direction: stream direction, SNDRV_PCM_STREAM_XXX
* @ops: the operator table
*
* Sets the given PCM operators to the pcm instance.
*/
void snd_pcm_set_ops(struct snd_pcm *pcm, int direction,
const struct snd_pcm_ops *ops)
{
struct snd_pcm_str *stream = &pcm->streams[direction];
struct snd_pcm_substream *substream;
for (substream = stream->substream; substream != NULL; substream = substream->next)
substream->ops = ops;
}
EXPORT_SYMBOL(snd_pcm_set_ops);
第 1 个参数是 snd_pcm 的指针,第 2 个参数是 SNDRV_PCM_STREAM_PLAYBACK 或
SNDRV_PCM_STREAM_CAPTURE,第 3 个参数是 PCM 操作结构体 snd_pcm_ops,这个结构体的定义
如代码清单 17.8 所示。
代码清单 17.8 snd_pcm_ops 结构体
include/sound/pcm.h
struct snd_pcm_ops {
int (*open)(struct snd_pcm_substream *substream);
int (*close)(struct snd_pcm_substream *substream);
int (*ioctl)(struct snd_pcm_substream * substream,
unsigned int cmd, void *arg);
int (*compat_ioctl)(struct snd_pcm_substream *substream,
unsigned int cmd, void *arg);
int (*hw_params)(struct snd_pcm_substream *substream,
struct snd_pcm_hw_params *params);
int (*hw_free)(struct snd_pcm_substream *substream);/* 资源释放*/
int (*prepare)(struct snd_pcm_substream *substream);
/* 在 PCM 被开始、停止或暂停时调用*/
int (*trigger)(struct snd_pcm_substream *substream, int cmd);
/ * 当前缓冲区的硬件位置*/
int (*delay_blk)(struct snd_pcm_substream *substream);
int (*wall_clock)(struct snd_pcm_substream *substream, struct timespec *audio_ts);
/* 缓冲区复制*/
void __user *buf, snd_pcm_uframes_t count);
int (*silence)(struct snd_pcm_substream *substream, int channel,
snd_pcm_uframes_t pos, snd_pcm_uframes_t count);
struct page *(*page)(struct snd_pcm_substream *substream,
unsigned long offset);
int (*mmap)(struct snd_pcm_substream *substream, struct vm_area_struct *vma);
int (*ack)(struct snd_pcm_substream *substream);
int (*restart)(struct snd_pcm_substream *substream);
};
备注:
snd_pcm_ops 中的所有操作都需事先通过 snd_pcm_substream_chip()获得 xxxchip (芯片特定的数据结构体)指针,例如:
int xxx()
{
struct xxxchip *chip = snd_pcm_substream_chip(substream);
...
}
当一个 PCM 子流被打开时,snd_pcm_ops 中的 open()函数将被调用,在这个函数中,至少需要初始化 runtime->hw 字段,代码清单 17.9 所示为 open()函数的范例。
代码清单 17.9 snd_pcm_ops 结构体中的 open()函数
static int snd_xxx_open(struct snd_pcm_substream *substream)
{
/* 从子流获得 xxxchip 指针*/struct xxxchip *chip = snd_pcm_substream_chip(substream);
/* 获得 PCM 运行时信息指针*/
struct snd_pcm_runtime *runtime = substream->runtime;
...
/* 初始化 runtime->hw */
runtime->hw = snd_xxxchip_playback_hw;
return 0;}
分析:
snd_xxxchip_playback_hw 是预先定义的硬件描述。在 open()函数中,可以分配一段私有数据。如果硬件配置需要更多的限制,也需设置硬件限制。
当 PCM 子流被关闭时,close()函数将被调用。如果 open()函数中分配了私有数据,则在 close()函数中应该释放 substream 的私有数据,代码清单 17.10 所示为 close()函数的范例。
代码清单 17.10 snd_pcm_ops 结构体中的 close()函数
static int snd_xxx_close(struct snd_pcm_substream *substream)
{
/* 释放子流私有数据*/
kfree(substream->runtime->private_data);
...
}
驱动中通常可以给 snd_pcm_ops 的 ioctl()传递通用的 snd_pcm_lib_ioctl()函数。
snd_pcm_ops 的 hw_params()在应用程序设置硬件参数(PCM 子流的周期大小、缓冲区大小和格式等)时被调用,它的形式如下:
static int snd_xxx_hw_params(struct snd_pcm_substream *substream,
struct snd_pcm_hw_params *hw_params);
在这个函数中,将完成大量硬件设置,甚至包括缓冲区分配,这时可调用如下辅助函数:
snd_pcm_lib_malloc_pages(substream, params_buffer_bytes(hw_params));
仅当 DMA 缓冲区已被预先分配的情况下,上述调用才可成立。
与 hw_params()对应的函数是 hw_free(),它释放由 hw_params()分配的资源,例如,通过如下调用释放 snd_pcm_lib_malloc_pages()缓冲区:snd_pcm_lib_free_pages(substream);
当 PCM 被“准备”时,prepare()函数将被调用,在其中设置采样率、格式等。prepare()函数与 hw_params()函数的不同在于对 prepare()的调用发生在 snd_pcm_prepare()每次被调用的时候。prepare()的形式如下:
static int snd_xxx_prepare(struct snd_pcm_substream *substream);
trigger()成员函数在 PCM 被开始、停止或暂停时调用,函数的形式如下:
static int snd_xxx_trigger(struct snd_pcm_substream *substream, int cmd);
cmd 参数定义具体的行为,在 trigger()成员函数中至少要处理 SNDRV_PCM_TRIGGER_START 和 SNDRV_PCM_TRIGGER_STOP 命令,如果 PCM 支持暂停,还应处理 SNDRV_PCM_TRIGGER_PAUSE_PUSH 和 SNDRV_PCM_TRIGGER_PAUSE_RELEASE 命令。如果设备支持挂起/恢复,当能量管理状态发生变化时将处理 SNDRV_PCM_TRIGGER_SUSPEND 和 SNDRV_PCM_TRIGGER_RESUME 这两个命令。
分析:
trigger()函数是原子的,中途不能睡眠。代码清单 17.11所示为 trigger()函数的范例。
代码清单 17.11 snd_pcm_ops 结构体中的 trigger()函数
static int snd_xxx_trigger(struct snd_pcm_substream *substream, int cmd)
{
switch (cmd) {
case SNDRV_PCM_TRIGGER_START:
/* 开启 PCM 引擎*/
break;
case SNDRV_PCM_TRIGGER_STOP:
/* 停止 PCM 引擎*/
break;
... /* 其他命令*/
default:
return - EINVAL;
}
}
pointer()函数用于 PCM 中间层查询目前缓冲区的硬件位置,该函数以帧的形式返回 0~buffer_size – 1 的位置,此函数也是原子的。
copy()和 silence()函数一般可以省略,但是,当硬件缓冲区不处于常规内存中时需要。例如,一些设备有自己的不能被映射的硬件缓冲区,这种情况下,将数据从内存缓冲区复制到硬件缓冲区。当内存缓冲区在物理和虚拟地址上都不连续时,这两个函数也必须被实现。
3.分配缓冲区
分配缓冲区的最简单方法是调用如下函数:
include/sound/pcm.h
int snd_pcm_lib_preallocate_pages_for_all(struct snd_pcm *pcm, int type, void *data, size_t size,
size_t max);
type 参数是缓冲区的类型,包含 SNDRV_DMA_TYPE_UNKNOWN(未知)、
SNDRV_DMA_TYPE_CONTINUOUS(连续的非 DMA 内存)、SNDRV_DMA_TYPE_DEV(连续的通用设备),SNDRV_DMA_TYPE_DEV_SG(通用设备SG-buffer)和SNDRV_DMA_TYPE_SBUS (连续的SBUS)。
如下代码将分配 64KB 的缓冲区:
snd_pcm_lib_preallocate_pages_for_all(pcm,SNDRV_DMA_TYPE_DEV,snd_dma_pci_data(chip->pci), 64*1024, 64*1024);
sound/core/pcm_memory.c
/**
* snd_pcm_lib_preallocate_pages_for_all - pre-allocation for continous memory type (all substreams)
* @pcm: the pcm instance
* @type: DMA type (SNDRV_DMA_TYPE_*)
* @data: DMA type dependant data
* @size: the requested pre-allocation size in bytes
* @max: the max. allowed pre-allocation size
*
* Do pre-allocation to all substreams of the given pcm for the
* specified DMA type.
*
* Returns zero if successful, or a negative error code on failure.
*/
int snd_pcm_lib_preallocate_pages_for_all(struct snd_pcm *pcm,
int type, void *data,
size_t size, size_t max)
{
struct snd_pcm_substream *substream;
int stream, err;
for (stream = 0; stream < 2; stream++)
for (substream = pcm->streams[stream].substream; substream; substream = substream->next)
if ((err = snd_pcm_lib_preallocate_pages(substream, type, data, size, max)) < 0)
return err;
return 0;
}
EXPORT_SYMBOL(snd_pcm_lib_preallocate_pages_for_all);
4.设置标志
在构造 PCM 实例、设置操作集并分配缓冲区之后,如果有需要,应设置 PCM 的信息标志,例如,如果 PCM 设备只支持半双工,则定义标志:
pcm->info_flags = SNDRV_PCM_INFO_HALF_DUPLEX;
5.PCM 实例析构
PCM 实例的“析构函数”并非是必须的,因为 PCM 实例会被 PCM 中间层代码自动释放,如果驱动中分配了一些特别的内存空间,则必须定义“析构函数”,代码清单 17.12 所示为 PCM“析构函数”与对应的“构造函数”,“析构函数”会释放“构造函数”中创建的 xxx_private__pcm_data。
代码清单 17.12 PCM 设备“析构函数”
static void xxxchip_pcm_free(struct snd_pcm *pcm)
{
/* 从 pcm 实例指针得到 chip指针(芯片特定的数据结构体) */
struct xxxchip *chip = snd_pcm_chip(pcm);
/* 释放自定义用途的内存 */
kfree(chip->xxx_private_pcm_data);
...
}
static int __devinit snd_xxxchip_new_pcm(struct xxxchip *chip)
{
struct snd_pcm *pcm;
...
/* 分配自定义用途的内存 */
chip->xxx_private_pcm_data = kmalloc(...);
pcm->private_data = chip; // 给 PCM 实例赋予的 xxxchip 指针
/* 设置“析构函数” */
pcm->private_free = xxxchip_pcm_free;
...
}
6.PCM 信息运行时结构体
当 PCM 子流被打开后,PCM 运行时实例(定义为结构体 snd_pcm_runtime,如代码清单 17.13所示)将被分配给这个子流,这个指针通过 substream->runtime 获得。运行时指针包含各种各样的信息:hw_params 及 sw_params 配置的拷贝、缓冲区指针、mmap 记录、自旋锁等,几乎 PCM的所有控制信息均能从中取得。
代码清单 17.13 snd_pcm_runtime 结构体
include/sound/pcm.h
struct snd_pcm_runtime {
/* -- Status -- */
struct snd_pcm_substream *trigger_master;
struct timespec trigger_tstamp; /* trigger timestamp */
int overrange;
snd_pcm_uframes_t avail_max;
snd_pcm_uframes_t hw_ptr_base; /* Position at buffer restart */
snd_pcm_uframes_t hw_ptr_interrupt; /* Position at interrupt time*/
/* -- HW params -- */
snd_pcm_access_t access; /* access mode */
snd_pcm_format_t format; /* SNDRV_PCM_FORMAT_* */
snd_pcm_subformat_t subformat; /* subformat */
unsigned int rate; /* rate in Hz */
unsigned int channels; /* channels */
snd_pcm_uframes_t period_size; /* period size */
unsigned int periods; /* periods */
snd_pcm_uframes_t buffer_size; /* buffer size */
unsigned int tick_time; /* tick time */
snd_pcm_uframes_t min_align; /* Min alignment for the format */
size_t byte_align;
unsigned int frame_bits;
unsigned int sample_bits;
unsigned int info;
unsigned int rate_num;
unsigned int rate_den;
/* -- SW params -- */
int tstamp_mode; /* mmap timestamp is updated */
unsigned int period_step;
unsigned int sleep_min; /* min ticks to sleep */
snd_pcm_uframes_t xfer_align; /* xfer size need to be a multiple */
snd_pcm_uframes_t start_threshold;
snd_pcm_uframes_t stop_threshold;
snd_pcm_uframes_t silence_threshold; /* Silence filling happens when
noise is nearest than this */
snd_pcm_uframes_t silence_size; /* Silence filling size */
snd_pcm_uframes_t boundary; /* pointers wrap point */
snd_pcm_uframes_t silence_start; /* starting pointer to silence area */
snd_pcm_uframes_t silence_filled; /* size filled with silence */
union snd_pcm_sync_id sync; /* hardware synchronization ID */
/* -- mmap -- */
volatile struct snd_pcm_mmap_status *status;
volatile struct snd_pcm_mmap_control *control;
/* -- locking / scheduling -- */
wait_queue_head_t sleep;
struct timer_list tick_timer;
struct fasync_struct *fasync;
/* -- private section -- */
void *private_data;
void (*private_free)(struct snd_pcm_runtime *runtime);
/* -- hardware description -- */
struct snd_pcm_hardware hw;
struct snd_pcm_hw_constraints hw_constraints;
/* -- interrupt callbacks -- */
void (*transfer_ack_begin)(struct snd_pcm_substream *substream);
void (*transfer_ack_end)(struct snd_pcm_substream *substream);
/* -- timer -- */
unsigned int timer_resolution; /* timer resolution */
/* -- DMA -- */
unsigned char *dma_area; /* DMA area */
dma_addr_t dma_addr; /* physical bus address (not accessible from main CPU) */
size_t dma_bytes; /* size of DMA area */
struct snd_dma_buffer *dma_buffer_p; /* allocated buffer */
#if defined(CONFIG_SND_PCM_OSS) || defined(CONFIG_SND_PCM_OSS_MODULE)
/* -- OSS things -- */
struct snd_pcm_oss_runtime oss;
#endif
};
分析:
snd_pcm_runtime 中的大多数记录对被声卡驱动操作集中的函数是只读的,仅仅 PCM(脉冲编码调制) 中间层可从更新或修改这些信息,但是硬件描述、中断回调函数、DMA 缓冲区信息和私有数据是例外的。
下面解释 snd_pcm_runtime 结构体中的几个重要成员。
(1)硬件描述。
硬件描述(snd_pcm_hardware 结构体)包含了基本硬件配置的定义,需要在 open()函数中赋值。runtime 实例保存的是硬件描述的拷贝,这意味着在 open()函数中可以修改被拷贝的描述(runtime->hw),例如:
struct snd_pcm_runtime *runtime = substream->runtime;
...runtime->hw = snd_xxchip_playback_hw; /* generic 的硬件描述 */
/* 特定的硬件描述 */
if (chip->model == VERY_OLD_ONE)
runtime->hw.channels_max = 1;
snd_pcm_hardware 结构体的定义如代码清单 17.14 所示。
代码清单 17.14 snd_pcm_hardware 结构体
/*
* Hardware (lowlevel) section
*/
struct snd_pcm_hardware {
unsigned int info; /* SNDRV_PCM_INFO_* */
u64 formats; /* SNDRV_PCM_FMTBIT_* */
unsigned int rates; /* SNDRV_PCM_RATE_* */
unsigned int rate_min; /* min rate */
unsigned int rate_max; /* max rate */
unsigned int channels_min; /* min channels */
unsigned int channels_max; /* max channels */
size_t buffer_bytes_max; /* max buffer size */
size_t period_bytes_min; /* min period size */
size_t period_bytes_max; /* max period size */
unsigned int periods_min; /* 最小周期数 */
unsigned int periods_max; /* 最大周期数 */
size_t fifo_size; /* FIFO 字节数 */
};
分析:
snd_pcm_hardware 结构体中的 info 字段标识 PCM 设备的类型和能力,形式为 SNDRV_PCM_INFO_XXX。
info 字段至少需要定义是否支持 mmap,当支持时,应设置 SNDRV_PCM_INFO_MMAP标志;当硬件支持 interleaved 或 non-interleaved 格式时,应设置 SNDRV_PCM_INFO _INTERLEAVED
或 SNDRV_PCM_INFO_NONINTERLEAVED 标志;如果都支持,则两者都可设置。
MMAP_VALID 和 BLOCK_TRANSFER 标志针对 OSS(Open Sound System) mmap,只有 mmap 被真正支持时,才可设置 MMAP_VALID;SNDRV_PCM_INFO_PAUSE 意味着设备可支持暂停操作,
SNDRV_PCM_INFO_RESUME 意味着设备可支持挂起/恢复操作;当 PCM 子流能被同步,如同步播放和录音流的 start/stop,可设置 SNDRV_PCM_INFO_SYNC_START 标志。
formats 包含 PCM 设备支持的格式,形式为 SNDRV_PCM_FMTBIT_XXX,如果设备支持多种模式,应将各种模式标志进行“或”操作。
rates 包含了 PCM 设备支持的采样率,形式如 SNDRV_PCM_RATE_XXX,如果支持连续的采样率,则传递 CONTINUOUS。
rate_min 和 rate_max 分别定义了最小和最大的采样率,注意:要与 rates 字段相符。
channels_min 和 channels_max 定义了最小和最大的通道数量。
buffer_bytes_max 定义最大的缓冲区大小,注意:没有 buffer_bytes_min 字段,这是因为它可以通过最小的周期大小和最小的周期数量计算出来。
period 信息与 OSS 中的 fragment 对应,定义了 PCM(脉冲编码调制) 中断产生的周期。更小的周期大小意味着更多的中断,在录音时,周期大小定义了输入延迟,在播放时,整个缓冲区大小对应着输出延迟。
PCM 可被应用程序通过 alsa-lib 发送 hw_params 来配置,配置信息将保存在运行时实例中。对缓冲区和周期大小的配置以帧形式存储,而 frames_to_bytes()和 bytes_to_frames()可完成帧和字节的转换,如:
period_bytes = frames_to_bytes(runtime, runtime->period_size);(2)DMA 缓冲区信息。
包含 dma_area(逻辑地址)、dma_addr(物理地址)、dma_bytes(缓冲区大小)和 dma_private(被 ALSA DMA 分配器使用)。可以由 snd_pcm_lib_malloc_pages()实现,ALSA 中间层会设置 DMA缓冲区信息的相关字段,这种情况下,驱动中不能再写这些信息,只能读取。也就是说,如果使用标准的缓冲区分配函数 snd_pcm_lib_malloc_pages()分配缓冲区,则不需要自己维护 DMA缓冲区信息。如果缓冲区由自己分配,则需要在 hw_params()函数中管理缓冲区信息,至少需管理dma_bytes 和 dma_addr,如果支持 mmap,则必须管理 dma_area,对 dma_private 的管理视情况而定。
(3)运行状态。
通过 runtime->status 可以获得运行状态,它是 snd_pcm_mmap_status 结构体的指针,例如,通过 runtime->status->hw_ptr 可以获得目前的 DMA 硬件指针。
include/sound/asound.h
struct snd_pcm_mmap_status {
snd_pcm_state_t state; /* RO: state - SNDRV_PCM_STATE_XXXX */
int pad1; /* Needed for 64 bit alignment */
snd_pcm_uframes_t hw_ptr; /* RO: hw ptr (0...boundary-1) */
struct timespec tstamp; /* Timestamp */
snd_pcm_state_t suspended_state; /* RO: suspended stream state */
};
此外,通过 runtime->control 可以获得 DMA 应用指针,它指向 snd_pcm_mmap_control 结构体指针,但是不建议直接访问该指针。
include/sound/asound.h
struct snd_pcm_mmap_control {
snd_pcm_uframes_t appl_ptr; /* RW: appl ptr (0...boundary-1) */
snd_pcm_uframes_t avail_min; /* RW: min available frames for wakeup */
};
(4)私有数据。
驱动中可以为子流分配一段内存并赋值给 runtime->private_data,注意不要与 pcm->private_data 混淆,后者一般指向 xxxchip,而前者是在 PCM 设备的 open()函数中分配的动态数据,例如:
static int snd_xxx_open(struct snd_pcm_substream *substream)
{
struct xxx_pcm_data *data;
....
data = kmalloc(sizeof(*data), GFP_KERNEL);
substream->runtime->private_data = data; /* 赋值 runtime->private_data */
....
}
(5)中断回调函数:
transfer_ack_begin()和transfer_ack_end()函数分别在snd_pcm_period_elapsed()的开始和结束时被调用。
根据以上分析,代码清单 17.15 给出了一个完整的 PCM 设备接口模板。
代码清单 17.15 PCM 设备接口模板
#include
....
/* 播放设备硬件定义 */
static struct snd_pcm_hardware snd_xxxchip_playback_hw = {
.info = (SNDRV_PCM_INFO_MMAP | SNDRV_PCM_INFO_INTERLEAVED |
SNDRV_PCM_INFO_BLOCK_TRANSFER | SNDRV_PCM_INFO_MMAP_VALID),
.formats = SNDRV_PCM_FMTBIT_S16_LE,
.rates = SNDRV_PCM_RATE_8000_48000,
.rate_min = 8000,
.rate_max = 48000,
.channels_min = 2,
.channels_max = 2,
.buffer_bytes_max = 32768,
.period_bytes_min = 4096,
.period_bytes_max = 32768,
.periods_min = 1,
.periods_max = 1024,
};
/* 录音设备硬件定义 */
static struct snd_pcm_hardware snd_xxxchip_capture_hw = {
.info = (SNDRV_PCM_INFO_MMAP | SNDRV_PCM_INFO_INTERLEAVED |
SNDRV_PCM_INFO_BLOCK_TRANSFER | SNDRV_PCM_INFO_MMAP_VALID),
.formats = SNDRV_PCM_FMTBIT_S16_LE,
.rates = SNDRV_PCM_RATE_8000_48000,
.rate_min = 8000,
.rate_max = 48000,
.channels_min = 2,
.channels_max = 2,
.buffer_bytes_max = 32768,
.period_bytes_min = 4096,
.period_bytes_max = 32768,
.periods_min = 1,
.periods_max = 1024,
};
/* 播放:打开函数 */
static int snd_xxxchip_playback_open(struct snd_pcm_substream*substream)
{
struct xxxchip *chip = snd_pcm_substream_chip(substream);
struct snd_pcm_runtime *runtime = substream->runtime;
runtime->hw = snd_xxxchip_playback_hw;
... /* 硬件初始化代码*/
return 0;
}
/* 播放:关闭函数 */
static int snd_xxxchip_playback_close(struct snd_pcm_substream*substream)
{
struct xxxchip *chip = snd_pcm_substream_chip(substream);
/* 硬件相关的代码*/
return 0;
}
/* 录音:打开函数 */
static int snd_xxxchip_capture_open(struct snd_pcm_substream*substream)
{
struct xxxchip *chip = snd_pcm_substream_chip(substream);
struct snd_pcm_runtime *runtime = substream->runtime;
runtime->hw = snd_xxxchip_capture_hw;
... /* 硬件初始化代码*/
return 0;
}
/* 录音:关闭函数 */
static int snd_xxxchip_capture_close(struct snd_pcm_substream*substream)
{
struct xxxchip *chip = snd_pcm_substream_chip(substream);
... /* 硬件相关的代码*/
return 0;
}
/* hw_params 函数 */
static int snd_xxxchip_pcm_hw_params(struct snd_pcm_substream*substream, struct
snd_pcm_hw_params *hw_params)
{
return snd_pcm_lib_malloc_pages(substream, params_buffer_bytes(hw_params));
}
/* hw_free 函数 */
static int snd_xxxchip_pcm_hw_free(struct snd_pcm_substream*substream)
{
return snd_pcm_lib_free_pages(substream);
}
/* prepare 函数 */
static int snd_xxxchip_pcm_prepare(struct snd_pcm_substream*substream)
{
struct xxxchip *chip = snd_pcm_substream_chip(substream);
struct snd_pcm_runtime *runtime = substream->runtime;
/* 根据目前的配置信息设置硬件
* 例如:
*/
xxxchip_set_sample_format(chip, runtime->format);
xxxchip_set_sample_rate(chip, runtime->rate);
xxxchip_set_channels(chip, runtime->channels);
xxxchip_set_dma_setup(chip, runtime->dma_addr, chip->buffer_size, chip->period_size);
return 0;
}
/* trigger 函数 */
static int snd_xxxchip_pcm_trigger(struct snd_pcm_substream*substream, int cmd)
{
switch (cmd) {
case SNDRV_PCM_TRIGGER_START:
/* do something to start the PCM engine */
break;
case SNDRV_PCM_TRIGGER_STOP:
/* do something to stop the PCM engine */
break;
default:
return - EINVAL;
}
}
/* pointer 函数 */
static snd_pcm_uframes_t snd_xxxchip_pcm_pointer(struct snd_pcm_substream *substream)
{
struct xxxchip *chip = snd_pcm_substream_chip(substream);
unsigned int current_ptr;
/*获得当前的硬件指针*/
current_ptr = xxxchip_get_hw_pointer(chip);
return current_ptr;
}
/* 放音设备操作集 */
static struct snd_pcm_ops snd_xxxchip_playback_ops = {
.open = snd_xxxchip_playback_open,
.close = snd_xxxchip_playback_close,
.ioctl = snd_pcm_lib_ioctl,
.hw_params = snd_xxxchip_pcm_hw_params,
.hw_free = snd_xxxchip_pcm_hw_free,
.prepare = snd_xxxchip_pcm_prepare,
.trigger = snd_xxxchip_pcm_trigger,
.pointer = snd_xxxchip_pcm_pointer,
};
/* 录音设备操作集 */
static struct snd_pcm_ops snd_xxxchip_capture_ops = {
.open = snd_xxxchip_capture_open,
.close = snd_xxxchip_capture_close,
.ioctl = snd_pcm_lib_ioctl,
.hw_params = snd_xxxchip_pcm_hw_params,
.hw_free = snd_xxxchip_pcm_hw_free,
.prepare = snd_xxxchip_pcm_prepare,
.trigger = snd_xxxchip_pcm_trigger,
.pointer = snd_xxxchip_pcm_pointer,
};
/* 创建一个 PCM 设备 */
static int _ _devinit snd_xxxchip_new_pcm(struct xxxchip *chip)
{
struct snd_pcm *pcm;
int err;
if ((err = snd_pcm_new(chip->card, "xxx Chip", 0, 1, 1, &pcm)) < 0)
return err;
pcm->private_data = chip;
strcpy(pcm->name, "xxx Chip");
chip->pcm = pcm;
/* 设置操作集 */
snd_pcm_set_ops(pcm, SNDRV_PCM_STREAM_PLAYBACK, &snd_xxxchip_playback_ops);
snd_pcm_set_ops(pcm, SNDRV_PCM_STREAM_CAPTURE, &snd_xxxchip_capture_ops);
/* 分配缓冲区 */
snd_pcm_lib_preallocate_pages_for_all(pcm, SNDRV_DMA_TYPE_DEV,
snd_dma_pci_data(chip - > pci), 64 *1024, 64 *1024);
return 0;
}