Servlet、ServletConfig、ServletContext、DispatcherServlet、ApplicationContext、WebApplicationContext区别?
文章目录
- Servlet
- ServletContext
- ServletConfig
- DispatcherServlet
- ApplicationContext
- WebApplicationContext
- 源码分析
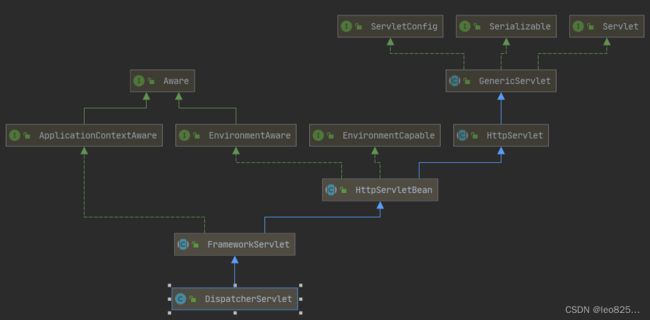
Servlet
Servlet: 是 Java 中的一个类,它被用来扩展服务器的性能,服务器上驻留着可以通过“请求-响应”编程模式来访问的应用程序。Tomcat 是 Web 应用服务器,一个 Servlet 容器,Tomcat 作为 Servlet 容器,负责处理客户端请求,把请求传给 Servlet ,并将 Servlet 的响应返回给客户端。简言之,Servlet 是一种运行在支持 Java 语言的服务器的组件。
ServletContext
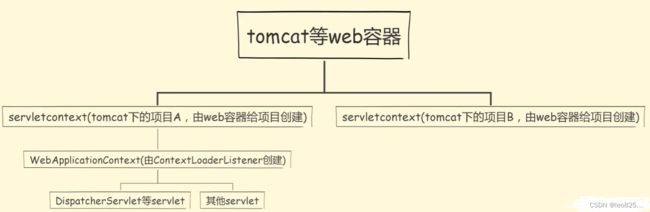
ServletContext: 这个是来自于servlet规范里的概念,它是servlet用来与容器间进行交互的接口的组合,也就是说,这个接口定义了一系列的方法,servlet通过这些方法可以很方便地与自己所在的容器进行一些交互,比如通过getMajorVersion与getMinorVersion来获取容器的版本信息等. 从它的定义中也可以看出,在一个应用中(一个JVM)只有一个ServletContext, 换句话说,容器中所有的servlet都共享同一个ServletContext。
<context-param>
<param-name>contextConfigLocationparam-name>
<param-value>classpath:applicationContext.xmlparam-value>
context-param>
<listener>
<listener-class>org.springframework.web.context.ContextLoaderListenerlistener-class>
listener>
ContextLoaderListener 里面的 initWebApplicationContext 就是初始化 WebApplicationContext,这个 context 其实就是 rootApplicationContext
public class ContextLoaderListener extends ContextLoader implements ServletContextListener {
public ContextLoaderListener() {
}
public ContextLoaderListener(WebApplicationContext context) {
super(context);
}
public void contextInitialized(ServletContextEvent event) {
this.initWebApplicationContext(event.getServletContext());
}
public void contextDestroyed(ServletContextEvent event) {
this.closeWebApplicationContext(event.getServletContext());
ContextCleanupListener.cleanupAttributes(event.getServletContext());
}
}
initWebApplicationContext 方法里面具体创建 WebApplicationContext 容器,其中 ROOT_WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE = WebApplicationContext.class.getName() + “.ROOT”。
public WebApplicationContext initWebApplicationContext(ServletContext servletContext) {
......
//主要代码,创建 WebApplicationContext 容器
this.context = this.createWebApplicationContext(servletContext);
......
// 配置参数并调用初始化方法
this.configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext(cwac, servletContext);
......
// 将 WebApplicationContext 容器作为一个属性放回到 ServletContext 容器中
servletContext.setAttribute(WebApplicationContext.ROOT_WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE, this.context);
.....
}
ServletConfig
ServletConfig: 它与 ServletContext 的区别在于,ServletConfig 是针对 Servlet 而言的,每个 Servlet 都有它独有的 ServeltConfig 信息,相互之间不共享。
/**
* Servlet配置对象: Servlet容器在初始化期间将信息传递给 Servlet
*/
public interface ServletConfig {
/**
* 返回此 Servlet 实例的名称
*/
String getServletName();
/**
* 获取 Servlet 上下文对象:ServletContext
*/
ServletContext getServletContext();
/**
* 根据名称获取参数值
*/
String getInitParameter(String var1);
/**
* 获取所有的参数名称
*/
Enumeration<String> getInitParameterNames();
}
DispatcherServlet
DispatcherServlet:本质上就是一个特殊的 Servlet , 由于 DispatcherServlet 继承自 FrameworkServlet ,因此这个方法在FrameworkServlet 中在 initServletBean 调用了 initWebApplicationContext 方法 ,通过这个方法首先获取了 rootContext 传入 wac ,从而 DispatcherServlet 里面的 WebApplicationContext 和 rootApplicationContext 构成父子关系。
ApplicationContext
ApplicationContext: 这个类是 Spring 实现容器功能的核心接口,它也是 Spring 实现 IoC 功能中最重要的接口,从它的名字中可以看出,它维护了整个程序运行期间所需要的上下文信息, 注意这里的应用程序并不一定是 web 程序,也可能是其它类型的应用。在 Spring 中允许存在多个applicationContext,这些context相互之间还形成了父与子,继承与被继承的关系,这也是通常我们所说的,在 Spring 中存在两个 Context ,一个是 root context ,一个是 servlet applicationContext 的意思. 这点后面会进一步阐述.
该接口具有三个常用的实现类:
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext:可以加载类路径下的配置文件,要求配置文件必须在类路径之下。FileSystemXmlApplicationContext:可以加载磁盘中任意路径下的配置文件,要求具有访问权限。AnnotationConfigApplicationContext:用于读取注解创建容器。
ApplicationContext 定义如下
public interface ApplicationContext extends EnvironmentCapable, ListableBeanFactory, HierarchicalBeanFactory, MessageSource, ApplicationEventPublisher, ResourcePatternResolver {
String getId();
String getApplicationName();
String getDisplayName();
long getStartupDate();
ApplicationContext getParent();
AutowireCapableBeanFactory getAutowireCapableBeanFactory() throws IllegalStateException;
}
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext 类图

WebApplicationContext
WebApplicationContext 继承 ApplicationContext、BeanFactory
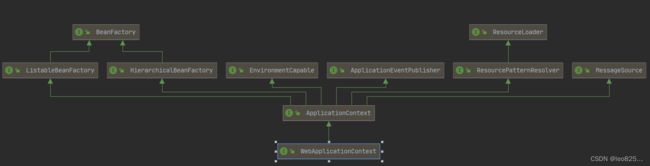
ApplicationContext和WebApplicationContext的区别,如下表所示:

源码分析
首先先来看 ServletContext 中的配置文件的加载过程. 这个过程是由 ContextLoaderListener 对象来完成的,因此我们找到相应的源码,去掉一些日志及不相关的源码后如下:
- 第一步是判断是否存在 RootApplicationContext,如果存在直接抛出异常结束
- 第二步是创建 Context 对象,并在 ServletContext 中把这个 Context 设置为名称为 ROOT_WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE 的属性. 到这里其实已经解释了 ApplicationContext 与 ServletContext 的区别,它不过是 ServletContext 中的一个属性值罢了,这个属性值中存有程序运行的所有上下文信息 由于这个 ApplicationContext 是全局的应用上下文信息,在 Spring 中就把它取名为 ’root application context’。
public WebApplicationContext initWebApplicationContext(ServletContext servletContext) {
if (servletContext.getAttribute(WebApplicationContext.ROOT_WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE) != null) {
}
try {
// Store context in local instance variable, to guarantee that
// it is available on ServletContext shutdown.
if (this.context == null) {
this.context = createWebApplicationContext(servletContext);
}
servletContext.setAttribute(WebApplicationContext.ROOT_WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE, this.context);
return this.context;
}
}
接着再来看DispatcherServlet的源码,作为servlet,根据规范它的配置信息应该是在Init方法中完成,因此我们找到这个方法的源码即可知道servletConfig以及servlet application context的初始化过程:
-
第一步是从 ServletConfig 中获取所有的配置参数, ServletConfigPropertyValues 的构造函数中会遍历 ServletConfig 对象的所有初始化参数,并把它们一一存储在 pvs 中;
-
第二步就是开始初始 Servlet ,由于 DispatcherServlet 是继承自 FrameworkServlet,因此这个方法在 FrameworkServlet 中找到,可以看到,在 initServletBean 中又调用了 initWebApplicationContext 方法,在这个方法中,首先获取到 rootContext , 接着就开始初始化 wac 这个对象,在创建这个 wac 对象的方法中,传入了 rootContext 作为它的 parent,也就是在这里,两者之间的父子关系建立,也就形成了我们平时常说的继承关系。
@Override
public final void init() throws ServletException {
// Set bean properties from init parameters.
PropertyValues pvs = new ServletConfigPropertyValues(getServletConfig(), this.requiredProperties);
// Let subclasses do whatever initialization they like.
initServletBean();
}
//遍历获取servletConfig的所有参数
public ServletConfigPropertyValues(ServletConfig config, Set<String> requiredProperties)
throws ServletException {
while (en.hasMoreElements()) {
String property = (String) en.nextElement();
Object value = config.getInitParameter(property);
addPropertyValue(new PropertyValue(property, value));
if (missingProps != null) {
missingProps.remove(property);
}
}
}
//初始化webApplicationContext
protected final void initServletBean() throws ServletException {
try {
this.webApplicationContext = initWebApplicationContext();
}
}
//具体的初始化操作实现
protected WebApplicationContext initWebApplicationContext() {
WebApplicationContext rootContext = WebApplicationContextUtils.getWebApplicationContext(getServletContext());
WebApplicationContext wac = null;
if (this.webApplicationContext != null) {
// A context instance was injected at construction time -> use it
wac = this.webApplicationContext;
if (wac instanceof ConfigurableWebApplicationContext) {
ConfigurableWebApplicationContext cwac = (ConfigurableWebApplicationContext) wac;
if (!cwac.isActive()) {
// The context has not yet been refreshed -> provide services such as
// setting the parent context, setting the application context id, etc
if (cwac.getParent() == null) {
// The context instance was injected without an explicit parent -> set
// the root application context (if any; may be null) as the parent
cwac.setParent(rootContext);
}
configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext(cwac);
}
}
}
if (wac == null) {
// No context instance was injected at construction time -> see if one
// has been registered in the servlet context. If one exists, it is assumed
// that the parent context (if any) has already been set and that the
// user has performed any initialization such as setting the context id
wac = findWebApplicationContext();
}
if (wac == null) {
// No context instance is defined for this servlet -> create a local one
//就是在这个方法中,servlet application context与root application context的继承关系正式建立
wac = createWebApplicationContext(rootContext);
}
if (this.publishContext) {
// Publish the context as a servlet context attribute.
String attrName = getServletContextAttributeName();
getServletContext().setAttribute(attrName, wac);
}
return wac;
}
//就是在这个方法中,servlet application context与root application context的继承关系正式建立
protected WebApplicationContext createWebApplicationContext(WebApplicationContext parent) {
return createWebApplicationContext((ApplicationContext) parent);
}