nginx七大核心应用场景详解 & 解决生产中的实际问题 & 二次开发扩展
nginx七大核心应用场景详解 & 解决生产中的实际问题
- 1、nginx的安装与简单配置
-
- 1.1、环境准备
- 1.2、nginx基本操作指令:
- 1.3、安装成系统服务
- 1.4、conf 配置文件说明
- 2、虚拟主机
-
- 2.1、nginx多主机配置
- 2.2、二级域名与短网址解析
- 3、基于反向代理的负载均衡
-
- 3.1、跳转到外部网站配置
- 3.2、跳转到局域网配置
- 3.3、负载均衡配置
- 3.4、负载均衡策略
-
- 3.4.1、轮询——weight(权重)
- 3.4.2、其他负载均衡策略
- 3.5、动静分离
-
- 3.5.1、动静分离原理
- 3.5.2、tomcat静态资源部署
- 3.5.3、nginx简单实现动静分离,
- 3.5.4、location的正则匹配
- 3.6、UrlRewrite
- 3.7、对资源机进行拦截
- 3.8、防盗链配置
- 4、HA高可用配置及解决方案
-
- 4.1、HA高可用原理(High Availability)
- 4.2、安装keepalived
- 4.3、Keepalived的选举机制和切换机制
- 5、HTTP协议配置
-
- 5.1、不安全的HTTP协议
- 5.2、CA认证
- 5.3、证书的安装
-
- 5.3.1、搭建一个网站
-
- 5.3.1.1、购买云服务器
- 5.3.1.2、购买域名
- 5.3.1.3、域名解析
- 5.3.2、安装证书到nginx
- 6、nginx优化——扩容
-
- 6.1、单机垂直扩容
- 6.2、水平扩展:集群化
-
- 6.2.1、ipHash维持会话
- 6.2.2、$request_uri维持会话
- 6.2.3、$cookie_jsessionid维持会话
- 6.2.4、使用sticky模块完成对Nginx的负载均衡
- 6.3、Keepalive
-
- 6.3.1、在浏览器中查看是否启用keepalive
- 6.3.2、抓包——charles
- 6.3.3、keepalive配置
- 6.3.4、apache-benchmark压力测试
- 6.3.5、nginx反向代理tomcat性能提升
- 6.4、Nginx反向代理核心流程
-
- 6.4.1、proxy_pass工作流程
- 6.4.2、获取真实的IP
- 6.5、服务端优化
-
-
- 6.5.1、Gzip压缩
- 6.5.2、gzip相关配置(Gzip动态压缩)
- 6.5.3、Gzip静态压缩
- 6.5.4、第三方zip模块Brotli与模块化加载
- 6.5.5、合并请求
-
- 6.6、资源静态化
-
- 6.6.1、ngx_http_ssi_module模块解决资源静态化
- 6.6.2、rsync资源同步
-
- 6.6.2.1、rsync 是什么
- 6.6.2.2、安装与简单使用 rsync 进行文件同步
- 6.6.2.3、安全认证以及免密登录
- 6.6.2.4、rsync 常用选项
- 6.6.2.5、安装inotify
- 6.6.2.6、inotify 配合 rsync 进行文件同步
- 6.6.2.7、inotify 常用选项
- 6.7、多级缓存
-
- 6.7.1、强制缓存与协商缓存
- 6.7.2、浏览器强制缓存
- 6.7.3、浏览器缓存原则
- 6.7.4、DNS缓存
-
- 6.7.4.1、GEOip
- 6.7.5、正向代理与反向代理缓存
-
- 6.7.5.1、Proxy缓存
- 7、nginx优化——高效
-
- 7.1、Nginx内存缓存
- 7.2、Nginx外置缓存
-
- 7.2.1、error_page配置
- 7.2.2、匿名Location
-
- 7.2.2.1、匿名Location和Return
- 7.2.2.2、nginx + memcached
- 7.2.2.3、redis2-nginx-module
- 7.3、Stream模块
- 7.3.1、QPS限流
- 7.3.2、并发数限制
- 7.3.3、日志
- 7.4、重试机制
-
- 7.4.1、重试机制配置
- 7.4.2、主动健康检查
- 8、nginx二次开发
-
- 8.1、Lua基础
- 8.2、Openresty Nginx + Lua
- 8.3、测试lua脚本
-
- 8.3.1、hello world
- 8.3.2、热部署
- 8.3.3、Lua处理Http请求
- 8.4 OpenResty缓存
-
- 8.4.1、全局内存缓存
- 8.4.2、lua-resty-lrucache
- 8.4.3、连接redis
- 8.4.4、连接MySQL
- 8.4.5、模板引擎
- 8.5、基于OpenResty的开源项目
1、nginx的安装与简单配置
1.1、环境准备
首先需要安装nginx所需要的依赖:
- 安装pcre依赖,首先下载对应的gz文件,上传到centos当中进行解压
- 执行 /configure 完成后,回到 pcre 目录下执行 make,最后执行 make install
- 在这里可能回缺少包导致安装失败,只需要将缺少的包yum下载下来即可
随后安装其余 openssl 、zlib 、 gcc 依赖,就直接使用yum进行安装
yum -y install make zlib zlib-devel gcc-c++ libtool openssl openssl-devel
之后进行安装nginx,当官网进行下载gz文件,进行解压,解压后进入解压缩目录,执行./configure。而后执行 make 和 make install 最后进入目录 /usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx 启动服务
启动nginx报错:nginx: [emerg] bind() to 0.0.0.0:80 failed (98: Address already in use)
首先还是想到去查看是哪个端口占用了nginx默认80端口,通过命令
netstat -natp |grep 80
netstat 找不到命令即进行安装
yum install net-tools -y
找到对应的端口进行kill掉即可 或者进入到安装目录下/conf目录下的nginx.conf文件将默认端口进行修改
./nginx -c /tools/nginx/nginx-1.23.3/conf/nginx.conf
1.2、nginx基本操作指令:
启动服务:./nginx
退出服务:./nginx -s quit
强制关闭服务:./nginx -s stop
重载服务:./nginx -s reload (重载服务配置文件,类似于重启,但服务不会中止)
验证配置文件:./nginx -t
使用配置文件:./nginx -c "配置文件路径"
./nginx -c /tools/nginx/nginx/nginx-1.12.2/conf/nginx.conf
使用帮助:./nginx -h
查看状态 systemctl status nginx
启动 systemctl start nginx
开放默认端口号:
# 启动、关闭防火墙
systemctl start firewalld.service
# 查看开放的端口号
firewall-cmd --list-all
# 设置开放的端口号
firewall-cmd --add-service=http –permanent
firewall-cmd --add-port=81/tcp --permanent
# 重启防火墙
firewall-cmd --reload
之后就可以直接使用ip进行访问了。查看nginx状态报错:systemctl status nginx --- Unit nginx.service could not be found. 错误的原因就是没有添加nginx服务,在/root/etc/init.d/目录下新建文件,文件名为nginx,插入以下代码,只需要对本机nginx的配置文件所在地址进行调整即可。
. /etc/rc.d/init.d/functions
. /etc/sysconfig/network
[ "$NETWORKING" = "no" ] && exit 0
nginx="/usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx"
prog=$(basename $nginx)
# nginx配置文件地址
NGINX_CONF_FILE="/tools/nginx/nginx/nginx-1.12.2/conf/nginx.conf"
lockfile=/var/lock/subsys/nginx
start() {
[ -x $nginx ] || exit 5
[ -f $NGINX_CONF_FILE ] || exit 6
echo -n $"Starting $prog: "
daemon $nginx -c $NGINX_CONF_FILE
retval=$?
echo
[ $retval -eq 0 ] && touch $lockfile
return $retval
}
stop() {
echo -n $"Stopping $prog: "
killproc $prog -QUIT
retval=$?
echo
[ $retval -eq 0 ] && rm -f $lockfile
return $retval
}
restart() {
configtest || return $?
stop
start
}
reload() {
configtest || return $?
echo -n $"Reloading $prog: "
killproc $nginx -HUP
RETVAL=$?
echo
}
force_reload() {
restart
}
configtest() {
$nginx -t -c $NGINX_CONF_FILE
}
rh_status() {
status $prog
}
rh_status_q() {
rh_status >/dev/null 2>&1
}
case "$1" in
start)
rh_status_q && exit 0
$1
;;
stop)
rh_status_q || exit 0
$1
;;
restart|configtest)
$1
;;
reload)
rh_status_q || exit 7
$1
;;
force-reload)
force_reload
;;
status)
rh_status
;;
condrestart|try-restart)
rh_status_q || exit 0
;;
*)
echo $"Usage: $0 {start|stop|status|restart|condrestart|try-restart|reload|force-reload|configtest}"
exit 2
esac
1.3、安装成系统服务
创建服务脚本(如果存在该文件,直接覆盖内容即可或者进行备份一下)
vi /usr/lib/systemd/system/nginx.service
服务脚本内容:在这里需要注意的是:通过这种方式进行启动nginx是读取的/usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf配置文件,当然如果你需要使用安装目录下的配置文件,只需要将地址进行修改即可。
[Unit]
Description=nginx - web server
After=network.target remote-fs.target nss-lookup.target
[Service]
Type=forking
PIDFile=/usr/local/nginx/logs/nginx.pid
ExecStartPre=/usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx -t -c /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf
ExecStart=/usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx -c /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf
ExecReload=/usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx -s reload
ExecStop=/usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx -s stop
ExecQuit=/usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx -s quit
PrivateTmp=true
[Install]
WantedBy=multi-user.target
重新加载系统服务
systemctl daemon-reload
启动服务
systemctl start/status/stop/reload nginx.service
设置开机自启动
systemctl enable nginx.service
1.4、conf 配置文件说明
最小配置文件说明
# 默认为1,表示默认开启一个业务进程
worker_processes 1;
# 单个进程可连接服务数
events {
worker_connections 1024;
}
http {
# 引入mime.types类型,该文件与nginx配置文件同级,在配置文件同级下mime.types,文件内容表示,不同的文件类型响应的方式不同
include mime.types;
# 如果mime类型没匹配上,默认使用二进制流的方式传输。
default_type application/octet-stream;
# 高效网络传输 -- 数据0拷贝
sendfile on;
# 连接超时时间
keepalive_timeout 65;
server {
# 监听端口
listen 80;
# 主机名:这里在etc/host当中配置了localhost也就是127.0.0.1
server_name localhost;
location / {
root html;
index index.html index.htm;
}
error_page 500 502 503 504 /50x.html;
location = /50x.html {
root html;
}
}
}
2、虚拟主机
原本一台服务器只能对应一个站点,通过虚拟主机技术可以虚拟化成多个站点同时对外提供服务
在C:\Windows\System32\drivers\etc下hosts文件当中添加一个虚拟主机地址
192.168.60.128 lzq.com
2.1、nginx多主机配置
在配置文件当中我们复制一个server出来,将端口号修改为82,并且设置其对应的root指定的位置
server {
listen 82;
server_name localhost;
location / {
root html/www;
index index.html index.htm;
}
error_page 500 502 503 504 /50x.html;
location = /50x.html {
root html;
}
}
2.2、二级域名与短网址解析
3、基于反向代理的负载均衡
3.1、跳转到外部网站配置
在这里我们修改localtion的配置,这里跳转到外网不支持https协议,如果键入https协议的地址就会被直接重定向到目标地址
location / {
proxy_pass http://www.redis.cn/;
}
3.2、跳转到局域网配置
location / {
proxy_pass http://192.168.60.129/;
}
3.3、负载均衡配置
upstream load{
server 192.168.60.129:81;
server 192.168.60.130:81;
}
server {
listen 81;
server_name localdomain;
location / {
proxy_pass http://load;
}
}
3.4、负载均衡策略
3.4.1、轮询——weight(权重)
默认情况下使用轮询方式,逐一转发,
- down:表示当前的server暂时不参与负载
- weight:默认为1.weight越大,负载的权重就越大。
- backup: 其它所有的非backup机器down或者忙的时候,请求backup机器
upstream load{
server 192.168.60.129:81 weight=5 down;
server 192.168.60.130:81 weight=3;
server 192.168.60.131:81 weight=2 backup;
}
3.4.2、其他负载均衡策略
3.5、动静分离
3.5.1、动静分离原理
动静分离指的就是将部署在tomcat服务器(或目标服务器)上的静态资源进行抽离出来单独部署在nginx上,这样一个请求打过来,直接就可以通过nginx将静态资源(img/css/js/mp4)进行返回,而其他的动态请求再打到后续的tomcat等服务器上,这样也就降低了后续服务器的压力,也减少了网络传输下的大静态资源文件的压力
3.5.2、tomcat静态资源部署
首先我们需要部署一个tomcat,在tomcat下下载一个gz包,上传到服务器,进行解压,切入到bin目录下执行 ./startup.sh进行启动tomcat服务,同时在webapps下上传一个前端页面资源包,如上传一个叫login的包,这个时候我们只需要访问 虚拟机IP:tomcat端口/login即可访问到这个静态资源了。
3.5.3、nginx简单实现动静分离,
这里简单说明一下前端包的内容,login下存了一个index.html和一个static静态资源包(包含了css/img/js等)这时我们将tomcat下的该静态资源都删掉,这个时候访问tomcat的时候无法获取静态资源就会导致页面混乱。
而nginx动静分离就是用于处理这个的,我们在nginx下进行代理到目标tomcat的地址,这个时候将静态资源上传到nginx服务器上,添加配置如下即可实现动静分离,并且这个时候再访问nginx服务器,会转到tomcat地址,并且页面以及静态资源都可以完整的加载出来。
location / {
proxy_pass http://192.168.60.130:8081/login/;
}
location /static {
root html;
}
3.5.4、location的正则匹配
| 匹配符 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| / | 通用匹配,任何请求都会匹配到。 |
| = | 精准匹配,不是以指定模式开头 |
| ~ | 正则匹配,区分大小写 |
| ~* | 正则匹配,不区分大小写 |
| ^~ | 非正则匹配,匹配以指定模式开头的location |
匹配顺序
- 多个正则location直接按书写顺序匹配,成功后就不会继续往后面匹配
- 普通(非正则)location会一直往下,直到找到匹配度最高的(最大前缀匹配)
- 当普通location与正则location同时存在,如果正则匹配成功,则不会再执行普通匹配
- 所有类型location存在时,“=”匹配 > “^~”匹配 > 正则匹配 > 普通(最大前缀匹配)
3.6、UrlRewrite
rewrite是实现URL重写的关键指令,根据regex (正则表达式)部分内容,重定向到replacement,简单的来说就是对页面入参的隐藏,
首先在目标tomcat下覆盖默认的jsp,也就是在webapp/ROOT/index.jsp,简单编写一个jsp文件,用来获取页面的url传参
<%@ page language="java" contentType="text/html; charset=UTF-8" pageEncoding="UTF-8" %>
DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd">
<html>
<head>
<title>入参解析title>
head>
<body>
<%
out.println("获取入参");
out.println(request.getParameter("page"));
%>
body>
<script>
let page = window.location.search.substr(1).split('=')[1]
console.log('page = ', page)
script>
html>
这个时候我可以对该index.jsp进行验证,直接访问tomcat根地址并且附带参数,如:http://192.168.60.130:8081/?page=4可以看到在page的值改变之后,页面展示也会变化,而对于nginx服务机修改nginx配置,表示当访问nginx下的2.html页面的时候会转到index.jsp?page=2这个页面,这样也就实现了对入参的隐藏。
location / {
rewrite ^/2.html$ /index.jsp?page=2 break;
proxy_pass http://192.168.60.130:8081;
}
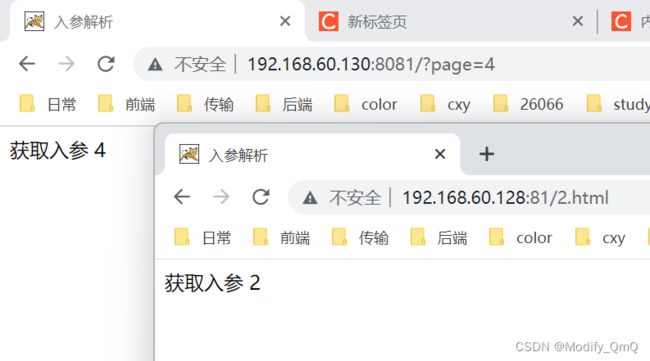
同理,这样对单个页面进行绑定肯定是不够的,所以这里还可以直接通过正则去进行匹配,如下:
location / {
rewrite ^/([0-9]+).html$ /index.jsp?page=$1 break;
proxy_pass http://192.168.60.130:8081;
}
flag标记说明
| flag标记 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| last | 本条规则匹配完成后,继续向下匹配新的location URI规则 |
| break | 本条规则匹配完成即终止,不再匹配后面的任何规则 |
| redirect | 返回302临时重定向,浏览器地址会显示跳转后的URL地址 |
| permanent | 返回301永久重定向,浏览器地址栏会显示跳转后的URL地址 |
3.7、对资源机进行拦截
我们现在配置了两台机器,一个是负载均衡nginx一个是tomcat服务器,这是如果我们想访问tomcat只能通过nginx进行反向代理才能进行访问,这个时候我们只需要打开tomcat机器防火墙以及对8081端口进行配置规则即可
# 开启防火墙
systemctl start firewalld
# 重载规则
firewall-cmd --reload
# 查看已有规则
firewall-cmd --list-all
# 指定端口和ip访问
firewall-cmd --permanent --add-rich-rule="rule family="ipv4" source address="192.168.60.128" port protocol="tcp" port="8081" accept"
# 移除规则
firewall-cmd --permanent --remove-rich-rule="rule family="ipv4" source address="192.168.60.128" port port="8081" protocol="tcp" accept"
3.8、防盗链配置
在我们现在的nginx当中有很多的静态资源,我们可以通过地址直接进行访问,如:http://192.168.60.128:81/static/img/in_top_bj1.jpg,但是我们只希望通过该ip才能进行访问并且返回,这个时候就需要使用到防盗链了。
在nginx当中加入配置,该表示只有通过128机器访问的静态资源才能被完整的返回,其他的将会被重定向到html/403.html
location ~*/(css|img|js) {
valid_referers 192.168.60.128;
if ($invalid_referer) {
# 或者将盗链请求转发给一张404.png的图片
# rewrite ^/ /static/img/404.jpg break;
return 403;
}
root html;
}
error_page 403 /403.html;
location = /403.html {
root html;
}
4、HA高可用配置及解决方案
4.1、HA高可用原理(High Availability)
4.2、安装keepalived
yum install -y keepalived
安装keepalived之后我们修改其对应的配置,配置文件存在 /etc/keepalived/keepalived.conf
! Configuration File for keepalived
global_defs {
# one 自己定义一个名称
router_id one
}
# one 自己定义一个名称
vrrp_instance one {
state MASTER
# ens160 这个对应自己虚拟机的网卡
interface ens160
virtual_router_id 51
priority 100
advert_int 1
authentication {
auth_type PASS
auth_pass 1111
}
# 使用到的虚拟ip,可以配置多个
virtual_ipaddress {
192.168.60.132
}
}
之后直接通过 systemctl start keepalived 命令进行启动
启动报错:pid 6465 exited with permanent error CONFIG. Terminating
查看对应的keepalived.service,发现没有keepalived.pid文件,将该文件添加到指定目录即可
[root@localhost keepalived]# cat /lib/systemd/system/keepalived.service
[Unit]
Description=LVS and VRRP High Availability Monitor
After=network-online.target syslog.target
Wants=network-online.target
[Service]
Type=forking
PIDFile=/var/run/keepalived.pid
KillMode=process
EnvironmentFile=-/etc/sysconfig/keepalived
ExecStart=/usr/sbin/keepalived $KEEPALIVED_OPTIONS
ExecReload=/bin/kill -HUP $MAINPID
[Install]
WantedBy=multi-user.target
[root@localhost keepalived]# cat /var/run/keepalived.pid
cat: /var/run/keepalived.pid: 没有那个文件或目录
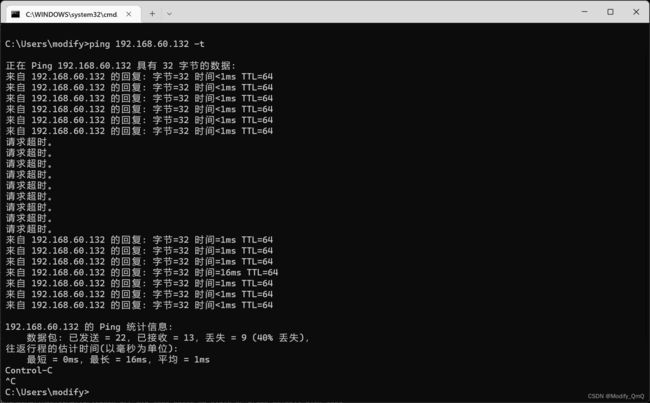
修改配置之后systemctl daemon-reload 重新载入之后再次重启即可,启动完成之后使用 ip addr 命令进行查看IP地址,在keepalived里面加入了一个192.168.60.132虚拟地址,可以看到132这个虚拟ip已经被添加进来了,这也就说明keepalived配置好了。
[root@localhost system]# ip addr
2: ens160: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 1500 qdisc mq state UP group default qlen 1000
。。。
link/ether 00:0c:29:e5:23:0b brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff
inet 192.168.60.132/32 scope global ens160
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
相同的配置再另外一台机器上也安装keepalived并且进行验证,这个时候虚拟ip还只在第一台机器,我们直接通过本机cmd进行ping查看效果。在ping一台目标主机的时候,我们突然手动关闭虚拟机,用来模拟服务器宕机的效果,可以看到在一段时间内请求不到,而后又可以请求得到,这个时候我们看备用的ip会发现虚拟IP已经被转移到该备用机上了。
4.3、Keepalived的选举机制和切换机制
keepalived中优先级高的节点为MASTER。MASTER其中一个职责就是响应VIP的arp包,将VIP和mac地址映射关系告诉局域网内其他主机,同时,它还会以多播的形式(默认目的地址224.0.0.18)向局域网中发送VRRP通告,告知自己的优先级。网络中的所有BACKUP节点只负责处理MASTER发出的多播包,当发现MASTER的优先级没自己高,或者没收到MASTER的VRRP通告时,BACKUP将自己切换到MASTER状态,然后做MASTER该做的事:响应arp包和发送VRRP通告,主要由keepalived的配置文件 priority 100 优先级进行配置决定谁为master。
5、HTTP协议配置
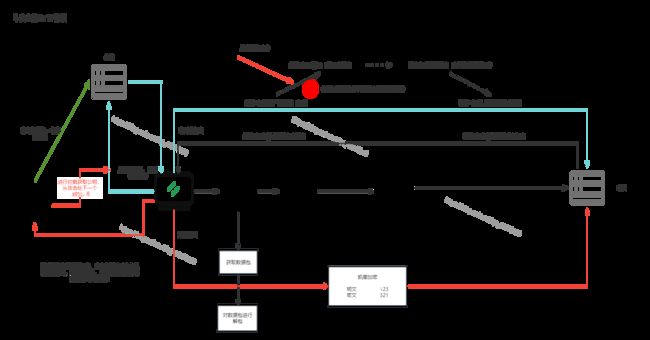
5.1、不安全的HTTP协议
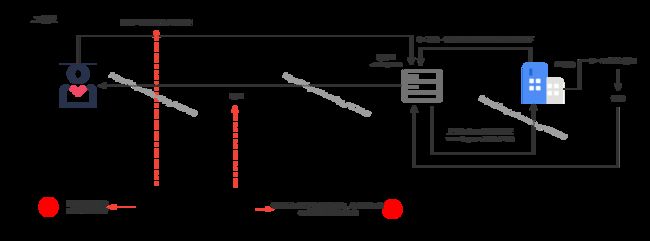
在http协议传输过程当中,数据传输是不安全的,如下图所示,可以看到当使用对称加密的时候,一当加密算法泄露或者破解,那就可以在中途进行密文的解密,再进行明文篡改再进行明文加密
5.2、CA认证
CA认证就避免了以上问题,因为直接获取的是CA发的证书,而操作系统又携带了对应的公钥,无论在哪一步进行网络攻击都达不到效果
5.3、证书的安装
5.3.1、搭建一个网站
在这里我们简单介绍如何搭建一个自己的云服务器,这里我们使用阿里云的云服务器,
5.3.1.1、购买云服务器
首先登录阿里云,在菜单当中选择 云服务器ECS 之后创建一个ECS,在这里我们可以选择服务器的相关配置,这里采用中国香港下 2vCPU和2GB内存、镜像使用centos 7.6 64位,在后续的系统设置当中设置密码即可。
5.3.1.2、购买域名
同样的在菜单当中找到 域名 这一个菜单,进去之后可以看到立即注册域名,然后搜索我们想用的域名如下,之后将其加入到清单当中,再点击域名清单进行购买即可。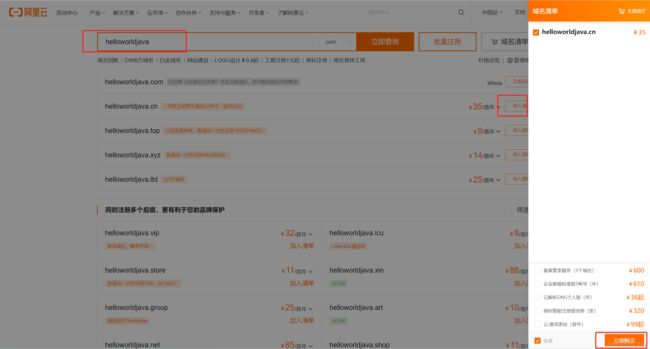
立即购买如果是第一次需要进行创建信息模板,也就相当于实名验证,等待实名验证通过之后进行购买即可
5.3.1.3、域名解析
这一步就是将购买的域名与云服务器进行绑定,在域名通过后,可以看到我们的全部域名,点一下就会跳转到域名列表,在域名列表当中我们进行解析域名。
5.3.2、安装证书到nginx
在阿里云上进行配置证书,在SSL证书这里我们可以选择一个免费证书,之后将对应的域名等信息填好之后进行申请证书即可。
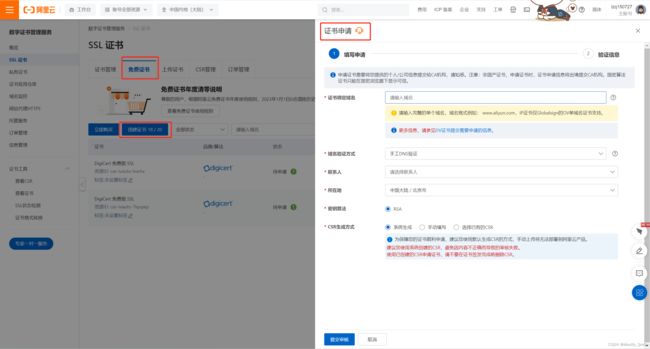
证书申请通过之后,将证书进行下载下来,下载后会得到两个文件,将该文件上传到nginx的conf目录下,之后修改nginx配置
server {
listen 443 ssl;
server_name qmqlzq.top;
ssl_certificate XXX.pem;
ssl_certificate_key XXX.key;
}
6、nginx优化——扩容
扩容无疑是最简单粗暴的解决性能问题的方案,
6.1、单机垂直扩容
加硬件资源通常更新以下几个硬件
- 云服务器
- 主机
- CPU/主板
- 网卡
- 磁盘:
6.2、水平扩展:集群化
6.2.1、ipHash维持会话
根据用户请求的ip,利用算法映射成hash值,分配到特定的tomcat服务器中。主要是为了实现负载均衡,只要用户ip固定,则hash值固定,特定用户只能访问特定服务器,解决了session的问题。
应用场景:中小型项目快速扩容
缺点
- 局域网内ip会被集中转发到同一台机器。
- 后端服务器宕机会导致会话过期
配置ipHash
upstream httpds {
ip_hash;
server 192.168.60.130 ;
server 192.168.60.131 ;
}
server {
listen 80;
server_name localhost;
location / {
proxy_pass http://httpds;
}
}
6.2.2、$request_uri维持会话
主要用来针对请求的uri中的参数进行控制。
配置$request_uri
upstream httpds {
hash $request_uri;
server 192.168.60.130 ;
server 192.168.60.131 ;
}
6.2.3、$cookie_jsessionid维持会话
主要用来针对浏览器当中携带的jsessionid进行控制
配置$request_uri
upstream httpds {
hash $cookie_jsessionid;
server 192.168.60.130 ;
server 192.168.60.131 ;
}
6.2.4、使用sticky模块完成对Nginx的负载均衡
下载地址:https://bitbucket.org/nginx-goodies/nginx-sticky-module-ng/downloads/?tab=tags
下载完成之后将gz包上传到centos上进行解压,解压完成之后在nginx目录下进行安装,后面的–add-module=指向sticky解压地址,
# 进行安装
./configure --add-module=/tools/nginx/nginx-goodies-nginx-sticky-module-ng-c78b7dd79d0d
# 再进行make
make
# 在make完成之后会生成一个objs文件夹,这个时候我们进行nginx升级,直接将objs/nginx 复制到之前的nginx安装目录下
cp nginx /usr/local/nginx/sbin/
安装报错
/tools/nginx/nginx-goodies-nginx-sticky-module-ng-c78b7dd79d0d/ngx_http_sticky_module.c: 在函数‘ngx_http_init_sticky_peer’中:
/tools/nginx/nginx-goodies-nginx-sticky-module-ng-c78b7dd79d0d/ngx_http_sticky_module.c:207:55: 错误:‘ngx_http_headers_in_t’ {或称 ‘struct <匿名>’} has no member named ‘cookies’; did you mean ‘cookie’?
if (ngx_http_parse_multi_header_lines(&r->headers_in.cookies, &iphp->sticky_conf->cookie_name, &route) != NGX_DECLINED) {
^~~~~~~
cookie
/tools/nginx/nginx-goodies-nginx-sticky-module-ng-c78b7dd79d0d/ngx_http_sticky_module.c:207:64: 错误:传递‘ngx_http_parse_multi_header_lines’的第 2 个参数时在不兼容的指针类型间转换 [-Werror=incompatible-pointer-types]
if (ngx_http_parse_multi_header_lines(&r->headers_in.cookies, &iphp->sticky_conf->cookie_name, &route) != NGX_DECLINED) {
^~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
In file included from /tools/nginx/nginx-goodies-nginx-sticky-module-ng-c78b7dd79d0d/ngx_http_sticky_module.c:9:
src/http/ngx_http.h:106:18: 附注:需要类型‘ngx_table_elt_t *’ {或称 ‘struct ngx_table_elt_s *’},但实参的类型为‘ngx_str_t *’ {或称 ‘struct <匿名> *’}
ngx_table_elt_t *ngx_http_parse_multi_header_lines(ngx_http_request_t *r,
^~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
/tools/nginx/nginx-goodies-nginx-sticky-module-ng-c78b7dd79d0d/ngx_http_sticky_module.c:207:6: 错误:提供给函数‘ngx_http_parse_multi_header_lines’的实参太少
if (ngx_http_parse_multi_header_lines(&r->headers_in.cookies, &iphp->sticky_conf->cookie_name, &route) != NGX_DECLINED) {
^~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
In file included from /tools/nginx/nginx-goodies-nginx-sticky-module-ng-c78b7dd79d0d/ngx_http_sticky_module.c:9:
src/http/ngx_http.h:106:18: 附注:在此声明
ngx_table_elt_t *ngx_http_parse_multi_header_lines(ngx_http_request_t *r,
^~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
cc1:所有的警告都被当作是错误
make[1]: *** [objs/Makefile:1206:objs/addon/nginx-goodies-nginx-sticky-module-ng-c78b7dd79d0d/ngx_http_sticky_module.o] 错误 1
make[1]: 离开目录“/tools/nginx/nginx-1.23.3”
make: *** [Makefile:10:build] 错误 2
这个时候需要修改sticky下的ngx_http_sticky_module.c代码,找到以下代码进行注释,并且添加一行
// if (ngx_http_parse_multi_header_lines(&r->headers_in.cookies, &iphp->sticky_conf->cookie_name, &route) != NGX_DECLINED) {
if (ngx_http_parse_multi_header_lines(r, r->headers_in.cookie, &iphp->sticky_conf->cookie_name, &route) != NULL) {
使用sticky和前面使用iphash一样。
6.3、Keepalive
6.3.1、在浏览器中查看是否启用keepalive
-
TCP的keepalive是侧重在保持客户端和服务端的连接,一方会不定期发送心跳包给另一方,当一方端掉的时候,没有断掉的定时发送几次心跳包,如果间隔发送几次,对方都返回的是RST,而不是ACK,那么就释放当前链接。设想一下,如果tcp层没有keepalive的机制,一旦一方断开连接却没有发送FIN给另外一方的话,那么另外一方会一直以为这个连接还是存活的,几天,几月。那么这对服务器资源的影响是很大的。
-
HTTP的keep-alive一般我们都会带上中间的横杠,普通的http连接是客户端连接上服务端,然后结束请求后,由客户端或者服务端进行http连接的关闭。下次再发送请求的时候,客户端再发起一个连接,传送数据,关闭连接。这么个流程反复。但是一旦客户端发送connection:keep-alive头给服务端,且服务端也接受这个keep-alive的话,两边对上暗号,这个连接就可以复用了,一个http处理完之后,另外一个http数据直接从这个连接走了。减少新建和断开TCP连接的消耗。
HTTP协议的Keep-Alive意图在于短时间内连接复用,希望可以短时间内在同一个连接上进行多次请求/响应。
TCP的KeepAlive机制意图在于保活、心跳,检测连接错误。当一个TCP连接两端长时间没有数据传输时(通常默认配置是2小时),发送keepalive探针,探测链接是否存活。
在nginx当中默认配置的keepalive_timeout为65秒,我们在浏览器当中访问nginx,打开F12可以在请求标头和响应标头当中可以看到
Connection: keep-alive
// 而当将其设置为0的时候,就会关闭keepalive连接
Connection: close
6.3.2、抓包——charles
首先在官网进行下载:https://www.charlesproxy.com/latest-release/download.do
6.3.3、keepalive配置
| 配置 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| keepalive | 向上游服务器的保留连接数 |
| keepalive_time | 限制keepalive保持连接的最大时间 keepalive_timeout = 0 即关闭 |
| send_timeout | 两次向客户端写操作之间的间隔 如果大于这个时间则关闭连接 默认60s |
| keepalive_request | 默认1000,单个连接中可处理的请求数 |
| keepalive_disable | 不对某些浏览器建立长连接 |
6.3.4、apache-benchmark压力测试
直接通过yum命令进行安装
yum install httpd-tools
# 安装完成之后使用以下命令进行测试是否安装好了
ab
并且对应ab的相关指令如下表:
| 指令 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| -n | 即requests,用于指定压力测试总共的执行次数。 |
| -c | 即concurrency,用于指定的并发数。 |
| -t | 即timelimit,等待响应的最大时间(单位:秒)。 |
| -b | 即windowsize,TCP发送/接收的缓冲大小(单位:字节)。 |
| -p | 即postfile,发送POST请求时需要上传的文件,此外还必须设置-T参数。 |
| -u | 即putfile,发送PUT请求时需要上传的文件,此外还必须设置-T参数。 |
| -T | 即content-type,用于设置Content-Type请求头信息,例如:application/x-www-form-urlencoded,默认值为text/plain。 |
| -v | 即verbosity,指定打印帮助信息的冗余级别。 |
| -w | 以HTML表格形式打印结果。 |
| -i | 使用HEAD请求代替GET请求。 |
| -x | 插入字符串作为table标签的属性。 |
| -y | 插入字符串作为tr标签的属性。 |
| -z | 插入字符串作为td标签的属性。 |
| -C | 添加cookie信息,例如:“Apache=1234”(可以重复该参数选项以添加多个)。 |
| -H | 添加任意的请求头,例如:“Accept-Encoding: gzip”,请求头将会添加在现有的多个请求头之后(可以重复该参数选项以添加多个)。 |
| -A | 添加一个基本的网络认证信息,用户名和密码之间用英文冒号隔开。 |
| -P | 添加一个基本的代理认证信息,用户名和密码之间用英文冒号隔开。 |
| -X | 指定使用的和端口号,例如:“126.10.10.3:88”。 |
| -V | 打印版本号并退出。 |
| -k | 使用HTTP的KeepAlive特性。 |
| -d | 不显示百分比。 |
| -S | 不显示预估和警告信息。 |
| -g | 输出结果信息到gnuplot格式的文件中。 |
| -e | 输出结果信息到CSV格式的文件中。 |
| -r | 指定接收到错误信息时不退出程序。 |
| -h | 显示用法信息,其实就是ab -help。 |
在这里进行压力测试,以下命令表示直接访问该地址,发送500次请求按50组进行发送,这里进行试验测试:分别对直连nginx、nginx反向代理、直连tomcat、通过nginx反向代理到tomcat,后续日志我们只需要观察其中的Requests per second(Qps)和 Transfer rate(传输速率)
[root@localhost ~]# ab -n 500 -c50 http://192.168.60.128:81/
This is ApacheBench, Version 2.3 <$Revision: 1843412 $>
Copyright 1996 Adam Twiss, Zeus Technology Ltd, http://www.zeustech.net/
Licensed to The Apache Software Foundation, http://www.apache.org/
Benchmarking 192.168.60.128 (be patient)
Completed 100 requests
Completed 200 requests
Completed 300 requests
Completed 400 requests
Completed 500 requests
Finished 500 requests
Server Software: nginx/1.23.3
Server Hostname: 192.168.60.128
Server Port: 81
Document Path: /
Document Length: 12793 bytes
Concurrency Level: 50
Time taken for tests: 34.643 seconds
Complete requests: 500
Failed requests: 0
Total transferred: 6558500 bytes
HTML transferred: 6396500 bytes
Requests per second: 14.43 [#/sec] (mean)
Time per request: 3464.304 [ms] (mean)
Time per request: 69.286 [ms] (mean, across all concurrent requests)
Transfer rate: 184.88 [Kbytes/sec] received
Connection Times (ms)
min mean[+/-sd] median max
Connect: 0 0 2.7 0 55
Processing: 72 2914 7169.3 956 34545
Waiting: 71 877 3028.2 382 34169
Total: 73 2914 7169.3 956 34546
Percentage of the requests served within a certain time (ms)
50% 956
66% 1052
75% 2035
80% 2086
90% 4263
95% 17098
98% 34262
99% 34343
100% 34546 (longest request)
6.3.5、nginx反向代理tomcat性能提升
在进行直连tomcat和通过nginx进行反向代理tomcat的压力测试后,可以发现通过反向代理的吞吐量和传输速率都有一定的提升,这是因为在nginx当中配置了keepalived,这时大量请求打到nginx上,会有很多的请求复用keepalived,不会中断连接,这也就是为什么通过反向代理的性能比直连要好的原因
6.4、Nginx反向代理核心流程
6.4.1、proxy_pass工作流程
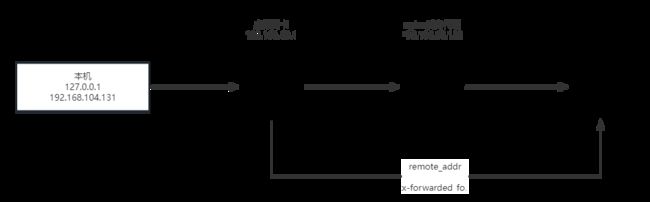
6.4.2、获取真实的IP
这里我们首先提供一个java代码用来打印日志表示获取对应的Head和ip信息。
@GetMapping("/getRealIp")
public void getRealIp(HttpServletRequest request) throws ServletException, IOException {
Enumeration<String> headerNames = request.getHeaderNames();
while (headerNames.hasMoreElements()) {
String hName = headerNames.nextElement();
logger.info(hName, "=====", request.getHeader(hName));
}
logger.info("getRemoteHost ==== ", request.getRemoteHost());
logger.info("getRemotePort ==== ", request.getRemotePort());
logger.info("getRemoteAddr ==== ", request.getRemoteAddr());
logger.info("x-forwarder-for ==== ", request.getHeader("x-forwarder-for"));
}
然后峰分别查看直接本地启动程序进行访问、放到linux下进行启动访问、通过nginx反向代理进行访问,通过这三个对比会发现获取到的IP地址其实并不是想要的ip地址、
# 本地启动访问 http://127.0.0.1:8888/getRealIp
getRemoteHost ==== 127.0.0.1
getRemotePort ==== 50699
getRemoteAddr ==== 127.0.0.1
# 虚拟机启动war包进行访问 http://192.168.60.128:8888/getRealIp
getRemoteHost ==== 192.168.60.1
getRemotePort ==== 50870
getRemoteAddr ==== 192.168.60.1
# 通过nginx反向代理访问 http://192.168.60.128:81/
getRemoteHost ==== 192.168.60.131
getRemotePort ==== 34836
getRemoteAddr ==== 192.168.60.131
这里通过nginx反向代理添加以下配置
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For $remote_addr;
# 这个时候再进行访问nginx,通过x-forwarded-for获取其真实ip地址
getRemoteHost ==== 192.168.60.131
getRemotePort ==== 34856
getRemoteAddr ==== 192.168.60.131
x-forwarded-for ==== 192.168.60.1
6.5、服务端优化
6.5.1、Gzip压缩
gzip不是一种算法,可以说它是一种压缩工具,或者说它是一种文件格式。因为不管是用什么软件去压,也不管用哪种实现库去压,只要最终结果是gzip的压缩结构,那么该结果肯定是按照gzip文件格式组织的,可以把gzip文件格式理解为一只虾(头、中间、尾),包括三个部分(文件头、文件尾、中间保存被压缩后的数据)
6.5.2、gzip相关配置(Gzip动态压缩)
| 配置 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| gzip on; | 开关,默认关闭 |
| gzip_buffers 32 4k / 16 8k | 缓冲区大小 |
| gzip_comp_level 1; | 压缩等级 1-9,数字越大压缩比越高 |
| gzip_http_version 1.1; | 使用gzip的最小版本 |
| gzip_min_length | 设置将被gzip压缩的响应的最小长度。 长度仅由“Content-Length”响应报头字段确定。 |
| gzip_proxied 多选 | off 为不做限制作为反向代理时,针对上游服务器返回的头信息进行压缩 expired - 启用压缩,如果header头中包含 “Expires” 头信息 no-cache - 启用压缩,如果header头中包含 “Cache-Control:no-cache” 头信息 no-store - 启用压缩,如果header头中包含 “Cache-Control:no-store” 头信息 private - 启用压缩,如果header头中包含 “Cache-Control:private” 头信息 no_last_modified - 启用压缩,如果header头中不包含 “Last-Modified” 头信息 no_etag - 启用压缩 ,如果header头中不包含 “ETag” 头信息 auth - 启用压缩 , 如果header头中包含 “Authorization” 头信息 any - 无条件启用压缩 |
| gzip_vary on; | 增加一个header,适配老的浏览器 Vary: Accept-Encoding |
| gzip_types | 哪些mime类型的文件进行压缩 |
| gzip_disable | 禁止某些浏览器使用gzip |
完整实例:
gzip on;
gzip_buffers 16 8k;
gzip_comp_level 6;
gzip_http_version 1.1;
gzip_min_length 256;
gzip_proxied any;
gzip_vary on;
gzip_types text/plain application/x-javascript text/css application/xml;
gzip_types
text/xml application/xml application/atom+xml application/rss+xml application/xhtml+xml image/svg+xml
text/javascript application/javascript application/x-javascript
text/x-json application/json application/x-web-app-manifest+json
text/css text/plain text/x-component
font/opentype application/x-font-ttf application/vnd.ms-fontobject
image/x-icon;
gzip_disable "MSIE [1-6]\.(?!.*SV1)";
6.5.3、Gzip静态压缩
因为在前面我们安装编译了sticky,这里对于sticky的配置还是不变,添加一个Gzip静态压缩的模块和解压模块。
./configure --add-module=/tools/nginx/nginx-goodies-nginx-sticky-module-ng-c78b7dd79d0d --with-http_gzip_static_module --with-http_gunzip_module
# 安装之后进行make,将生成的objs下的nginx复制到usr/local/nginx下
make
首先了解一下这两个模块的作用
ngx_http_gzip_static_module模块允许发送扩展名为“.gz”的预压缩文件,而不是常规文件。
语法: gzip_static on | off | always;
默认值: gzip_static off;
作用于: http, server, location
说明:on和off分别表示是否开启静态压缩,对于“always”值(1.3.6),在所有情况下都使用gzip文件,而不检查客户端是否支持它。如果磁盘上没有未压缩的文件,可以使用ngx_http_gunzip模块配合使用。
ngx_http_gunzip模块是一个过滤器,它为不支持“gzip”编码方法的客户端使用“Content Encoding:gzip”对响应进行解压缩。当需要存储压缩数据以节省空间并降低I/O成本时,该模块将非常有用。
语法: gunzip on | off;
默认值: gunzip off;
作用于: http, server, location
语法: gunzip_buffers number size;
默认值: gunzip_buffers 32 4k|16 8k;
作用于: http, server, location
说明:设置用于解压缩响应的缓冲区的数量和大小。默认情况下,缓冲区大小等于一个内存页。这是4K或8K,取决于平台。
这个时候添加了静态压缩模块和解压模块,在nginx配置当中加入以下配置,这样配置的作用在于当无论说静态压缩是否存在gz包、客户端是否支持gzip,都会通过gunzip进行解压发送到客户端。
gunzip: on;
gzip_static: always;
6.5.4、第三方zip模块Brotli与模块化加载
首先我们在对应的官网下进行下载gz包,这两个项目都托管在github,在其tag下选择版本进行下载。
https://github.com/google/ngx_brotli
https://github.com/google/brotli
下载之后将gz包上传到虚拟机上
# 进行解压
tar -zxvf ngx_brotli-1.0.0rc.tar.gz
tar -zxvf brotli-1.0.9.tar.gz
cd brotli-1.0.9
# 将brotli-1.0.9全部内容移动到ngx_brotli-1.0.0rc/deps/brotli目录下
mv ./* /tools/nginx/ngx_brotli-1.0.0rc/deps/brotli/
# 进行编译--add-dynamic-module后跟上对应的存放目录
./configure --add-module=/tools/nginx/nginx-goodies-nginx-sticky-module-ng-c78b7dd79d0d --with-http_gzip_static_module --with-http_gunzip_module --with-compat --add-dynamic-module=/tools/nginx/ngx_brotli-1.0.0rc
make
# 切换到nginx启动目录下新增一个modules目录
cd /usr/local/nginx/
mkdir modules
# 切换到make后的objs目录下,将以下三个文件进行拷贝到nginx启动目录下
cd objs
cp ngx_http_brotli_filter_module.so /usr/local/nginx/modules/
cp ngx_http_brotli_static_module.so /usr/local/nginx/modules/
cp nginx /usr/local/nginx/sbin/
使用Brotli,修改nginx的配置文件,添加如下配置(这里Brotli的配置不过多说明了,可以在github上查看配置说明)
load_module "/usr/local/nginx/modules/ngx_http_brotli_filter_module.so";
load_module "/usr/local/nginx/modules/ngx_http_brotli_static_module.so";
brotli on;
brotli_static on;
brotli_comp_level 6;
brotli_buffers 16 8k;
brotli_min_length 20;
brotli_types text/plain text/css text/javascript application/javascript text/xml application/xml application/xml+rss application/json image/jpeg image/gif image/png;
[root@localhost sbin]# curl -H 'accept-encoding:br' -I 'http://192.168.60.128:81/'
HTTP/1.1 200 OK
Server: nginx/1.23.3
Date: Mon, 13 Feb 2023 06:48:24 GMT
Content-Type: text/html; charset=utf-8
Connection: keep-alive
Last-Modified: Tue, 22 Feb 2022 13:43:36 GMT
Cache-Control: private, max-age=0, proxy-revalidate, no-store, no-cache, must-revalidate
Content-Encoding: br
6.5.5、合并请求
在一些大型应用当中,一个页面会加载很多的js、css等文件,这个时候我们可以将这些请求进行合并处理,如下:这是淘宝当中的一个获取js文件的请求,可以看到他是通过??和,(逗号)进行分割,一个请求获取多个js文件。
https://g.alicdn.com/??kissy/k/6.2.4/seed-min.js,kg/global-util/1.0.7/index-min.js,secdev/sufei_data/3.8.7/index.js
mod_concat模块由淘宝开发,目前已经包含在tengine中,并且淘宝已经在使用这个nginx模块。https://github.com/alibaba/nginx-http-concat
从github上下载对应的代码上传到linux下进行解压,再进行打包nginx的打包
./configure --add-module=/tools/nginx/nginx-http-concat
make
添加合并请求的配置
# 开启合并请求
concat on;
# 最大合并文件数
concat_max_files 20;
在html当中通常会引用很多的css文件和js文件,而当开启了合并请求之后将引用进行改写也就完成了合并请求
<link rel="stylesheet" href="demo.css">
<link rel="stylesheet" href="index.css">
<link rel="stylesheet" href="??demo.css,index.css">
这样修改之后再访问nginx会发现获取css样式的请求变成了:http://192.168.60.128:81/??demo.css,index.css 本质上就是将两个css文件的内容进行合并了。
6.6、资源静态化
6.6.1、ngx_http_ssi_module模块解决资源静态化
在进行访问页面的时候,对于java来说页面响应有很多种方式,比如:模板引擎或者jsp,这些都是通过返回静态文件并且携带上动态数据,在这里可以直接将访问的模板存在nginx当中,这样就省去了一定的nginx与后端服务器的连接,这也就是资源静态化的意义。并且在nginx当中需要部署多个,可以同rsync进行保证nginx上的数据一致性
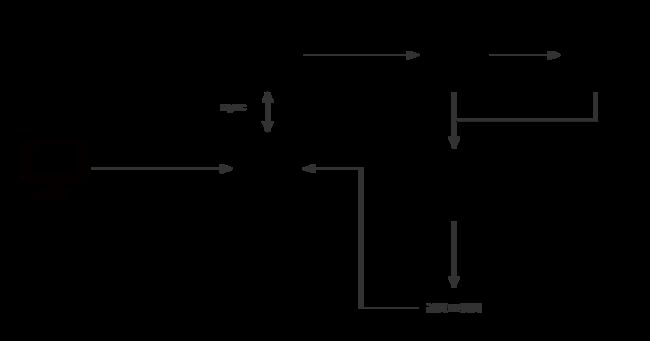
这里需要了解一下nginx当中的一个模块:ngx_http_ssi_module ,该模块是一个过滤器,它在通过它的响应中处理ssi(服务器端包含)命令。目前,支持的ssi命令列表不完整。
在nginx的配置文件当中打开ssi, ssi on; 添加该配置就可以直接通过其模板进行使用了
<h1>Welcome to nginx 192.168.60.128!h1>
ssi模块配置说明
| 语法 | 默认值 | 说明 |
|---|---|---|
| ssi on/off | on | 启用或禁用响应中SSI命令的处理 |
| ssi_last_modified on / off | off | 允许在SSI处理期间保留原始响应中的“Last Modified”标头字段,以便于响应缓存。 默认情况下,在处理过程中修改响应的内容时,标头字段将被删除,并且可能包含动态生成的元素或部分,这些元素或部分独立于原始响应进行更改 |
| ssi_min_file_chunk size; | 1k | 设置存储在磁盘上的响应部分的最小大小,从使用sendfile发送响应开始 |
| ssi_silent_errors on / off | off | 如果启用,则在SSI处理过程中发生错误时,禁止输出“[处理指令时发生错误]”字符串 |
| ssi_types mime-type | text/html | 除了“text/html”之外,还允许处理具有指定MIME类型的响应中的SSI命令 |
| ssi_value_length length | 256 | 设置SSI命令中参数值的最大长度 |
6.6.2、rsync资源同步
6.6.2.1、rsync 是什么
rsync(remote synchronize)是Liunx/Unix下的一个远程数据同步工具。它可通过LAN/WAN快速同步多台主机间的文件和目录,并适当利用rsync算法(差分编码)以减少数据的传输。rsync算法并不是每一次都整份传输,而是只传输两个文件的不同部分,因此其传输速度相当快。除此之外,rsync可拷贝、显示目录属性,以及拷贝文件,并可选择性的压缩以及递归拷贝。
6.6.2.2、安装与简单使用 rsync 进行文件同步
首先准备两台服务器,这里就以128和130进行命名,其中128作为资源同步的主机,现在两台机器上都安装rsync
yum install -y rsync
而后先在128机器上进行rsync配置:
# 修改配置文件
vi /etc/rsyncd.conf
文件内容
[ftp]
path=/usr/local/nginx/html
# 启动rsync
rsync --daemon
# 查看进程判断是否启动成功 (rsync没有重启命令,在进行重启时先kill掉其进程再进行启动)
ps -ef | grep rsync
进行同步
# 查看改机器所需要同步的文件
rsync --list-only 192.168.60.128::ftp/
rsync -avz 192.168.60.128::ftp/
# 切到130机器下进行同步文件
rsync -avz 192.168.60.128::ftp/ /usr/local/nginx/html/
6.6.2.3、安全认证以及免密登录
添加账号密码进行登录
# 进行配置账号密码
echo "admin:123456" >> /etc/rsyncd.pwd
chmod 600 /etc/rsyncd.pwd
# 修改配置文件 添加一下内容
vi /etc/rsyncd.conf
auth users = admin
secrets file = /etc/syncd.pwd
# 连接进行测试
rsync --list-only [email protected]::ftp/
免密登录
# 新增存放密码文件 将123456存放该文件当中
vi /etc/rsyncd.pwd.clinet
# 修改权限
chmod 600 /etc/rsyncd.pwd.clinet
# 进行测试
rsync --list-only --password-file=/etc/rsyncd.pwd.clinet [email protected]::ftp/
6.6.2.4、rsync 常用选项
| 选项 | 含义 |
|---|---|
| -a | 包含-rtplgoD |
| -r | 同步目录时要加上,类似cp时的-r选项 |
| -v | 同步时显示一些信息,让我们知道同步的过程 |
| -l | 保留软连接 |
| -L | 加上该选项后,同步软链接时会把源文件给同步 |
| -p | 保持文件的权限属性 |
| -o | 保持文件的属主 |
| -g | 保持文件的属组 |
| -D | 保持设备文件信息 |
| -t | 保持文件的时间属性 |
| –delete | 删除DEST中SRC没有的文件 |
| –exclude | 过滤指定文件,如–exclude “logs”会把文件名包含logs的文件或者目录过滤掉,不同步 |
| -P | 显示同步过程,比如速率,比-v更加详细 |
| -u | 加上该选项后,如果DEST中的文件比SRC新,则不同步 |
| -z | 传输时压缩 |
6.6.2.5、安装inotify
直接通过源进行安装,安装之后进行解压编译
wget http://github.com/downloads/rvoicilas/inotify-tools/inotify-tools-3.14.tar.gz
tar -zxvf inotify-tools-3.14.tar.gz
cd inotify-tools-3.14
./configure --prefix=/usr/local/inotify
make && make install
6.6.2.6、inotify 配合 rsync 进行文件同步
在inotify的安装目录下新增脚本,并且对于两台机器上监听的文件夹需要可写权限 chmod 777 xxx 之后启动脚本,在130机器上的新增等文件在该机器上都会进行同步
/usr/local/inotify/bin/inotifywait -mrq --timefmt '%d/%m/%y %H:%M' --format '%T %w%f %e' -e close_write,modify,delete,create,attrib,move //usr/local/nginx/html/ | while read file
do
rsync -az --delete --password-file=/etc/rsyncd.passwd.client /usr/local/nginx/html/ [email protected]::ftp/
done
6.6.2.7、inotify 常用选项
| 参数 | 说明 | 含义 |
|---|---|---|
| -r | –recursive | 递归查询目录 |
| -q | –quiet | 打印很少的信息,仅仅打印监控事件信息 |
| -m | –monitor | 始终保持事件监听状态 |
| –excludei | 排除文件或目录时,不区分大小写 | |
| –timefmt | 指定事件输出格式 | |
| –format | 打印使用指定的输出类似格式字符串 | |
| -e | –event[ -e|–event … ]accessmodifyattribcloseopenmove_tomove createdeleteumount | 通过此参数可以指定要监控的事件 #文件或目录被读取#文件或目录的内容被修改#文件或目录属性被改变#文件或目录封闭,无论读/写模式#文件或目录被打开#文件或目录被移动至另外一个目录#文件或目录被移动另一个目录或从另一个目录移动至当前目录#文件或目录被创建在当前目录#文件或目录被删除#文件系统被卸载 |
6.7、多级缓存
6.7.1、强制缓存与协商缓存
强制缓存:直接从本机读取,不请求服务器
协商缓存:发送请求header中携带Last-Modified,服务器可能会返回304 Not Modified
6.7.2、浏览器强制缓存
| 标记 | 类型 | 功能 |
|---|---|---|
| public | 响应头 | 响应的数据可以被缓存,客户端和代理层都可以缓存 |
| private | 响应头 | 可私有缓存,客户端可以缓存,代理层不能缓存(CDN,proxy_pass) |
| no-cache | 请求头 | 可以使用本地缓存,但是必须发送请求到服务器回源验证 |
| no-store | 请求和响应 | 应禁用缓存 |
| max-age | 请求和响应 | 文件可以在浏览器中缓存的时间以秒为单位 |
| s-maxage | 请求和响应 | 用户代理层缓存,CDN下发,当客户端数据过期时会重新校验 |
| max-stale | 请求和响应 | 缓存最大使用时间,如果缓存过期,但还在这个时间范围内则可以使用缓存数据 |
| min-fresh | 请求和响应 | 缓存最小使用时间, |
| must-revalidate | 请求和响应 | 当缓存过期后,必须回源重新请求资源。比no-cache更严格。因为HTTP 规范是允许客户端在某些特殊情况下直接使用过期缓存的,比如校验请求发送失败的时候。那么带有must-revalidate的缓存必须校验,其他条件全部失效。 |
| proxy-revalidate | 请求和响应 | 和must-revalidate类似,只对CDN这种代理服务器有效,客户端遇到此头,需要回源验证 |
| stale-while-revalidate | 响应 | 表示在指定时间内可以先使用本地缓存,后台进行异步校验 |
| stale-if-error | 响应 | 在指定时间内,重新验证时返回状态码为5XX的时候,可以用本地缓存 |
| only-if-cached | 响应 | 那么只使用缓存内容,如果没有缓存 则504 getway timeout |
6.7.3、浏览器缓存原则
- 多级集群负载时last-modified必须保持一致
- 还有一些场景下我们希望禁用浏览器缓存。比如轮训api上报数据数据
- 浏览器缓存很难彻底禁用,大家的做法是加版本号,随机数等方法。
- 只缓存200响应头的数据,像3XX这类跳转的页面不需要缓存。
- 对于js,css这类可以缓存很久的数据,可以通过加版本号的方式更新内容
- 不需要强一致性的数据,可以缓存几秒
- 异步加载的接口数据,可以使用ETag来校验。
- 在服务器添加Server头,有利于排查错误
- 分为手机APP和Client以及是否遵循http协议
- 在没有联网的状态下可以展示数据
- 流量消耗过多
- 提前下发 避免秒杀时同时下发数据造成流量短时间暴增
- 兜底数据 在服务器崩溃和网络不可用的时候展示
- 临时缓存 退出即清理
- 固定缓存 展示框架这种,可能很长时间不会更新,可用随客户端下发
- 首页有的时候可以看做是框架 应该禁用缓存,以保证加载的资源都是最新的
- 父子连接 页面跳转时有一部分内容不需要重新加载,可用从父菜单带过来
- 预加载 某些逻辑可用判定用户接下来的操作,那么可用异步加载那些资源
- 漂亮的加载过程 异步加载 先展示框架,然后异步加载内容,避免主线程阻塞
6.7.4、DNS缓存
DNS作为将域名和IP地址相互映射的一个分布式数据库,能够使人更方便地访问互联网。DNS使用UDP端口53。当前,对于每一级域名长度的限制是63个字符,域名总长度则不能超过253个字符。
6.7.4.1、GEOip
GeoIP是IP地理位置数据库,可以根据IP获得地理位置信息。
官网:https://www.maxmind.com/en/home 首先需要注册一个账号,注册帐号之后登录之后可以进行下载数据库,这里下载 GeoLite2 Country
并且在github上下载其依赖文件:https://github.com/maxmind/libmaxminddb/releases/tag/1.7.1
libmaxminddb-1.7.1.tar.gz包安装
tar zxvf libmaxminddb-1.7.1.tar.gz
cd libmaxminddb-1.7.1
./configure
make
make install
echo /usr/local/lib >> /etc/ld.so.conf.d/local.conf
ldconfig
安装nginx依赖:github下载地址 https://github.com/leev/ngx_http_geoip2_module 以及官方模块说明:https://nginx.org/en/docs/http/ngx_http_geoip_module.html
tar -zxvf ngx_http_geoip2_module-3.4.tar.gz
cd nginx-1.23.3
./configure --add-module=/tools/nginx/ngx_http_geoip2_module-3.4
make
配置完成之后修改nginx配置文件
# server 同级
geoip2 /tools/nginx/GeoLite2-Country_20230217/GeoLite2-Country.mmdb {
$geoip2_country_code country iso_code;
}
location / {
add_header country $geoip2_country_code;
}
6.7.5、正向代理与反向代理缓存
6.7.5.1、Proxy缓存
http模块:
proxy_cache_path /ngx_tmp levels=1:2 keys_zone=test_cache:100m inactive=1d max_size=10g ;
location模块:
add_header Nginx-Cache "$upstream_cache_status";
proxy_cache test_cache;
proxy_cache_valid 1h;
tar -zxvf ngx_cache_purge-2.3.tar.gz
./configure --add-module=/tools/nginx/ngx_cache_purge-2.3
make
7、nginx优化——高效
7.1、Nginx内存缓存
strace:一般应用为静态文件元数据信息缓存
open_file_cache max=500 inactive=60s
open_file_cache_min_uses 1;
open_file_cache_valid 60s;
open_file_cache_errors on
- max缓存最大数量,超过数量后会使用LRU淘汰
- inactive 指定时间内未被访问过的缓存将被删除
- pen_file_cache_min_uses:被访问到多少次后会开始缓存
- open_file_cache_valid:间隔多长时间去检查文件是否有变化
- open_file_cache_errors:对错误信息是否缓存
7.2、Nginx外置缓存
7.2.1、error_page配置
error_page配置,可以将错误的访问页面地址进行控制
error_page 404 =200 /403.html;
# error_page 404 =403 https://www.baidu.com;
7.2.2、匿名Location
7.2.2.1、匿名Location和Return
在这里将访问404的请求直接转发给到@666这个localhost,当这个localhost直接返回200时,浏览器将会下一一个空白文件,在200后面可以添加文件内容如hello world,并且可以在localhost当中添加请求头这样浏览器将不会对文件进行下载而是通过html进行展示
error_page 404 = @666;
location @666{
add_header content-type 'text/html; charset=utf-8';
return 200 "hello world";
}
7.2.2.2、nginx + memcached
首先安装memcached,同时安装一个telnet用来连接memcached
yum -y install memcached
systemctl start memcached
memcached-tool 127.0.0.1:11211 stats
yum install -y telnet
telnet 127.0.0.1 11211
而后修改nginx配置
# 在location当中加入以下配置
set $memcached_key "$uri?$args";
memcached_pass 127.0.0.1:11211;
add_header X-Cache-Satus HIT;
add_header Content-Type 'text/html; charset=utf-8';
默认直接访问nginx的时候,这是获取到的key为/? 同时在memcached当中设置其键值。而后访问。
set name 0 0 5
12345
7.2.2.3、redis2-nginx-module
首先安装好一个redis,这里可以直接通过源码安装:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_44973159/article/details/121736321 或者直接通过yum命令进行安装
yum install epel-release
yum install -y redis
nginx+redis依赖:github地址:https://github.com/openresty/redis2-nginx-module/releases/tag/v0.15
tar -zxvf redis2-nginx-module-0.15.tar.gz
./configure --add-module=/tools/nginx/redis2-nginx-module-0.15
make
这里我们简单对nginx+redis的配置,详细配置还是可以参考依赖的说明文档
location = /foo {
default_type text/html;
# redis2_query auth 123123;
set $value 'first';
redis2_query set one $value;
redis2_pass 127.0.0.1:6379;
}
location = /get {
default_type text/html;
redis2_pass 127.0.0.1:6379;
# redis2_query auth 123123;
# set_unescape_uri $key $arg_key; # this requires ngx_set_misc
redis2_query get $arg_key;
}
7.3、Stream模块
ngx_stream_core_module模块自1.9.0版起可用。默认情况下不构建此模块,应使用–withstream配置参数启用它。http://nginx.org/en/docs/stream/ngx_stream_core_module.html
./configure --with-stream
make
7.3.1、QPS限流
QPS限流模块:http://nginx.org/en/docs/http/ngx_http_limit_req_module.html
limit_req_zone $binary_remote_addr zone=test:10m rate=15r/s;
# 在location当中进行配置
# 平均每秒允许不超过1个请求,突发不超过5个请求。如果不希望在限制请求时延迟过多请求,则应使用参数nodelay:
limit_req zone=one burst=5 nodelay;
# 最开始下载传输带宽速度1m 后续速度限制为1k
limit_rate_after 1m;
limit_rate 1k;
7.3.2、并发数限制
7.3.3、日志
日志模块:http://nginx.org/en/docs/http/ngx_http_log_module.html
ngx_http_empty_gif_module模块发出单像素透明gif。http://nginx.org/en/docs/http/ngx_http_empty_gif_module.html
location = /_.gif {
empty_gif;
}
在默认日志配置当中,日志会写入到logs文件夹当中。
设置缓冲日志写入的路径、格式和配置。可以在同一配置级别上指定多个日志。可以通过在第一个参数中指定“syslog:”前缀来配置syslog的日志记录。特殊值off取消当前级别上的所有access_log指令。如果未指定格式,则使用预定义的“组合”格式。
# https下配置
log_format compression '$remote_addr - $remote_user [$time_local] '
'"$request" $status $bytes_sent '
'"$http_referer" "$http_user_agent" "$gzip_ratio"';
access_log /ngx_log/logs/nginx-access.log compression gzip buffer=32k;
# 设置缓存中描述符的最大数量;如果缓存已满,则关闭最近最少使用的(LRU)描述符
open_log_file_cache max = 5
如果使用gzip进行压缩,可以对gzip文件进行解压
# 修改日志文件为.gz后缀
gzip -d xxxx.gz
error_log(异常日志记录):http://nginx.org/en/docs/ngx_core_module.html#error_log
7.4、重试机制
7.4.1、重试机制配置
proxy_next_upstream :http://nginx.org/en/docs/http/ngx_http_proxy_module.html#proxy_next_upstream
# location下配置
proxy_next_upstream error timeout;
# 限制将请求传递到下一个服务器的时间。0值将关闭此限制。
proxy_next_upstream_timeout 0;
# 限制将请求传递到下一个服务器的可能尝试次数。0值将关闭此限制。
proxy_next_upstream_tries 0;
# 并且可以在upstream下配置下线 表示10s内失败5次就将该服务器下线
server 192.168.20.128 max_fails = 5 fail_timeout = 10s;
7.4.2、主动健康检查
nginx_upstream_check_module模块 https://github.com/yaoweibin/nginx_upstream_check_module
找到对应自己nginx的版本的patch脚本
yum install -y patch
patch -p1 < /tools/nginx/nginx-1.20/
./configure --add-module=/tools/nginx/nginx_upstream_check_module-0.4.0
make
make install
之后修改配置文件
upstream backend {
server 192.168.60.128:8081;
server 192.168.60.130:8081;
check interval=3000 rise=2 fall=5 timeout=1000 type=http;
check_http_send "HEAD / HTTP/1.0\r\n\r\n";
check_http_expect_alive http_2xx http_3xx;
}
location /status {
check_status;
access_log off;
}
location / {
proxy_pass http://backend;
root html;
}
8、nginx二次开发
8.1、Lua基础
首先我们在Lua官网下下载包:https://luabinaries.sourceforge.net/
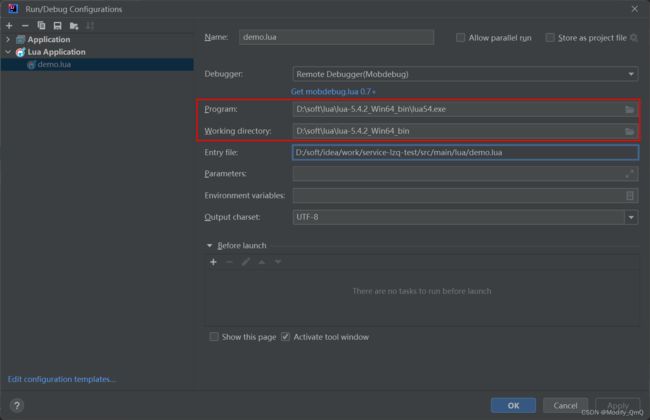
下载zip包后直接解压,而后我们采用idea进行编写,先在idea安装一个EmmyLua的插件,而后创建一个简单的lua文件,并且在运行时修改其配置:指定program和working directory的目录为刚才下载解压的Lua目录,这里就不对Lua脚本做过多介绍,可以在自行了解一下其基本语法等等
8.2、Openresty Nginx + Lua
openResty官网:http://openresty.org/cn/download.html
tar -zxvf openresty-1.21.4.1.tar.gz
./configure --prefix=/usr/local/openresty
# 编译失败报错 ./configure: error: the HTTP rewrite module requires the PCRE library.
# 解决方案 yum -y install pcre-devel
gmake
gmake install
cd /usr/local/openresty/nginx/sbin
# 退出重启
./nginx -s quit
./nginx -c /usr/local/openresty/nginx/conf/nginx.conf
# 查看端口88占用的进程
lsof -i:88
# 访问 http://192.168.60.128:88/
8.3、测试lua脚本
8.3.1、hello world
在nginx的配置文件当中加入:并且创建conf/lua/hello.lua文件,文件内容与/lua路由的打印日志相同格式进行测试
location /lua {
default_type text/html;
content_by_lua '
ngx.say("Hello, World!
")
';
}
location /luaout {
default_type text/html;
content_by_lua_file conf/lua/hello.lua;
}
8.3.2、热部署
在上述测试当中,每当修改hello.lua文件,都需要重新加载nginx才能生效,这时我们可以通过热部署配置进行实时生效
# serve下配置
lua_code_cache off;
8.3.3、Lua处理Http请求
这里是通过lua脚本对于http请求到nginx服务器进行解析操作
-- 获取Nginx请求头信息
local headers = ngx.req.get_headers()
ngx.say("Host : ", headers["Host"], "
")
ngx.say("user-agent : ", headers["user-agent"], "
")
ngx.say("user-agent : ", headers.user_agent, "
")
for k, v in pairs(headers) do
if type(v) == "table" then
ngx.say(k, " : ", table.concat(v, ","), "
")
else
ngx.say(k, " : ", v, "
")
end
end
-- 获取post请求参数
ngx.req.read_body()
ngx.say("post args begin", "
")
local post_args = ngx.req.get_post_args()
for k, v in pairs(post_args) do
if type(v) == "table" then
ngx.say(k, " : ", table.concat(v, ", "), "
")
else
ngx.say(k, ": ", v, "
")
end
end
-- http协议版本
ngx.say("ngx.req.http_version : ", ngx.req.http_version(), "
")
--请求方法
ngx.say("ngx.req.get_method : ", ngx.req.get_method(), "
")
--原始的请求头内容
ngx.say("ngx.req.raw_header : ", ngx.req.raw_header(), "
")
--body内容体
ngx.say("ngx.req.get_body_data() : ", ngx.req.get_body_data(), "
")
8.4 OpenResty缓存
8.4.1、全局内存缓存
在nginx+lua当中可以使用lua_shared_dict 表示一个全局缓存,而后在lua脚本当中可以获取当前缓存进行操作,就相当于java当中的synchronize关键字修饰的方法一样,保持了全局缓存操作的一个原子性
# https下 serve外
lua_shared_dict shared_data 1m;
local shared_data = ngx.shared.shared_data
local i = shared_data:get("i")
if not i then
i = 1
shared_data:set("i", i)
ngx.say("lazy set i ", i, "
")
end
i = shared_data:incr("i", 1)
ngx.say("i=", i, "
")
8.4.2、lua-resty-lrucache
location /luaout {
default_type text/html;
# content_by_lua_file conf/lua/hello.lua;
content_by_lua_block {
require("cache").go();
}
}
cache.lua,此时该文件目录地址为:/usr/local/openresty/nginx/conf/lua/cache.lua,代码如下
local _M = {}
lrucache = require "resty.lrucache"
c, err = lrucache.new(200) -- allow up to 200 items in the cache
ngx.say("count=init")
if not c then
error("failed to create the cache: " .. (err or "unknown"))
end
function _M.go()
count = c:get("count")
c:set("count",100)
ngx.say("count=", count, " --
")
if not count then
c:set("count",1)
ngx.say("lazy set count ", c:get("count"), "
")
else
c:set("count",count+1)
ngx.say("count=", count, "
")
end
end
return _M
此时直接访问location对应的路由会发现报错,因为此时还不知道对应的cache.lua文件去哪找,在报错日志当中可以看到会去一下目录下进行匹配,所以这个cache.lua文件就应该在这些文件下,
2023/03/05 09:14:20 [error] 105981#0: *1 lua entry thread aborted: runtime error: content_by_lua(nginx.conf:62):2: module 'my/cache' not found:
no field package.preload['my/cache']
no file '/usr/local/openresty/site/lualib/my/cache.ljbc'
no file '/usr/local/openresty/site/lualib/my/cache/init.ljbc'
no file '/usr/local/openresty/lualib/my/cache.ljbc'
no file '/usr/local/openresty/lualib/my/cache/init.ljbc'
no file '/usr/local/openresty/site/lualib/my/cache.lua'
no file '/usr/local/openresty/site/lualib/my/cache/init.lua'
no file '/usr/local/openresty/lualib/my/cache.lua'
no file '/usr/local/openresty/lualib/my/cache/init.lua'
no file './my/cache.lua'
no file '/usr/local/openresty/luajit/share/luajit-2.1.0-beta3/my/cache.lua'
no file '/usr/local/share/lua/5.1/my/cache.lua'
no file '/usr/local/share/lua/5.1/my/cache/init.lua'
no file '/usr/local/openresty/luajit/share/lua/5.1/my/cache.lua'
no file '/usr/local/openresty/luajit/share/lua/5.1/my/cache/init.lua'
no file '/usr/local/openresty/site/lualib/my/cache.so'
no file '/usr/local/openresty/lualib/my/cache.so'
no file './my/cache.so'
no file '/usr/local/lib/lua/5.1/my/cache.so'
no file '/usr/local/openresty/luajit/lib/lua/5.1/my/cache.so'
no file '/usr/local/lib/lua/5.1/loadall.so'
stack traceback:
coroutine 0:
[C]: in function 'require'
content_by_lua(nginx.conf:62):2: in main chunk, client: 192.168.60.1, server: localhost, request: "GET /luaout HTTP/1.1", host: "192.168.60.128:88"
当然,也可以进行文件目录的配置,设置将lua-resty-lrucache源树的路径添加到ngx_lua的lua模块搜索路径中,
# hhtp下
lua_package_path "/usr/local/openresty/nginx/conf/lua/?.lua;;";
# 注释改配置(并且要开启缓存)
# lua_code_cache off;
8.4.3、连接redis
先还是一样加上一个location路由配置指向对应的lua脚本
location /redis {
default_type text/html;
content_by_lua_file conf/lua/redis.lua;
}
在lua脚本当中,先连接了本地的redis,然后创建一个一个key为dog值为an animal 的键值对,最后打印输出
local redis = require "resty.redis"
local red = redis:new()
red:set_timeouts(1000, 1000, 1000) -- 1 sec
local ok, err = red:connect("127.0.0.1", 6379)
if not ok then
ngx.say("failed to connect: ", err)
return
end
ok, err = red:set("dog", "an animal")
if not ok then
ngx.say("failed to set dog: ", err)
return
end
ngx.say("set result: ", ok)
local res, err = red:get("dog")
if not res then
ngx.say("failed to get dog: ", err)
return
end
if res == ngx.null then
ngx.say("dog not found.")
return
end
ngx.say("dog: ", res)
8.4.4、连接MySQL
lua-resty-mysql:https://github.com/openresty/lua-resty-mysql
首先先通过ip连接上本地数据库,而后发送建表语句与查询语句,将查询返回的结果进行展示
local mysql = require "resty.mysql"
local db, err = mysql:new()
if not db then
ngx.say("failed to instantiate mysql: ", err)
return
end
db:set_timeout(1000) -- 1 sec
local ok, err, errcode, sqlstate = db:connect{
host = "192.168.60.128",
port = 3306,
database = "student",
user = "root",
password = "1234",
charset = "utf8",
max_packet_size = 1024 * 1024,
}
ngx.say("connected to mysql.
")
local res, err, errcode, sqlstate = db:query("drop table if exists cats")
if not res then
ngx.say("bad result: ", err, ": ", errcode, ": ", sqlstate, ".")
return
end
res, err, errcode, sqlstate =
db:query("create table cats "
.. "(id serial primary key, "
.. "name varchar(5))")
if not res then
ngx.say("bad result: ", err, ": ", errcode, ": ", sqlstate, ".")
return
end
ngx.say("table cats created.")
res, err, errcode, sqlstate =
db:query("select * from t_emp")
if not res then
ngx.say("bad result: ", err, ": ", errcode, ": ", sqlstate, ".")
return
end
local cjson = require "cjson"
ngx.say("result: ", cjson.encode(res))
local ok, err = db:set_keepalive(10000, 100)
if not ok then
ngx.say("failed to set keepalive: ", err)
return
end
8.4.5、模板引擎
lua-resty-template:https://github.com/bungle/lua-resty-template
tar -zxvf lua-resty-template-2.0.tar.gz
cd lua-resty-template-2.0/lib/resty
cp -r template /usr/local/openresty/lualib/resty/
cp template.lua /usr/local/openresty/lualib/resty/
8.5、基于OpenResty的开源项目
Kong : https://konghq.com/
APISIX
ABTestingGateway:https://github.com/CNSRE/ABTestingGateway