C/C++最全排序算法汇总,原理+代码
1、简介
排序是计算机内经常进行的一种操作,其目的是将一组“无序”的记录序列调整为“有序”的记录序列。分内部排序和外部排序。若整个排序过程不需要访问外存便能完成,则称此类排序问题为内部排序。反之,若参加排序的记录数量很大,整个序列的排序过程不可能在内存中完成,则称此类排序问题为外部排序。内部排序的过程是一个逐步扩大记录的有序序列长度的过程。
将杂乱无章的数据元素,通过一定的方法按关键字顺序排列的过程叫做排序。假定在待排序的记录序列中,存在多个具有相同的关键字的记录,若经过排序,这些记录的相对次序保持不变,即在原序列中,ri=rj,且ri在rj之前,而在排序后的序列中,ri仍在rj之前,则称这种排序算法是稳定的;否则称为不稳定的。
分类
稳定排序:假设在待排序的文件中,存在两个或两个以上的记录具有相同的关键字,在用某种排序法排序后,若这些相同关键字的元素的相对次序仍然不变,则这种排序方法是稳定的。其中冒泡,插入,基数,归并属于稳定排序,选择,快速,希尔,堆属于不稳定排序。
就地排序:若排序算法所需的辅助空间并不依赖于问题的规模n,即辅助空间为O(1),则称为就地排序。(百度百科)
2、交换排序
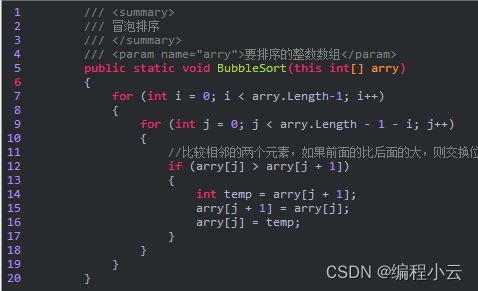
(1)冒泡排序
已知一组无序数据a[1]、a[2]、……a[n],需将其按升序排列。首先比较a[1]与a[2]的值,若a[1]大于a[2]则交换两者的值,否则不变。再比较a[2]与a[3]的值,若a[2]大于a[3]则交换两者的值,否则不变。再比较a[3]与a[4],以此类推,最后比较a[n-1]与a[n]的值。这样处理一轮后,a[n]的值一定是这组数据中最大的。再对a[1]a[n-1]以相同方法处理一轮,则a[n-1]的值一定是a[1]a[n-1]中最大的。再对a[1]~a[n-2]以相同方法处理一轮,以此类推。共处理n-1轮后a[1]、a[2]、……a[n]就以升序排列了。降序排列与升序排列相类似,若a[1]小于a[2]则交换两者的值,否则不变,后面以此类推。总的来讲,每一轮排序后最大(或最小)的数将移动到数据序列的最后,理论上总共要进行n(n-1)/2次交换。
简单测试
1 class Program
2 {
3 static void Main(string[] args)
4 {
5 int[] arry = new int[] { 1, 2, 3, 4, 1, -1 };
6 arry.BubbleSort();
7 for (int i = 0; i < arry.Length; i++)
8 {
9 Console.Write("\t" + arry[i]);
10 }
11 Console.Read();
12 }
13 }
结果
![]()
这里采用的是为整型数组添加扩展方法实现的冒泡排序。
优点:稳定
缺点:慢,每次只移动相邻的两个元素。
时间复杂度:理想情况下(数组本来就是有序的),此时最好的时间复杂度为o(n),最坏的时间复杂度(数据反序的),此时的时间复杂度为o(nn) 。冒泡排序的平均时间负责度为o(nn).
(2)快速排序
设要排序的数组是A[0]……A[N-1],首先任意选取一个数据(通常选用数组的第一个数)作为关键数据,然后将所有比它小的数都放到它前面,所有比它大的数都放到它后面,这个过程称为一趟快速排序。值得注意的是,快速排序不是一种稳定的排序算法,也就是说,多个相同的值的相对位置也许会在算法结束时产生变动。
一趟快速排序的算法是:
1)设置两个变量i、j,排序开始的时候:i=0,j=N-1;
2)以第一个数组元素作为关键数据,赋值给key,即key=A[0];
3)从j开始向前搜索,即由后开始向前搜索(j–),找到第一个小于key的值A[j],将A[j]和A[i]互换;
4)从i开始向后搜索,即由前开始向后搜索(i++),找到第一个大于key的A[i],将A[i]和A[j]互换;
5)重复第3、4步,直到i=j;(3,4步中,没找到符合条件的值,即3中A[j]不小于key,4中A[i]不大于key的时候改变j、i的值,使得j=j-1,i=i+1,直至找到为止。找到符合条件的值,进行交换的时候i, j指针位置不变。另外,i==j这一过程一定正好是i+或j-完成的时候,此时令循环结束)。
代码实现
1 /// 简单测试
1 static void Main(string[] args)
2 {
3 int[] arry = new int[] { 34,1,221,50,44,58,12,1,1};
4 //arry.BubbleSort();
5 arry.QuickSort(0, arry.Length-1 );
6 for (int i = 0; i < arry.Length; i++)
7 {
8 Console.Write("\t" + arry[i]);
9 }
10 Console.Read();
11 }
结果
3、插入排序
(1)直接插入排序
每次从无序表中取出第一个元素,把它插入到有序表的合适位置,使有序表仍然有序。
第一趟比较前两个数,然后把第二个数按大小插入到有序表中;第二趟把第三个数据与前两个数从前向后扫描,把第三个数按大小插入到有序表中;依次进行下去,进行了(n-1)趟扫描以后就完成了整个排序过程。
直接插入排序属于稳定的排序,最坏时间复杂性为O(n^2),空间复杂度为O(1)。
直接插入排序是由两层嵌套循环组成的。外层循环标识并决定待比较的数值。内层循环为待比较数值确定其最终位置。直接插入排序是将待比较的数值与它的前一个数值进行比较,所以外层循环是从第二个数值开始的。当前一数值比待比较数值大的情况下继续循环比较,直到找到比待比较数值小的并将待比较数值置入其后一位置,结束该次循环。
值得注意的是,我们必需用一个存储空间来保存当前待比较的数值,因为当一趟比较完成时,我们要将待比较数值置入比它小的数值的后一位 插入排序类似玩牌时整理手中纸牌的过程。插入排序的基本方法是:每步将一个待排序的记录按其关键字的大小插到前面已经排序的序列中的适当位置,直到全部记录插入完毕为止。
代码实现
1 /// 测试
1 static void Main(string[] args)
2 {
3 int[] arry = new int[] { 34,1,221,50,44,58,12};
4 //arry.BubbleSort();
5 //arry.QuickSort(0, arry.Length-1 );
6 arry.InsertSort();
7 for (int i = 0; i < arry.Length; i++)
8 {
9 Console.Write("\t" + arry[i]);
10 }
11 Console.Read();
12 }
结果
![]()
(2)希尔排序
希尔排序(Shell Sort)是插入排序的一种。也称缩小增量排序,是直接插入排序算法的一种更高效的改进版本。希尔排序是非稳定排序算法。该方法因DL.Shell于1959年提出而得名。
希尔排序是基于插入排序的以下两点性质而提出改进方法的:
插入排序在对几乎已经排好序的数据操作时,效率高,即可以达到线性排序的效率。
但插入排序一般来说是低效的,因为插入排序每次只能将数据移动一位。
基本思想
先取一个小于n的整数d1作为第一个增量,把文件的全部记录分组。所有距离为d1的倍数的记录放在同一个组中。先在各组内进行直接插入排序;然后,取第二个增量d2
比较相隔较远距离(称为增量)的数,使得数移动时能跨过多个元素,则进行一次比[2] 较就可能消除多个元素交换。D.L.shell于1959年在以他名字命名的排序算法中实现了这一思想。算法先将要排序的一组数按某个增量d分成若干组,每组中记录的下标相差d.对每组中全部元素进行排序,然后再用一个较小的增量对它进行,在每组中再进行排序。当增量减到1时,整个要排序的数被分成一组,排序完成。
一般的初次取序列的一半为增量,以后每次减半,直到增量为1。
代码实现
1 /// 测试
1 static void Main(string[] args)
2 {
3 int[] arry = new int[] { 34,1,221,50,44,58,12};
4 //arry.BubbleSort();
5 //arry.QuickSort(0, arry.Length-1 );
6 //arry.InsertSort();
7 arry.ShellSort();
8 for (int i = 0; i < arry.Length; i++)
9 {
10 Console.Write("\t" + arry[i]);
11 }
12 Console.Read();
13 }
结果
![]()
4、选择排序
(1)简单选择排序
设所排序序列的记录个数为n。i取1,2,…,n-1,从所有n-i+1个记录(Ri,Ri+1,…,Rn)中找出排序码最小的记录,与第i个记录交换。执行n-1趟 后就完成了记录序列的排序。
在简单选择排序过程中,所需移动记录的次数比较少。最好情况下,即待排序记录初始状态就已经是正序排列了,则不需要移动记录。
最坏情况下,即待排序记录初始状态是按逆序排列的,则需要移动记录的次数最多为3(n-1)。简单选择排序过程中需要进行的比较次数与初始状态下待排序的记录序列的排列情况无关。当i=1时,需进行n-1次比较;当i=2时,需进行n-2次比较;依次类推,共需要进行的比较次数是(n-1)+(n-2)+…+2+1=n(n-1)/2,即进行比较操作的时间复杂度为O(n^2),进行移动操作的时间复杂度为O(n)。
代码实现
1 /// 测试
1 static void Main(string[] args)
2 {
3 int[] arry = new int[] { 34,1,221,50,44,58,12};
4 //arry.BubbleSort();
5 //arry.QuickSort(0, arry.Length-1 );
6 //arry.InsertSort();
7 //arry.ShellSort();
8 arry.SimpleSelectSort();
9 for (int i = 0; i < arry.Length; i++)
10 {
11 Console.Write("\t" + arry[i]);
12 }
13 Console.Read();
14 }
(2)堆排序
堆排序(Heapsort)是指利用堆积树(堆)这种数据结构所设计的一种排序算法,它是选择排序的一种。可以利用数组的特点快速定位指定索引的元素。堆分为大根堆和小根堆,是完全二叉树。大根堆的要求是每个节点的值都不大于其父节点的值,即A[PARENT[i]] >= A[i]。在数组的非降序排序中,需要使用的就是大根堆,因为根据大根堆的要求可知,最大的值一定在堆顶。
代码实现
1 /// 测试
1 static void Main(string[] args)
2 {
3 int[] arry = new int[] { 34,1,221,50,44,58,12};
4 //arry.BubbleSort();
5 //arry.QuickSort(0, arry.Length-1 );
6 //arry.InsertSort();
7 //arry.ShellSort();
8 //arry.SimpleSelectSort();
9 arry.HeapSort(arry.Length);
10 for (int i = 0; i < arry.Length; i++)
11 {
12 Console.Write("\t" + arry[i]);
13 }
14 Console.Read();
15 }
结果
![]()
5、归并排序
归并排序是建立在归并操作上的一种有效的排序算法,该算法是采用分治法(Divide and Conquer)的一个非常典型的应用。将已有序的子序列合并,得到完全有序的序列;即先使每个子序列有序,再使子序列段间有序。若将两个有序表合并成一个有序表,称为二路归并。
归并过程为:比较a[i]和a[j]的大小,若a[i]≤a[j],则将第一个有序表中的元素a[i]复制到r[k]中,并令i和k分别加上1;否则将第二个有序表中的元素a[j]复制到r[k]中,并令j和k分别加上1,如此循环下去,直到其中一个有序表取完,然后再将另一个有序表中剩余的元素复制到r中从下标k到下标t的单元。归并排序的算法我们通常用递归实现,先把待排序区间[s,t]以中点二分,接着把左边子区间排序,再把右边子区间排序,最后把左区间和右区间用一次归并操作合并成有序的区间[s,t]。
归并操作(merge),也叫归并算法,指的是将两个顺序序列合并成一个顺序序列的方法。
如 设有数列{6,202,100,301,38,8,1}
初始状态:6,202,100,301,38,8,1
第一次归并后:{6,202},{100,301},{8,38},{1},比较次数:3;
第二次归并后:{6,100,202,301},{1,8,38},比较次数:4;
第三次归并后:{1,6,8,38,100,202,301},比较次数:4;
总的比较次数为:3+4+4=11,;
逆序数为14;
归并操作的工作原理如下:
第一步:申请空间,使其大小为两个已经排序序列之和,该空间用来存放合并后的序列
第二步:设定两个指针,最初位置分别为两个已经排序序列的起始位置
第三步:比较两个指针所指向的元素,选择相对小的元素放入到合并空间,并移动指针到下一位置
重复步骤3直到某一指针超出序列尾
将另一序列剩下的所有元素直接复制到合并序列尾
代码实现
1 /// 测试
1 /// 测试
1 static void Main(string[] args)
2 {
3 int[] arry = new int[] { 34,1,221,50,44,58,12};
4 //arry.BubbleSort();
5 //arry.QuickSort(0, arry.Length-1 );
6 //arry.InsertSort();
7 //arry.ShellSort();
8 //arry.SimpleSelectSort();
9 //arry.HeapSort(arry.Length);
10 //arry.MergeSort(0, arry.Length);
11 arry.RadixSort();
12 for (int i = 0; i < arry.Length; i++)
13 {
14 Console.Write("\t" + arry[i]);
15 }
16 Console.Read();
17 }
结果
![]()
7、总结
整数数组各种排序算法扩展类
1 using System;
2 using System.Collections.Generic;
3 using System.Linq;
4 using System.Text;
5 using System.Threading.Tasks;
6
7 namespace Wolfy.Sort
8 {
9 /// 