Spring 远程加载配置
本文以携程的Apollo和阿里的Nacos为例。
pom中引入一下依赖:
<dependency>
<groupId>com.ctrip.framework.apollogroupId>
<artifactId>apollo-clientartifactId>
<version>2.0.1version>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba.cloudgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-alibaba-nacos-configartifactId>
<version>2021.1version>
dependency>
不管是Apollo还是Nacos,实现从远程加载配置都是通过ConfigurableEnvironment和PropertySource完成的,步骤如下:
- 远程拉取配置,生成
PropertySource - 从
ConfigurableEnvironment获取聚合类MutablePropertySources propertySources = ConfigurableEnvironment#getPropertySources(); - 将拉取的
PropertySource添加到从ConfigurableEnvironment获取的聚合类MutablePropertySources#add...(PropertySource propertySource)
至于这个过程是怎么触发和运行的,要看具体实现。
- 在apollo-client中,使用BeanFactoryPostProcessor。
- 在spring-cloud-starter-alibaba-nacos-config中,由于 cloud-nacos实现了spring cloud config规范(处于
org.springframework.cloud.bootstrap.config包下),nacos实现该规范即可,即实现spring cloud 的PropertySourceLocator接口。
Apollo
关注PropertySourcesProcessor ,该类为一个BeanFactoryPostProcessor,同时为了获取ConfigurableEnvironment,该类实现了EnvironmentAware回调接口。该类何时被加入spring容器?是通过@EnableApolloConfig的@Import注解的类ApolloConfigRegistrar来加入,常规套路。
public class PropertySourcesProcessor implements BeanFactoryPostProcessor, EnvironmentAware,
ApplicationEventPublisherAware, PriorityOrdered {
// aware回调接口设置
private ConfigurableEnvironment environment;
@Override
public void setEnvironment(Environment environment) {
//it is safe enough to cast as all known environment is derived from ConfigurableEnvironment
this.environment = (ConfigurableEnvironment) environment;
}
@Override
public void postProcessBeanFactory(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) throws BeansException {
// 获取配置
this.configUtil = ApolloInjector.getInstance(ConfigUtil.class);
// 从远程获取PropertySource
initializePropertySources();
// 为每个ConfigPropertySource注册ConfigChangeEvent监听器
// 监听器监听到ConfigChangeEvent后publish一个ApolloConfigChangeEvent
// 等于将apollo自定义的ConfigChangeEvent事件机制转化为了spring的ApolloConfigChangeEvent事件
initializeAutoUpdatePropertiesFeature(beanFactory);
}
private void initializePropertySources() {
// 聚合类,该类也是一个PropertySource,代理了一堆PropertySource
// 该类中有一个 Set> 字段
CompositePropertySource composite = new ...;
...
// 从 远程 或 本地缓存 获取配置
Config config = ConfigService.getConfig(namespace);
// 适配Config到PropertySource,并加入聚合类
composite.addPropertySource(configPropertySourceFactory.getConfigPropertySource(namespace, config));
// 添加到ConfigurableEnvironment
environment.getPropertySources().addFirst(composite);
}
private void initializeAutoUpdatePropertiesFeature(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) {
if (!AUTO_UPDATE_INITIALIZED_BEAN_FACTORIES.add(beanFactory)) {
return;
}
// 定义监听器,监听器监听到ConfigChangeEvent后发布ApolloConfigChangeEvent
ConfigChangeListener configChangeEventPublisher = changeEvent ->
applicationEventPublisher.publishEvent(new ApolloConfigChangeEvent(changeEvent));
// 注册监听器到每个PropertySource
List<ConfigPropertySource> configPropertySources = configPropertySourceFactory.getAllConfigPropertySources();
for (ConfigPropertySource configPropertySource : configPropertySources) {
configPropertySource.addChangeListener(configChangeEventPublisher);
}
}
...
}
从上面可知初始化时会从ConfigService远程拉取配置,并保存到内部缓存。而后续远程配置中心配置发生变化时本地会拉去最新配置并发布事件,PropertySource根据事件进行更新。
无论是开始从远程拉取配置初始化,还是后续远程配置更新,最终都是通过RemoteConfigRepository以http形式定时获取配置:
public class RemoteConfigRepository extends AbstractConfigRepository implements ConfigRepository{
public RemoteConfigRepository(String namespace) {
...
// 定时拉取
this.schedulePeriodicRefresh();
// 长轮询
this.scheduleLongPollingRefresh();
...
}
private void schedulePeriodicRefresh() {
// 定时线程池
m_executorService.scheduleAtFixedRate(
new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
// 调用父抽象类trySync()
// trySync()调用模版方法sync()
trySync();
}
}, m_configUtil.getRefreshInterval(), m_configUtil.getRefreshInterval(),
m_configUtil.getRefreshIntervalTimeUnit());
}
@Override
protected synchronized void sync() {
// 事务
Transaction transaction = Tracer.newTransaction("Apollo.ConfigService", "syncRemoteConfig");
try {
ApolloConfig previous = m_configCache.get();
// http远程拉取配置
ApolloConfig current = loadApolloConfig();
// reference equals means HTTP 304
if (previous != current) {
logger.debug("Remote Config refreshed!");
// 设置缓存
m_configCache.set(current);
// 发布事件,该方法在父抽象类中
this.fireRepositoryChange(m_namespace, this.getConfig());
}
if (current != null) {
Tracer.logEvent(String.format("Apollo.Client.Configs.%s", current.getNamespaceName()),
current.getReleaseKey());
}
transaction.setStatus(Transaction.SUCCESS);
} catch (Throwable ex) {
transaction.setStatus(ex);
throw ex;
} finally {
transaction.complete();
}
...
}
可以看到,在构造方法中,就执行了 3 个本地方法,其中就包括定时刷新和长轮询刷新。这两个功能在 apollo 的 github 文档中也有介绍:
-
客户端和服务端保持了一个长连接,从而能第一时间获得配置更新的推送。
-
客户端还会定时从Apollo配置中心服务端拉取应用的最新配置。
-
这是一个fallback机制,为了防止推送机制失效导致配置不更新。
-
客户端定时拉取会上报本地版本,所以一般情况下,对于定时拉取的操作,服务端都会返回304 - Not Modified。
-
定时频率默认为每5分钟拉取一次,客户端也可以通过在运行时指定System Property: apollo.refreshInterval来覆盖,单位为分钟。
所以,长连接是更新配置的主要手段,然后用定时任务辅助长连接,防止长连接失败。
org.springframework.cloud.bootstrap.config
nacos实现了spring cloud config规范,规范代码的maven坐标如下:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloudgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-contextartifactId>
<version>...version>
<scope>compilescope>
dependency>
这里介绍规范内容,nacos的实现略。
PropertySource
PropertySource用于存储k-v键值对,远程或本地的配置最终都转化为PropertySource,放入ConfigurableEnvironment中,通常EnumerablePropertySource中会代理一个PropertySource的list。
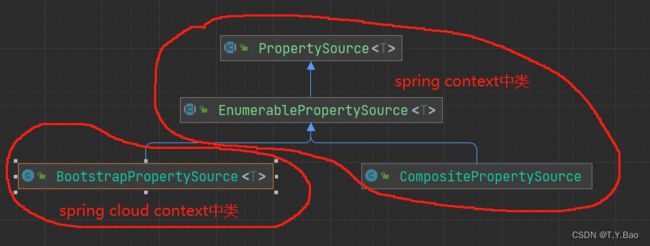
PropertySourceLocator
规范接口主要为PropertySourceLocator接口,该接口用于定位PropertySource,注释如下:
Strategy for locating (possibly remote) property sources for the Environment. Implementations should not fail unless they intend to prevent the application from starting.
public interface PropertySourceLocator {
// 实现类实现该方法
PropertySource<?> locate(Environment environment);
default Collection<PropertySource<?>> locateCollection(Environment environment) {
return locateCollection(this, environment);
}
static Collection<PropertySource<?>> locateCollection(PropertySourceLocator locator, Environment environment) {
// 调用实现类
PropertySource<?> propertySource = locator.locate(environment);
if (propertySource == null) {
return Collections.emptyList();
}
// 如果该PropertySource是代理了list的CompositePropertySource,提取全部
if (CompositePropertySource.class.isInstance(propertySource)) {
Collection<PropertySource<?>> sources = ((CompositePropertySource) propertySource).getPropertySources();
List<PropertySource<?>> filteredSources = new ArrayList<>();
for (PropertySource<?> p : sources) {
if (p != null) {
filteredSources.add(p);
}
}
return filteredSources;
}
else {
return Arrays.asList(propertySource);
}
}
}
PropertySourceBootstrapConfiguration
调用PropertySourceLocator接口将PropertySource加入ConfigurableEnvironment中。
@Configuration(proxyBeanMethods = false)
@EnableConfigurationProperties(PropertySourceBootstrapProperties.class)
public class PropertySourceBootstrapConfiguration
implements ApplicationContextInitializer<ConfigurableApplicationContext>, Ordered {
@Autowired(required = false)
private List<PropertySourceLocator> propertySourceLocators = new ArrayList<>();
public void setPropertySourceLocators(Collection<PropertySourceLocator> propertySourceLocators) {
this.propertySourceLocators = new ArrayList<>(propertySourceLocators);
}
@Override
public void initialize(ConfigurableApplicationContext applicationContext) {
List<PropertySource<?>> composite = new ArrayList<>();
// 排序
AnnotationAwareOrderComparator.sort(this.propertySourceLocators);
boolean empty = true;
// applicationContext由回调接口提供
ConfigurableEnvironment environment = applicationContext.getEnvironment();
for (PropertySourceLocator locator : this.propertySourceLocators) {
// 调用PropertySourceLocator
Collection<PropertySource<?>> source = locator.locateCollection(environment);
...
for (PropertySource<?> p : source) {
// 是否代理了PropertySource的list做分类
if (p instanceof EnumerablePropertySource) {
EnumerablePropertySource<?> enumerable = (EnumerablePropertySource<?>) p;
sourceList.add(new BootstrapPropertySource<>(enumerable));
}
else {
sourceList.add(new SimpleBootstrapPropertySource(p));
}
}
composite.addAll(sourceList);
empty = false;
}
if (!empty) {
// 获取 ConfigurableEnvironment中的MutablePropertySources
MutablePropertySources propertySources = environment.getPropertySources();
...
// 执行插入到ConfigurableEnvironment的MutablePropertySources
insertPropertySources(propertySources, composite);
...
}
}
}
总结
可以看到从远程获取配置都是通过向ConfigurableEnvironment插入从远程获取的数据转化的PropertySource。而从远程获取就涉及到长轮询、本地缓存等内容,设计都比较一致。