CenOS 7安装nginx-yum安装方式
CenOS 7安装nginx-yum安装方式
文章目录
- CenOS 7安装nginx-yum安装方式
-
- 一、安装和配置
-
- 1.yum源
- 2.安装
- 3.启停nginx
- 4.开机自启动
- 5.防火墙
- 6.重新加载配置文件
- 二、配置文件
-
- 1.配置文件可视化
- 2.遇到问题
- 三、高级配置
-
- 1.限流配置说明
- 2.负载均衡
-
- (1)nginx 支持的负载均衡方式
- (2)示例
- (3)session粘滞
一、安装和配置
1.yum源
sudo yum install yum-utils
vim /etc/yum.repos.d/nginx.repo
[nginx-stable]
name=nginx stable repo
baseurl=http://nginx.org/packages/centos/$releasever/$basearch/
gpgcheck=1
enabled=1
gpgkey=https://nginx.org/keys/nginx_signing.key
module_hotfixes=true
[nginx-mainline]
name=nginx mainline repo
baseurl=http://nginx.org/packages/mainline/centos/$releasever/$basearch/
gpgcheck=1
enabled=0
gpgkey=https://nginx.org/keys/nginx_signing.key
module_hotfixes=true
2.安装
sudo yum-config-manager --enable nginx-mainline
sudo yum install nginx
3.启停nginx
systemctl start nginx
systemctl stop nginx
4.开机自启动
systemctl enable nginx
systemctl status nginx
5.防火墙
firewall-cmd --zone=public --add-port=80/tcp --permanent
firewall-cmd --reload
6.重新加载配置文件
sudo nginx -t && sudo systemctl reload nginx
二、配置文件
1.配置文件可视化
nginxconfig.io
# Generated by nginxconfig.io
# https://www.digitalocean.com/community/tools/nginx?domains.0.https.https=false&domains.0.php.php=false&domains.0.reverseProxy.reverseProxy=true&domains.0.reverseProxy.path=%2Fapi&domains.0.routing.index=index.html&domains.0.routing.fallbackPhp=false&global.nginx.user=nginx&global.nginx.clientMaxBodySize=50&global.tools.modularizedStructure=false&global.tools.symlinkVhost=false&global.app.lang=zhCN
user nginx;
pid /run/nginx.pid;
worker_processes auto;
worker_rlimit_nofile 65535;
# Load modules
include /etc/nginx/modules-enabled/*.conf;
events {
multi_accept on;
worker_connections 65535;
}
http {
charset utf-8;
sendfile on;
tcp_nopush on;
tcp_nodelay on;
server_tokens off;
log_not_found off;
types_hash_max_size 2048;
types_hash_bucket_size 64;
client_max_body_size 50M;
# MIME
include mime.types;
default_type application/octet-stream;
# Logging
access_log /var/log/nginx/access.log;
error_log /var/log/nginx/error.log warn;
# Connection header for WebSocket reverse proxy
map $http_upgrade $connection_upgrade {
default upgrade;
"" close;
}
map $remote_addr $proxy_forwarded_elem {
# IPv4 addresses can be sent as-is
~^[0-9.]+$ "for=$remote_addr";
# IPv6 addresses need to be bracketed and quoted
~^[0-9A-Fa-f:.]+$ "for=\"[$remote_addr]\"";
# Unix domain socket names cannot be represented in RFC 7239 syntax
default "for=unknown";
}
map $http_forwarded $proxy_add_forwarded {
# If the incoming Forwarded header is syntactically valid, append to it
"~^(,[ \\t]*)*([!#$%&'*+.^_`|~0-9A-Za-z-]+=([!#$%&'*+.^_`|~0-9A-Za-z-]+|\"([\\t \\x21\\x23-\\x5B\\x5D-\\x7E\\x80-\\xFF]|\\\\[\\t \\x21-\\x7E\\x80-\\xFF])*\"))?(;([!#$%&'*+.^_`|~0-9A-Za-z-]+=([!#$%&'*+.^_`|~0-9A-Za-z-]+|\"([\\t \\x21\\x23-\\x5B\\x5D-\\x7E\\x80-\\xFF]|\\\\[\\t \\x21-\\x7E\\x80-\\xFF])*\"))?)*([ \\t]*,([ \\t]*([!#$%&'*+.^_`|~0-9A-Za-z-]+=([!#$%&'*+.^_`|~0-9A-Za-z-]+|\"([\\t \\x21\\x23-\\x5B\\x5D-\\x7E\\x80-\\xFF]|\\\\[\\t \\x21-\\x7E\\x80-\\xFF])*\"))?(;([!#$%&'*+.^_`|~0-9A-Za-z-]+=([!#$%&'*+.^_`|~0-9A-Za-z-]+|\"([\\t \\x21\\x23-\\x5B\\x5D-\\x7E\\x80-\\xFF]|\\\\[\\t \\x21-\\x7E\\x80-\\xFF])*\"))?)*)?)*$" "$http_forwarded, $proxy_forwarded_elem";
# Otherwise, replace it
default "$proxy_forwarded_elem";
}
# Load configs
include /etc/nginx/conf.d/*.conf;
# example.com
server {
listen 80;
listen [::]:80;
server_name example.com;
root /var/www/example.com/public;
# security headers
add_header X-XSS-Protection "1; mode=block" always;
add_header X-Content-Type-Options "nosniff" always;
add_header Referrer-Policy "no-referrer-when-downgrade" always;
add_header Content-Security-Policy "default-src 'self' http: https: data: blob: 'unsafe-inline'; frame-ancestors 'self';" always;
add_header Permissions-Policy "interest-cohort=()" always;
# . files
location ~ /\.(?!well-known) {
deny all;
}
# reverse proxy
location /api {
proxy_pass http://127.0.0.1:3000;
proxy_http_version 1.1;
proxy_cache_bypass $http_upgrade;
# Proxy headers
proxy_set_header Upgrade $http_upgrade;
proxy_set_header Connection $connection_upgrade;
proxy_set_header Host $host;
proxy_set_header X-Real-IP $remote_addr;
proxy_set_header Forwarded $proxy_add_forwarded;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For $proxy_add_x_forwarded_for;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-Proto $scheme;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-Host $host;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-Port $server_port;
# Proxy timeouts
proxy_connect_timeout 60s;
proxy_send_timeout 60s;
proxy_read_timeout 60s;
}
# favicon.ico
location = /favicon.ico {
log_not_found off;
access_log off;
}
# robots.txt
location = /robots.txt {
log_not_found off;
access_log off;
}
# assets, media
location ~* \.(?:css(\.map)?|js(\.map)?|jpe?g|png|gif|ico|cur|heic|webp|tiff?|mp3|m4a|aac|ogg|midi?|wav|mp4|mov|webm|mpe?g|avi|ogv|flv|wmv)$ {
expires 7d;
access_log off;
}
# svg, fonts
location ~* \.(?:svgz?|ttf|ttc|otf|eot|woff2?)$ {
add_header Access-Control-Allow-Origin "*";
expires 7d;
access_log off;
}
# gzip
gzip on;
gzip_vary on;
gzip_proxied any;
gzip_comp_level 6;
gzip_types text/plain text/css text/xml application/json application/javascript application/rss+xml application/atom+xml image/svg+xml;
}
# subdomains redirect
server {
listen 80;
listen [::]:80;
server_name *.example.com;
return 301 http://example.com$request_uri;
}
}
2.遇到问题
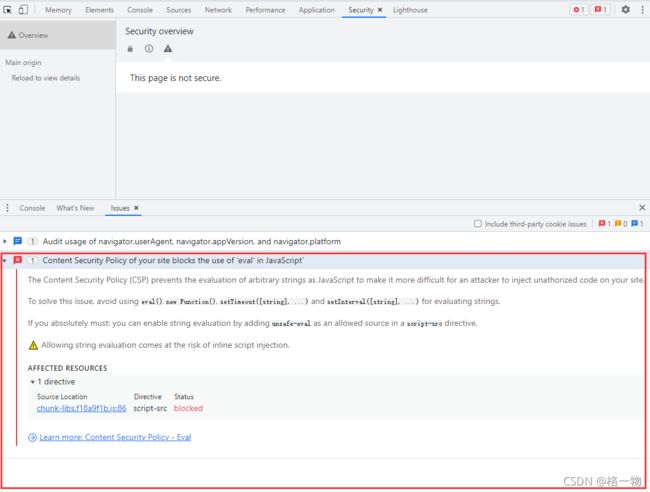
- 问题
vue+element前端代码部署到nginx后无法访问
- 解决办法
注释代码
add_header Content-Security-Policy "default-src 'self' http: https: data: blob: 'unsafe-inline'; frame-ancestors 'self';" always;即可!
三、高级配置
1.限流配置说明
- limit_req_zone 参数配置
Syntax: limit_req zone=name [burst=number] [nodelay];
Default: —
Context: http, server, location
limit_req_zone $binary_remote_addr zone=one:10m rate=1r/s;
第一个参数:$binary_remote_addr 表示通过remote_addr这个标识来做限制,“binary_”的目的是缩写内存占用量,是限制同一客户端ip地址。
第二个参数:zone=one:10m表示生成一个大小为10M,名字为one的内存区域,用来存储访问的频次信息。
第三个参数:rate=1r/s表示允许相同标识的客户端的访问频次,这里限制的是每秒1次,还可以有比如30r/m的。
limit_req zone=one burst=5 nodelay;
第一个参数:zone=one 设置使用哪个配置区域来做限制,与上面limit_req_zone 里的name对应。
第二个参数:burst=5,重点说明一下这个配置,burst爆发的意思,这个配置的意思是设置一个大小为5的缓冲区当有大量请求(爆发)过来时,超过了访问频次限制的请求可以先放到这个缓冲区内。
第三个参数:nodelay,如果设置,超过访问频次而且缓冲区也满了的时候就会直接返回503,如果没有设置,则所有请求会等待排队。
- 示例
http {
limit_req_zone $binary_remote_addr zone=one:10m rate=1r/s;
server {
location /search/ {
limit_req zone=one burst=5 nodelay;
}
}
2.负载均衡
(1)nginx 支持的负载均衡方式
- round-robin(轮询) 默认方式
- least-connected(最少连接)
- ip-hash
(2)示例
upstream backend {
server backend1.example.com weight=5;
server backend2.example.com:8080;
server unix:/tmp/backend3;
server backup1.example.com:8080 backup;
server backup2.example.com:8080 backup;
}
server {
location / {
proxy_pass http://backend;
}
}
(3)session粘滞
nginx session粘滞提供了3中实现方案,cookie、route、learn(商用订阅)。
- cookie方式示例
实现原理,nginx在cookie中增加srv_id属性值,默认为后端服务的IP和端口的MD5值或unix-socket path,若设置route参数则值为route值
upstream backend {
server backend1.example.com;
server backend2.example.com;
sticky cookie srv_id expires=1h domain=.example.com path=/;
}
upstream backend {
server backend1.example.com route=a;
server backend2.example.com route=b;
sticky cookie srv_id expires=1h domain=.example.com path=/;
}
更多配置:ngx_http_upstream_module.html,使用对应指令时注意nginx
版本要求及商用订阅限制。
参考:
nginx: Linux packages
配置参数
死磕nginx系列–nginx 限流配置