【力扣/牛客刷题】二叉树篇
作者:✿✿ xxxflower. ✿✿
博客主页:xxxflower的博客
专栏:【力扣、牛客刷题】篇
语录:⭐每一个不曾起舞的日子,都是对生命的辜负。⭐
文章目录
- 100. 相同的树
- 572. 另一棵树的子树
- 226. 翻转二叉树
- 平衡二叉树
- 101.对称二叉树
- 层序遍历
- 二叉树的遍历
- 二叉树的最近公共祖先
- 非递归实现前序遍历
- 非递归实现中序遍历
- 非递归实现后序遍历
- 二叉搜索树与双向链表
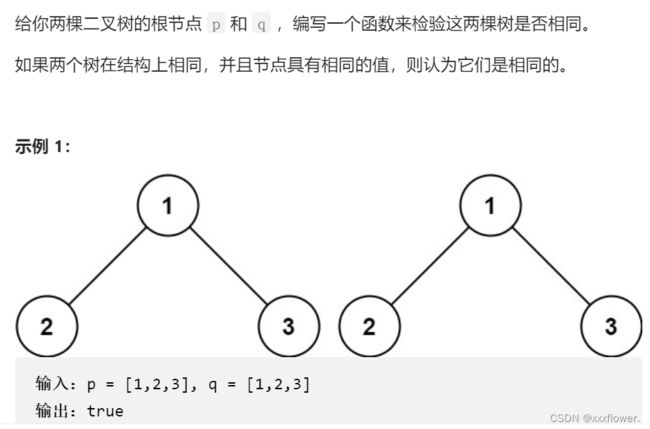
100. 相同的树
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public boolean isSameTree(TreeNode p, TreeNode q) {
if(p ==null && q == null){
return true;
}
if(p ==null || q == null){
return false;
}if(p.val == q.val){
return isSameTree(p.left,q.left) &&
isSameTree(p.right,q.right);
}else{
return false;
}
}
}
572. 另一棵树的子树
题目oj:572. 另一棵树的子树

本题采用子问题思路。先判断root是否为空的情况,然后判断两棵树是否为相同的树,判断subRoot是不是root.left的子树,判断subRoot是不是root.right的子树。
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public boolean isSubtree(TreeNode root, TreeNode subRoot) {
if(root == null || subRoot == null){
return false;
}
//1.判断两棵树是否为相同的树
if(isSameTree(root,subRoot)){
return true;
}
//2.判断subRoot是不是root.left的子树
if(isSubtree(root.left,subRoot)){
return true;
}
//3.判断subRoot是不是root.right的子树
if(isSubtree(root.right,subRoot)){
return true;
}
return false;
}
public boolean isSameTree(TreeNode p, TreeNode q) {
if(p ==null && q == null){
return true;
}
if(p ==null || q == null){
return false;
}if(p.val != q.val){
return false;
} return isSameTree(p.left,q.left) &&
isSameTree(p.right,q.right);
}
}
226. 翻转二叉树
题目oj:226. 翻转二叉树

要翻转整棵树,实际上是翻转整棵树的左树和右树。
1.翻转左树和右树
2.处理root.left的子树
3.处理root.right的子树
class Solution {
public TreeNode invertTree(TreeNode root) {
if(root != null){
TreeNode tmp = root.left;
root.left = root.right;
root.right = tmp;
invertTree(root.left);
invertTree(root.right);
}
return root;
}
}
平衡二叉树
题目oj:110.平衡二叉树
思路1:要想判断一棵树是否为平衡二叉树,我们可以判断跟节点的左数高度和右树高度。查找每一个节点的左树高度和右树高度然后相减求绝对值,如果绝对值小于2,那么证明这个节点是平衡的。
class Solution {
public boolean isBalanced(TreeNode root) {
if(root == null){
return true;
}
int leftHeigh = isHeight(root.left);
int rightHeigh = isHeight(root.right);
return Math.abs(leftHeigh-rightHeigh) < 2
&& isBalanced(root.left)
&& isBalanced(root.right);
}
public int isHeight(TreeNode root){
if(root == null){
return 0;
}
int lHeigh = isHeight(root.left);
int rHeigh = isHeight(root.right);
if(lHeigh >= 0 && rHeigh >= 0
&&Math.abs(lHeigh - rHeigh) <= 1){
return Math.max(lHeigh,rHeigh)+1;
}else{
return -1;
}
}
}
由思路可以得到,最坏的结果是每一个节点都要计算一次其左右子树的高度,所以这种思路的时间复杂度达到了O(N²)。那么有没有一种方法让实践复杂度为O(N)就可以达到呢?那么我们来看一下思路二:在判断根结点左子树和右子树是否平衡的时候,我们可以标记一下,如果左树的高减右树的高度大于2时,则此树一定不是平衡二叉树,那么返回-1;(注意:假如左子树求出来的值是-1,右子树是0,这种情况下也不属于平衡二叉树,所以注意条件的书写)
class Solution {
public boolean isBalanced(TreeNode root) {
if(root == null){
return true;
}
return isHeight(root) >= 0;
}
public int isHeight(TreeNode root){
if(root == null){
return 0;
}
int lHeigh = isHeight(root.left);
int rHeigh = isHeight(root.right);
if(lHeigh >= 0 && rHeigh >= 0
&&Math.abs(lHeigh - rHeigh) <= 1){
return Math.max(lHeigh,rHeigh)+1;
}else{
return -1;
}
}
}
101.对称二叉树
题目oj:对称二叉树


如图所示,要想判断一棵树是否对称,先判断一下根结点是否为空。再判断左子树和右子树的值是否相同。此处的相同有两种情况,即结构相同和数值相同。数值相同又分为两种情况:即左子树的左端的值和右子树右端的值相同,左子树右端的值和右子树左端的值相同。代码如下:
class Solution {
public boolean isSymmetric(TreeNode root) {
if(root == null){
return true;
}
return isSymmetricChild(root.left,root.right);
}
private boolean isSymmetricChild(TreeNode leftNode,TreeNode rightNode){
if(leftNode == null && rightNode != null
||leftNode != null && rightNode == null){
return false;
}
if(leftNode == null && rightNode == null){
return true;
}
if(leftNode.val != rightNode.val){
return false;
}
return isSymmetricChild(leftNode.left,rightNode.right)
&& isSymmetricChild(leftNode.right,rightNode.left);
}
}
思考:如果有两棵树,如下图,那么如何判断他们两个是否为镜像对称?

class Solution6 {
public boolean isSymmetricTwo(TreeNode root1,TreeNode root2) {
if(root1 == null && root2 == null){
return true;
}
if(root1 == null && root2 != null || root1 != null && root2 == null){
return false;
}
if(root1.val != root2.val){
return false;
}
return isSymmetricTwo(root1.left,root2.right) &&
isSymmetricTwo(root1.right,root2.left);
}
}
层序遍历
关于层序遍历,我们前文有过讲解。但是不一样的是本题的返回值是List
思路:现将A放入队列中,然后判断队列是否为空?不为空的话获取一下队列的大小size,根据size的大小确定往list当中放入元素的多少,此处可以用循环。然后弹出A给cur,size–,再将cur的值添加到list当中。如果cur的左边不为空,则放入到队列中,右边同理。size为0,此循环结束.再判断队列是否为空。。。。
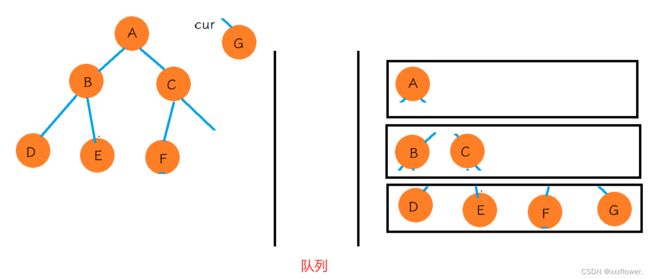
class Solution {
public List<List<Integer>> levelOrder(TreeNode root) {
List<List<Integer>> list = new ArrayList<>();
if(root == null){
return list;
}
Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.offer(root);
while(! queue.isEmpty()){
int size = queue.size();
List<Integer> tmp = new ArrayList<>();
while(size > 0){
TreeNode cur = queue.poll();
size--;
tmp.add(cur.val);
if(cur.left != null){
queue.offer(cur.left);
}
if(cur.right != null){
queue.offer(cur.right);
}
}
list.add(tmp);
}
return list;
}
}
二叉树的遍历
题目oj:二叉树的遍历

从题中可以得出,这是先序遍历,那么我们要采用先序遍历的思想去解决问题。

import java.util.Scanner;
class TreeNode{
public char val;
public TreeNode left;
public TreeNode right;
public TreeNode(char val){
this.val = val;
}
}
// 注意类名必须为 Main, 不要有任何 package xxx 信息
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
// 注意 hasNext 和 hasNextLine 的区别
while (in.hasNextLine()) { // 注意 while 处理多个 case
String str = in.nextLine();
TreeNode root = createTree(str);
//中序遍历二叉树
inOder(root);
}
}
private static void inOder(TreeNode root){
if(root == null){
return;
}
inOder(root.left);
System.out.print(root.val + " ");
inOder(root.right);
}
private static int i = 0;
private static TreeNode createTree(String str){
TreeNode root = null;
if(str.charAt(i) != '#'){
root = new TreeNode(str.charAt(i));
i++;
root.left = createTree(str);
root.right = createTree(str);
}else{
i++;
}
return root;
}
}
二叉树的最近公共祖先
题目oj:二叉树的最近公共祖先
如图所示,我们要找4和8的最近公共祖先3。

那么我们应该怎么做呢?
思路:我们可以创建两个栈,寻找左树中根结点到4并存储路径放入第一个栈中,然后寻找右树中根结点到8的路径放入第二个栈中。然后我们弹出两个栈相差的元素个数,再写个循环看每一次弹出的元素是否相同,如果相同,则就是两个值的最近公共祖先。

class Solution {
public TreeNode lowestCommonAncestor(TreeNode root, TreeNode p, TreeNode q) {
if(root == null || p == null || q == null){
return null;
}
Stack<TreeNode> stack1 = new Stack<>();
getPath(root,p,stack1);
Stack<TreeNode> stack2 = new Stack<>();
getPath(root,q,stack2);
int size1 = stack1.size();
int size2 = stack2.size();
if(size1 > size2){
int ret = size1 - size2;
while(ret > 0){
stack1.pop();
ret--;
}
} else{
int ret = size2 - size1;
while(ret > 0){
stack2.pop();
ret--;
}
}
while(stack1.peek() != stack2.peek()){
stack1.pop();
stack2.pop();
}
return stack1.peek();
}
public boolean getPath(TreeNode root,TreeNode node,Stack stack){
if(root == null || node == null){
return false;
}
stack.push(root);
if(root == node){
return true;
}
boolean flg1 = getPath(root.left,node,stack);
if(flg1){
return true;
}
boolean flg2 = getPath(root.right,node,stack);
if(flg2){
return true;
}
stack.pop();
return false;
}
}
那么,除了以上方式外,还有一种方法。即子问题方式。
非递归实现前序遍历
思路:定义一个栈,定义一个cur = root,如果cur不为空,将元素入栈并打印放入ret(要返回的链表)中,然后让cur = cur.left。如果cur为空,那么定一个一个变量top,用于存储栈中弹出的节点,让cur = top.right。循环的条件是cur!=null 或者栈不为空的情况下。

class Solution {
//非递归实现前序遍历
public List<Integer> preorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
TreeNode cur =root;
List<Integer> ret = new ArrayList<>();
Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack<>();
while(cur != null || !stack.isEmpty()){
while(cur != null){
stack.push(cur);
System.out.print(cur.val +" ");
ret.add(cur.val);
cur = cur.left;
}
TreeNode top = stack.pop();
cur = top.right;
}
return ret;
}
}
非递归实现中序遍历
本题思路和上一题前序遍历打印类似,只不过打印的时机不同,在前一题代码的基础上稍加修改即可。
class Solution {
public List<Integer> inorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
TreeNode cur =root;
List<Integer> ret = new ArrayList<>();
Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack<>();
while(cur != null || !stack.isEmpty()){
while(cur != null){
stack.push(cur);
cur = cur.left;
}
TreeNode top = stack.pop();
System.out.print(top.val + " ");
ret.add(top.val);
cur = top.right;
}
return ret;
}
}
非递归实现后序遍历
class Solution {
public List<Integer> postorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
List<Integer> ret = new ArrayList<>();
Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack<>();
TreeNode cur = root;
TreeNode prev = null;
while(cur != null || !stack.isEmpty()){
while(cur != null){
stack.push(cur);
cur = cur.left;
}
TreeNode top = stack.peek();
if(top.right == null || top.right == prev){
ret.add(top.val);
stack.pop();
prev = top;
}else{
cur = top.right;
}
}
return ret;
}
}