第三阶段:Web前端:02数据库(sql语言、JDBC数据库连接) | 03(1)SpringBoot
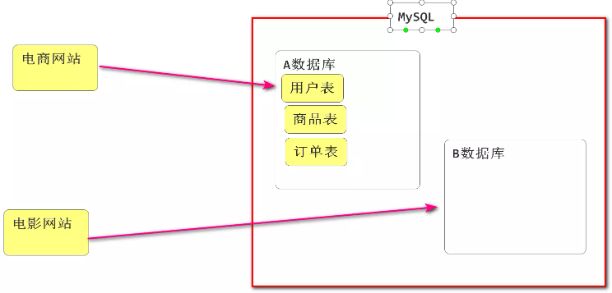
二、数据库——> MySQl或MariaDB
0.1、Mysql—安装步骤
- 进入网址 http://doc.canglaoshi.org/——>常用下载:Windows必备——>MariaDB 10.5.13 WinX64(MySQL) 官网下载
0.2、Mysql—卸载步骤
MySQL数据库是一款非常好用的数据库管理系统,
但是相对来说卸载起来麻烦一些
这里给大家分享下MySQL数据库如何卸载干净~
(1)停止MySQL的所有服务
就像一个正在使用中的文件是无法删除的一样
我们想要卸载MySQL,首先就需要把计算机中MySQL相关的所有服务都停止。
给大家提供两种方式:
方式一:
我的电脑——>
右键管理——>
选择“服务和应用程序”——>
继续选择"服务"——>
将页面中所有MySQL相关的服务逐一的全部关闭: 找到mysql服务,右键停止服务
方式2:
win+R键打开运行窗口,
输入“cmd”,
点击“确定”或直接回车,
输入命令 net stop mysql 回车————>这个命令的作用也是关闭MySQL的所有服务
(2)卸载MySQL程序
右键“此电脑”,
选择“属性”,
点击“控制面板主页”,
在打开的页面中选择“卸载程序”
Mysql相关的全部卸载
(3)删除电脑上的MySQL文件
删除MySQL安装目录文件夹:
如果安装位置是默认位置,一般为 C:\ProgramData\MySQL: SQL数据库数据存放文件(用户自己设定的路径)
(4)删除电脑上MySQL注册表的相关信息
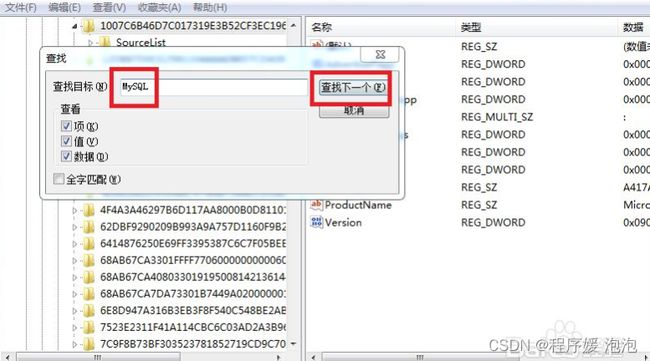
1、杀出注册表
01.用“Win+R”快捷键打开运行窗口,输入“regedit”
02.在打开的注册表编辑器页面,用“Ctrl+F”查找所有关于“MySQL”的注册表,全部删掉
2、删除注册表:
我的电脑->HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE->SYSTEM->ControlSet001-> Services->Eventlog->Applacion->MySQL
我的电脑->HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE->SYSTEM->ControlSet002-> Services->Eventlog->Applacion->MySQL
我的电脑->HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE->SYSTEM->CurrentControlSet-> Services->Eventlog->Applacion->MySQL
(5)删除电脑C盘MySQL相关文件夹
如果有的话就删除,没有此步骤跳过
将C:\Documents and Settings\All Users\Application Data\MySQL 下的文件夹删除,
该文件夹有可能是隐藏的,需设为可见后才能删除。
以上MySQL就卸载完成啦,可以重启电脑后再安装MySQL.
0、关于数据库
1.数据库(DBMS)简介
:学习数据库阶段内容,主要学习的就是如何对数据进行增删改查操作
(1)常见DBMS(数据库管理系统)
DataBaseManagementSystem,数据库管理系统(数据库软件)
常见的DBMS:
MySQL: Oracle公司产品 08年被Sun收购 09年Sun被Oracle收购, 原MySQL团队从Oracle
离职又创建了MariaDB(开源产品), MaraDB实际上就是MySQL的一个分支使用方式和
MySQL一样。 市占率第一
Oracle: Oracle公司当家产品 闭源产品 ,性能最强 价格最贵, 市占率排名第二
SqlServer: 微软公司产品 , 闭源产品. 市占率第三
net 编程语言+web服务软件+操作系统+数据库软件
DB2: IBM公司产品 闭源产品
SQLite: 轻量级数据库, 安装包只有几十k , 只有最基础的增删改查功能
(2)SQL语言
Structured Query Language: 结构化查询语言,通过此语言让程序员和数据库软件进行交流
例:
刘德华 30 5000
insert into emp values("刘德华",30,5000);
2.数据库常见错误
0.当输入密码时没有进到数据库里,可以点击我的电脑——>右键管理——>服务和应用程序——>服务——>找到mysql——>右键把服务重新打开——>进入mysql客户端重新输入密码——>发现可以登录成功!
 1.用户名或密码错误: 检查用户名或密码
1.用户名或密码错误: 检查用户名或密码
2.值的数量 和字段数量不匹配, 检查表的字段是否正确,检查插入的值是否正确

3.主键值重复了

4.值不能为null
![]()
5.JDBC链接数据库时的报错: 代表没有启动MySQL服务, 在我的电脑上右键管理 找到Mysql服务右键开启即可
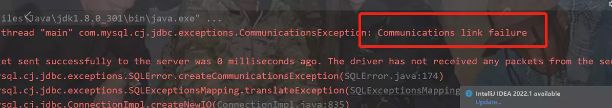
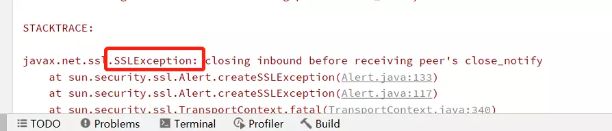
6.个别MySQL版本出现的SSL异常, 在连接数据库的url上面添加&useSSL=false 即可解决
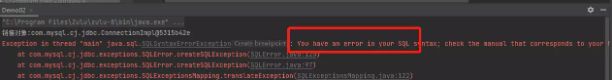
7.SQL语句拼写错误
8.参数位置超出范围, ?的数量和替换问号时

3.优化数据库
1、SQL语言
(0)SQL官方分类
DDL: 数据定义语言, 包括: 对数据库和表相关的SQL
DML: 数据操作语言, 包括: 对表中的数据进行增删改查
DQL: 数据查询语言, 包括: 对表中的数据进行select查询
DCL: 数据控制语言, 对数据库进行权限控制(包含用户管理,权限分配相关SQL)
TCL: 事务控制语言, 包含和事务相关的内容
(1)如何连接数据库执行SQL语句?
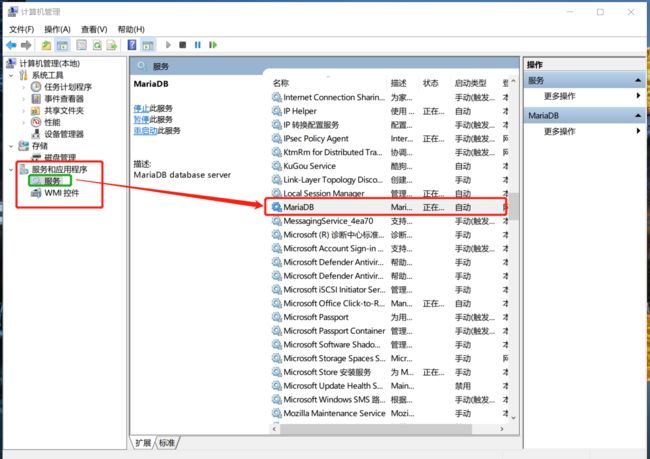
(1)检查本机电脑MySQL服务是否开启?
通过命令行/终端 和数据库软件建立连接
首先检查MySQL/MariaDB服务是否开启:
在:我的电脑/此电脑上右键->管理->服务和应用程序->服务->找到MariaDB后右键启动
 (2)两种登录Mysql客户端的方式:
(2)两种登录Mysql客户端的方式:
1.
从开始菜单中找到:`MariaDB或MySQL`,
然后打开找到里面的客户端:`MySQL Client` 打开 ,
然后`输入密码后回车`
显示Welcome … 说明建立好了连接
退出指令: exit
建立连接指令: mysql -uroot -p 回车后输入密码 再回车
:C:\Program Files\MariaDB 10.5\bin>mysql -uroot -p 回车
Enter password: **** ————>(输入密码)
MariaDB [(none)]> ————>(成功登录到mysql)
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
2.在IDEA中:点击界面下面的【Terminal】按钮,
(1)首先切换到c盘:执行指令:————————————————>【c:】
(2)切换到Mysql数据库的bin目录下————————————>【cd Program Files\MariaDB 10.5\bin】
(3)连接数据库的指令————————————————————————>【mysql -uroot -p 回车】
(4)此时在IDEA中已经和数据库建立连接了!可以输入sql语句进行对应的操作!
(2)数据库和表的概念
在MySQL数据库软件中保存数据, 需要:先建库,然后在库里面建表,然后把数据保存到表中
(3)UTF8字符集
目前utf8 和utf8mb3 一样,
代表的是用3个字节表示一个字符(mb3 = most byte 3)
utf8mb4: 最多不超过4个字节表示一个字符
00.SQL语句格式
以;号结尾
关键字不区分大小写
可以有空格或换行,但一定要以;结尾
单行注释: -- ——>跟在sql语句后面
多行注释: /* */ ——>跟在sql语句后面
退出数据库: exit
01.数据库的增删改查:
(0)数据库sql语句
查询所有: show databases;
创建: create database 数据库名 charset=utf8/gbk;
创建(判断,若不存在则创建): create database if not exits
查看数据库信息: show create database 数据库名;
删除数据库: drop database 数据库名;
使用数据库: use 数据库名;
(1)查询所有数据库: show databases;
(2)创建数据库:
默认字符集格式: create database 数据库名;
指定字符集格式: create database 数据库名 charset=utf8/gbk;
例:
create database db1;
create database db2 charset=utf8;
create database db3 charset=gbk;
(3)查看数据库信息: show create database 数据库名;
(4)删除数据库: drop database 数据库名;
例:drop database db1;
再查看数据库:show databases;
(5)使用数据库: use 数据库名;
注:在执行表相关和数据相关的SQL语句之前必须使用(创建)了某个数据库,
否则如下图提示:【 Unknown database 'db3' 】
:未知数据库 'db3'
(1)数据库相关练习题:
1.创建 mydb1和mydb2 数据库 字符集分别为utf8和gbk
create database mydb1 charset=utf8;
create database mydb1 charset=gbk;
2.查询所有数据库检查是否创建成功
show databases;
3.检查两个数据库的字符集是否正确
show create database mydb1;
show create database mydb2;
4.先使用mydb2 再使用 mydb1
use mydb2;
use mydb1;
5.删除两个数据库
drop database mydb1;
drop database mydb2;
02.表相关:
(1)表的增删改查
创建: create table 表名(name varchar(20),age int)charset=utf8/gbk;
char: 定长字符串 10个字符空间 存储的性能高 浪费空间 255个字节
varchar:可变长度字符串 2个字符空间 存储性能低 节约空间 0~65535字节
查询所有: show tables;
查看表信息: show create table 表名;
表字段: desc 表名;
desc:查询表的结构 例:desc func;--查看数据表的详细结构
删除表: drop table 表名;
改表名: rename table 原表名 to 新表名;
添加字段: alter table 表名 add age int first/ after xxx;
删除字段: alter table 表名 drop age;
修改字段: alter table 表名 change 原名 新名 新类型;
varchar:规定字符长度
0.前提:执行表相关的SQL语句必须已经使用(创建完后又使用了)了某个数据库: use db1;
即————>先创建了数据库才能在里面创建表!!
1.创建表: create table 表名(字段1名 类型,字段2名 类型,.......);
举例:
create table person(name varchar(50),age int);
create table student(name varchar(50),chinese int,math int,english int)charset=utf8;
创建一个员工表emp 保存名字,工资和工作 :
create table emp(name varchar(50),salary int,job varchar(20));
2. 查询所有表: show tables;
3.查询表信息: show create table 表名; 例:show create table emp;
4.查询表字段: desc 表名; 例;desc emp;
5.修改表名: rename table 原名 to 新名; 例:rename table emp to stu;
(1)表相关练习题:
1.创建数据库mydb3 字符集gbk 并使用:
create database mydb3 charset=gbk;
use mydb3;
2.创建t_hero英雄表, 有名字和年龄字段 默认字符集:
create table t_hero(name varchar(50),age int);
3.修改表名为hero: rename table t_hero to hero;
4.查看表的字符集: show create table hero;
5.查询表字段: desc hero;
6.删除表: drop table hero;
7.删除数据库: drop database mydb3;
(2)表相关的SQL语句——续!
1.添加表字段
create database db1;
use db1;
create table stu(name varchar(30));
在表格属性这一列的最后面添加格式: alter table 表名 add 字段名 类型;
在表格属性这一列的最前面添加格式: alter table 表名 add 字段名 类型 first;
在表格属性这一列的某字段后面添加格式: alter table 表名 add 字段名 类型 after 指定的字段名;
举例:
alter table 表名 add age int;
alter table 表名 add id int first;
alter table 表名 add gender varchar(10) after name;
2.删除表的字段
alter table 表名 drop 字段名;
例:alter table stu drop name;
3.修改表字段
alter table 表名 change 原名 新名 新类型;
例:alter table stu change job hahaha int;
(3)表相关SQL语句回顾:
创建表 create table t1(name varchar(20),age int) charset=utf8/gbk;
查询所有表 show tables;
查询表信息 show create table 表名;
查询表的字段 desc 表名;
删除表 drop table 表名;
修改表名 rename table 原表名 to 新表名;
在表格属性这一列的 最后面 添加格式: alter table 表名 add 字段名 类型;
在表格属性这一列的 最前面 添加格式: alter table 表名 add 字段名 类型 first;
在表格属性这一列的 某字段 后面添加格式: alter table 表名 add 字段名 类型 after 指定的字段名;
修改表的字段 alter table 表名 change 原名(name) 新名(job) 新类型(int);
(4)表相关练习题:
1.创建数据库mydb4 字符集utf8 并使用
create database mydb4 charset=utf8;
use mydb4;
2.创建teacher表 有名字字段
create table teacher(name varchar(50));
3.添加表字段: 最后添加age 最前面添加id , age前面添加salary工资(即在name后添加salary)
alter table teacher add age int;
alter table teacher add id int first;
alter table teacher add salary int after name;
4.删除age字段
alter table teacher drop age;
5.修改表名为t
rename table teacher to t;
6.删除表
drop table t;
7.删除数据库
drop database mydb4;
02.1表设计之——权限管理
任何网站中只要是存在权限管理的需求,表格都是设计成5张表,其中:
三张主表:用户表 两张关系表:用户-角色 关系表
角色表 角色-权限 关系表
权限表
1、
(1)创建三张主表
create database lastdb charset=utf8; //创建数据库
use lastdb;
create table user(id int primary key auto_increment,name varchar(50))charset=utf8;
create table role(id int primary key auto_increment,name varchar(50))charset=utf8;
create table module(id int primary key auto_increment,name varchar(50))charset=utf8;
(2)创建两张关系表
用户角色关系表: create table u_r(uid int,rid int);
角色权限关系表: create table r_m(rid int,mid int);
(3)准备数据
insert into user values(null,'刘德华'),(null,'王菲');
insert into role values(null,'男游客'),(null,'女会员');
insert into module values(null,'男浏览'),(null,'男发帖'),(null,'女浏览'),(null,'女发帖');
(4)建立关系
刘德华——>男游客和女会员 王菲————>女会员
男游客——>男浏览 女会员——>女浏览,女发帖
例:
刘德华第一个添加进去的,
男游客第一个添加进去的
————>所以下面第一行第一个values后边的对应关系是:(1,1)
insert into u_r values(1,1),(1,2),(2,2);
insert into r_m values(1,1),(2,3),(2,4);
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
(1)权限管理关联查询相关练习题
use lastdb;
1.查询刘德华有哪些角色?
select r.name
from user u join u_r ur on u.id=ur.uid
join role r on r.id=ur.rid where u.name="刘德华";
MariaDB [lastdb]> select r.name
-> from user u join u_r ur on u.id=ur.uid
-> join role r on r.id=ur.rid where u.name="刘德华";
+--------+
| name |
+--------+
| 男游客 |
| 女会员 |
+--------+
2.查询女会员这个角色对应的用户都有谁?
select u.name
from user u join u_r ur on u.id=ur.uid
join role r on r.id=ur.rid where r.name="女会员";
MariaDB [lastdb]> select u.name
-> from user u join u_r ur on u.id=ur.uid
-> join role r on r.id=ur.rid where r.name="女会员";
+--------+
| name |
+--------+
| 刘德华 |
| 王菲 |
+--------+
3.查询男游客这个角色拥有什么权限?
select m.name
from role r join r_m rm on r.id=rm.rid
join module m on rm.mid=m.id where r.name="男游客";
MariaDB [lastdb]> select m.name
-> from role r join r_m rm on r.id=rm.rid join module m on rm.mid=m.id where r.name="男游客";
+--------+
| name |
+--------+
| 男浏览 |
+--------+
4.查询女会员这个角色拥有什么权限?
select m.name
from role r join r_m rm on r.id=rm.rid
join module m on rm.mid=m.id where r.name="女会员";
MariaDB [lastdb]> select m.name
-> from role r join r_m rm on r.id=rm.rid
-> join module m on rm.mid=m.id where r.name="女会员";
+--------+
| name |
+--------+
| 女浏览 |
| 女发帖 |
+--------+
5.查询刘德华这个用户拥有什么权限?
select m.name
from user u join u_r ur on u.id=ur.uid
join r_m rm on ur.rid=rm.rid
join module m on m.id=rm.mid
where u.name="刘德华";
MariaDB [lastdb]> select m.name
-> from user u join u_r ur on u.id=ur.uid
-> join r_m rm on ur.rid=rm.rid
-> join module m on m.id=rm.mid
-> where u.name="刘德华";
+--------+
| name |
+--------+
| 男浏览 |
| 女浏览 |
| 女发帖 |
+--------+
6.查询拥有女发帖这个权限的用户都有谁?
select u.name
from user u join u_r ur on u.id=ur.uid
join r_m rm on ur.rid=rm.rid
join module m on m.id=rm.mid
where m.name="女发帖";
MariaDB [lastdb]> select u.name
-> from user u join u_r ur on u.id=ur.uid
-> join r_m rm on ur.rid=rm.rid
-> join module m on m.id=rm.mid
-> where m.name="女发帖";
+--------+
| name |
+--------+
| 刘德华 |
| 王菲 |
+--------+
03.数据相关:
0.操作数据的前提:必须保证已经使用了【某个数据库】并且已经准备好了【保存数据的表】。
create database 数据库名 charset=utf8;
use 数据库名;
create table 表名(name varchar(50),age int);
1.往表中插入数据(只是插入需要用查询语句才可看出来)
(1)全表插入: insert into 表名 values(值1,值2);
(2)指定字段插入: insert into 表名(字段1名,字段2名)values(值1,值2);
举例:
insert into person values('tom',18);
insert into person(name) values('jerry');
(3)批量插入格式:
全表插入: insert into person values('aaa',10),('bbb',20),('ccc',30);
指定字段插入: insert into person(name) values('xxx'),("yyy"),("zzz");
2.查询数据: select 字段信息 from 表名 where 条件;
举例:
insert into person values('刘备',40),('关羽',30),('悟空',20),('八戒',10),('张学友',5);
select name from person;
select name,age from person;
select * from person;
select * from person where age=50;
select age from person where name="悟空";
3.修改数据: update 表名 set 字段名=值 where 条件;
举例:
update person set age=88 where name='刘备';
update person set name='张飞',age=18 where name='关羽';
update person set name='黎明' where age=5;
4.删除数据: delete from 表名 where 条件;
举例:
delete from person where name='张飞';
delete from person where age<30;
delete from person;
(1)插入中文的值时报错(16进制) 问题:
错误原因是客户端和MySQL之间编解码字符集不一致导致的
解决方案: 修改MySQL的解码字符集为gbk ——> set names gbk;
04.综合练习题:
1.创建数据库day1db 字符集utf8并使用
create database day1db charset=utf8;
use day1db;
2.创建t_hero表, 有name字段 字符集utf8
create table t_hero(name varchar(20))charset=utf8;
3.修改表名为hero
rename table t_hero to hero;
4.最后面添加价格字段money, 最前面添加id字段, name后面添加age字段
alter table hero add money int;
alter table hero add id int first;
alter table hero add age int after name;
5.表中添加以下数据: 1,李白,50,6888 2,赵云,30,13888 3,刘备,25,6888
insert into hero values(1,‘李白’,50,6888),(2,‘赵云’,30,13888),(3,‘刘备’,25,6888);
6.查询价格为6888的英雄名
select name from hero where money=6888;
7.修改刘备年龄为52岁update hero set age=52 where name='刘备';
update hero set age=52 where name=‘刘备’;
8.修改年龄小于等于50岁的价格为5000
update hero set money=5000 where age<=50;
9.删除价格为5000的信息
delete from hero where money=5000;
10.删除表, 删除数据库
drop table hero;
drop database day1db;
05.主键
(1)主键约束
主键: 表示数据唯一性的字段称为主键
约束: 创建表时,给表字段添加的限制条件
主键约束:限制主键的值 唯一且非空.
如何使用:
use day2db;
create table t1 (id int primary key,name varchar(50))charset=utf8;
insert into t1 values(1,"aaa");
insert into t1 values(1,"bbb");//报错 主键值重复
insert into t1 values(null,"ccc");//报错 限制主键的值 唯一且非空.
(2)主键约束+自增
自增规则:从历史最大值基础上+1
如何使用:
create table t2(id int primary key auto_increment,name varchar(50))charset=utf8;
下面每次插入属性后都可用【select * from t2;】来查看一下表格的变化:
insert into t2 values(null,"aaa");
insert into t2 values(null,"bbb");
insert into t2 values(10,"ccc");
insert into t2 values(null,"ddd");
delete from t2 where id>=10;
insert into t2 values(null,"eee");
——————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
在 数据库 中的真实表现:
MariaDB [day2db]> select * from t2;
+----+------+
| id | name |
+----+------+
| 1 | aaa |
| 2 | bbb |
| 10 | ccc |
+----+------+
3 rows in set (0.000 sec)
MariaDB [day2db]> insert into t2 values(null,"ddd");
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.003 sec)
MariaDB [day2db]> select * from t2;
+----+------+
| id | name |
+----+------+
| 1 | aaa |
| 2 | bbb |
| 10 | ccc |
| 11 | ddd |
+----+------+
06.数据类型:整数、浮点数、字符串、日期
1.整数: int(m)和bigint(m) m代表显示长度, m=5 存18 查询得到00018
create table t3(age int(5) zerofill);
insert into t3 values(18);
select * from t3;
在 数据库 中的真实表现:
MariaDB [day2db]> create table t3(age int(5) zerofill);
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.009 sec)
MariaDB [day2db]> insert into t3 values(18);
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.003 sec)
MariaDB [day2db]> select * from t3;
+-------+
| age |
+-------+
| 00018 |
+-------+
1 row in set (0.002 sec)
——————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
2.浮点数: double(m,d) m代表总长度,d代表小数长度,存23.212 m=5 d=3
create table t5(price double(5,3));
insert into t5 values(23.32123);//因为上边控制了长度,所以在表里存的是:23.321
insert into t5 values(233.32123);//报错:第 1 行的“价格”列的值超出范围,因为规定m总长是5,d:小数位显示3位,那么整数位只能显示两位。但是此时有三位所以存不进去报错!
在 数据库 中的真实表现:
MariaDB [day2db]> create table t5(price double(5,3)); insert into t5 values(23.32123);
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.010 sec)
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.002 sec)
MariaDB [day2db]> select * from t5;
+--------+
| price |
+--------+
| 23.321 |
+--------+
1 row in set (0.000 sec)
——————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
3.字符串:
(1)char(m), 固定长度, m=10 存abc 占10,执行效率略高,当保存数据的长度相对固定时使用,最大值255
(2)varchar(m),可变长度,m=10 存abc 占3,更节省空间, 最大值65535 但推荐保存短的数据(255以内)
(3)text(m),可变长度, 最大值65535,建议保存长度大于255的
——————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
4.日期:
(1)date:保存年月日
(2)time:保存时分秒
(3)datetime:保存年月日时分秒,默认值null, 最大值 9999-12-31
(4)timestamp(时间戳,距离1970年1月1日的毫秒数): 保存年月日时分秒,默认值为当前系统时间,最大值 2038-1-19
举例:
create table t6(t1 date,t2 time,t3 datetime,t4 timestamp);
insert into t6 values("2022-5-15",null,null,null);
insert into t6 values(null,"14:20:25","2011-10-22 10:20:30",null);
在 数据库 中的真实表现:
MariaDB [day2db]> create table t6(t1 date,t2 time,t3 datetime,t4 timestamp);
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.013 sec)
MariaDB [day2db]> select * from t6;
Empty set (0.002 sec)
MariaDB [day2db]> insert into t6 values("2022-5-15",null,null,null);
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.002 sec)
MariaDB [day2db]> select * from t6;
+------------+------+------+---------------------+
| t1 | t2 | t3 | t4 |
+------------+------+------+---------------------+
| 2022-05-15 | NULL | NULL | 2022-05-07 14:12:22 |
+------------+------+------+---------------------+
1 row in set (0.000 sec)
MariaDB [day2db]> insert into t6 values(null,"14:20:25","2011-10-22 10:20:30",null);
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.003 sec)
MariaDB [day2db]> select * from t6;
+------------+----------+---------------------+---------------------+
| t1 | t2 | t3 | t4 |
+------------+----------+---------------------+---------------------+
| 2022-05-15 | NULL | NULL | 2022-05-07 14:12:22 |
| NULL | 14:20:25 | 2011-10-22 10:20:30 | 2022-05-07 14:13:11 |
+------------+----------+---------------------+---------------------+
2 rows in set (0.000 sec)
07.导入( *.sql )批处理文件:导入emp数据库
(1)把老师的emp.zip解压出来得到一个emp.sql文件,
建议把这个文件放到某个盘的根目录 比如 F盘根目录,
然后在mysql客户端执行指令:————>格式: source 路径;
例: source f:/danei/Java/emp/emp.sql;
(2)在mysql客户端测试以下SQL语句 检查是否成功:
show databases; //检查里面是否多了一个empdb;
show tables; //会出现两个表 emp 和dept
select * from emp; //检查是否出现了数据, 如果格式错乱 正常
(3)如果出现乱码执行 set names utf8;
(4)在mysql客户端执行sql语句查看是否导入数据库的数据成功。
- show databases;
- show tables;
在 数据库 中的真实表现:
MariaDB [empdb]> source f:/danei/Java/emp/emp.sql;
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.000 sec)
MariaDB [empdb]> show databases;
+--------------------+
| Database |
+--------------------+
| day1 |
| day2db |
| db1 |
| empdb |
| information_schema |
| mydb5 |
| mysql |
| performance_schema |
| test |
+--------------------+
9 rows in set (0.001 sec)
MariaDB [empdb]> show tables;
+-----------------+
| Tables_in_empdb |
+-----------------+
| dept |
| emp |
+-----------------+
2 rows in set (0.000 sec)
MariaDB [empdb]> select * from emp;
+----+--------+----------+---------+------------+---------+---------+---------+
| id | name | job | manager | hiredate | sal | comm | dept_id |
+----+--------+----------+---------+------------+---------+---------+---------+
| 1 | 孙悟空 | 销售 | 4 | 1980-12-17 | 800.00 | NULL | 1 |
| 2 | 猪八戒 | 销售 | 4 | 1981-02-20 | 1600.00 | 300.00 | 1 |
| 3 | 沙僧 | 销售 | 4 | 1981-02-22 | 1250.00 | 500.00 | 1 |
| 4 | 唐僧 | 销售经理 | 8 | 1981-04-02 | 2975.00 | NULL | 1 |
| 5 | 刘备 | 项目经理 | NULL | 1981-09-28 | 1250.00 | 1400.00 | 3 |
| 6 | 关羽 | 程序员 | 5 | 1981-05-01 | 2850.00 | NULL | 3 |
| 7 | 张飞 | 程序员 | 5 | 1981-06-09 | 2450.00 | NULL | 3 |
| 8 | 观音 | CEO | NULL | 1981-11-17 | 5000.00 | NULL | 1 |
| 9 | 白骨精 | 人事 | 8 | 1981-09-08 | 1500.00 | 0.00 | 2 |
| 10 | 蜘蛛精 | 人事 | 8 | 1981-12-03 | 950.00 | NULL | 2 |
| 11 | 黑熊怪 | 市场 | 8 | 1981-12-03 | 3000.00 | NULL | 2 |
+----+--------+----------+---------+------------+---------+---------+---------+
11 rows in set (0.000 sec)
(1)去重: distinct
(1)查询员工表中有哪几种不同的工作?
select distinct job from emp;
(2)查询员工表中有哪几个不同的部门id?
select distinct dept_id from emp;
在 数据库 中的真实表现:
MariaDB [empdb]> select distinct job from emp;
+----------+
| job |
+----------+
| 销售 |
| 销售经理 |
| 项目经理 |
| 程序员 |
| CEO |
| 人事 |
| 市场 |
+----------+
MariaDB [empdb]> select distinct dept_id from emp;
+---------+
| dept_id |
+---------+
| 1 |
| 3 |
| 2 |
+---------+
(2)is null和is not null
(1)查询有领导的员工姓名和领导
select name,manager from emp where manager is not null;
(2)查询没有领导的员工姓名
select name from emp where manager is null;
在 数据库 中的真实表现:
MariaDB [empdb]> select name,manager from emp where manager is not null;
+--------+---------+
| name | manager |
+--------+---------+
| 孙悟空 | 4 |
| 猪八戒 | 4 |
| 沙僧 | 4 |
| 唐僧 | 8 |
| 关羽 | 5 |
| 张飞 | 5 |
| 白骨精 | 8 |
| 蜘蛛精 | 8 |
| 黑熊怪 | 8 |
+--------+---------+
9 rows in set (0.000 sec)
MariaDB [empdb]> select name from emp where manager is null;
+------+
| name |
+------+
| 刘备 |
| 观音 |
+------+
2 rows in set (0.000 sec)
(3)and 和 or
多个条件同时满足时使用and
多个条件满足一个就可以时 使用or
(1)查询1号部门工资高于2000的员工信息
select * from emp where dept_id=1 and sal>2000;
(2)查询3号部门或工资等于5000的员工信息
select * from emp where dept_id=3 or sal=5000;
(3)查询出孙悟空和猪八戒的员工信息
select * from emp where name="孙悟空" or name="猪八戒";
在 数据库 中的真实表现:
MariaDB [empdb]> select * from emp where dept_id=1 and sal>2000;
+----+------+----------+---------+------------+---------+------+---------+
| id | name | job | manager | hiredate | sal | comm | dept_id |
+----+------+----------+---------+------------+---------+------+---------+
| 4 | 唐僧 | 销售经理 | 8 | 1981-04-02 | 2975.00 | NULL | 1 |
| 8 | 观音 | CEO | NULL | 1981-11-17 | 5000.00 | NULL | 1 |
+----+------+----------+---------+------------+---------+------+---------+
2 rows in set (0.001 sec)
MariaDB [empdb]> select * from emp where dept_id=3 or sal=5000;
+----+------+----------+---------+------------+---------+---------+---------+
| id | name | job | manager | hiredate | sal | comm | dept_id |
+----+------+----------+---------+------------+---------+---------+---------+
| 5 | 刘备 | 项目经理 | NULL | 1981-09-28 | 1250.00 | 1400.00 | 3 |
| 6 | 关羽 | 程序员 | 5 | 1981-05-01 | 2850.00 | NULL | 3 |
| 7 | 张飞 | 程序员 | 5 | 1981-06-09 | 2450.00 | NULL | 3 |
| 8 | 观音 | CEO | NULL | 1981-11-17 | 5000.00 | NULL | 1 |
+----+------+----------+---------+------------+---------+---------+---------+
4 rows in set (0.000 sec)
MariaDB [empdb]> select * from emp where name="孙悟空" or name="猪八戒";
+----+--------+------+---------+------------+---------+--------+---------+
| id | name | job | manager | hiredate | sal | comm | dept_id |
+----+--------+------+---------+------------+---------+--------+---------+
| 1 | 孙悟空 | 销售 | 4 | 1980-12-17 | 800.00 | NULL | 1 |
| 2 | 猪八戒 | 销售 | 4 | 1981-02-20 | 1600.00 | 300.00 | 1 |
+----+--------+------+---------+------------+---------+--------+---------+
2 rows in set (0.000 sec)
(4)比较运算符 > < >= <= =、 !=和<>(相当于!=)
(1)查询工资大于等于3000的员工信息
select * from emp where sal>=3000;
(2)查询工作不是程序员的员工信息(两种写法)
select * from emp where job!="程序员";
select * from emp where job<>"程序员";
在 数据库 中的真实表现:
MariaDB [empdb]> select * from emp where sal>=3000;
+----+--------+------+---------+------------+---------+------+---------+
| id | name | job | manager | hiredate | sal | comm | dept_id |
+----+--------+------+---------+------------+---------+------+---------+
| 8 | 观音 | CEO | NULL | 1981-11-17 | 5000.00 | NULL | 1 |
| 11 | 黑熊怪 | 市场 | 8 | 1981-12-03 | 3000.00 | NULL | 2 |
+----+--------+------+---------+------------+---------+------+---------+
2 rows in set (0.000 sec)
MariaDB [empdb]> select * from emp where job!="程序员";
+----+--------+----------+---------+------------+---------+---------+---------+
| id | name | job | manager | hiredate | sal | comm | dept_id |
+----+--------+----------+---------+------------+---------+---------+---------+
| 1 | 孙悟空 | 销售 | 4 | 1980-12-17 | 800.00 | NULL | 1 |
| 2 | 猪八戒 | 销售 | 4 | 1981-02-20 | 1600.00 | 300.00 | 1 |
| 3 | 沙僧 | 销售 | 4 | 1981-02-22 | 1250.00 | 500.00 | 1 |
| 4 | 唐僧 | 销售经理 | 8 | 1981-04-02 | 2975.00 | NULL | 1 |
| 5 | 刘备 | 项目经理 | NULL | 1981-09-28 | 1250.00 | 1400.00 | 3 |
| 8 | 观音 | CEO | NULL | 1981-11-17 | 5000.00 | NULL | 1 |
| 9 | 白骨精 | 人事 | 8 | 1981-09-08 | 1500.00 | 0.00 | 2 |
| 10 | 蜘蛛精 | 人事 | 8 | 1981-12-03 | 950.00 | NULL | 2 |
| 11 | 黑熊怪 | 市场 | 8 | 1981-12-03 | 3000.00 | NULL | 2 |
+----+--------+----------+---------+------------+---------+---------+---------+
9 rows in set (0.000 sec)
MariaDB [empdb]> select * from emp where job<>"程序员";
+----+--------+----------+---------+------------+---------+---------+---------+
| id | name | job | manager | hiredate | sal | comm | dept_id |
+----+--------+----------+---------+------------+---------+---------+---------+
| 1 | 孙悟空 | 销售 | 4 | 1980-12-17 | 800.00 | NULL | 1 |
| 2 | 猪八戒 | 销售 | 4 | 1981-02-20 | 1600.00 | 300.00 | 1 |
| 3 | 沙僧 | 销售 | 4 | 1981-02-22 | 1250.00 | 500.00 | 1 |
| 4 | 唐僧 | 销售经理 | 8 | 1981-04-02 | 2975.00 | NULL | 1 |
| 5 | 刘备 | 项目经理 | NULL | 1981-09-28 | 1250.00 | 1400.00 | 3 |
| 8 | 观音 | CEO | NULL | 1981-11-17 | 5000.00 | NULL | 1 |
| 9 | 白骨精 | 人事 | 8 | 1981-09-08 | 1500.00 | 0.00 | 2 |
| 10 | 蜘蛛精 | 人事 | 8 | 1981-12-03 | 950.00 | NULL | 2 |
| 11 | 黑熊怪 | 市场 | 8 | 1981-12-03 | 3000.00 | NULL | 2 |
+----+--------+----------+---------+------------+---------+---------+---------+
9 rows in set (0.000 sec)
(5)两者之间:between x and y 包含x和y
(1)查询工资在2000到3000之间的员工信息
select * from emp where sal>=2000 and sal<=3000;
select * from emp where sal between 2000 and 3000;
select * from emp where sal not between 2000 and 3000;
(6)in关键字
当查询某个字段的值为多个值的时候使用in
(1)查询工资等于5000,1500,3000的员工信息
select * from emp where sal=5000 or sal=1500 or sal=3000;
select * from emp where sal in(5000,1500,3000);
select * from emp where sal not in(5000,1500,3000);
(7)综合练习题
(1)查询1号部门有哪几种不同的工作
select distinct job from emp where dept_id=1;
(2)查询查询1号部门中有上级领导的员工信息
select * from emp where dept_id=1 and manager is not null;
(3)查询工作是程序员,销售和人事的员工信息
select * from emp where job in("程序员","销售","人事");
(4)查询工资不在1000-2000之间的员工信息
select * from emp where sal not between 1000 and 2000;
(5)查询有奖金的员工信息
select * from emp where comm>0;
(8)模糊查询like
(1)% : 代表0或多个未知字符
(2)_ : 代表1个未知字符
(3)举例:
以x开头 x%
以x结尾 %x
包含x %x%
第二个字符是x _x%
以x开头以y结尾 x%y
第二个是x,倒数第三个是y x%y
1.查询姓孙的员工信息
select * from emp where name like “孙%”;
2.查询名字以精结尾的员工姓名
select name from emp where name like "%精";
3.查询工作第二个字是售的员工姓名和工作
select name,job from emp where job like "_售%";
4.查询名字中包含僧并且工资大于2000的员工姓名和工资
select name,sal from emp where name like "%僧%" and sal>2000;
5.模糊查询like: concat是SQL语句中将多个字符串进行拼接的函数:
select id,title,url,price,old_price,sale_count from product where title like concat('%',#{wd},'%')
(9)排序 order by
格式: order by 字段名 asc(默认是升序)/desc降序;
(1)查询员工姓名和工资,按照工资升序
select name,sal from emp order by sal;
(2)查询员工姓名和工资,按照工资降序
select name,sal from emp order by sal desc;
(3)查询1号部门的姓名和工资并且按照工资降序排序
select name,sal from emp where dept_id=1 order by sal desc;
(4)查询每个员工的姓名,工资和部门id;并按照部门id升序排序,如果部门id相同则按照工资降序排序
select name,sal,dept_id from emp order by dept_id,sal desc;
(10)分页查询 limit
格式: limit 跳过的条数,请求的条数(每页的条数)
跳过的条数=(请求页数-1)*每页条数
举例:
查询第1页的5条数据(1-5条) limit 0,5
查询第2页的5条数据(6-10条) limit 5,5
请求第1页的10条数据 limit 0,10
请求第3页的10条数据 limit 20,10
公式:
SELECT * FROM emp ORDER BY empno LIMIT 每页显示记录数 * (第几页-1) , 每页显示记录数
-- 查询工资最低的3个员工的信息(按照工资升序排序的第一页的3条数据)
select * from emp order by sal limit 0,3;
-- 按照入职日期(hiredate) 升序排序 查询第3页的3条数据
select * from emp order by hiredate limt 6,3;
-- 查询工资最高的员工信息
select * from emp order by sal desc limit 0,1;
-- 查询按照工资降序第2页的5条数据
select * from emp order by sal desc limit 5,5;
(11)综合练习题:
(1)查询员工表中3号部门工资高于1500的员工信息
select * from emp where dept_id=3 and sal>1500;
(2)查询2号部门员工信息 或者 没有领导的员工信息
select * from emp where dept_id=2 or manager is null;
(3)查询有领导的员工姓名,工资按照工资降序排序
select name,sal from emp where manager is not null order by sal desc;
(4)查询2号和3号部门的员工姓名 和 入职日期hiredate 按照入职日期降序排序
select name,hiredate from emp where dept_id in(2,3) order by hiredate desc;
(5)查询名字中包含僧和包含精的员工姓名
select name from emp where name like "%僧%" or name like "%精%";
(6)查询工资高于2000的工作有哪几种?
select distinct job from emp where sal>2000;
(7)查询工资升序第4页的2条数据
select * from emp order by sal limit 6,2;
(12)别名
select name as "姓名" from emp;
select name "姓名" from emp;
select name 姓名 from emp;
(13)聚合函数
通过聚合函数可以对查询的多条数据进行统计查询,
统计查询的方式包括: 求平均值, 求最大值,求最小值,求和,计数
1.平均值avg(字段名)
(1)查询1号部门的平均工资
select avg(sal) from emp where dept_id=1;
(2)查询销售的平均工资
select avg(sal) from emp where job="销售";
2.最大值max(字段名)
(1)查询程序员的最高工资
select max(sal) from emp where job="程序员";
3.最小值min(字段名)
(1)查询3号部门的最低工资
select min(sal) from emp where dept_id=3;
4.求和sum(字段名)
(1)查询2号部门的工资总和
select sum(sal) from emp where dept_id=2;
5.计数count(*)
(0)查询程序员的数量
select count(*) from emp where job="程序员";
(1)查询工资高于2000的员工人数
select count(*) from emp where sal>2000;
(2)查询2号部门的平均工资,最高工资,最低工资,工资总和,人数
select avg(sal) 平均工资,max(sal) 最高工资,min(sal) 最低工资,sum(sal) 工资总和,count(*) 人数 from emp where dept_id=2;
(14)数值计算
(1)查询每个员工的姓名,工资和年终奖(年终奖=5个月的工资)
select name,sal,sal*5 年终奖 from emp;
(2)给3号部门的员工每人涨薪5块钱
update emp set sal=sal+5 where dept_id=3;
(15)——>《综合练习题:40个需求》<———
前提:
show databases;
use empdb;
1.查询工资大于等于3000的员工姓名和工资
select * from emp where sal>=3000;
2.查询1号部门的员工姓名和工作
3.查询不是程序员的员工姓名和工作(两种写法)
select * from emp where job!="程序员";
select * from emp where job<>"程序员";
4.查询奖金等于300的员工姓名,工资和工作
5.查询1号部门工资大于2000的员工信息
select * from emp where dept_id=1 and sal>2000;
6.查询3号部门或工资等于5000的员工信息
select * from emp where dept_id=3 or sal=5000;
7.查询出CEO和项目经理的名字
8.查询工资为3000,1500和5000的员工信息
select * from emp where sal=3000 or sal=1500 or sal=5000;
select * from emp where sal in(3000,1500,5000);
9.查询工资不等于3000,1500和5000的员工信息
10.查询工资在1000到2000之间的员工信息
select * from emp where sal>=2100 and sal<=2000;
select * from emp where sal between 1000 and 2000;
select * from emp where sal not between 1000 and 2000;
11.查询工资在1000到2000以外的员工信息
select * from emp where sal not between 1000 and 2000;
12.查询有领导的员工姓名和领导id
select name,manager from emp where manager is not null;
13.查询没有领导的员工姓名和领导id
select name from emp where manager is null;
14.查询员工表中出现了哪几种不同的工作
select distinct job from emp;
15.查询员工表中出现了那几个部门的id
select distinct dept_id from emp;
16.查询姓孙的员工姓名
select name from emp where name like "孙%";
17.查询名字最后一个字是精的员工信息
select * from emp where name like "%精";
18.查询工作中包含销售的员工信息
select * from emp where job like "%销售%";
19.查询工作中第二个字是售的员工信息
select * from emp where job like "_售%";
20.查询名字中包含僧的员工并且工资高于2000的员工信息
select * from emp where name like "%僧%" and sal>2000;
21.查询1号和2号部门中工作以市开头的员工信息
22.查询所有员工的姓名和工资 按照工资升序排序
23.查询所有员工的姓名和工资 按照工资降序排序
24.查询所有员工姓名 工资和部门id 按照部门id降序排序,如果部门id一致则按照工资升序排序
25.查询员工表中3号部门工资高于1500的员工信息
26.查询2号部门员工或者没有领导的员工信息
27.查询有领导的员工姓名,工资按照工资降序排序
28.查询2号和3号部门的员工姓名和入职日期hiredate 按照入职日期降序排序
29.查询名字中包含僧和包含精的员工姓名
30.查询工资高于2000的工作有哪几种?
31.查询工资最高的前三个员工
32.查询员工表按照id排序, 第2页的5条数据
33.查询员工表按照id排序, 第3页的4条数据
34.查询3号部门工资最低的员工姓名和工资
35.查询工作不是人事的员工中工资降序第二页的3条数据
36.查询每个员工的姓名,工资和年终奖(年终奖=5个月的工资)
37.给3号部门所有员工涨薪5块钱
38.查询没有领导的员工和3号部门的员工,工资降序取前三条
39.查询2号部门的最高工资
40.查询有领导的员工中工资在1000到2000之间的人数
41.查询3号部门的工资总和
42.查询程序员和销售的总人数
43.查询1号部门有领导的员工的平均工资
44.查询1号部门的最低工资和最高工资
45.查询和销售相关的工作人数
46.查询工资不是1500和3000的员工人数
47.查询1号部门出现了哪几种工作
select distinct job from emp where dept_id=1;
(16)分组查询group by——>关键字:每个
:将某个字段相同值的数据划分为一组, 然后以组为单位进行统计查询
格式: group by 分组的字段名
(1)查询每个部门的平均工资:
select dept_id,avg(sal) from emp group by dept_id;
(2)查询每个部门的最高工资
select dept_id,max(sal) from emp group by dept_id;
(3)查询每种工作的最高工资
select job,max(sal) from emp group by job;
(4)查询每种工作的人数
select job,count(*) from emp group by job;
(5)查询每个部门工资高于2000的人数
select dept_id,count(*) from emp where sal>2000 group by dept_id;
(6)查询每个部门有领导的员工的人数
select dept_id,count(*) from emp where manager is not null group by dept_id;
(17)having:后面可跟聚合函数的条件,结合group by使用
where后面只能写普通字段的条件,不能包含聚合函数
having后面可以包含聚合函数的条件,需要和group by结合使用,写在group by的后面
(1)查询每个部门的平均工资要求平均工资高于2000
select dept_id,avg(sal) from emp group by dept_id having avg(sal)>2000;
(2)查询每种工作的人数,只查询人数大于1的 :两种写法
select job,count(*) from emp group by job having count(*)>1;
select job,count(*) c from emp group by job having c>1;//起个别名,起到复用的作用
(3)查询每个部门的工资总和,只查询有领导的员工, 并且要求工资总和大于5400
select dept_id,sum(sal) s from emp where manager is not null group by dept_id having s>5400;
(4)查询每个部门的平均工资, 只查询工资在1000到3000之间的,并且过滤掉平均工资低于2000的
select dept_id,avg(sal) a from emp where sal between 1000 and 3000 group by dept_id having a>=2000;
(18)各个关键字的顺序
select 查询的字段信息 from 表名 where 普通字段条件 group by 分组字段名 having 聚合函数条件 order by 排序字段名 desc limit 跳过条数,请求条数;
select 查询的字段信息 from 表名 where 普通字段条件
group by 分组字段名 having 聚合函数条件
order by 排序字段名 limit 跳过条数,请求条数;
(1)查询工资大于2号部门平均工资的员工信息
select * from emp where sal>(select avg(sal) from emp where dept_id=2);
(19)子查询(嵌套查询)
子查询:是指嵌入在其它 sql 语句中的 select 语句,也叫嵌套查询
单行子查询:是指只返回一行数据的子查询语句
多行子查询:指返回多行数据的子查询 使用关键字 in
多列子查询:指查询返回多个列数据的子查询语句
use empdb;
-- 查询工资大于2号部门平均工资的员工信息
首先查询 2号部门平均工资的员工信息:
select avg(sal) from emp where dept_id=2;
再查询工资大于2号部门...:
select * from emp where sal>(select avg(sal) from emp where dept_id=2);
-- 查询工资高于程序员最高工资的员工信息
首先查询程序员最高工资的员工信息:
select max(sal) from emp where job="程序员";
再查询工资高于...:
select * from emp where sal>(select max(sal) from emp where job="程序员");
-- 查询工资最高的员工信息
首先查询emp表中工资最高的信息:
select max(sal) from emp;
再查询表中工资最高的员工信息:
select * from emp where sal=(select max(sal) from emp);
-- 查询和孙悟空相同工作的员工信息
首先查询孙悟空工作的信息:
select job from emp where name="孙悟空";
再查询和孙悟空相同工作的员工信息:
select * from emp where job=(select job from emp where name="孙悟空") and name!="孙悟空";
-- 查询拿最低工资员工的同事们的信息(同事指同一部门)
首先查最低工资:
select min(sal) from emp;
再查询拿最低工资的部门:
select dept_id from emp where sal=(select min(sal) from emp);
最后查询拿最低工资员工的同事们的信息:
select * from emp where dept_id=(select dept_id from emp where sal=(select min(sal) from emp)) and sal!=(select min(sal) from emp);
08.关联关系
- 指创建的表和表之间存在的业务关系
- 有哪几种关系?————>(一对一、一对多、多对多)
①一对一: 有AB两张表,A表中的一条数据对应B表中的一条数据, 同时B表中的一条数据也对应A表中的一条数据

②一对多:有AB两张表,A表中一条数据对应B表中的多条数据, 同时B表中的一条数据对应A表中的一条.

③多对多: 有AB两张表,A表中一条数据对应B表中的多条数据, 同时B表中的一条数据也对应A表中的多条.
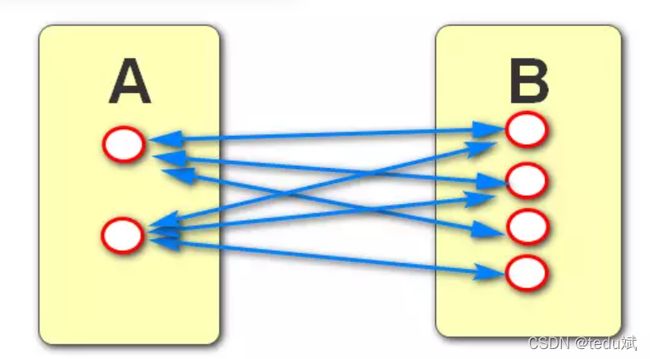
(1)表和表之间如何建立关系: 通过外键字段
一对一: 在AB任意一张表里面添加一个建立关系的字段(外键) 指向另外一张表的主键
一对多: 在一对多的两张表中, 在"多"的表里面添加建立关系的字段 指向另外一张表的主键
多对多: 创建一个单独的关系表, 表里面有两个字段指向另外两个表的主键
(2)关联查询
同时查询多张表数据的查询方式 称为 关联查询
关联查询包括: 等值链接, 内连接和外连接
(3)关联查询之——等值连接(=)
格式: select * from A,B where 关联关系
(1)查询每个员工的姓名和对应的部门名
select e.name,d.name 按回车
from emp e,dept d where e.dept_id=d.id; 回车
(2)查询工资高于2000的员工的姓名和对应的部门名
select e.name,d.name 按回车
from emp e,dept d where e.dept_id=d.id and sal>2000; 回车
(4)关联查询之——内连接(join … on)
等值连接和内连接查询到的是一样的数据, 推荐使用内连接
格式: select * from A join B on 关联关系
(1)查询每个员工的姓名和对应的部门名
select e.name,d.name
from emp e join dept d on e.dept_id=d.id;
(2)查询工资高于2000的员工姓名和对应的部门名
select e.name,d.name,sal
from emp e join dept d on e.dept_id=d.id where sal>2000;
(5)关联查询之——外连接(left/right join … on)
等值连接 和 内连接 查询到的 都是两个表的交集数据
外连接查询到的是: 一张表的全部和另外一张表的交集
格式:
select * from A left/right join B on 关联关系 where 其它条件;
(1)查询所有员工姓名和对应的部门名:
首先在表emp中插入灭霸:
insert into emp(name,sal) values("灭霸",5);
再查询所有员工姓名和对应的部门名(此时查灭霸是查不到的):
select e.name,d.name from emp e join dept d on e.dept_id=d.id;
* 需要加left 或 right 才可查到:
select e.name,d.name from emp e left join dept d on e.dept_id=d.id;
(2)查询所有部门的名称,地点和对应的员工姓名和工资 (可以查询到赛亚人的信息)
select d.name,loc,e.name,sal
from emp e right join dept d on e.dept_id=d.id;
(6)如何查询多对多表中的数据
前提:
查询所有数据库: show databases;
用empdb数据库:use empdb;
1.创建表:
create table student(id int primary key auto_increment,name varchar(50))charset=utf8;
create table teacher(id int primary key auto_increment,name varchar(50))charset=utf8;
create table t_s(tid int,sid int);
查看所有表: show tables;
2.插入数据
insert into student values(null,"小明"),(null,"小红"),(null,"小绿"),(null,"小狗"),(null,"小黄");
查看该表内所有字段: desc student;
insert into teacher values(null,"苍老师"),(null,"传奇哥");
desc teacher;
insert into t_s values(1,1),(1,5),(1,4),(2,2),(2,3),(2,1),(2,5);
desc t_s;
3.
(1)查询每个老师对应的学生
select t.name,s.name 按回车
from teacher t join t_s ts on t.id=ts.tid 按回车
join student s on s.id=ts.sid; 按回车后就会出现多对多表格
(2)查询苍老师的学生都有谁?
select s.name
from teacher t join t_s ts on t.id=ts.tid
join student s on s.id=ts.sid
where t.name="苍老师";
(3)查询小明的老师是谁?
select t.name
from teacher t join t_s ts on t.id=ts.tid
join student s on s.id=ts.sid
where s.name="小明";
(7)关联查询总结
1.如果需要同时查询多张表的数据使用关联查询
2.关联查询包括:等值链接,内连接和外连接
3.等值链接和内连接查询的是两个表的交集数据, 推荐使用内连接
4.如果需要查询一张表的全部和另外一张表的交集时 使用外连接,只需要掌握左外即可,
因为表的位置可以交换
(8)多表设计———>面试题
2021年过年时小明在这些天都收到了许多亲戚\朋友还有同事的红包,也发出了一些红包,
有的是微信,有的是支付宝也有现金,请参考下面的题目帮小明设计表格保存红包的信息
(至少包含一张流水表)
先列出需要保存的数据有哪几种
1、设计表
01.创建流水表 和 人物表:
(1)创建流水表:id,红包金额,时间,红包类型
代码:
use empdb;
create table trade(id int primary key auto_increment,money int,time date,type varchar(10),person_id int)charset=utf8;
(2)创建人物表: id,名字,性别,关系
代码:
create table person(id int primary key auto_increment,name varchar(50),gender char(1),rel varchar(5))charset=utf8;
02.准备数据:
(1)流水表中:————>插入流水数据:
刘德华 微信 收1000 2021-03-20
杨幂 现金 收500 发50 2021-04-14
马云 支付宝 收20000 发5 2021-03-11
特朗普 微信 收2000 2021-05-18
貂蝉 微信 发20000 2021-07-22
代码:
insert into trade values(null,1000,"2021-03-20","微信",1),(null,500,"2021-04-14","现金",2),(null,-50,"2021-04-14","现金",2),(null,20000,"2021-03-11","支付宝",3),(null,-5,"2021-03-11","支付宝",3),(null,2000,"2021-05-18","微信",4),(null,-20000,"2021-07-22","微信",5);
(2)人物表中:————>插入人物数据:
刘德华 男 亲戚 ,杨幂 女 亲戚 ,马云 男 同事,特朗普 男 朋友, 貂蝉 女 朋友
代码:
insert into person values(null,'刘德华','男','亲戚'),(null,'杨幂','女','亲戚'),(null,'马云','男','同事'),(null,'特朗普','男','朋友'),(null,'貂蝉','女','朋友');
2、统计2021年2月15号到现在的所有红包收益
代码:————————> select sum(money) from trade where time>"2021-7-15";
数据库中代码实现:
MariaDB [empdb]> select sum(money) from trade where time>"2021-7-15";
+------------+
| sum(money) |
+------------+
| -20000 |
+------------+
3、查询2021年2月15号到现在 金额大于100 所有女性亲戚的名字和金额(关联查询)
代码:
select name,money
from person p join trade t on p.id=t.person_id
where time>"2021-2-15" and money not between -100 and 100 and gender="女" and rel="亲戚";
数据库代码实现:
MariaDB [empdb]> select name,money
-> from person p join trade t on p.id=t.person_id
-> where time>"2021-2-15" and money not between -100 and 100 and gender="女" and rel="亲戚";
+------+-------+
| name | money |
+------+-------+
| 杨幂 | 500 |
+------+-------+
4、查询三个平台(微信,支付宝,现金)分别收入的红包金额
代码:
select type,sum(money) from trade where money>0 group by type;
数据库代码实现:MariaDB [empdb]> select type,sum(money) from trade where money>0 group by type;
+--------+------------+
| type | sum(money) |
+--------+------------+
| 微信 | 3000 |
| 支付宝 | 20000 |
| 现金 | 500 |
+--------+------------+
2、JDBC( :Java数据库连接)
- Java DataBase Connectivity: Java数据库连接
- 学习JDBC主要学习的就是如何通过Java语言和数据库软件进行连接并执行SQL语句.
- JDBC是Sun公司提供的一套用于Java语言和数据库软件进行连接的API (Application Programma Interface应用程序编程接口)
- 为什么Sun公司定义JDBC系列接口?
Sun公司为了避免Java程序员,每一种数据库软件都学习一套全新的方法,通过JDBC接口将方法名定义好, 让各个数据库厂商根据 此接口中 方法名 写各自的实现类(就是一个jar文件,称为数据库的驱动),
这样Java程序员只需要掌握 JDBC接口中方法的调用 即可访问任何数据库软件.
01.如何通过JDBC连接MySQL(用 DriverManager 类连接数据库)
DriverManager类:用于管理一组 JDBC 驱动程序的基本服务。
注意: javax.sql.DataSource 接口是 JDBC 2.0 API 中的新接口,它提供了另一种连接数据源的方法。
调用方法:getConnection(url,user,password):尝试建立到给定数据库 URL 的连接 密码:就是数据库的登录密码root
1、
《首先导入emp数据库》:
导入( *.sql )批处理文件:导入emp数据库:
(1)把老师的emp.zip解压出来得到一个emp.sql文件,
建议把这个文件放到某个盘的根目录 比如 F盘根目录,
然后在mysql客户端执行指令:————>格式: source 路径;
例: source f:/danei/Java/emp/emp.sql;
(2)在mysql客户端测试以下SQL语句 检查是否成功:
show databases; //检查里面是否多了一个empdb;
show tables; //会出现两个表 emp 和dept
select * from emp; //检查是否出现了数据, 如果格式错乱 正常
(3)如果出现乱码执行 set names utf8;
(4)在mysql客户端执行sql语句查看是否导入数据库的数据成功。
- show databases;
- show tables;
2、
(1)创建Maven工程
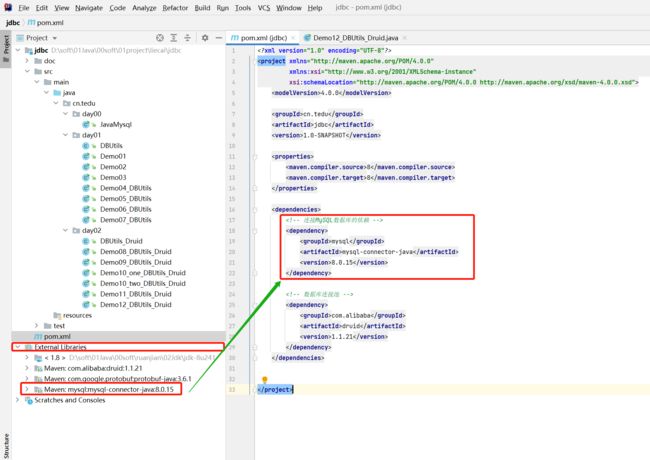
(2)在工程的pom.xml文件中 添加MySQL驱动的依赖坐标
(苍老师文档服务器中【配置文件】打开【pom.xml常用配置】中的【MySQL驱动】
下的代码复制MySQL驱动的依赖: )
<!-- 连接MySQL数据库的依赖 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
<version>8.0.15</version>
</dependency>
(3)IDEA页面右侧出现maven图标——>点击刷新maven
(4)检查工程目录中 External Libraries 里面 是否出现了 mysql相关的内容
(5)添加《Demo01.java》并在main方法中添加以下代码以在mysql数据库创建jdbct1表格:
package cn.tedu;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.DriverManager;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.sql.Statement;
/**
* 要求:连接数据库,用java程序创建一个表格
*
* 1.Connection接口:与特定数据库的连接(会话)。在连接的上下文中执行 SQL 语句并返回结果。
* Connection 对象的数据库能够提供描述它的表、它支持的 SQL 语法、它的存储过程、这个连接的能力等等的信息。
* 此信息是通过 getMetaData 方法获得的。
* (1)createStatement():创建一个 Statement 对象,用于将 SQL 语句发送到数据库
*
* 2.DriverManager类:用于管理一组 JDBC 驱动程序的基本服务。
* 注意: javax.sql.DataSource 接口是 JDBC 2.0 API 中的新接口,它提供了另一种连接数据源的方法。
* (1)getConnection(url,user,password):尝试建立到给定数据库 URL 的连接 密码:就是数据库的登录密码root
*
* 3.Statement类:用于执行静态 SQL 语句并返回它产生的结果的对象
* (1)execute(String sql):执行给定的 SQL 语句,该语句可能返回多个结果
*/
public class Demo01 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws SQLException {
//1.创建链接对象 异常抛出
Connection conn =
DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/empdb?characterEncoding=utf8&serverTimezone=Asia/Shanghai",
"root",
"root");
System.out.println("链接对象:"+conn);
//2.创建执行SQL语句的对象
Statement s = conn.createStatement();
//3.执行SQL语句 execute执行
s.execute("create table jdbct1(age int)");//创建一个jdbt1的表
//4.关闭资源
conn.close();
System.out.println("执行完成!");//此时回到mysql客户端 输入命令:【use empdeb; 、 show tables 】发现有了jdbt1这个表格
}
}
(6)再创建《Demo02.java》,在此文件中删除刚才创建的表格(jdbct1):
只有第三步执行SQL语句不一样: 改为删除表格:【s.execute("drop table jdbct1");】
package cn.tedu.day01;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.DriverManager;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.sql.Statement;
/**
* 此案例用来:《删除刚才创建的表格(jdbct1)》
*/
public class Demo02 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws SQLException {
//1.创建链接对象
Connection conn = DriverManager.getConnection(
"jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/empdb?characterEncoding=utf8&serverTimezone=Asia/Shanghai",
"root",
"root");
System.out.println("链接对象:"+conn);
//2.创建执行SQL语句的对象
Statement s = conn.createStatement();
//3.执行SQL语句的对象(创建一个jdbt1的表)
s.execute("drop table jdbc1");
//40.关闭资源
conn.close();
System.out.println("执行完成!");//此时回到mysql客户端 输入命令:【use empdeb; 、 show tables 】发现没有了jdbt1这个表格
}
}
02.执行SQL语句的对象Statement
execute("sql");
此方法可以执行任意SQL语句, 但建议执行DDL(数据库相关和表相关的SQL语句)
int row = executeUpdate("sql");
此方法用来执行增删改【executeUpdate("sql")】相关的SQL语句, 返回值表示生效的行数
ResultSet rs = executeQuery(sql);
此方法用来执行查询相关的SQL语句,返回值ResultSet叫做结果集对象,
查询到的数据都装在此对象中
(1)增删改插练习题:
package cn.tedu;
import java.sql.*;
/**
* 《本案例用来练习 java 操作数据库进行增删改查的练习》
*
* (1)int executeUpdate(String sql):此方法用来执行增删改【executeUpdate("sql")】相关的SQL语句, 返回值表示生效的行数
* (2)execute("sql"):此方法可以执行任意SQL语句, 但建议执行DDL(数据库相关和表相关的SQL语句)
*
* 1、ResultSet类:表示数据库结果集的数据表,通常通过执行查询数据库的语句生成。
* ResultSet 对象维护一个指向其当前数据行的游标。最初,光标位于第一行之前。
* next方法:将光标移动到下一行,并且因为它在ResultSet对象中没有更多行时返回false,
* 所以可以在while循环中使用它来遍历结果集。
* (1)ResultSet rs = executeQuery(sql);
* 此方法用来执行查询相关的SQL语句,返回值ResultSet叫做结果集对象,查询到的数据都装在此对象中
*/
public class Demo03 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws SQLException {
//1.创建链接(Connection)对象 有异常抛出
Connection conn =
DriverManager.getConnection(
"jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/empdb?characterEncoding=utf8&serverTimezone=Asia/Shanghai&useSSL=false",
"root",
"root");
//2.创建执行SQL语句的对象
Statement s = conn.createStatement();
//3.1 执行插入数据SQL
// s.executeUpdate("insert into emp(name) values('tom')");//在emp表中插入 tom信息
//3.2 执行修改的SQL语句:将tom修改为jerry
// s.executeUpdate("update emp set name='jerry' where name='tom'");
//3.3 执行删除的SQL语句
s.executeUpdate("delete from emp where name='jerry'");
//3.4 执行查询的SQL语句:查询emp表中的名字对应工资
ResultSet rs = s.executeQuery("select name,sal from emp;");
//(1)遍历 结果集 中的数据在控制台显示:两种方式①②
while(rs.next()){//若为true,有下一条数据,则走循环
//①获取游标指向的这条数据的某个字段的值,通过字段名获取
// String name = rs.getString("name");
// double sal = rs.getDouble("sal");
//②通过查询回来的位置获取数据:
String name = rs.getString(1);//查询回来的第1个字段
double sal = rs.getDouble(2);//查询回来的第2个字段
System.out.println(name+":"+sal);
}
//4.关闭资源
conn.close();
System.out.println("执行完成!");
//3.1 此时回到mysql客户端 输入命令:【use empdb; show tables; select * from emp;】发现emp这个表中添加了tom信息
//3.2 此时回到mysql客户端 输入命令:【select * from emp;】发现emp这个表中tom换为了"jerry"!
//3.3 此时回到mysql客户端 输入命令:【select * from emp;】发现emp这个表中的字段:"jerry"被删除成功!
}
}
(2)创建 数据库实用程序:DBUtils类
将 DriverManager 类 调用 getConnection() 方法 连接数据库的代码封装成一个 数据库实用程序:DBUtils 方便调用。
package cn.tedu;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.DriverManager;
import java.sql.SQLException;
/**
* 数据库实用程序:DBUtils
*
* 此代码实现:将 DriverManager 类 调用 getConnection() 方法 连接数据库的代码封装成一个 数据库实用程序:DBUtils 方便调用。
*/
public class DBUtils {
public static Connection getConn() throws SQLException {
Connection conn = DriverManager.getConnection(
"jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/empdb?characterEncoding=utf8&serverTimezone=Asia/Shanghai&useSSL=false",
"root","root");
return conn;
}
}
(3)用java程序遍历表格的name属性的数据
package cn.tedu.day01;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.ResultSet;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.sql.Statement;
/**
* 用java程序来遍历数据库中表格的属性name
* 以下两种方法都可以
*/
public class Demo04_DBUtils {
public static void main(String[] args) throws SQLException {
/**
* 第一种方法:
*/
//从工具类获取链接对象
try (Connection conn = DBUtils.getConn()) {//若还是有报错:alt+回车选择:set language...即可
//创建执行SQL语句的对象
Statement s = conn.createStatement();
//执行查询
ResultSet rs = s.executeQuery("select name from emp");
//遍历 结果集 中的数据在控制台显示:
while(rs.next()){
//通过查询回来的位置获取数据:
String name = rs.getString(1);
System.out.println(name);
}
} catch (SQLException throwables) {
throwables.printStackTrace();
}
/**
* 第二种方法:
*/
// //从工具类获取链接对象
// Connection conn = DBUtils.getConn();//若还是有报错:alt+回车选择:抛出异常即可
// //创建执行SQL语句的对象
// Statement s = conn.createStatement();
// //执行查询
// ResultSet rs = s.executeQuery("select name from emp");
// //遍历 结果集 中的数据在控制台显示:
// while(rs.next()){
// //通过查询回来的位置获取数据:
// String name = rs.getString(1);
// System.out.println(name);
// }
/*
孙悟空
猪八戒
沙僧啊
唐僧啊
刘备啊
关羽啊
张飞啊
观音啊
白骨精
蜘蛛精
黑熊怪
灭霸
tom
*/
}
}
(4)创建一个hero表 有id,name,money价格 id自增
package cn.tedu;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.DriverManager;
import java.sql.SQLException;
public class DBUtils {
public static Connection getConn() throws SQLException {
Connection conn = DriverManager.getConnection(
"jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/empdb?characterEncoding=utf8&serverTimezone=Asia/Shanghai&useSSL=false",
"root","root");
return conn;
}
}
package cn.tedu;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.sql.Statement;
/**
* 要求:创建hero表格
* (1)添加main方法,方法中创建一个hero表 有id,name,money价格 id自增
* (2)需要用上DBUtils工具类
*/
public class Demo05_DBUtils {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//从工具类中获取链接对象
try (Connection conn = DBUtils.getConn()){//若还是有报错:alt+回车选择:set language...即可
//创建执行SQL语句的对象
Statement s = conn.createStatement();
s.execute("create table hero"+"(id int primary key auto_increment,name varchar(50),money int)");
System.out.println("执行完成!");
} catch (SQLException throwables) {
throwables.printStackTrace();
}
}
//此时回到mysql客户端 输入命令:【use empdb; show tables; desc hero; 】发现hero表中相关信息
}
(5.1)创建hero表,通过扫描控制台信息存入该表
package cn.tedu;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.DriverManager;
import java.sql.SQLException;
/**
* 1、DBUtils(数据库实用程序):提供getConnection方法被其他类调用
* (1)getConnection(url,user,password):尝试建立到给定数据库 URL 的连接 密码:就是数据库的登录密码root
*/
public class DBUtils {
public static Connection getConn() throws SQLException {
Connection conn = DriverManager.getConnection(
"jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/empdb?characterEncoding=utf8&serverTimezone=Asia/Shanghai&useSSL=false",
"root","root");
return conn;
}
}
package cn.tedu.day01;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.sql.Statement;
import java.util.Scanner;
/**
* 创建hero表,通过扫描仪来扫描控制台输入的信息来存入该表
*/
public class Demo06_DBUtils {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 创建扫描仪Scanner:
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("请输入英雄名");
String name = sc.nextLine();
System.out.println("请输入价格");
int money = sc.nextInt();
//获取数据库链接:把得到的英雄名和价格 保存到hero表里
try(Connection conn = DBUtils.getConn()) {
//创建执行sql语句的对象
Statement s = conn.createStatement();
//执行插入数据sql语句:
//因为name是字符串所以加单引号(在java代码中:若造双引号里添加字符串就需要写出:'"xxx"'的样子
// money是数字所以不用加单引号直接双引号即可)
s.executeUpdate("insert into hero values(null, '"+name+"' , "+money+")");
System.out.println("添加数据成功!");
} catch (SQLException throwables) {
throwables.printStackTrace();
}
}
//此时回到mysql客户端 输入命令:【use empdb; 、 select * from hero; 】发现hero这个表格存在且在控制台输入的内容可以存进来
}
(5.2)遍历hero的表并在控制台显示
package cn.tedu;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.DriverManager;
import java.sql.SQLException;
/**
* 1、DBUtils(数据库实用程序):提供getConnection方法被其他类调用
* (1)getConnection(url,user,password):尝试建立到给定数据库 URL 的连接 密码:就是数据库的登录密码root
*/
public class DBUtils {
public static Connection getConn() throws SQLException {
Connection conn = DriverManager.getConnection(
"jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/empdb?characterEncoding=utf8&serverTimezone=Asia/Shanghai&useSSL=false",
"root","root");
return conn;
}
}
package cn.tedu;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.ResultSet;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.sql.Statement;
/**
* 要求:遍历hero的表中的数据并在控制台显示
*
* 1.Connection接口:与特定数据库的连接(会话)。在连接的上下文中执行 SQL 语句并返回结果。
* Connection 对象的数据库能够提供描述它的表、它支持的 SQL 语法、它的存储过程、这个连接的能力等等的信息。
* 此信息是通过 getMetaData 方法获得的。
* (1)createStatement():创建一个 Statement 对象,用于将 SQL 语句发送到数据库
*
* 2.ResultSet rs = executeQuery(sql)
* :此方法用来执行查询相关的SQL语句,返回值ResultSet叫做结果集对象,查询到的数据都装在此对象中
*/
public class Demo07_DBUtils {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//把英雄表的所有信息查询出来并在控制台输出:
try (Connection conn = DBUtils.getConn()){
//创建执行SQL语句的对象:
Statement s = conn.createStatement();
//执行查询SQL语句:
ResultSet r = s.executeQuery("select * from hero");
//遍历 结果集 中的数据在控制台显示
while(r.next()){
int id = r.getInt(1);
String name = r.getString(2);
int money = r.getInt(3);
System.out.println(id+":"+name+":"+money);//此时在控制台即可遍历到hero表中的信息:【1:牛魔王:500】
}
} catch (SQLException throwables) {
throwables.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
03.数据库连接池DBCP
DataBaseConnectionPool : 数据库连接池
作用: 将连接重用,从而提高执行效率
(1)如何使用数据库连接池?
在苍老师网站:配置文件:pom.xml常用下载中的: Druid数据库连接池代码(下面↓)复制粘贴到:
IDEA中:maven下:pom.xml文件中的:添加依赖:<dependencies></dependencies>中,
和<dependency>并列,
点击右侧刷新按钮后,External Libraries下多了一个阿里巴巴的maven文件,成功!
<!-- 数据库连接池 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba</groupId>
<artifactId>druid</artifactId>
<version>1.1.21</version>
</dependency>
创建 Demo08_DBUtils_Druid:
package cn.tedu;
import com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.SQLException;
/**
* 要求:导入数据库连接池依赖并设置数据库连接信息
* :在maven的pom.xml文件中导入阿里巴巴的数据库连接池依赖
*
* (1)getConnection(url,user,password):尝试建立到给定数据库 URL 的连接 密码:就是数据库的登录密码root
*/
public class Demo08_DBUtils_Druid {
public static void main(String[] args) throws SQLException {
//创建连接池对象
DruidDataSource ds = new DruidDataSource();
//设置数据库连接信息 url 用户名 密码
ds.setUrl("jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/empdb?characterEncoding=utf8&serverTimezone=Asia/Shanghai");
ds.setUsername("root");
ds.setPassword("root");
//设置初始连接数量
ds.setInitialSize(3);
//设置最大连接数量
ds.setMaxActive(5);
//从连接池中获取连接 有异常抛出
Connection conn = ds.getConnection();
System.out.println("连接对象:"+conn);
/*
控制台输出以下信息则表示连接成功!:
十一月 12, 2022 11:31:37 上午 com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource info
信息: {dataSource-1} inited
连接对象:com.mysql.cj.jdbc.ConnectionImpl@3159c4b8
*/
}
}
(2)改造DBUtils(数据库实用程序)
package cn.tedu;
import com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.DriverManager;
import java.sql.SQLException;
/**
* 《数据库实用程序:DBUtils》
* 下面的代码会实现:
* 【将 DriverManager 类 调用 getConnection() 方法 连接数据库的代码封装成一个 数据库实用程序:DBUtils 方便调用。】
*
* public class DBUtils {
* public static Connection getConn() throws SQLException {
* Connection conn = DriverManager.getConnection(
* "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/empdb?characterEncoding=utf8&serverTimezone=Asia/Shanghai&useSSL=false",
* "root",
* "root"
* );
* return conn;
* }
* }
*
* ————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
*
* 《下面的代码将 改造上边的 DBUtils(数据库实用程序)》:
* 1、DBUtils(数据库实用程序):提供getConnection方法被其他类调用
* (1)getConnection(url,user,password):尝试建立到给定数据库 URL 的连接 密码:就是数据库的登录密码root
*
*/
public class DBUtils_Druid {
//全局变量ds(斜体):————>为什么加static? 因为在静态块和静态方法中使用该成员变量。
private static DruidDataSource ds;
static{ //把创建连接池对象放在静态块中:随着类的加载只加载一次
//创建连接池对象:
ds = new DruidDataSource();
//设置数据库连接信息 url 用户名 密码:
ds.setUrl("jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/empdb?characterEncoding=utf8&serverTimezone=Asia/Shanghai&useSSL=false");
ds.setUsername("root");
ds.setPassword("root");
//设置初始连接数量
ds.setInitialSize(3);
//设置最大连接数量
ds.setMaxActive(5);
}
public static Connection getConn() throws SQLException {
//从连接池中获取连接 异常抛出
Connection conn = ds.getConnection();
System.out.println("连接对象:"+conn);
return conn;
}
}
(3.1)创建用户表并实现注册登录功能(步骤1-5)
《Demo09要求》:——————>【 在数据库中创建user用户表 并实现 注册用户名相关信息的功能(Demo09(1、)】
《Demo10_one要求》:——————>【在 Demo09 的基础上完成 Demo10(2、) 的登录功能,但该Demo10有sql注入危险】
《Demo10_two要求》:——————>【该 Demo10_two(3、) 程序用来解决Demo10_one的sql注入问题】
1.把扫描仪得到的3个信息保存到user表 参考Demo06
package cn.tedu.day02;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.sql.Statement;
import java.util.Scanner;
/**
* 《Demo09要求》:——————>【 在数据库中创建user用户表 并实现 注册用户名相关信息的功能(Demo09(1、)】
*
* 1、把扫描仪得到的3个信息保存到user表 参考Demo06
* 步骤:
* (1)首先在mysql客户端例:
* ①use empdb;
* ②create table user(id int primary key auto_increment,username varchar(50),password varchar(50),nick varchar(50))charset=utf8;
* ③用户名小猪猪 密码root 昵称root
* (2)完成【下面的代码】后,
* .............. ;
* ①用【 desc user;】查看该表添加的内容
* MariaDB [empdb]> desc user;
* +----------+-------------+------+-----+---------+----------------+
* | Field | Type | Null | Key | Default | Extra |
* +----------+-------------+------+-----+---------+----------------+
* | id | int(11) | NO | PRI | NULL | auto_increment |
* | username | varchar(50) | YES | | NULL | |
* | password | varchar(50) | YES | | NULL | |
* | nick | varchar(50) | YES | | NULL | |
* +----------+-------------+------+-----+---------+----------------+
* ②再用【select username,password,nick from user;】查看具体添加的用户信息
* MariaDB [empdb]> select username,password,nick from user;
* +----------+----------+------+
* | username | password | nick |
* +----------+----------+------+
* | 小猪猪 | root | root |
* +----------+----------+------+
*
* 知识点:
* 1.执行插入数据SQL语句固定格式:
* s.executeUpdate("insert into hero values(null, '"+xxx+"' , '"+xxx+"' , '"+xxx+"' )");
*
* 2.Statement类:用于执行静态 SQL 语句并返回它产生的结果的对象
* (1)execute(String sql):执行给定的 SQL 语句,该语句可能返回多个结果
*/
public class Demo09_DBUtils_Druid {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 创建扫描仪
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("请输入用户名");
String username = sc.nextLine();
System.out.println("请输入密码");
String password = sc.nextLine();
System.out.println("请输入昵称");
String nick = sc.nextLine();
//获取数据库连接:把得到的英雄名和价格 保存到hero表里面
try (Connection conn = DBUtils_Druid.getConn()){
//创建执行SQL语句的对象:
Statement s = conn.createStatement();
//执行插入数据SQL语句:
//固定格式: s.executeUpdate("insert into hero values(null, '"+xxx+"' , "+xxx+" , '"+xxx+"' )");
s.executeUpdate("insert into user values(null, '"+username+"','"+password+"','"+nick+"')");
System.out.println("执行完成!");
} catch (SQLException throwables) {
throwables.printStackTrace();
}
/*
控制台输出:
请输入用户名
小猪猪
请输入密码
root
请输入昵称
root
十一月 12, 2022 11:53:48 上午 com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource info
信息: {dataSource-1} inited
连接对象:com.mysql.cj.jdbc.ConnectionImpl@5649fd9b
执行完成!
*/
}
}
2.完成登录功能(该Demo10有sql注入危险)
package cn.tedu.day02;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.ResultSet;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.sql.Statement;
import java.util.Scanner;
/**
*《Demo10_one要求》:——————>【在 Demo09 的基础上完成 Demo10(2、) 的登录功能,但该Demo10有sql注入危险】
*
* 2、完成登录功能(有sql注入问题)
* 步骤:
* (1)完成下面的代码,
* // 运行该程序后,控制台输入之前注册的用户名小猪猪,密码root即可登陆成功!
* (2)再进行【SQL注入【' or '1'='1】:发现登陆成功!】:
* // 运行该程序后,用户名随便输入,然后密码输入【' or '1'='1】测试发现SQL注入成功,可以登录成功!
*
* 知识点:
* ResultSet结果集:表示数据库结果集的数据表,通常通过执行查询数据库的语句生成。
* (1)方法:executeQuery(sql):
* :此方法用来执行查询相关的SQL语句,查询结束后,返回值ResultSet叫做结果集对象,查询到的数据都装在此对象中
* (2)方法:getString(...):
* :意为取得该列的数据以字符串的形式返回
* (3)方法:getString(String c):
* :获取数据库中某个类型(可以是varchar类型)字段值的方法,
* (4)方法:next():
* :ResultSet 对象维护一个指向其当前数据行的游标。最初,光标位于第一行之前。
* next方法:将光标移动到下一行,并且因为它在ResultSet对象中没有更多行时返回false,
* 所以可以在while循环中使用它来遍历结果集。
*
*/
public class Demo10_one_DBUtils_Druid {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//创建扫描仪
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("请输入用户名");
String username = sc.nextLine();
System.out.println("请输入密码");
String password = sc.nextLine();
//获取连接 判断用户输入的是否正确
//获取数据库连接:
try(Connection conn = DBUtils_Druid.getConn()){
//创建执行SQL语句的对象:
Statement s = conn.createStatement();
//固定格式: s.executeUpdate("insert into hero values(null, '"+xxx+"' , "+xxx+" , '"+xxx+"' )");
ResultSet rs = s.executeQuery(
"select count(*) from user where username='"+username+"' and password='" +password+"'"
);
//游标往下移动 指向查询回来的数据
rs.next();
//从结果集对象中取出此时游标指向的数据
int count = rs.getInt(1);
if(count > 0){
System.out.println("登录成功!");
}else {
System.out.println("用户名或密码错误!");
}
}catch (SQLException throwables){
throwables.printStackTrace();
}
/*
//运行该程序后,控制台输入之前注册的用户名小猪猪,密码root即可登陆成功!
控制台显示:
请输入用户名
小猪猪
请输入密码
root
十一月 14, 2022 10:06:29 上午 com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource info
信息: {dataSource-1} inited
连接对象:com.mysql.cj.jdbc.ConnectionImpl@5649fd9b
登录成功!
//【进行SQL注入【' or '1'='1】:发现登陆成功!】:
// 运行程序后,用户名随便输入,然后密码输入【' or '1'='1】测试发现SQL注入成功,可以登录成功!
控制台显示:
请输入用户名
ferg
请输入密码
' or '1'='1
十一月 14, 2022 10:09:02 上午 com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource info
信息: {dataSource-1} inited
连接对象:com.mysql.cj.jdbc.ConnectionImpl@5649fd9b
登录成功!
*/
}
}
3.查询是否有该用户信息
select count(*) from user where username='tom' and password='123456';
因为没有添加该用户,所以显示:无
MariaDB [empdb]> select count(*) from user where username='tom' and password='123456';
+----------+
| count(*) |
+----------+
| 0 |
+----------+
1 row in set (0.000 sec)
4.查询有几个用户:count(*)
select count(*) from user;
5.where username='abcd' and password='' or '1'='1'
进行SQL注入【' or '1'='1】:发现登陆成功!
↓↓↓↓↓↓↓↓↓↓↓
控制台显示:
请输入用户名
ferg
请输入密码
' or '1'='1
十一月 14, 2022 10:09:02 上午 com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource info
信息: {dataSource-1} inited
连接对象:com.mysql.cj.jdbc.ConnectionImpl@5649fd9b
登录成功!
(3.2)解决SQL注入问题—>通过PreparedStatement(表示预编译 SQL 语句的对象)
ResultSet结果集:表示数据库结果集的数据表,通常通过执行查询数据库的语句生成。
(1)方法:executeQuery(sql):
:此方法用来执行查询相关的SQL语句,查询结束后,返回值ResultSet叫做结果集对象,查询到的数据都装在此对象中
(2)方法:getString(...):
:意为取得该列的数据以字符串的形式返回
(3)方法:getString(String c):
:获取数据库中某个类型(可以是varchar类型)字段值的方法,
(4)方法:next():
:ResultSet 对象维护一个指向其当前数据行的游标。最初,光标位于第一行之前。
next方法:将光标移动到下一行,并且因为它在ResultSet对象中没有更多行时返回false,
所以可以在while循环中使用它来遍历结果集。
——————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
PreparedStatement:表示预编译 SQL 语句的对象。
SQL 语句被预编译并存储在 PreparedStatement 对象中。
然后可以使用该对象多次有效地执行该语句
(1)PreparedStatement对象可以将编译SQL语句的时间点提前,
提前后可以将SQL语句逻辑部分提前锁死,
用户输入的内容将不能影响原有SQL语句的逻辑部分,从而解决了SQL注入的问题
(2)如果SQL语句中《存在》变量,则必须使用PreparedStatement,解决SQL注入问题,
而且可以提高开发效率(避免了拼接字符串) 。
(3)如果SQL语句中《没有》变量,可以使用Statement或PreparedStatement
(4)方法:prepareStatement(String sql):
:创建一个 PreparedStatement 对象,用于将参数化的 SQL 语句发送到数据库。
带或不带 IN 参数的 SQL 语句可以预编译并存储在 PreparedStatement 对象中。
然后可以使用该对象多次有效地执行该语句。
(5)总结:通过PreparedStatement可以避免出现SQL注入
往传递值的地方传递进来了SQL语句,导致原有SQL语句逻辑改变
——————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
改造Demo10后的代码,成功解决sql注入问题:
package cn.tedu.day02;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.PreparedStatement;
import java.sql.ResultSet;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.util.Scanner;
/**
*《Demo10_two要求》:——————>【该 Demo10_two(3、) 程序用来解决Demo10_one的sql注入问题】
*
* 3、完成登录功能(解决sql注入问题)
* 步骤:
* (1)完成下面的代码,
* //运行该程序后,控制台输入之前注册的用户名小猪猪,密码root即可登陆成功!
* //运行该程序后,用户名随便输入,然后密码输入【' or '1'='1】测试发现SQL注入已经解决成功,不可以登录!
*
* 知识点:
* ResultSet结果集:表示数据库结果集的数据表,通常通过执行查询数据库的语句生成。
* (1)方法:executeQuery(sql):
* :此方法用来执行查询相关的SQL语句,查询结束后,返回值ResultSet叫做结果集对象,查询到的数据都装在此对象中
* (2)方法:getString(...):
* :意为取得该列的数据以字符串的形式返回
* (3)方法:getString(String c):
* :获取数据库中某个类型(可以是varchar类型)字段值的方法,
* (4)方法:next():
* :ResultSet 对象维护一个指向其当前数据行的游标。最初,光标位于第一行之前。
* next方法:将光标移动到下一行,并且因为它在ResultSet对象中没有更多行时返回false,
* 所以可以在while循环中使用它来遍历结果集。
*
* PreparedStatement:表示预编译 SQL 语句的对象。
* SQL 语句被预编译并存储在 PreparedStatement 对象中。
* 然后可以使用该对象多次有效地执行该语句
* (1)PreparedStatement对象可以将编译SQL语句的时间点提前,
* 提前后可以将SQL语句逻辑部分提前锁死,
* 用户输入的内容将不能影响原有SQL语句的逻辑部分,从而解决了SQL注入的问题
* (2)如果SQL语句中《存在》变量,则必须使用PreparedStatement,解决SQL注入问题,
* 而且可以提高开发效率(避免了拼接字符串) 。
* (3)如果SQL语句中《没有》变量,可以使用Statement或PreparedStatement
* (4)方法:prepareStatement(String sql):
* :创建一个 PreparedStatement 对象,用于将参数化的 SQL 语句发送到数据库。
* 带或不带 IN 参数的 SQL 语句可以预编译并存储在 PreparedStatement 对象中。
* 然后可以使用该对象多次有效地执行该语句。
* (5)总结:通过PreparedStatement可以避免出现SQL注入
* 往传递值的地方传递进来了SQL语句,导致原有SQL语句逻辑改变
*/
public class Demo10_two_DBUtils_Druid {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//创建一个扫描仪:
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("请输入用户名");
String username = sc.nextLine();
System.out.println("请输入密码");
String password = sc.nextLine();
//获取连接 判断用户输入的是否正确
//获取数据库连接:
try(Connection conn = DBUtils_Druid.getConn()){
//通过PreparedStatement 解决SQL注入问题
String sql = "select count(*) from user where username=? and password=?";
//编译SQL语句的时间点从之前执行时,提前到了创建对象时,好处是此时编译用户输入的内容
// -还不在SQL语句里面,只是将原有SQL语句进行编译,此时可以将原有SQL语句的逻辑部分锁死
PreparedStatement ps = conn.prepareStatement(sql);
//把?替换成变量1和2代表?的位置 此时替换时只能以值的形式添加到原有SQL语句中,因为
// -逻辑部分已经编译好 已经锁死,这样用户输入的内容则不会影响原有SQL语句的逻辑。
ps.setString(1,username);
ps.setString(2,password);
ResultSet rs = ps.executeQuery();
//游标往下移动 指向查询回来的数据
rs.next();
//从结果集对象中取出此时游标指向的数据
int count = rs.getInt(1);
if(count > 0){
System.out.println("登录成功!");
}else {
System.out.println("用户名或密码错误!");
}
} catch (SQLException throwables) {
throwables.printStackTrace();
}
}
/*
//运行该程序后,控制台输入之前注册的用户名小猪猪,密码root即可登陆成功!
控制台显示:
请输入用户名
小猪猪
请输入密码
root
十一月 14, 2022 10:48:54 上午 com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource info
信息: {dataSource-1} inited
连接对象:com.mysql.cj.jdbc.ConnectionImpl@5649fd9b
登录成功!
//【进行SQL注入【' or '1'='1】:发现不可以登录!】:
// 运行程序后,用户名随便输入,然后密码输入【' or '1'='1】测试发现SQL注入已经解决成功,不可以登录!
控制台显示:
请输入用户名
ferg
请输入密码
' or '1'='1
十一月 14, 2022 10:50:10 上午 com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource info
信息: {dataSource-1} inited
连接对象:com.mysql.cj.jdbc.ConnectionImpl@5649fd9b
用户名或密码错误!
*/
}
(4.1)实现验证用户名密码登录更清楚的提示功能
package cn.tedu.day02;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.PreparedStatement;
import java.sql.ResultSet;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.util.Scanner;
/**
* 实现验证用户名密码登录更清楚的提示功能
*/
public class Demo11_DBUtils_Druid {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//创建一个扫描仪:
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("请输入用户名");
String username = sc.nextLine();
System.out.println("请输入密码");
String password = sc.nextLine();
//获取连接 判断用户输入的是否正确
//获取数据库连接:
try (Connection conn = DBUtils_Druid.getConn()){
//通过PreparedStatement 解决SQL注入问题
String sql = "select password from user where username=?";
//编译SQL语句的时间点从之前执行时,提前到了创建对象时,好处是此时编译用户输入的内容
// -还不在SQL语句里面,只是将原有SQL语句进行编译,此时可以将原有SQL语句的逻辑部分锁死
PreparedStatement ps = conn.prepareStatement(sql);
//把?替换成变量1和2代表?的位置 此时替换时只能以值的形式添加到原有SQL语句中,因为
// -逻辑部分已经编译好 已经锁死,这样用户输入的内容则不会影响原有SQL语句的逻辑。
ps.setString(1,username);//1:代表的第一个“?”问号
//执行查询
ResultSet rs = ps.executeQuery();
//判断是否有数据
if(rs.next()){
//得到查询到的密码
String pw = rs.getString(1);//代表查询的第一个字段
//拿用户输入的密码和查询到的密码比较
if(pw.equals(password)){
System.out.println("登陆成功");
}else{
System.out.println("密码错误");
}
}else{
System.out.println("用户名不存在!");
}
} catch (SQLException throwables) {
throwables.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
(4.2)使用PreparedStatement实现注册功能(并实现用户名不能重复的功能)
package cn.tedu.day02;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.PreparedStatement;
import java.sql.ResultSet;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.util.Scanner;
/**
* 要求:使用PreparedStatement实现注册功能 并实现用户名不能重复的功能
*/
public class Demo12_DBUtils_Druid {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//创建一个扫描仪:
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("请输入用户名");
String username = sc.nextLine();
System.out.println("请输入密码");
String password = sc.nextLine();
System.out.println("请输入昵称");
String nick = sc.nextLine();
//获取连接 判断用户输入的是否正确
//获取数据库连接:
try (Connection conn = DBUtils_Druid.getConn()){
/**
* 使用PreparedStatement(可以避免SQL注入问题)实现注册功能 并实现用户名不能重复的功能
*/
//1.查询用户名是否存在:
String sql = "select password from user where username=?";
//编译SQL语句的时间点从之前执行时,提前到了创建对象时,好处是此时编译用户输入的内容
// -还不在SQL语句里面,只是将原有SQL语句进行编译,此时可以将原有SQL语句的逻辑部分锁死
PreparedStatement ps = conn.prepareStatement(sql);
//把?替换成变量1和2代表?的位置 此时替换时只能以值的形式添加到原有SQL语句中,因为
// -逻辑部分已经编译好 已经锁死,这样用户输入的内容则不会影响原有SQL语句的逻辑。
ps.setString(1,username);//1:代表的第一个“?”问号
//执行查询
ResultSet rs = ps.executeQuery();
//判断是否有数据
if(rs.next()){
System.out.println("用户名已存在");
return;
}
//2.实现往user表中添加数据:
String insertSql = "insert into user values(null,?,?,?)";
PreparedStatement insertPs = conn.prepareStatement(insertSql);
insertPs.setString(1,username);
insertPs.setString(2,password);
insertPs.setString(3,nick);
//执行插入
insertPs.executeUpdate();
System.out.println("注册完成!");
} catch (SQLException throwables) {
throwables.printStackTrace();
}
}
/*
(1)测试输入 重复 的用户名会 提示用户名用户名已存在:
请输入用户名
小猪猪
请输入密码
哈
请输入昵称
哈
十一月 14, 2022 11:22:45 上午 com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource info
信息: {dataSource-1} inited
连接对象:com.mysql.cj.jdbc.ConnectionImpl@5649fd9b
用户名已存在
(2)测试输入 不重复 的用户名会 注册成功:
请输入用户名
猪猪侠
请输入密码
root
请输入昵称
猪猪侠
十一月 14, 2022 11:23:45 上午 com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource info
信息: {dataSource-1} inited
连接对象:com.mysql.cj.jdbc.ConnectionImpl@5649fd9b
注册完成!
*/
}
三、SpringBoot
1、SpringBoot工程:boot1-1/boot2-1
[0]解决问题的思路:
a.检查页面中是否报错,在浏览器中按F12 查看console控制台的报错,
此时可能会得到前端的错误,提示信息和后端相关的错误码(404,500,400),
b.查看idea控制台里面的报错
c.如果页面中没有展示出数据可以通过浏览器直接向异步请求的地址发出请求,检查是否得到了数据,
如果浏览器中显示了JSON格式的数据说明服务器正常返回了数据
此时Controller和Mapper是没有问题的,说明此时出错的是页面,
如果说没有数据代表服务器的问题检查Controller和Mapper相关的代码
d.万能解决方案:
有正确代码的前提下, 实现一个功能总共设计到三部分代码:VCM,
从正确的代码中按照VCM划分三部分,替换一部分后立即测试看问题是否解决
e.代码全部正确(前提是已经用老师代码替换过) 还有错:
/1.刷新mave+Rebuild工程+重启工程
/2.检查数据库中的表是否有错
/3.检查application.properties配置文件是否有错
/4.重启idea测试 有时idea会莫名出错
[1]SpringBoot常见错误列表:
(1)浏览器中显示404状态码———>404代表找不到资源
(1)找不到静态资源: 比如 *.html *.jpg *.xxx
检查浏览器请求路径是否正确
检查文件是否保存在了正确的位置(一般放在static文件夹下面)
如果上面两种情况都没有问题,重新编译工程并重启工程 Build->ReBuild
(2)找不到动态资源: 比如 /hello 由controller处理的路径称为动态资源
检查浏览器请求路径是否正确
检查Controller是否创建在了工程自带的包的里面
检查是否在Controller类里面的类名上面添加@Controller注解
检查Controller里面RequestMapping注解中处理的路径是否正确
如果上面两种情况都没有问题,重新编译工程并重启工程 Build->ReBuild
(2)浏览器中显示500状态码———>500代表服务器执行错误
500代表服务器执行错误,
此时第一时间查看idea控制台的错误,里面会有错误相关的提示,
根据提示信息再分析具体哪里错了.
(2.1)浏览器中显示400状态码——>传参出错
浏览器中显示400状态码,
是传参出错,
比如接收参数的类型是数值类型,测试时传递过去一个字符串内容,这时会报400错误
(3)Controller中处理了相同的路径

(4)创建完包含Mybatis框架的工程直接运行时会报以下错误,需要在application.properties配置文件中添加以下内容
spring.datasource.username=root
spring.datasource.password=root
spring.datasource.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/empdb?characterEncoding=utf8&serverTimezone=Asia/Shanghai&useSSL=false
1.检查是不是有其它正在运行的工程, 将其关闭后再运行新工程
2.如果没有正在运行的工程,可通过以下几种方式:
(1)重启电脑
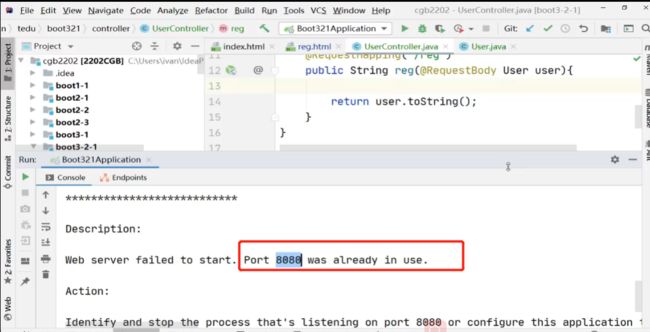
(2)修改工程的端口号:
在工程下的src/main/resources下的【application.properties】中:
额外添加一个指定端口号(注意此方式应用后每次访问页面也要记得修改):
server.port=8081;
(3)在dos窗口命令行中,
[1]找出使用8080端口的PID:
执行以下指令(netstat -o -n -a | findstr :8080)找到占用8080端口的进程,
会发现dos窗口中会显示此占用8080端口的pid(比如是1990)
[2]Kill掉目前8080端口所占用的线程:
然后执行杀掉该进程的指令(taskkill /F /PID 1990), 释放出8080端口

**(6)**在Vue对象实例化之前访问对象报错, 目前我们接触到的写代码的位置只有created方法中是实例化过程中的方法,在此方法中访问Vue对象需要用this而不是变量名v, 如果使用v则会在浏览器控制台中报以下错误

(7)如果上传的图片不显示按照以下步骤检查:
检查文件是否保存到了指定的文件夹
检查数据库里面保存的图片路径是否正确 和文件夹中图片名是否一致
检查配置的静态资源文件夹是否成功(往文件夹中放一张文件名比较简单的图片,
通过localhost:8080/图片名 访问)
在页面中图片标签上面右键检查 查看图片的路径是否正常
[2]常用注解@:
(1)@SpringBootApplication
:包含@Configuration、@EnableAutoConfiguration、@ComponentScan 通常用在主类上。
例:
package cn.tedu.boot42;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
//下面注解:包含@Configuration、@EnableAutoConfiguration、@ComponentScan 通常用在主类上。
@SpringBootApplication
public class Boot42Application {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(Boot42Application.class, args);
}
}
———————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
(2)@RestController
:用于标注控制层组件(如struts中的action),包含@Controller和@ResponseBody
/此注解相当于在每一个方法上面添加ResponseBody注解
例:
package cn.tedu.boot31.controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestBody;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
//此注解相当于在每一个方法上面添加ResponseBody注解
@RestController
public class AxiosController {
/** 异步请求get时:进行点击事件弹窗的传参用info表示 */
@RequestMapping("/hello1Axios")
public String hello1(String info){
return "请求成功! info="+info;
}
/** 异步请求post时:进行点击事件弹窗的传参用info表示 */
//@RequestBody注解作用, 当客户端发出post请求并且提交的是自定义对象时,
// 服务器端接收参数必须使用此注解 否则得不到传递过来的参数.
@RequestMapping("/hello2Axios")
public String hello2(@RequestBody String info){
return "请求成功! info="+info;
}
}
———————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
(3)
①@ResponseBody
:表示该方法的返回结果直接写入HTTP response body中。
一般在异步获取数据时使用,在使用@RequestMapping后,返回值通常解析为跳转路径,
加上@responsebody后返回结果不会被解析为跳转路径,而是直接写入HTTP response body中。
比如异步获取json数据,加上@responsebody后,会直接返回json数据。
例:
package cn.tedu.boot21.controller;
import cn.tedu.boot21.entity.Emp;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ResponseBody;
@Controller
public class HelloController {
/** 1.通过浏览器的地址栏中发出请求(简单响应一句话内容) */
// @RequestMapping("/hello")
// public void hello(HttpServletResponse response) throws IOException {
// response.setContentType("text/html;charset=utf-8");
// PrintWriter pw = response.getWriter();
// pw.print("测试成功");
// pw.close();
// }
/* 简单写法: */
@RequestMapping("/hello")
@ResponseBody //SpringMVC框架提供的注解,作用:可以通过返回值的方式给客户端响应数据
public String hello(){
return "测试成功!222";
}
/** 3.表单提交的三种方式: */
/** 2.通过html页面中的超链接发出请求(测试相对路径和绝对路径)这一段代码: */
// @RequestMapping("/param1")
// @ResponseBody
// public String param1(HttpServletRequest request){
// String info = request.getParameter("info");
// return "接收到了参数:"+info;
// }
@RequestMapping("/param2")
@ResponseBody
public String param2(String name,int age){
return "接收到参数:"+name+"年龄:"+age;
}
@RequestMapping("/param3")
@ResponseBody
public String param3(Emp emp){
return emp.toString();
}
}
— — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — —
②@RequestBody
:当客户端发出post请求并且提交的是自定义对象时,
服务器端接收参数必须使用此注解 否则得不到传递过来的参数.
/参数前加上这个注解之后,认为该参数必填。表示接受json字符串转为对象 List等;
例:
package cn.tedu.boot31.controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestBody;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
//此注解相当于在每一个方法上面添加ResponseBody注解
@RestController
public class AxiosController {
/** 异步请求get时:进行点击事件弹窗的传参用info表示 */
@RequestMapping("/hello1Axios")
public String hello1(String info){
return "请求成功! info="+info;
}
/** 异步请求post时:进行点击事件弹窗的传参用info表示 */
//@RequestBody注解作用, 当客户端发出post请求并且提交的是自定义对象时,
// 服务器端接收参数必须使用此注解 否则得不到传递过来的参数.
@RequestMapping("/hello2Axios")
public String hello2(@RequestBody String info){
return "请求成功! info="+info;
}
}
———————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
(4)@Autowired
:byType方式。把配置好的Bean拿来用,完成属性、方法的组装,它可以对类成员变量、方法及构造函数进行标
注,完成自动装配的工作。当加上(required=false)时,就算找不到bean也不报错。
/Spring框架结合Mybatis框架会自动将HeroMapper生成一个实现类和实现里面的方法,
而且会自动实例化对象,required = false告诉idea编译器此对象是非必要的,
因此"mapper"若报错的话需要这样写: @Autowired(required = false)
例:
package cn.tedu.boot41.controller;
import cn.tedu.boot41.mapper.ProductMapper;
import cn.tedu.boot41.entity.Product;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestBody;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
import java.util.List;
//此注解相当于在每一个方法上面添加ResponseBody注解
@RestController
public class ProductController {
/*
此注解的作用是:
Spring框架结合Mybatis框架会自动将HeroMapper生成一个实现类和实现里面的方法,
而且会自动实例化对象,required = false告诉idea编译器此对象是非必要的,
因此"mapper"若报错的话需要这样写: @Autowired(required = false)
*/
@Autowired
ProductMapper mapper;
//@RequestBody注解作用, 当客户端发出post请求并且提交的是自定义对象时,
// 服务器端接收参数必须使用此注解 否则得不到传递过来的参数.
@RequestMapping("/insert")
public void insert(@RequestBody Product product){
System.out.println("product = " + product);
mapper.insert(product);
}
@RequestMapping("/select")
public List<Product> select(){
// SpringMVC框架当发现返回值类型为集合或自定义的对象类型时,
//会将集合或对象转成JSON格式的字符串,然后再将JSON格式字符串转成二进制数据进行网络传输
/*
此时测试: http://localhost:8080/select
可以跳转到一个用list集合显示数据库里的product的信息的页面!
[{"id":5,"title":"狮子","price":520.0,"saleCount":22},
{"id":6,"title":"老虎狮子","price":2000.0,"saleCount":2155},
{"id":7,"title":null,"price":null,"saleCount":null}]
*/
//此时想看数据库真实商品信息时,需要把这句代码注释后,改为下边两句
// return mapper.select();
List<Product> list = mapper.select();
return list;
}
}
———————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
(5)@RequestMapping
:RequestMapping是一个用来处理请求地址映射的注解,可用于类或方法上。
用于类上,表示类中的所有响应请求的方法都是以该地址作为父路径。
该注解有六个属性:
1)params:指定request中必须包含某些参数值是,才让该方法处理。
2)headers:指定request中必须包含某些指定的header值,才能让该方法处理请求。
3)value:指定请求的实际地址,指定的地址可以是URI Template 模式
4)method:指定请求的method类型, GET、POST、PUT、DELETE等
5)consumes:指定处理请求的提交内容类型(Content-Type),如application/json,text/html;
6)produces:指定返回的内容类型,仅当request请求头中的(Accept)类型中包含该指定类型才返回
例:
package cn.tedu.boot51.controller;
import cn.tedu.boot51.entity.User;
import cn.tedu.boot51.entity.Weibo;
import cn.tedu.boot51.mapper.WeiboMapper;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestBody;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpSession;
import java.util.Date;
import java.util.List;
//此注解相当于在每一个方法上面添加ResponseBody注解
@RestController
public class WeiboController {
/*
此注解的作用是:
Spring框架结合Mybatis框架会自动将HeroMapper生成一个实现类和实现里面的方法,
而且会自动实例化对象,required = false告诉idea编译器此对象是非必要的,
因此"mapper"若报错的话需要这样写: @Autowired(required = false)
*/
@Autowired
WeiboMapper mapper;
/*
@RequestBody注解:
当客户端发出post请求并且提交的是自定义对象时,
服务器端接收参数必须使用此注解 否则得不到传递过来的参数.
@RequestMapping:
是一个用来处理请求地址映射的注解,可用于类或方法上。
*/
@RequestMapping("/insert")
public int insert(@RequestBody Weibo weibo, HttpSession session){
//得到当前登录的用户对象
User u = (User) session.getAttribute("user");
if (u==null){ return 2;//代表未登录
}
//new Date()得到当前的系统时间
weibo.setCreated(new Date());
//把当前登录的用户信息 添加到weibo对象中
weibo.setUserId(u.getId());
weibo.setNick(u.getNick());
System.out.println("weibo = " + weibo);
mapper.insert(weibo);
return 1;//代表发布微博成功!
}
@RequestMapping("/select")
public List<Weibo> select(){
return mapper.select();
}
}
00.SpringBoot
(1)Web服务软件做了那些事儿?
web服务软件就是传奇老师带着写的webServer, 也就是Tomcat
1.负责建立底层的网络连接
2.根据客户端请求的静态资源路径找到对应的静态资源文件并把该文件返回给客户端
举例:http://localhost:8080/index.html
3.根据客户端请求的动态资源路径找到对应的Controller里面的方法并且执行
举例:http://localhost:8080/hello
Web服务软件自身不提供任何业务功能,通过Controller给工程添加具体的业务功能
(2)SSM三大框架
Spring框架(第四阶段讲)
SpringMVC框架(第二阶段到第四阶段)
Mybatis框架(第三阶段到第四阶段)
(3)SpringBoot框架
如果创建一个空工程,在此工程中使用SSM框架时需要添加大量的依赖和书写大量的配置文件,
通过SpringBoot框架可以更加便捷的让工程中引入各种框架,
SpringBoot框架帮助我们构建工程。
01.如何创建SpringBoot工程:(步骤1-9)
(1)在IDEA中:点击左上角File创建新的Module 或者 alt+insert选择Module
(2)设置以下内容:
①点击左侧的:Spring Initializr
并修改右侧的相关内容:
Group: cn.tedu
java: 8
Artifact:boot1-1
②设置完成后点击 Next
③第一个页面中可以修改创建工程的网址:
(3)跳转到新的页面:点击Web——>Spring Web——>点击Finishi等待下载内容
(4)如何检查工程是否创建成功?
(6)检查maven是否已经改成aliyun(阿里云)的配置文件
(7)如果已经改成:aliyun(阿里云)的 还有错的话, 找到.m2文件夹下的repository文件夹删除 ,删除完之后再次重复第5步 刷新maven
(8)
1)
①项目boot1-1下的src/main/java下: 新建包:cn/tedu/boot-1
②项目boot1-1下的src/main/static下:新建index.html页面 输入一行内容:< h1>Hello SpringBoot!< /h1>
2)点击idea界面右上角小锤子右边的: 启动Boot1-1模块程序
3)浏览器访问:http://localhost:8080 页面会显示index页面的内容!
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>Hello SpringBoot!</h1>
</body>
</html>
(9)
①在项目boot1-1下的java内创建包:cn/tedu/boot-1/controller 新建响应类:HelloController
②在里面添加hello方法处理/hello请求,给客户端响应一句话, 重启工程,浏览器访问http://localhost:8080/hello 测试是否成功
package cn.tedu.boot11.controller;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.PrintWriter;
@Controller
public class HelloController {
@RequestMapping("/hello")//当浏览器往该网址(http://localhost:8080/hello)发请求时,这个方法会响应
public void hello(HttpServletResponse response) throws IOException {
//设置响应类型 甘肃客户端服务器响应的是什么类型的内容 和 字符集
response.setContentType("text/html;charset=utf-8");
//得到输出对象 异常抛出
PrintWriter pw = response.getWriter();
//输出数据
pw.print("服务器收到了请求!测试成功
");
//关闭资源
pw.close();
}
}
(1)任务: 练习五遍
依次创建至少5个工程将创建工程的流程熟练掌握
(每次运行新工程之前需要关闭之前的工程,不然会出现端口被占用的问题)
boot1-1
boot1-2
boot1-3
boot1-4
.......
02.客户端发请求的4种方式:boot1-1
1.通过浏览器的地址栏中发出请求
2.通过html页面中的超链接发出请求
3.通过html页面中的form表单发出请求
4.通过前端框架发出请求
(1)通过浏览器的地址栏中发出请求(简单响应一句话内容)
1.通过浏览器的地址栏中发出请求(简单SpringBoot响应一句话内容)
新建类HelloController 新建页面index
(1)①项目boot1-1下的src/main/static下:新建index.html页面
输入一行内容:<h1>工程首页</h1>
(2)点击idea界面右上角小锤子右边的: 启动Boot2-1模块程序
(3)浏览器访问:http://localhost:8080 页面会显示index页面的内容!
package cn.tedu.boot21.controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ResponseBody;
@Controller
public class HelloController {
/** 1.通过浏览器的地址栏中发出请求(简单响应一句话内容) */
// @RequestMapping("/hello")
// public void hello(HttpServletResponse response) throws IOException {
// response.setContentType("text/html;charset=utf-8");
// PrintWriter pw = response.getWriter();
// pw.print("测试成功");
// pw.close();
// }
/* 简单写法: */
@RequestMapping("/hello")
@ResponseBody //SpringMVC框架提供的注解,作用:可以通过返回值的方式给客户端响应数据
public String hello(){
return "测试成功!222";
}
}
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>工程首页</h1>
</body>
</html>
(2)通过html页面中的超链接发出请求(测试相对路径和绝对路径)
2.通过html页面中的超链接发出请求(测试相对路径和绝对路径)
改动的类:HelloController 改动的页面:index
(1)在项目boot2-1下的java内创建包:cn/tedu/boot-1/controller 新建响应类:HelloController
(2)启动该类 网站测试:http://localhost:8080/hello 页面会显示测试成功!
(3)修改首页内容,添加相对路径和绝对路径:
<h2>通过超链接发送请求</h2>
<!--localhost:8080/hello-->
<!--相对路径:相对于当前页面所处位置-->
<a href="hello">相对路径</a>
<!--绝对路径1:相对于工程的根路径(:http://localhost:8080/hello)-->
<a href="/hello">绝对路径1</a>
<!--绝对路径2:这种写法用于一般访问其它网站资源时使用-->
<a href="http://localhost:8080/hello">绝对路径2</a>
(4)测试: http://localhost:8080
页面显示【工程首页】和【通过超链接发送请求】和【三个超链接】
package cn.tedu.boot21.controller;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ResponseBody;
@Controller
public class HelloController {
/** 1.通过浏览器的地址栏中发出请求(简单响应一句话内容) */
/* 简单写法: */
@RequestMapping("/hello")
@ResponseBody //SpringMVC框架提供的注解,作用:可以通过返回值的方式给客户端响应数据
public String hello(){
return "测试成功!222";
}
/** 2.通过html页面中的超链接发出请求(测试相对路径和绝对路径)这一段代码: */
@RequestMapping("/param1")
@ResponseBody
public String param1(HttpServletRequest request){
String info = request.getParameter("info");
return "接收到了参数:"+info;
}
}
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>工程首页</h1>
<h2>通过超链接发送请求</h2>
<!--localhost:8080/hello-->
<!--相对路径:相对于当前页面所处位置-->
<a href="hello">相对路径</a>
<!--**********绝对路径1:相对于工程的根路径(:http://localhost:8080/hello)-->
<a href="/hello">绝对路径1</a>
<!--绝对路径2:这种写法用于一般访问其它网站资源时使用-->
<a href="http://localhost:8080/hello">绝对路径2</a>
</body>
</html>
(3)form表单提交的三种方式
3.form表单提交的三种方式
改动的类:HelloController 改动的页面:index 新建类:Emp
(1)①首页写【通过form表单发出请求:第一种传参方式】相关代码,
②在HelloController类里添加一个param1方法。
③测试:http://localhost:8080
页面会多一个表单提交的文本框,输入内容点击提交,
则会跳转到一个:【接收到参数:xxx】
(2)①首页写【通过form表单发出请求:第二种传参方式】相关代码,
②在HelloController类里添加一个param2方法。
③测试:http://localhost:8080
页面中在提交表单数据的下面会多一个表单提交的文本框,输入内容点击提交,
则会跳转到一个回复信息:【接收到参数:"+name+"年龄:"+age】页面
(3)①首页写【通过form表单发出请求:第三种传参方式】相关代码,
②在HelloController类里添加一个param3方法。
③在项目boot2-1下的java内创建包:cn/tedu/boot-1/entity 新建响应类:Emp
④测试:http://localhost:8080
页面中最下面会多一个第三种方式的表单提交的文本框,输入内容点击提交,
则会跳转到一个回复信息:【Emp{name='xxx', sal=xxx, job='xxx'}】页面
package cn.tedu.boot21.controller;
import cn.tedu.boot21.entity.Emp;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ResponseBody;
@Controller
public class HelloController {
/** 1.通过浏览器的地址栏中发出请求(简单响应一句话内容) */
// @RequestMapping("/hello")
// public void hello(HttpServletResponse response) throws IOException {
// response.setContentType("text/html;charset=utf-8");
// PrintWriter pw = response.getWriter();
// pw.print("测试成功");
// pw.close();
// }
/* 简单写法: */
@RequestMapping("/hello")
@ResponseBody //SpringMVC框架提供的注解,作用:可以通过返回值的方式给客户端响应数据
public String hello(){
return "测试成功!222";
}
/** 3.表单提交的三种方式: */
/** 2.通过html页面中的超链接发出请求(测试相对路径和绝对路径)这一段代码: */
// @RequestMapping("/param1")
// @ResponseBody
// public String param1(HttpServletRequest request){
// String info = request.getParameter("info");
// return "接收到了参数:"+info;
// }
@RequestMapping("/param2")
@ResponseBody
public String param2(String name,int age){
return "接收到参数:"+name+"年龄:"+age;
}
@RequestMapping("/param3")
@ResponseBody
public String param3(Emp emp){
return emp.toString();
}
}
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>工程首页</h1>
<h2>通过超链接发送请求</h2>
<!--localhost:8080/hello-->
<!--相对路径:相对于当前页面所处位置-->
<a href="hello">相对路径</a>
<!--**********绝对路径1:相对于工程的根路径(:http://localhost:8080/hello)-->
<a href="/hello">绝对路径1</a>
<!--绝对路径2:这种写法用于一般访问其它网站资源时使用-->
<a href="http://localhost:8080/hello">绝对路径2</a>
<h2>通过form表单发出请求:第一种传参方式</h2>
<form action="param1">
<input type="text" name="info">
<input type="submit">
</form>
<h2>通过form表单发出请求:第二种传参方式</h2>
<form action="/param2">
<input type="text" name="name">
<input type="text" name="age">
<input type="submit" >
</form>
<h2>通过form表单发出请求:第三种方式</h2>
<form action="/param3">
<input type="text" name="name">
<input type="text" name="sal">
<input type="text" name="job">
<input type="submit">
</form>
</body>
</html>
package cn.tedu.boot21.entity;
public class Emp {
private String name;
private double sal;
private String job;
//生成Set Get方法 和toString方法
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Emp{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", sal=" + sal +
", job='" + job + '\'' +
'}';
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public double getSal() {
return sal;
}
public void setSal(double sal) {
this.sal = sal;
}
public String getJob() {
return job;
}
public void setJob(String job) {
this.job = job;
}
}
(4)通过前端框架发出请求(测试注册)
4.通过前端框架发出请求(测试注册)
新建类UserController、user 新建页面:reg
(1)在boot2-1下的src/main/resources下新建页面:reg.html()
(2)在controller包下新建类:UserController
(3)①在项目boot2-1下的src/main/java/cn/tedu/boot2-1/entity 新建类:User
②在User类里写id 用户名 密码 昵称四个成员变量,
并alt+insert生成set get和toString方法
③UserController类里写一个reg方法。
④测试: http://localhost:8080/reg.html
输入信息(牛/123/牛)点击注册,
会跳转新页面显示一个回复信息:
【User{id=null, username='牛', password='123', nick='牛'}】
package cn.tedu.boot21.controller;
import cn.tedu.boot21.entity.User;
import cn.tedu.boot21.utils.DBUtils;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ResponseBody;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.SQLException;
@Controller
public class UserController {
@RequestMapping("/reg")
@ResponseBody
public String reg(User user){
return user.toString();
}
}
package cn.tedu.boot21.entity;
public class User {
private Integer id;
private String username;
private String password;
private String nick;
//生成Set Get 和 toString:
@Override
public String toString() {
return "User{" +
"id=" + id +
", username='" + username + '\'' +
", password='" + password + '\'' +
", nick='" + nick + '\'' +
'}';
}
public Integer getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(Integer id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getUsername() {
return username;
}
public void setUsername(String username) {
this.username = username;
}
public String getPassword() {
return password;
}
public void setPassword(String password) {
this.password = password;
}
public String getNick() {
return nick;
}
public void setNick(String nick) {
this.nick = nick;
}
}
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>注册页面</h1>
<form action="/reg">
<input type="text" name="username" placeholder="用户名">
<input type="text" name="password" placeholder="密码">
<input type="text" name="nick" placeholder="昵称">
<input type="submit" value="注册">
</form>
</body>
</html>
03.工程中使用数据库需要做的几件事:boot2-1
(1)在模块Jdbc01的pom.xml中把【连接MySQL数据库的依赖】和【数据库连接池】,
粘贴到boot2-1的pom.xml中的上面(必须做)
(2)①在boot2-1下的src/main/java/cn/tedu/boot21下:创建包utils
②在模块Jdbc01里把DBUtils粘贴到①中的包utils下
(1)完成注册功能
5.工程中使用数据库需要做的几件事(完成注册功能):
(1)在模块Jdbc01的pom.xml中把【连接MySQL数据库的依赖】和【数据库连接池】,
粘贴到boot2-1的pom.xml中的</dependencies>上面(必须做)
(2)①在boot2-1下的src/main/java/cn/tedu/boot21下:创建包utils
②在模块Jdbc01里把DBUtils粘贴到①中的包utils下
(3)①在UserController中添加【得到数据库连接】部分代码:
②测试:http://localhost:8080/reg.html
输入信息(牛1/123/牛1)后点击注册,跳转到注册成功页面!
再次输入信息(牛1/123/牛1)后点击注册,跳转到用户已存在页面!
package cn.tedu.boot21.utils;
import com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.SQLException;
/**
* 1、DBUtils(数据库实用程序):提供getConnection方法被其他类调用
* (1)getConnection(url,user,password):尝试建立到给定数据库 URL 的连接 密码:就是数据库的登录密码root
*
*/
public class DBUtils {
//全局变量ds(斜体):————>为什么加static? 因为在静态块和静态方法中使用该成员变量。
private static DruidDataSource ds;
static{ //把创建连接池对象放在静态块中:随着类的加载只加载一次
//创建连接池对象:
ds = new DruidDataSource();
//设置数据库连接信息 url 用户名 密码:
ds.setUrl("jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/empdb?characterEncoding=utf8&serverTimezone=Asia/Shanghai&useSSL=false");
ds.setUsername("root");
ds.setPassword("root");
//设置初始连接数量
ds.setInitialSize(3);
//设置最大连接数量
ds.setMaxActive(5);
}
public static Connection getConn() throws SQLException {
//从连接池中获取连接 异常抛出
Connection conn = ds.getConnection();
System.out.println("连接对象:"+conn);
return conn;
}
}
package cn.tedu.boot21.controller;
import cn.tedu.boot21.entity.User;
import cn.tedu.boot21.utils.DBUtils;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ResponseBody;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.PreparedStatement;
import java.sql.ResultSet;
import java.sql.SQLException;
@Controller
public class UserController {
/** 注册功能 */
@RequestMapping("/reg")
@ResponseBody
public String reg(User user){
//得到数据库连接:
try(Connection conn = DBUtils.getConn()) {
//参考Jdbc01里的Demo12
String sql = "select id from user where username=?";
PreparedStatement ps = conn.prepareStatement(sql);
ps.setString(1,user.getUsername());
ResultSet rs = ps.executeQuery();
if (rs.next()) {
return "用户名已存在!";
}
String insertSql = "insert into user values(null,?,?,?)";
PreparedStatement insertPs = conn.prepareStatement(insertSql);
insertPs.setString(1,user.getUsername());
insertPs.setString(2,user.getPassword());
insertPs.setString(3,user.getNick());
insertPs.executeUpdate();
} catch (SQLException throwables) {
throwables.printStackTrace();
}
return "注册成功!";
}
}
(2)完成登录功能
6.完成登录功能
改动的类UserController 新建页面login.html
(1)①在boot2-1下的src/main/resources下新建页面:login.html
当在浏览器页面点击登录按钮时,会往这里发请求
(2)UserController中写一个登录功能是方法
(3)测试:http://localhost:8080/login.html
输入信息(牛/123)点击登录————>跳转到 密码错误 页面!
输入信息(牛1/123)点击登录———>跳转到 登录成功 页面!
输入不存在信息是点击登录—————>跳转到 用户名不存在 页面!
package cn.tedu.boot21.controller;
import cn.tedu.boot21.entity.User;
import cn.tedu.boot21.utils.DBUtils;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ResponseBody;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.PreparedStatement;
import java.sql.ResultSet;
import java.sql.SQLException;
@Controller
public class UserController {
/** 注册功能 */
@RequestMapping("/reg")
@ResponseBody
public String reg(User user){
//得到数据库连接:
try(Connection conn = DBUtils.getConn()) {
//参考Jdbc01里的Demo12
String sql = "select id from user where username=?";
PreparedStatement ps = conn.prepareStatement(sql);
ps.setString(1,user.getUsername());
ResultSet rs = ps.executeQuery();
if (rs.next()) {
return "用户名已存在!";
}
String insertSql = "insert into user values(null,?,?,?)";
PreparedStatement insertPs = conn.prepareStatement(insertSql);
insertPs.setString(1,user.getUsername());
insertPs.setString(2,user.getPassword());
insertPs.setString(3,user.getNick());
insertPs.executeUpdate();
} catch (SQLException throwables) {
throwables.printStackTrace();
}
return "注册成功!";
}
/** 登录功能 */
@RequestMapping("/login")
@ResponseBody
public String login(User user){
System.out.println("user = " + user);//soutp
try (Connection conn = DBUtils.getConn()){
String sql = "select password from user where username=?";
PreparedStatement ps = conn.prepareStatement(sql);
ps.setString(1,user.getUsername());
ResultSet rs = ps.executeQuery();
if (rs.next()){//代表查询到了信息
//判断用户输入的和查询到的数据是否一致
if (rs.getString(1).equals(user.getPassword())){
return "登录成功!";
}
return "密码错误!";
}
} catch (SQLException throwables) {
throwables.printStackTrace();
}
return "用户名不存在!";
}
}
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>登录页面</h1>
<form action="/login">
<input type="text" name="username" placeholder="用户名">
<input type="password" name="password" placeholder="密码">
<input type="submit" value="登录">
</form>
</body>
</html>