【GUI】用于电动助力车性能分析的GUI(Matlab代码实现)
个人主页: 研学社的博客
欢迎来到本博客 ❤️ ❤️
博主优势: 博客内容尽量做到思维缜密,逻辑清晰,为了方便读者。
⛳ 座右铭:行百里者,半于九十。
本文目录如下:
目录
1 概述
2 运行结果
3 参考文献
4 Matlab代码及文章讲解
1 概述
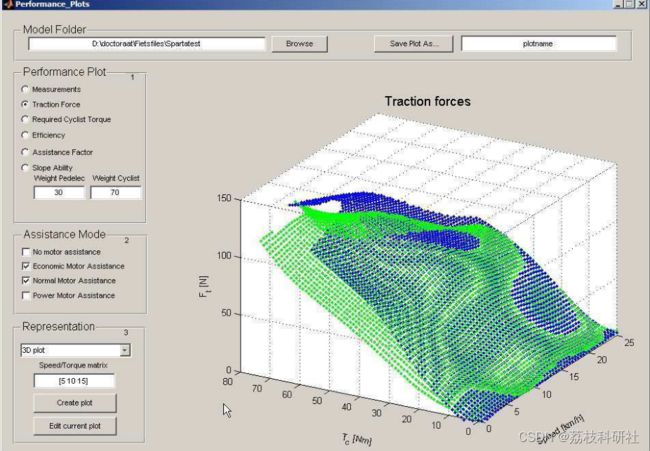
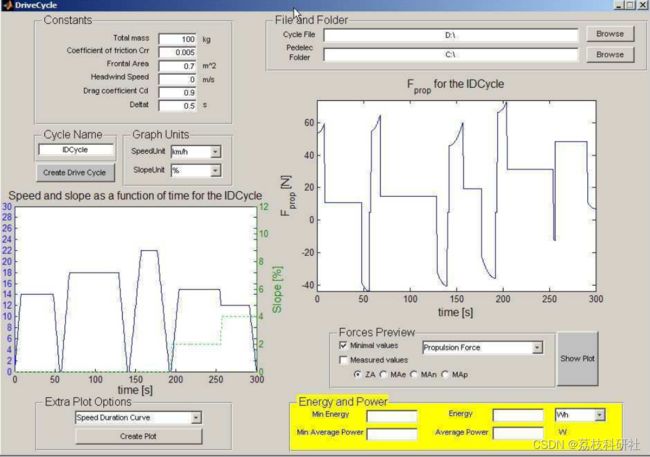
当给定的电动自行车(=电动助力自行车)的自行车速度、踏板扭矩和牵引力的测量数据可用时,此图形用户界面将分析该电动助力车的性能。GUI 将与 LS-SVM 工具箱一起使用。
用所开发的第6节测试装置对脚踏车的表征分几个步骤进行:
1 . pedelec2的测量。LS - SVM建模
3 .表演情节的创设
4 .性能参数的计算5 .与其他脚型的比较
第一步相当耗时。每一种援助模式都需要采取很多措施。自行车骑行者力矩、脚踏车速度和牵引力在一个工况点的记录耗时约20秒。第二个电池的可用性被推荐为能够在没有重新加载中断的情况下进行测量。共同,测量步骤快速耗时数小时。
通过引入图形用户界面( GUI )来控制其他步骤的时间,包括步骤2到步骤5的所有工具。本章将描述用户界面最重要的功能,并将其编写为详细文章。
2 运行结果
部分代码:
% Begin initialization code - DO NOT EDIT
gui_Singleton = 1;
gui_State = struct('gui_Name', mfilename, ...
'gui_Singleton', gui_Singleton, ...
'gui_OpeningFcn', @Performance_Plots_OpeningFcn, ...
'gui_OutputFcn', @Performance_Plots_OutputFcn, ...
'gui_LayoutFcn', [], ...
'gui_Callback', []);
if nargin && ischar(varargin{1})
gui_State.gui_Callback = str2func(varargin{1});
end
if nargout
[varargout{1:nargout}] = gui_mainfcn(gui_State, varargin{:});
else
gui_mainfcn(gui_State, varargin{:});
end
% End initialization code - DO NOT EDIT
% --- Executes just before Performance_Plots is made visible.
function Performance_Plots_OpeningFcn(hObject, eventdata, handles, varargin)
% This function has no output args, see OutputFcn.
% hObject handle to figure
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)
% varargin unrecognized PropertyName/PropertyValue pairs from the
% command line (see VARARGIN)
% Choose default command line output for Performance_Plots
handles.output = hObject;
handles.folderput=0; %says if folder input is given
addpath(genpath(fullfile(matlabroot,'toolbox\Pedelecs')));
addpath(genpath(fullfile(matlabroot,'toolbox\LSSVM\LS-SVMlab1.5')));
handles.Plottype=1;
%Determine some constants for plotting
handles.vmax=25;
handles.Tmax=80;
handles.Pmax=400;
handles.deltav=0.5;
handles.deltaT=1;
%initialize the checkboxes
handles.ZA1=0;
handles.MA1=0;
handles.MA2=0;
handles.MA3=0;
handles.velocities=[5 10 15];
handles.Mped=30;
handles.Mcyc=70;
handles.PlotName=0;
handles.ThisPlot=plot(0,0);
%initializes the radiobutton performance parameter
handles.PP=1;
%initializes the total mass
handles.mtot=100;
%update the handles
guidata(hObject, handles);
% UIWAIT makes Performance_Plots wait for user response (see UIRESUME)
% uiwait(handles.figure1);
% --- Outputs from this function are returned to the command line.
function varargout = Performance_Plots_OutputFcn(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% varargout cell array for returning output args (see VARARGOUT);
% hObject handle to figure
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)
% Get default command line output from handles structure
varargout{1} = handles.output;
% --- Executes on button press in ZA.
function ZA1_Callback(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% hObject handle to ZA (see GCBO)
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)
handles.ZA1=get(hObject,'Value');
guidata(hObject, handles);
% Hint: get(hObject,'Value') returns toggle state of ZA
% val=get(hObject,'Value')
% model=get(ReadModel.handles.Load1)
% if val==1
% axes(handles.Figuurveld)
% plotlssvm_GUI1(model,'Traction force without assistance','Cyclist Torque T_c [Nm]','Speed v [km/h]','Traction Force F_t [N]',handles.Z);
% end
3 参考文献
部分理论来源于网络,如有侵权请联系删除。
[1]Jan Cappelle (2023). GUI for the performance analysis of pedelecs.