存储之Block-MultiQueue机制详解(二)
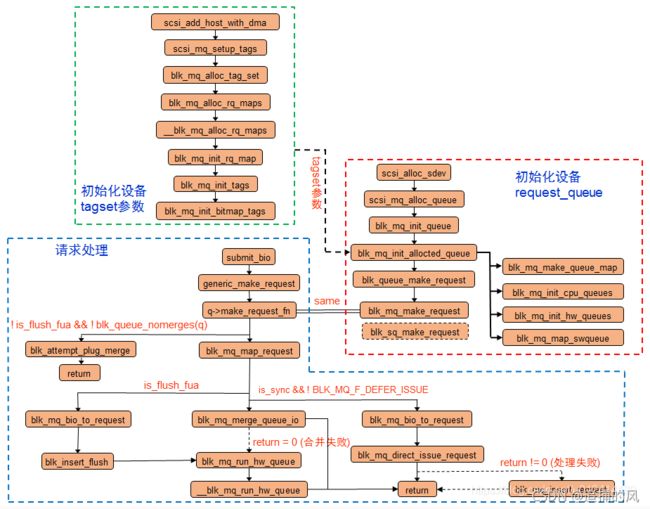
1、首先看一下blk-mq的处理流程图(不同内核版本之间会有一些差异,但整体结构基本一样)
从整个流程图可以看到,主要是分为三个部分:(1)初始化硬件设备的相关参数(2)初始化请求队列request_queue(3)bio请求的处理过程。前面两个过程主要是完成底层存储设备向文件系统的注册,同时完成软硬队列映射关系等初始化,后一个部分是bio在MQ机制最后生成对应子请求并挂载在硬件队列上的过程。
2、接下来我们来分析具体的函数
(1)int blk_mq_alloc_tag_set(struct blk_mq_tag_set *set)——为一个或者多个request queue分配tag
/*
* Alloc a tag set to be associated with one or more request queues.
* May fail with EINVAL for various error conditions. May adjust the
* requested depth down, if it's too large. In that case, the set
* value will be stored in set->queue_depth.
*/
//为一个或者多个请求队列分配tag(tag set可以是多个request queue共享的)
int blk_mq_alloc_tag_set(struct blk_mq_tag_set *set)
{
int i, ret;
BUILD_BUG_ON(BLK_MQ_MAX_DEPTH > 1 << BLK_MQ_UNIQUE_TAG_BITS);
if (!set->nr_hw_queues) //硬件队列身量
return -EINVAL;
if (!set->queue_depth) //软件队列深度
return -EINVAL;
if (set->queue_depth < set->reserved_tags + BLK_MQ_TAG_MIN) //块设备保留的tag数
return -EINVAL;
if (!set->ops->queue_rq) //ops表示块设备驱动的抽象集合
return -EINVAL;
if (!set->ops->get_budget ^ !set->ops->put_budget)
return -EINVAL;
if (set->queue_depth > BLK_MQ_MAX_DEPTH) {
pr_info("blk-mq: reduced tag depth to %u\n",
BLK_MQ_MAX_DEPTH);
set->queue_depth = BLK_MQ_MAX_DEPTH;
}
if (!set->nr_maps) //映射表数量
set->nr_maps = 1;
else if (set->nr_maps > HCTX_MAX_TYPES)
return -EINVAL;
/*
* If a crashdump is active, then we are potentially in a very
* memory constrained environment. Limit us to 1 queue and
* 64 tags to prevent using too much memory.
*/
if (is_kdump_kernel()) {
set->nr_hw_queues = 1;
set->nr_maps = 1;
set->queue_depth = min(64U, set->queue_depth);
}
/*
* There is no use for more h/w queues than cpus if we just have
* a single map
*/
if (set->nr_maps == 1 && set->nr_hw_queues > nr_cpu_ids)
set->nr_hw_queues = nr_cpu_ids;
set->tags = kcalloc_node(nr_hw_queues(set), sizeof(struct blk_mq_tags *),
GFP_KERNEL, set->numa_node);
if (!set->tags)
return -ENOMEM;
ret = -ENOMEM;
for (i = 0; i < set->nr_maps; i++) {
set->map[i].mq_map = kcalloc_node(nr_cpu_ids,
sizeof(set->map[i].mq_map[0]),
GFP_KERNEL, set->numa_node);
if (!set->map[i].mq_map)
goto out_free_mq_map;
set->map[i].nr_queues = is_kdump_kernel() ? 1 : set->nr_hw_queues;
}
ret = blk_mq_update_queue_map(set); //更新映射表
if (ret)
goto out_free_mq_map;
ret = blk_mq_alloc_rq_maps(set); //分配request和tag
if (ret)
goto out_free_mq_map;
mutex_init(&set->tag_list_lock);
INIT_LIST_HEAD(&set->tag_list);
return 0;
out_free_mq_map:
for (i = 0; i < set->nr_maps; i++) {
kfree(set->map[i].mq_map);
set->map[i].mq_map = NULL;
}
kfree(set->tags);
set->tags = NULL;
return ret;
}
EXPORT_SYMBOL(blk_mq_alloc_tag_set);(2)static struct request *blk_mq_get_request(struct request_queue *q,
struct bio *bio,
struct blk_mq_alloc_data *data)——为bio分配request
//为bio分配request
static struct request *blk_mq_get_request(struct request_queue *q,
struct bio *bio,
struct blk_mq_alloc_data *data)
{
struct elevator_queue *e = q->elevator;
struct request *rq;
unsigned int tag;
bool clear_ctx_on_error = false;
u64 alloc_time_ns = 0;
blk_queue_enter_live(q);
/* alloc_time includes depth and tag waits */
if (blk_queue_rq_alloc_time(q))
alloc_time_ns = ktime_get_ns();
data->q = q;
if (likely(!data->ctx)) {
data->ctx = blk_mq_get_ctx(q); //获取当前cpu的软件队列(ctx)
clear_ctx_on_error = true;
}
if (likely(!data->hctx))
data->hctx = blk_mq_map_queue(q, data->cmd_flags, //找到软件队列(ctx)对应的硬件队列(hctx)
data->ctx);
if (data->cmd_flags & REQ_NOWAIT)
data->flags |= BLK_MQ_REQ_NOWAIT;
if (e) {
data->flags |= BLK_MQ_REQ_INTERNAL;
/*
* Flush requests are special and go directly to the
* dispatch list. Don't include reserved tags in the
* limiting, as it isn't useful.
*/
if (!op_is_flush(data->cmd_flags) &&
e->type->ops.limit_depth &&
!(data->flags & BLK_MQ_REQ_RESERVED))
e->type->ops.limit_depth(data->cmd_flags, data);
} else {
blk_mq_tag_busy(data->hctx);
}
tag = blk_mq_get_tag(data); //获取tag,可能因为当前无可用tag进入iowait状态
if (tag == BLK_MQ_TAG_FAIL) {
if (clear_ctx_on_error)
data->ctx = NULL;
blk_queue_exit(q);
return NULL;
}
rq = blk_mq_rq_ctx_init(data, tag, data->cmd_flags, alloc_time_ns); //初始化tag对应的request
if (!op_is_flush(data->cmd_flags)) {
rq->elv.icq = NULL;
if (e && e->type->ops.prepare_request) {
if (e->type->icq_cache)
blk_mq_sched_assign_ioc(rq);
e->type->ops.prepare_request(rq, bio);
rq->rq_flags |= RQF_ELVPRIV;
}
}
data->hctx->queued++;
return rq;
}(3)struct request_queue *blk_mq_init_queue(struct blk_mq_tag_set *set)——基于blk_mq的块设备驱动初始化时,调用blk_mq_init_queue初始化IO请求队列(request_queue)
struct request_queue *blk_mq_init_queue(struct blk_mq_tag_set *set)
{
struct request_queue *uninit_q, *q;
uninit_q = blk_alloc_queue_node(GFP_KERNEL, set->numa_node); //分配请求队列的内存,所分配内存结点与设备NUMA节点一致,避免远端内存访问问题
if (!uninit_q)
return ERR_PTR(-ENOMEM);
/*
* Initialize the queue without an elevator. device_add_disk() will do
* the initialization.
*/
q = blk_mq_init_allocated_queue(set, uninit_q, false); //初始化分配的请求队列,即软件队列和硬件队列
if (IS_ERR(q))
blk_cleanup_queue(uninit_q);
return q;
}(4)、static blk_qc_t blk_mq_make_request(struct request_queue *q, struct bio *bio)——将上层提交的bio封装成request并提交到块设备层
//将上层提交的bio封装成request并提交到块设备层
static blk_qc_t blk_mq_make_request(struct request_queue *q, struct bio *bio)
{
const int is_sync = op_is_sync(bio->bi_opf);
const int is_flush_fua = op_is_flush(bio->bi_opf);
struct blk_mq_alloc_data data = { .flags = 0};
struct request *rq;
struct blk_plug *plug;
struct request *same_queue_rq = NULL;
unsigned int nr_segs;
blk_qc_t cookie;
blk_queue_bounce(q, &bio);
__blk_queue_split(q, &bio, &nr_segs);
if (!bio_integrity_prep(bio))
return BLK_QC_T_NONE;
if (!is_flush_fua && !blk_queue_nomerges(q) &&
blk_attempt_plug_merge(q, bio, nr_segs, &same_queue_rq))
return BLK_QC_T_NONE;
if (blk_mq_sched_bio_merge(q, bio, nr_segs))
return BLK_QC_T_NONE;
rq_qos_throttle(q, bio);
data.cmd_flags = bio->bi_opf;
rq = blk_mq_get_request(q, bio, &data);
if (unlikely(!rq)) {
rq_qos_cleanup(q, bio);
if (bio->bi_opf & REQ_NOWAIT)
bio_wouldblock_error(bio);
return BLK_QC_T_NONE;
}
trace_block_getrq(q, bio, bio->bi_opf);
rq_qos_track(q, rq, bio);
cookie = request_to_qc_t(data.hctx, rq);
blk_mq_bio_to_request(rq, bio, nr_segs); //生产request后,后续准备将request插入到请求队列中
plug = blk_mq_plug(q, bio);
if (unlikely(is_flush_fua)) { //若是flush或fua请求,则将request插入到flush队列,并调用blk_mq_run_hw_queue启动请求派发
/* bypass scheduler for flush rq */
blk_insert_flush(rq);
blk_mq_run_hw_queue(data.hctx, true);
} else if (plug && (q->nr_hw_queues == 1 || q->mq_ops->commit_rqs ||
!blk_queue_nonrot(q))) {
//若当前线程正在做IO plug且块设备是硬件单队列,则将request插入到当前线程的plug list中
/*
* Use plugging if we have a ->commit_rqs() hook as well, as
* we know the driver uses bd->last in a smart fashion.
*
* Use normal plugging if this disk is slow HDD, as sequential
* IO may benefit a lot from plug merging.
*/
unsigned int request_count = plug->rq_count;
struct request *last = NULL;
if (!request_count)
trace_block_plug(q);
else
last = list_entry_rq(plug->mq_list.prev);
if (request_count >= BLK_MAX_REQUEST_COUNT || (last &&
blk_rq_bytes(last) >= BLK_PLUG_FLUSH_SIZE)) {
blk_flush_plug_list(plug, false);
trace_block_plug(q);
}
blk_add_rq_to_plug(plug, rq);
} else if (q->elevator) {
//若配置了调度器,则调用blk_mq_sched_insert_request将请求插入到调度器队列中,否则插入到当前CPU的软件队列中
blk_mq_sched_insert_request(rq, false, true, true);
} else if (plug && !blk_queue_nomerges(q)) {
/*
* We do limited plugging. If the bio can be merged, do that.
* Otherwise the existing request in the plug list will be
* issued. So the plug list will have one request at most
* The plug list might get flushed before this. If that happens,
* the plug list is empty, and same_queue_rq is invalid.
*/
if (list_empty(&plug->mq_list))
same_queue_rq = NULL;
if (same_queue_rq) {
list_del_init(&same_queue_rq->queuelist);
plug->rq_count--;
}
blk_add_rq_to_plug(plug, rq);
trace_block_plug(q);
//若硬件多队列是IO同步请求,则调用blk_mq_try_issue_directly尝试将request直接派发到块设备驱动
if (same_queue_rq) {
data.hctx = same_queue_rq->mq_hctx;
trace_block_unplug(q, 1, true);
blk_mq_try_issue_directly(data.hctx, same_queue_rq,
&cookie);
}
} else if ((q->nr_hw_queues > 1 && is_sync) ||
!data.hctx->dispatch_busy) {
blk_mq_try_issue_directly(data.hctx, rq, &cookie);
} else {
blk_mq_sched_insert_request(rq, false, true, true);
}
return cookie;
}参考链接: