SpringMVC——入门介绍
目录
- 1.SpringMVC简介
-
- (1)MVC概述
- (2)SpringMVC概述
- (3)SpringMVC的特点
- 2.SpringMVC入门案例——Hello World !
-
- (1)开发环境介绍
- (2)创建Maven工程
- (3)配置web.xml
- (4)创建请求控制器
- (5)创建springMVC的配置文件
- (6)测试HelloWorld
- (7)总结
- 3.@RequestMapping注解
-
- (1)@RequestMapping注解的功能
- (2)@RequestMapping注解的位置
- (3)@RequestMapping注解的value属性
- (4)@RequestMapping注解的method属性
- (5)@RequestMapping注解的params属性(了解)
- (6)@RequestMapping注解的headers属性(了解)
- (7)SpringMVC支持ant风格的路径
- (8)SpringMVC支持路径中的占位符(重点)
- 4.SpringMVC获取请求参数
-
- (1)通过ServletAPI获取
- (2)通过控制器方法的形参获取请求参数
- (3)@RequestParam
- (4)@RequestHeader
- (5)@CookieValue
- (6)通过POJO获取请求参数
- (7)解决获取请求参数的乱码问题
- 5.域对象共享数据
-
- (1)使用ServletAPI向request域对象共享数据
- (2)使用ModelAndView向request域对象共享数据
- (3)使用Model向request域对象共享数据
- (4)使用map向request域对象共享数据
- (5)使用ModelMap向request域对象共享数据
- (6)Model、ModelMap、Map的关系
- (7)向session域共享数据
- (8)向application域共享数据
- 6.SpringMVC的视图
-
- (1)ThymeleafView
- (2)转发视图
- (3)重定向视图
- (4)视图控制器view-controller
- 7.RESTful
-
- (1)RESTful简介
- (2)RESTful的实现
- (3)HiddenHttpMethodFilter
- 8.RESTful案例
-
- (1)准备工作
- (2)功能清单
- (3)具体功能:访问首页
- (4)具体功能:查询所有员工数据
- (5)具体功能:删除一条员工信息
- (6)具体功能:跳转到添加数据页面
- (7)具体功能:添加员工信息
- (8)具体功能:跳转到更新数据页面
- (9)具体功能:对员工信息进行修改
- 9.HttpMessageConverter
-
- (1)@RequestBody
- (2)RequestEntity
- (3)@ResponseBody
- (4)SpringMVC处理json数据
- (5)SpringMVC处理axios
- (6)@RestController注解
- (7)ResponseEntity
- 10.文件上传和下载
-
- (1)文件下载
- (2)文件上传
- 11.拦截器
- 12.异常处理器
-
- (1)基于配置的异常处理
- (2)基于注解的异常处理
- 13.注解配置SpringMVC
-
- (1)创建初始化类,代替web.xml
- (2)创建SpringConfig配置类,代替spring的配置文件
- (3)创建WebConfig配置类,代替SpringMVC的配置文件
本文章的笔记整理来自尚硅谷视频系列https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1Ry4y1574R
1.SpringMVC简介
(1)MVC概述
① MVC是一种软件架构的思想,将软件按照模型、视图、控制器来划分。
| M | Model,模型层,指工程中的JavaBean,作用是处理数据。 |
|---|---|
| V | View,视图层,指工程中的html或jsp等页面,作用是与用户进行交互,展示数据。 |
| C | Controller,控制层,指工程中的servlet,作用是接收请求和响应浏览器。 |
② JavaBean分为两类:
1)一类称为实体类Bean:专门存储业务数据的,如 Student、User 等。
2)一类称为业务处理 Bean:指 Service 或 Dao 对象,专门用于处理业务逻辑和数据访问。
③ MVC的具体工作流程如下:
用户通过视图层发送请求到服务器,在服务器中请求被Controller接收,Controller调用相应的Model层处理请求,处理完毕将结果返回到Controller,Controller再根据请求处理的结果找到相应的View视图,渲染数据后最终响应给浏览器。
(2)SpringMVC概述
SpringMVC是Spring的一个后续产品,也是Spring的一个子项目。SpringMVC 是 Spring 为表述层开发提供的一整套完备的解决方案。在表述层框架历经 Strust、WebWork、Strust2 等诸多产品的历代更迭之后,目前业界普遍选择了 SpringMVC 作为首选方案。
注:三层架构分为表述层(或表示层)、业务逻辑层、数据访问层,表述层表示前台页面以及后台servlet。
(3)SpringMVC的特点
① Spring 家族原生产品,与 IOC 容器等基础设施无缝对接。
② 基于原生的Servlet,通过了功能强大的前端控制器DispatcherServlet,对请求和响应进行统一处理。
③ 表述层各细分领域需要解决的问题全方位覆盖,提供全面解决方案。
④ 代码清新简洁,大幅度提升开发效率。
⑤ 内部组件化程度高,可插拔式组件即插即用,想要什么功能配置相应组件即可。
⑥ 性能卓著,尤其适合现代大型、超大型互联网项目要求。
2.SpringMVC入门案例——Hello World !
(1)开发环境介绍
① IDE:IDEA 2019.3
② 构建工具:Maven3.8.1
③ 服务器:Tomcat7
④ Spring版本:5.3.1
⑤ 数据库:MySQL5.5
(2)创建Maven工程
为了方便代码的集中管理,这里是先创建一个普通的Java项目,然后再在里面创建各个需要的模块。
① 创建一个普通的 Java 项目,取名为SpringMVC。
② 在该项目中创建Maven模块
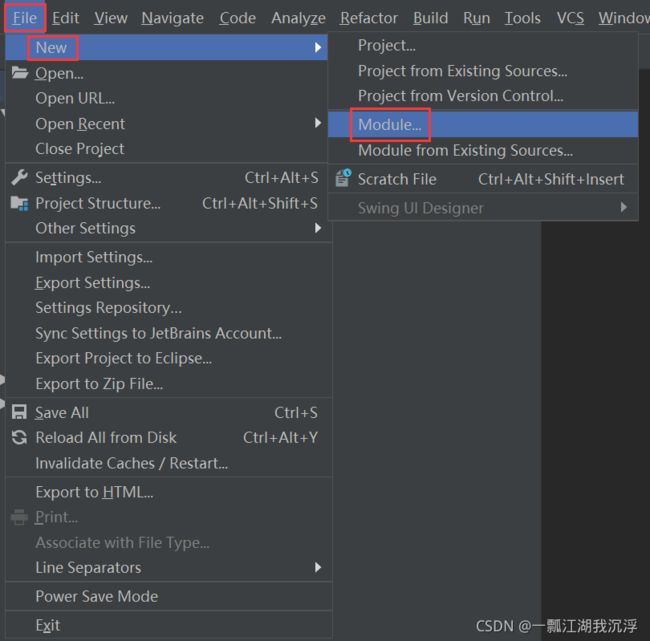

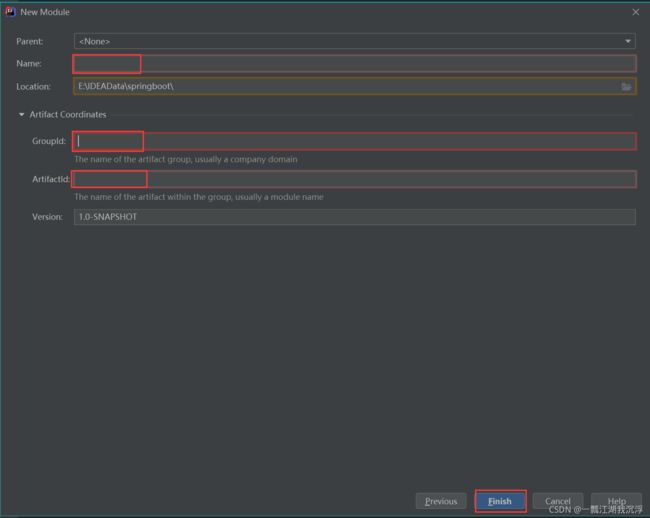
③ 添加web模块




④ 将打包方式设置为war
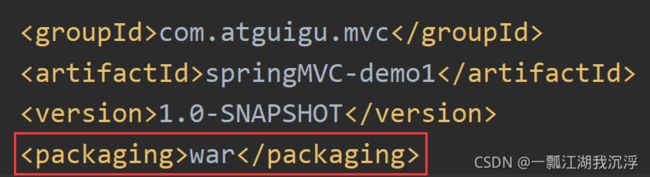
⑤ 在pom.xml中引入相关依赖
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframeworkgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-webmvcartifactId>
<version>5.3.1version>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>ch.qos.logbackgroupId>
<artifactId>logback-classicartifactId>
<version>1.2.3version>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>javax.servletgroupId>
<artifactId>javax.servlet-apiartifactId>
<version>3.1.0version>
<scope>providedscope>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.thymeleafgroupId>
<artifactId>thymeleaf-spring5artifactId>
<version>3.0.12.RELEASEversion>
dependency>
dependencies>
(3)配置web.xml
<servlet>
<servlet-name>springMVCservlet-name>
<servlet-class>org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServletservlet-class>
<init-param>
<param-name>contextConfigLocationparam-name>
<param-value>classpath:springMVC.xmlparam-value>
init-param>
<load-on-startup>1load-on-startup>
servlet>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>springMVCservlet-name>
<url-pattern>/url-pattern>
servlet-mapping>
(4)创建请求控制器
由于前端控制器对浏览器发送的请求进行了统一的处理,但是具体的请求有不同的处理过程,因此需要创建处理具体请求的类,即请求控制器请求控制器中每一个处理请求的方法成为控制器方法。又因为SpringMVC的控制器由一个POJO(普通的Java类)担任,因此需要通过@Controller注解将其标识为一个控制层组件,交给Spring的IoC容器管理,此时SpringMVC才能够识别控制器的存在。
package com.atguigu.restful.controller;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
@Controller
public class HelloController {
}
(5)创建springMVC的配置文件
根据web.xml中的配置,在resources目录下创建springMVC的配置文件,其文件名称为springMVC.xml。
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context https://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd">
<context:component-scan base-package="com.atguigu.restful.controller">context:component-scan>
<bean id="viewResolver" class="org.thymeleaf.spring5.view.ThymeleafViewResolver">
<property name="order" value="1"/>
<property name="characterEncoding" value="UTF-8"/>
<property name="templateEngine">
<bean class="org.thymeleaf.spring5.SpringTemplateEngine">
<property name="templateResolver">
<bean class="org.thymeleaf.spring5.templateresolver.SpringResourceTemplateResolver">
<property name="prefix" value="/WEB-INF/templates/"/>
<property name="suffix" value=".html"/>
<property name="templateMode" value="HTML5"/>
<property name="characterEncoding" value="UTF-8" />
bean>
property>
bean>
property>
bean>
beans>
(6)测试HelloWorld
① 实现对首页的访问,即在请求控制器中创建处理请求的方法。
package com.atguigu.restful.controller;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
@Controller
public class HelloController {
/*
1.通过@RequestMapping注解,可以通过请求路径匹配要处理的具体的请求
2./表示的当前工程的上下文路径
*/
@RequestMapping("/")
public String index(){
return "index";
}
@RequestMapping("/target")
public String toTarget(){
return "target";
}
}
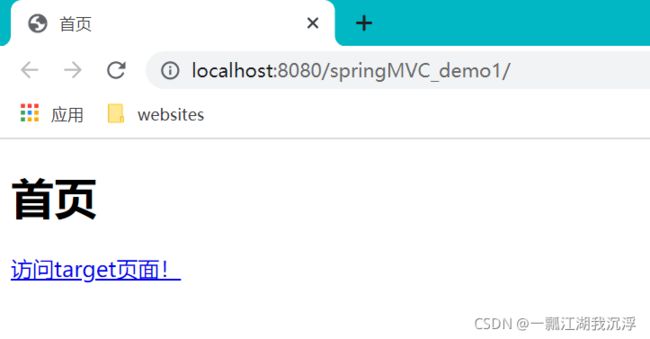
② 通过超链接跳转到指定页面,在主页index.html中设置超链接
DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en" xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>首页title>
head>
<body>
<h1>首页h1>
<a th:href="@{/target}">访问target页面!a>
body>
html>
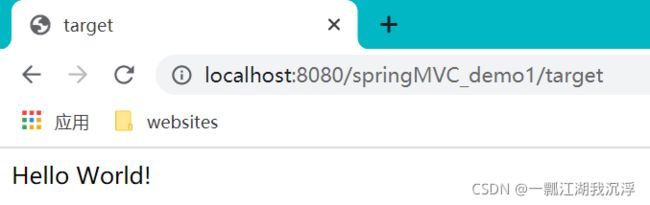
target.html页面代码如下:
DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en" xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>targettitle>
head>
<body>
Hello World!
body>
html>
③ 项目的总体结构如下图所示:
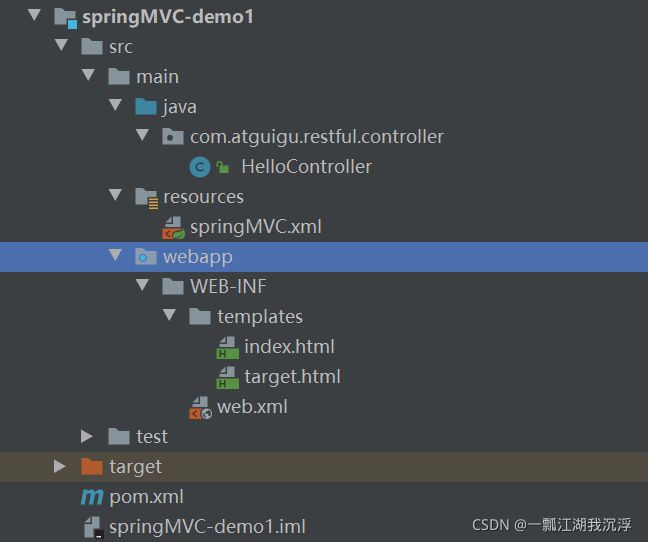
④ 在IDEA中配置项目并启动

(7)总结
① 浏览器发送请求,若请求地址符合前端控制器的url-pattern,该请求就会被前端控制器DispatcherServlet处理。
② 前端控制器会读取SpringMVC的核心配置文件,通过扫描组件找到控制器,将请求地址和控制器中@RequestMapping注解的value属性值进行匹配,若匹配成功,该注解所标识的控制器方法就是处理请求的方法
③ 处理请求的方法需要返回一个字符串类型的视图名称,该视图名称会被视图解析器解析,加上前缀和后缀组成视图的路径,通过Thymeleaf对视图进行渲染,最终转发到视图所对应页面。
3.@RequestMapping注解
(1)@RequestMapping注解的功能
从注解名称上我们可以看到,@RequestMapping注解的作用就是将请求和处理请求的控制器方法关联起来,建立映射关系。SpringMVC 接收到指定的请求,就会来找到在映射关系中对应的控制器方法来处理这个请求。
(2)@RequestMapping注解的位置
@RequestMapping注解既可以标识在类上,也可以标识在方法上。
| @RequestMapping标识一个类 | 设置映射请求的请求路径的初始信息 |
|---|---|
| @RequestMapping标识一个方法 | 设置映射请求请求路径的具体信息 |
@Controller
@RequestMapping("/test") //映射所有以/test开始的请求路径,例如/test/aaa、/test/xxx等
public class RequestMappingController {
//此时请求映射所映射的具体请求的请求路径为:/test/testRequestMapping
@RequestMapping("/testRequestMapping")
public String testRequestMapping(){
//跳转到 /WEB-INF/templates/success.html页面
return "success";
}
}
(3)@RequestMapping注解的value属性
① @RequestMapping注解的value属性通过请求的请求地址匹配请求映射。
② @RequestMapping注解的value属性是一个字符串类型的数组,表示该请求映射能够匹配多个请求地址所对应的请求。并且value属性必须设置,至少通过请求地址匹配请求映射。
③ 当@RequestMapping注解中只有value属性时,value可以省略不写。
<a th:href="@{/testRequestMapping}">测试RequestMapping注解的value属性-->/testRequestMappinga><br>
<a th:href="@{/test}">测试RequestMapping注解的value属性-->/testa><br>
//当请求路径为 /testRequestMapping或者/test 时,调用该方法
@RequestMapping(value = {"/testRequestMapping", "/test"})
public String testRequestMapping(){
return "success";
}
(4)@RequestMapping注解的method属性
@RequestMapping注解的method属性通过请求的请求方式(get或post)来匹配请求映射,该属性是一个RequestMethod类型的数组,表示该请求映射能够匹配多种请求方式的请求。
<a th:href="@{/test}">测试@RequestMapping的value属性-->/testa><br>
<form th:action="@{/test}" method="post">
<input type="submit">
form>
//当请求路径为 /testRequestMapping或者/test,并且请求方式为get或者post时,调用该方法
@RequestMapping(
value = {"/testRequestMapping", "/test"},
method = {RequestMethod.GET, RequestMethod.POST}
)
public String success(){
return "success";
}
注:对于处理指定请求方式的控制器方法,SpringMVC中提供了@RequestMapping的派生注解:
| 处理get请求的映射 | @GetMapping |
|---|---|
| 处理post请求的映射 | @PostMapping |
| 处理put请求的映射 | @PutMapping |
| 处理delete请求的映射 | @DeleteMapping |
| 常用的请求方式有get,post,put,delete,但是目前浏览器只支持get和post,若在form表单提交时,为method设置了其他请求方式的字符串(put或delete),则按照默认的请求方式get处理。若要发送put和delete请求,则需要通过spring提供的过滤器HiddenHttpMethodFilter,这些在后面的RESTful部分会详细说明。 |
(5)@RequestMapping注解的params属性(了解)
@RequestMapping注解的params属性通过请求的请求参数匹配请求映射,该属性是一个字符串类型的数组,可以通过四种表达式设置请求参数和请求映射的匹配关系:
| “param” | 要求请求映射所匹配的请求必须携带param请求参数 |
|---|---|
| “!param” | 要求请求映射所匹配的请求必须不能携带param请求参数 |
| “param=value” | 要求请求映射所匹配的请求必须携带param请求参数且param=value |
| “param!=value” | 要求请求映射所匹配的请求必须携带param请求参数但是param!=value |
<a th:href="@{/test(username='admin',password=123456)">
测试@RequestMapping的 params属性-->/test
a>
@RequestMapping(
value = {"/testRequestMapping", "/test"} ,
method = {RequestMethod.GET, RequestMethod.POST} ,
params = {"username","password!=123456"}
)
public String testRequestMapping(){
return "success";
}
注:若当前请求满足@RequestMapping注解的value和method属性,但是不满足params属性,此时页面回报错400:Parameter conditions “username, password!=123456” not met for actual request parameters: username={admin}, password={123456}
(6)@RequestMapping注解的headers属性(了解)
@RequestMapping注解的headers属性通过请求的请求头信息匹配请求映射,该属性是一个字符串类型的数组,可以通过四种表达式设置请求头信息和请求映射的匹配关系:
| “header” | 要求请求映射所匹配的请求必须携带header请求头信息 |
|---|---|
| “!header” | 要求请求映射所匹配的请求必须不能携带header请求头信息 |
| “header=value” | 要求请求映射所匹配的请求必须携带header请求头信息且header=value |
| “header!=value” | 要求请求映射所匹配的请求必须携带header请求头信息且header!=value |
<a th:href="@{/testParamsAndHeaders(username='admin',password=123)}">
测试RequestMapping注解的params属性-->/testParamsAndHeaders
a>
@RequestMapping(
value = "/testParamsAndHeaders",
params = {"username","password!=123456"},
headers = {"Host=localhost:8080"}
)
public String testParamsAndHeaders(){
return "success";
}
若当前请求满足@RequestMapping注解的value和method属性,但是不满足headers属性,此时页面显示404错误,即资源未找到。
(7)SpringMVC支持ant风格的路径
| ? | 表示任意的单个字符 |
|---|---|
| * | 表示任意的0个或多个字符 |
| ** | 表示任意的一层或多层目录 |
<a th:href="@{/a1a/testAnt}">测试@RequestMapping可以匹配ant风格的路径-->使用?a><br>
<a th:href="@{/a1a/testAnt}">测试@RequestMapping可以匹配ant风格的路径-->使用*a><br>
<a th:href="@{/a1a/testAnt}">测试@RequestMapping可以匹配ant风格的路径-->使用**a><br>
//注意:在使用**时,只能使用/**/xxx的方式
//@RequestMapping("/a?a/testAnt")
//@RequestMapping("/a*a/testAnt")
@RequestMapping("/**/testAnt")
public String testAnt(){
return "success";
}
(8)SpringMVC支持路径中的占位符(重点)
| 原始方式 | /deleteUser?id=1 |
|---|---|
| rest方式 | /deleteUser/1 |
| SpringMVC路径中的占位符常用于RESTful风格中,当请求路径中将某些数据通过路径的方式传输到服务器中,就可以在相应的@RequestMapping注解的value属性中通过占位符{xxx}表示传输的数据,在通过@PathVariable注解,将占位符所表示的数据赋值给控制器方法的形参。 |
<a th:href="@{/testRest/1/admin}">测试路径中的占位符-->/testResta><br>
@RequestMapping("/testPath/{id}/{username}")
public String testPath(@PathVariable("id")Integer id, @PathVariable("username") String username){
System.out.println("id:"+id+",username:"+username);
return "success";
}
4.SpringMVC获取请求参数
(1)通过ServletAPI获取
将HttpServletRequest作为控制器方法的形参,此时HttpServletRequest类型的参数表示封装了当前请求的请求报文的对象。
<a th:href="@{/testServletAPI(username='admin',password=123456)}">
测试使用servletAPI获取请求参数
a>
//形参位置的request表示当前请求
@RequestMapping("/testServletAPI")
public String testServletAPI(HttpServletRequest request){
HttpSession session = request.getSession();
String username = request.getParameter("username");
String password = request.getParameter("password");
System.out.println("username:"+username+",password:"+password);
return "success";
}
(2)通过控制器方法的形参获取请求参数
在控制器方法的形参位置,设置和请求参数同名的形参,当浏览器发送请求,匹配到请求映射时,在DispatcherServlet中就会将请求参数赋值给相应的形参。
<a th:href="@{/testParam(username='admin',password=123456)}">
测试使用控制器的形参获取请求参数
a>
@RequestMapping("/testParam")
public String testParam(String username, String password){
System.out.println("username:"+username+",password:"+password);
return "success";
}
通过控制器方法的形参获取请求参数时,需要注意以下几点:
① 若请求所传输的请求参数中有多个同名的请求参数,此时可以在控制器方法的形参中设置字符串数组或者字符串类型的形参来接收此请求参数。
② 若使用字符串数组类型的形参,此参数的数组中包含了每一个数据。
③ 若使用字符串类型的形参,此参数的值为每个数据中间使用逗号拼接的结果。
(3)@RequestParam
@RequestParam是将请求参数和控制器方法的形参创建映射关系,一共有三个属性:
| value | 指定为形参赋值的请求参数的参数名 |
|---|---|
| required | 设置是否必须传输此请求参数,默认值为true |
| defaultValue | 不考虑required属性值,当value所指定的请求参数没有传输或传输的值为""时,则使用默认值为形参赋值 |
<form th:action="@{/testParam}" method="get">
用户名:<input type="text" name="username"><br>
密码:<input type="password" name="password"><br>
爱好:<input type="checkbox" name="hobby" value="a">a
<input type="checkbox" name="hobby" value="b">b
<input type="checkbox" name="hobby" value="c">c<br>
<input type="submit" value="测试使用控制器的形参获取请求参数">
form>
@RequestMapping("/testParam")
public String testParam(
//required=fasle表示传过来的参数不一定要有user_name
@RequestParam(value = "user_name", required = false, defaultValue = "testName")
String username,String password,String[] hobby
)
System.out.println("username:"+username+",password:"+password+",hobby:"+ Arrays.toString(hobby));
return "success";
}
需要注意的是,若required 设置为true时,则当前请求必须传输value所指定的请求参数,若没有传输该请求参数,且没有设置defaultValue属性,则页面报错400:Required String parameter ‘xxx’ is not present;若设置为false,则当前请求不是必须传输value所指定的请求参数,若没有传输,则注解所标识的形参的值为null。
(4)@RequestHeader
@RequestHeader是将请求头信息和控制器方法的形参创建映射关系,它一共有三个属性:value、required、defaultValue,其用法与@RequestParam一样。
(5)@CookieValue
@CookieValue是将cookie数据和控制器方法的形参创建映射关系,它一共有三个属性:value、required、defaultValue,其用法与@RequestParam一样。
(6)通过POJO获取请求参数
可以在控制器方法的形参位置设置一个实体类类型的形参,此时若浏览器传输的请求参数的参数名和实体类中的属性名一致,那么请求参数就会为此属性赋值。
//定义实体类对象
package com.atguigu.restful.bean;
public class User {
private Integer id;
private String username;
private String password;
private Integer age;
private String sex;
private String email;
public User() {
}
public User(Integer id, String username, String password, Integer age, String sex, String email) {
this.id = id;
this.username = username;
this.password = password;
this.age = age;
this.sex = sex;
this.email = email;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "User{" +
"id=" + id +
", username='" + username + '\'' +
", password='" + password + '\'' +
", age=" + age +
", sex='" + sex + '\'' +
", email='" + email + '\'' +
'}';
}
public Integer getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(Integer id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getUsername() {
return username;
}
public void setUsername(String username) {
this.username = username;
}
public String getPassword() {
return password;
}
public void setPassword(String password) {
this.password = password;
}
public Integer getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(Integer age) {
this.age = age;
}
public String getSex() {
return sex;
}
public void setSex(String sex) {
this.sex = sex;
}
public String getEmail() {
return email;
}
public void setEmail(String email) {
this.email = email;
}
}
<form th:action="@{/testBean}" method="post">
用户名:<input type="text" name="username"><br>
密码:<input type="password" name="password"><br>
性别:<input type="radio" name="sex" value="男">男<input type="radio" name="sex" value="女">女<br>
年龄:<input type="text" name="age"><br>
邮箱:<input type="text" name="email"><br>
<input type="submit" value="使用实体类接收请求参数">
form>
@RequestMapping("/testBean")
public String testBean(User user){
System.out.println(user);
return "success";
}
(7)解决获取请求参数的乱码问题
解决获取请求参数的乱码问题,可以使用SpringMVC提供的编码过滤器CharacterEncodingFilter,但是必须在web.xml中进行注册。除此之外,SpringMVC中处理编码的过滤器一定要配置到其他过滤器之前,否则无效。
<filter>
<filter-name>CharacterEncodingFilterfilter-name>
<filter-class>org.springframework.web.filter.CharacterEncodingFilterfilter-class>
<init-param>
<param-name>encodingparam-name>
<param-value>UTF-8param-value>
init-param>
<init-param>
<param-name>forceResponseEncodingparam-name>
<param-value>trueparam-value>
init-param>
filter>
<filter-mapping>
<filter-name>CharacterEncodingFilterfilter-name>
<url-pattern>/*url-pattern>
filter-mapping>
5.域对象共享数据
(1)使用ServletAPI向request域对象共享数据
<a th:href="@{/testRequestByServletAPI}">
testRequestByServletAPI
a>
//使用servletAPI向request域对象共享数据
@RequestMapping("/testRequestByServletAPI")
public String testRequestByServletAPI(HttpServletRequest request){
request.setAttribute("testRequestScope","hello,servletAPI");
return "success";
}
<p th:text="${testRequestScope}">p>
(2)使用ModelAndView向request域对象共享数据
<a th:href="@{/testModelAndView}">
testModelAndView
a>
@RequestMapping("/testModelAndView")
public ModelAndView testModelAndView(){
ModelAndView mav = new ModelAndView();
//处理模型数据,即向请求域request共享数据
mav.addObject("testRequestScope", "hello,ModelAndView");
//设置视图名称
mav.setViewName("success");
return mav;
}
<p th:text="${testRequestScope}">p>
(3)使用Model向request域对象共享数据
<a th:href="@{/testModel}">
testModel
a>
@RequestMapping("/testModel")
public String testModel(Model model){
model.addAttribute("testRequestScope", "hello,model");
System.out.println(model.getClass().getName());
return "success";
}
<p th:text="${testRequestScope}">p>
(4)使用map向request域对象共享数据
<a th:href="@{/testMap}">
testMap
a>
@RequestMapping("/testMap")
public String testMap(Map<String, Object> map){
map.put("testRequestScope", "hello,map");
System.out.println(map.getClass().getName());
return "success";
}
<p th:text="${testRequestScope}">p>
(5)使用ModelMap向request域对象共享数据
<a th:href="@{/testModelMap}">
testModelMap
a>
@RequestMapping("/testModelMap")
public String testModelMap(ModelMap modelMap){
modelMap.addAttribute("testRequestScope", "hello,ModelMap");
System.out.println(modelMap.getClass().getName());
return "success";
}
<p th:text="${testRequestScope}">p>
(6)Model、ModelMap、Map的关系
Model、ModelMap、Map类型的参数其实本质上都是 BindingAwareModelMap 类型的。
public interface Model{}
public class ModelMap extends LinkedHashMap<String, Object> {}
public class ExtendedModelMap extends ModelMap implements Model {}
public class BindingAwareModelMap extends ExtendedModelMap {}
(7)向session域共享数据
<a th:href="@{/testSession}">
testSessionScope
a>
@RequestMapping("/testSession")
public String testSession(HttpSession session){
session.setAttribute("testSessionScope", "hello,session");
return "success";
}
<p th:text="${session.testSessionScope}">p>
(8)向application域共享数据
<a th:href="@{/testApplication}">
testApplication
a>
@RequestMapping("/testApplication")
public String testApplication(HttpSession session){
ServletContext application = session.getServletContext();
application.setAttribute("testApplicationScope", "hello,application");
return "success";
}
<p th:text="${application.testApplicationScope}">p>
6.SpringMVC的视图
SpringMVC中的视图是View接口,视图的作用渲染数据,将模型Model中的数据展示给用户。**SpringMVC视图的种类很多,默认有转发视图和重定向视图。**当工程引入jstl的依赖,转发视图会自动转换为JstlView,若使用的视图技术为Thymeleaf,在SpringMVC的配置文件中配置了Thymeleaf的视图解析器,由此视图解析器解析之后所得到的是ThymeleafView。
(1)ThymeleafView
当控制器方法中所设置的视图名称没有任何前缀时,此时的视图名称会被SpringMVC配置文件中所配置的视图解析器解析,视图名称拼接视图前缀和视图后缀所得到的最终路径,会通过转发的方式实现跳转。
<bean id="viewResolver" class="org.thymeleaf.spring5.view.ThymeleafViewResolver">
<property name="order" value="1"/>
<property name="characterEncoding" value="UTF-8"/>
<property name="templateEngine">
<bean class="org.thymeleaf.spring5.SpringTemplateEngine">
<property name="templateResolver">
<bean class="org.thymeleaf.spring5.templateresolver.SpringResourceTemplateResolver">
<property name="prefix" value="/WEB-INF/templates/"/>
<property name="suffix" value=".html"/>
<property name="templateMode" value="HTML5"/>
<property name="characterEncoding" value="UTF-8" />
bean>
property>
bean>
property>
bean>
@RequestMapping("/testHello")
public String testHello(){
//转发到的页面为/WEB-INF/templates/hello.html(该页面必须存在,否则会出错)
return "hello";
}
(2)转发视图
① SpringMVC中默认的转发视图是InternalResourceView。
② SpringMVC中创建转发视图的具体情况如下:
当控制器方法中所设置的视图名称以"forward:"为前缀时,创建InternalResourceView视图,此时的视图名称不会被SpringMVC配置文件中所配置的视图解析器解析,而是会将前缀"forward:"去掉,剩余部分作为最终路径通过转发的方式实现跳转。
@RequestMapping("/testForward")
public String testForward(){
// "/testHello"作为最终路径通过转发的方式实现跳转
return "forward:/testHello";
}
(3)重定向视图
① SpringMVC中默认的重定向视图是RedirectView。
② 当控制器方法中所设置的视图名称以"redirect:"为前缀时,创建RedirectView视图,此时的视图名称不会被SpringMVC配置文件中所配置的视图解析器解析,而是会将前缀"redirect:"去掉(然后会判断剩余部分是否以/开头,若是则会自动拼接上下文路径),剩余部分作为最终路径通过重定向的方式实现跳转。
@RequestMapping("/testRedirect")
public String testRedirect(){
// "/testHello"作为最终路径通过重定向的方式实现跳转
return "redirect:/testHello";
}
注:具体有关转发与重定向的区别可以查看这篇文章。
(4)视图控制器view-controller
当控制器中的方法仅仅用来实现页面跳转,即只需要设置视图名称时,可以将处理器方法使用view-controller标签进行表示。特别需要注意的是,当SpringMVC中设置任何一个view-controller时,其他控制器中的请求映射将全部失效,此时需要在SpringMVC的核心配置文件中设置开启mvc注解驱动的标签。
<mvc:view-controller path="/" view-name="index">mvc:view-controller>
<mvc:annotation-driven />
上述配置可以替代以下控制器中的方法:
@RequestMapping("/")
public String index(){
return "index";
}
7.RESTful
(1)RESTful简介
REST:Representational State Transfer,即表现层资源状态转移。
① 资源
资源是一种看待服务器的方式,即,将服务器看作是由很多离散的资源组成。每个资源是服务器上一个可命名的抽象概念。因为资源是一个抽象的概念,所以它不仅仅能代表服务器文件系统中的一个文件、数据库中的一张表等等具体的东西,可以将资源设计的要多抽象有多抽象,只要想象力允许而且客户端应用开发者能够理解。与面向对象设计类似,资源是以名词为核心来组织的,首先关注的是名词。一个资源可以由一个或多个URI来标识。URI既是资源的名称,也是资源在Web上的地址。对某个资源感兴趣的客户端应用,可以通过资源的URI与其进行交互。
② 资源的表述
资源的表述是一段对于资源在某个特定时刻的状态的描述。可以在客户端-服务器端之间转移(交换)。资源的表述可以有多种格式,例如HTML/XML/JSON/纯文本/图片/视频/音频等等。资源的表述格式可以通过协商机制来确定。请求-响应方向的表述通常使用不同的格式。
③ 状态转移
状态转移说的是:在客户端和服务器端之间转移(transfer)代表资源状态的表述。通过转移和操作资源的表述,来间接实现操作资源的目的。
(2)RESTful的实现
① 具体说,就是HTTP协议里面,四个表示操作方式的动词:GET、POST、PUT、DELETE。它们分别对应四种基本操作:GET 用来获取资源,POST 用来新建资源,PUT 用来更新资源,DELETE用来删除资源。
② REST 风格提倡 URL 地址使用统一的风格设计,从前到后各个单词使用斜杠分开,不使用问号键值对方式携带请求参数,而是将要发送给服务器的数据作为 URL 地址的一部分,以保证整体风格的一致性。
| 操作 | 传统方式 | REST风格 |
|---|---|---|
| 查询操作 | getUserById?id=1 | user/1–>get请求方式 |
| 保存操作 | saveUser | user–>post请求方式 |
| 删除操作 | deleteUser?id=1 | user/1–>delete请求方式 |
| 更新操作 | updateUser | user–>put请求方式 |
(3)HiddenHttpMethodFilter
① 由于浏览器只支持发送get和post方式的请求,所以SpringMVC 提供了 HiddenHttpMethodFilter,它可以将 POST 请求转换为 DELETE 或 PUT 请求。
② HiddenHttpMethodFilter 处理put和delete请求的条件有以下两点:
1)当前请求的请求方式必须为post
2)当前请求必须传输请求参数_method
满足以上条件,HiddenHttpMethodFilter 过滤器就会将当前请求的请求方式转换为请求参数_method的值,因此请求参数_method的值才是最终的请求方式。
③ 在web.xml中注册HiddenHttpMethodFilter:
<filter>
<filter-name>HiddenHttpMethodFilterfilter-name>
<filter-class>org.springframework.web.filter.HiddenHttpMethodFilterfilter-class>
filter>
<filter-mapping>
<filter-name>HiddenHttpMethodFilterfilter-name>
<url-pattern>/*url-pattern>
filter-mapping>
④ 目前为止,SpringMVC中提供了两个过滤器:CharacterEncodingFilter和HiddenHttpMethodFilter,在web.xml中注册时,必须先注册CharacterEncodingFilter,再注册HiddenHttpMethodFilter,原因如下:
1)在 CharacterEncodingFilter 中通过 request.setCharacterEncoding(encoding) 方法设置字符集的。
2)request.setCharacterEncoding(encoding) 方法要求前面不能有任何获取请求参数的操作。
3)而 HiddenHttpMethodFilter 恰恰有一个获取请求方式的操作:
String paramValue = request.getParameter(this.methodParam);
8.RESTful案例
(1)准备工作
① 搭建环境
以前面的入门案例为基础,此处主要指的是在web.xml文件中注册HiddenHttpMethodFilter,完整的web.xml内容如下:
<web-app xmlns="http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee/web-app_4_0.xsd"
version="4.0">
<filter>
<filter-name>CharacterEncodingFilterfilter-name>
<filter-class>org.springframework.web.filter.CharacterEncodingFilterfilter-class>
<init-param>
<param-name>encodingparam-name>
<param-value>UTF-8param-value>
init-param>
<init-param>
<param-name>forceResponseEncodingparam-name>
<param-value>trueparam-value>
init-param>
filter>
<filter-mapping>
<filter-name>CharacterEncodingFilterfilter-name>
<url-pattern>/*url-pattern>
filter-mapping>
<filter>
<filter-name>HiddenHttpMethodFilterfilter-name>
<filter-class>org.springframework.web.filter.HiddenHttpMethodFilterfilter-class>
filter>
<filter-mapping>
<filter-name>HiddenHttpMethodFilterfilter-name>
<url-pattern>/*url-pattern>
filter-mapping>
<servlet>
<servlet-name>DispatcherServletservlet-name>
<servlet-class>org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServletservlet-class>
<init-param>
<param-name>contextConfigLocationparam-name>
<param-value>classpath:springMVC.xmlparam-value>
init-param>
<load-on-startup>1load-on-startup>
servlet>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>DispatcherServletservlet-name>
<url-pattern>/url-pattern>
servlet-mapping>
web-app>
② 引入vue.js文件

在/webapp/static/js/目录下,引入静态资源vue.js,方便前端与后端进行数据交互。此外,需要注意的是,为了使新加入的静态资源生效,一是要保证服务器中有static资源,即需要重新打包该项目(在IDEA中点击该项目右侧的Maven->该模块的Lifucycle->package);二是要在springMVC.xml中开放对静态资源的访问,即添加如下代码:
<mvc:default-servlet-handler />
③ 准备实体类
package com.atguigu.restful.bean;
public class Employee {
private Integer id;
private String lastName;
private String email;
//1 male, 0 female
private Integer gender;
public Integer getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(Integer id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getLastName() {
return lastName;
}
public void setLastName(String lastName) {
this.lastName = lastName;
}
public String getEmail() {
return email;
}
public void setEmail(String email) {
this.email = email;
}
public Integer getGender() {
return gender;
}
public void setGender(Integer gender) {
this.gender = gender;
}
public Employee(Integer id, String lastName, String email, Integer gender) {
super();
this.id = id;
this.lastName = lastName;
this.email = email;
this.gender = gender;
}
public Employee() {
}
}
④ 在DAO层准备模拟数据以及增删改查的方法
package com.atguigu.restful.dao;
import com.atguigu.restful.bean.Employee;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Repository;
import java.util.Collection;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
@Repository
public class EmployeeDao {
private static Map<Integer, Employee> employees = null;
static{
employees = new HashMap<Integer, Employee>();
employees.put(1001, new Employee(1001, "E-AA", "[email protected]", 1));
employees.put(1002, new Employee(1002, "E-BB", "[email protected]", 1));
employees.put(1003, new Employee(1003, "E-CC", "[email protected]", 0));
employees.put(1004, new Employee(1004, "E-DD", "[email protected]", 0));
employees.put(1005, new Employee(1005, "E-EE", "[email protected]", 1));
}
private static Integer initId = 1006;
/*
该方法包含两种情况:添加数据和修改数据
1.如果传入的employee的id为空,则说明是添加操作
2.如果传入的employee的id不为空。则说明是修改操作
*/
public void save(Employee employee){
if(employee.getId() == null){
employee.setId(initId++);
}
employees.put(employee.getId(), employee);
}
public Collection<Employee> getAll(){
return employees.values();
}
public Employee get(Integer id){
return employees.get(id);
}
public void delete(Integer id){
employees.remove(id);
}
}
(2)功能清单
| 功能 | URL 地址 | 请求方式 |
|---|---|---|
| 访问首页 | / | GET |
| 查询全部数据 | /employee | GET |
| 删除 | /employee/2 | DELETE |
| 跳转到添加数据页面 | /toAdd | GET |
| 执行保存 | /employee | POST |
| 跳转到更新数据页面 | /employee/2 | GET |
| 执行更新 | /employee | PUT |
(3)具体功能:访问首页
① 由于访问首页不需要其它操作,即控制器中的方法仅仅用来实现页面跳转,此时可以在SpringMVC.xml中配置相应的视图控制器view-controller(也可以直接写相应的方法)
<mvc:view-controller path="/" view-name="index"/>
② 首页index.html页面代码如下:
DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en" xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>首页title>
head>
<body>
<h1>首页h1>
<a th:href="@{/employee}">查看所有员工信息a>
body>
html>
(4)具体功能:查询所有员工数据
① 在上面的index.html页面中,已经写好了查询所有员工数据的请求路径,现需要在EmployeeController中编写对应的控制器方法:
//注入EmployeeDao(此处为了方便,并未按照正规情况编写service层代码,而是直接调用DAO层的方法)
@Autowired
private EmployeeDao employeeDao;
//1.查询所有员工
@RequestMapping(value="/employee",method = RequestMethod.GET)
public String getAllEmployee(Model model){
//掉用DAO层的getAll()方法
Collection<Employee> employeeList = employeeDao.getAll();
model.addAttribute("employeeList",employeeList);
//通过转发跳转到/WEB-INF/templates/employee_list.html页面,并且展示Model中的数据
return "employee_list";
}
② 前端建employee_list.html的代码如下:
DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en" xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>employee_listtitle>
head>
<body>
<table id="dataTable" border="1" cellspacing="0" cellpadding="0" style="text-align: center;">
<tr>
<th colspan="5">Employee Infoth>
tr>
<tr>
<th>idth>
<th>lastNameth>
<th>emailth>
<th>genderth>
<th>options(<a th:href="@{/toAdd}">adda>)th>
tr>
<tr th:each="employee : ${employeeList}">
<td th:text="${employee.id}">td>
<td th:text="${employee.lastName}">td>
<td th:text="${employee.email}">td>
<td th:text="${employee.gender}">td>
<td>
<a @click="deleteEmployee" th:href="@{'/employee/'+${employee.id}}">deletea>
<a th:href="@{'/employee/'+${employee.id}}">updatea>
td>
tr>
table>
body>
html>
③ 在index.html页面点击"查看所有员工信息"后,跳转得到的页面如下(在该页面可以跳转到添加、修改页面,也可以对员工信息进行删除操作):

(5)具体功能:删除一条员工信息
① 在employee_list.html页面中,先创建处理delete请求方式的表单:
<form id="deleteForm" method="post">
<input type="hidden" name="_method" value="delete">
form>
然后引入vue.js:
<script type="text/javascript" th:src="@{/static/js/vue.js}">script>
通过vue处理点击事件:
<script type="text/javascript">
var vue = new Vue({
el:"#dataTable",
methods:{
deleteEmployee:function (event) {
//根据id获取表单元素
var deleteForm = document.getElementById("deleteForm");
//将触发点击事件的超链接的href属性赋值给表单的action
deleteForm.action = event.target.href;
//提交表单
deleteForm.submit();
//取消超链接的默认行为
event.preventDefault();
}
}
});
script>
② 编写EmployeeController中对应的控制器方法:
//2.根据id删除员工
@RequestMapping(value = "employee/{id}",method = RequestMethod.DELETE)
public String deleteEmployee(@PathVariable("id") Integer id){
employeeDao.delete(id);
//重定向(默认为GET方法)
return "redirect:/employee";
}
(6)具体功能:跳转到添加数据页面
① 在SpringMVC.xml中为跳转到添加数据页面配置view-controller:
<mvc:view-controller path="/toAdd" view-name="employee_add">mvc:view- controller>
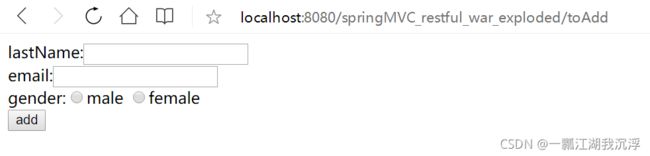
② 创建employee_add.html
DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en" xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>employee_addtitle>
head>
<body>
<form th:action="@{/employee}" method="post">
lastName:<input type="text" name="lastName"><br>
email:<input type="text" name="email"><br>
gender:<input type="radio" name="gender" value="1">male
<input type="radio" name="gender" value="0">female<br>
<input type="submit" value="add">
form>
body>
html>
(7)具体功能:添加员工信息
编写EmployeeController中对应的控制器方法:
//3.添加员工
@RequestMapping( value = "/employee",method = RequestMethod.POST)
public String addEmployee(Employee employee){
employeeDao.save(employee);
return "redirect:/employee";
}
(8)具体功能:跳转到更新数据页面
① 编写EmployeeController中对应的控制器方法:
//4.将要修改的员工信息查出来,跳转到employee_update页面
@RequestMapping(value = "/employee/{id}",method = RequestMethod.GET)
public String getEmpById(@PathVariable("id") Integer id,Model model){
//通过前端请求路径中传来的员工id获取该员工的信息
Employee employee = employeeDao.get(id);
//将需要修改的员工信息封装到model中,然后在employee_update.html页面进行展示
model.addAttribute("employee",employee);
return "employee_update";
}
② 创建employee_update.html:
DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en" xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>employee_updatetitle>
head>
<body>
<form th:action="@{/employee}" method="post">
<input type="hidden" name="_method" value="put">
<input type="hidden" name="id" th:value="${employee.id}">
lastName:<input type="text" name="lastName" th:value="${employee.lastName}"><br>
email:<input type="text" name="email" th:value="${employee.email}"><br>
gender:<input type="radio" name="gender" value="1" th:field="${employee.gender}">male
<input type="radio" name="gender" value="0" th:field="${employee.gender}">female<br>
<input type="submit" value="update"><br>
form>
body>
html>
(9)具体功能:对员工信息进行修改
① 编写EmployeeController中对应的控制器方法:
//5.修改员工信息
@RequestMapping(value = "/employee",method = RequestMethod.PUT)
public String updateEmployee(Employee employee){
employeeDao.save(employee);
return "redirect:/employee";
}
9.HttpMessageConverter
HttpMessageConverter,即报文信息转换器,将请求报文转换为Java对象,或将Java对象转换为响应报文。HttpMessageConverter提供了两个注解和两个类型:@RequestBody和@ResponseBody、RequestEntity和ResponseEntity。
(1)@RequestBody
@RequestBody可以获取请求体,需要在控制器方法设置一个形参,使用@RequestBody进行标识,当前请求的请求体就会为当前注解所标识的形参赋值。
<form th:action="@{/testRequestBody}" method="post">
用户名:<input type="text" name="username"><br>
密码:<input type="password" name="password"><br>
<input type="submit" value="测试@RequestBody">
form>
@RequestMapping("/testRequestBody")
public String testRequestBody(@RequestBody String requestBody){
System.out.println("requestBody:"+requestBody);
return "success";
}
(2)RequestEntity
RequestEntity封装请求报文的一种类型,需要在控制器方法的形参中设置该类型的形参,当前请求的请求报文就会赋值给该形参,可以通过getHeaders()获取请求头信息,通过getBody()获取请求体信息。
<form th:action="@{/testRequestEntity}" method="post">
用户名:<input type="text" name="username"><br>
密码:<input type="password" name="password"><br>
<input type="submit" value="测试RequestEntity">
form>
@RequestMapping("/testRequestEntity")
public String testRequestEntity(RequestEntity<String> requestEntity){
//当前requestEnity表示整个请求报文的信息
System.out.println("请求头:"+requestEntity.getHeaders());
System.out.println("请求体:"+requestEntity.getBody());
return "success";
}
(3)@ResponseBody
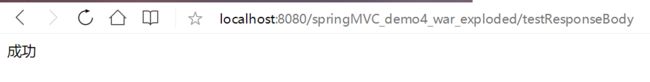
@ResponseBody用于标识一个控制器方法,可以将该方法的返回值直接作为响应报文的响应体响应到浏览器。
<a th:href="@{/testResponseBody}">
通过@ResponseBody响应浏览器数据
a>
@RequestMapping(value = "/testResponseBody", produces = "text/html;charset=UTF-8")
@ResponseBody
public String testResponseBody(){
return "成功!";
}
(4)SpringMVC处理json数据
① 在pom.xml中导入jackson的依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>com.fasterxml.jackson.coregroupId>
<artifactId>jackson-databindartifactId>
<version>2.12.1version>
dependency>
② 在SpringMVC.xml配置文件中开启mvc的注解驱动,此时在HandlerAdaptor中会自动装配一个消息转换器MappingJackson2HttpMessageConverter,它可以将响应到浏览器的Java对象转换为json格式的字符串。
<mvc:annotation-driven />
③ 在控制器方法上使用@ResponseBody注解进行标识
④ 将Java对象直接作为控制器方法的返回值返回,就会自动转换为Json格式的字符串。
<a th:href="@{/testResponseUser}">
通过@ResponseBody响应浏览器User对象
a>
//实体类User
package com.atguigu.mvc.bean;
public class User {
private Integer id;
private String username;
private String password;
private Integer age;
private String sex;
public User(Integer id, String username, String password, Integer age, String sex) {
this.id = id;
this.username = username;
this.password = password;
this.age = age;
this.sex = sex;
}
public User() {
}
public Integer getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(Integer id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getUsername() {
return username;
}
public void setUsername(String username) {
this.username = username;
}
public String getPassword() {
return password;
}
public void setPassword(String password) {
this.password = password;
}
public Integer getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(Integer age) {
this.age = age;
}
public String getSex() {
return sex;
}
public void setSex(String sex) {
this.sex = sex;
}
}
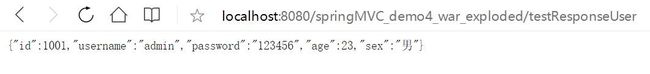
@RequestMapping("/testResponseUser")
@ResponseBody
public User testResponseUser(){
return new User(1001, "admin", "123456", 23, "男");
}
(5)SpringMVC处理axios
① 请求超链接
<div id="app">
<a @click="testAxios" th:href="@{/testAxios}">SpringMVC处理ajaxa>
div>
② 通过vue和axios处理点击事件
<script type="text/javascript" th:src="@{/static/js/vue.js}">script>
<script type="text/javascript" th:src="@{/static/js/axios.min.js}">script>
<script type="text/javascript">
new Vue({
el:"#app",
methods:{
testAxios:function (event) {
axios({
method:"post",
url:event.target.href,
params:{
username:"admin",
password:"123456"
}
}).then(function (response) {
alert(response.data);
});
event.preventDefault();
}
}
});
script>
③ 控制器方法
@RequestMapping("/testAxios")
@ResponseBody
public String testAxios(String username, String password){
System.out.println(username+","+password);
return "hello,axios!";
}
(6)@RestController注解
@RestController注解是SpringMVC提供的一个复合注解,标识在控制器的类上,就相当于为类添加了@Controller注解,并且为其中的每个方法添加了@ResponseBody注解。
(7)ResponseEntity
ResponseEntity用于控制器方法的返回值类型,该控制器方法的返回值就是响应到浏览器的响应报文。
<a th:href="@{/testResponseEntity}">
测试ResponseEntity
a>
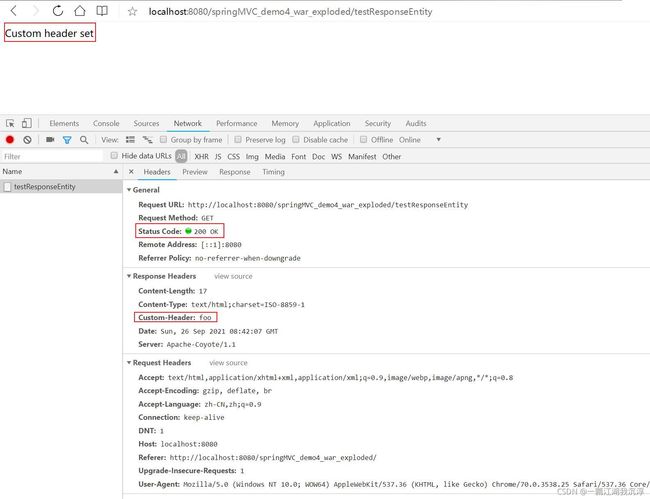
@RequestMapping("/testResponseEntity")
@ResponseBody
public ResponseEntity testResponseEntity(){
HttpHeaders headers = new HttpHeaders();
headers.add("Custom-Header", "foo");
return new ResponseEntity<>(
"Custom header set", headers, HttpStatus.OK);
}
10.文件上传和下载
(1)文件下载
文件下载功能可以使用ResponseEntity来实现。
<a th:href="@{/testDown}">
下载图片1.jpg
a>
//下载文件
@RequestMapping("/testDown")
public ResponseEntity<byte[]> testResponseEntity(HttpSession session) throws IOException {
//获取ServletContext对象
ServletContext servletContext = session.getServletContext();
//获取服务器中文件的真实路径
//servletContext.getRealPath:获取服务器部署的真实路径
String realPath = servletContext.getRealPath("/static/img/1.jpg");
System.out.println(realPath);
//创建输入流
InputStream is = new FileInputStream(realPath);
//创建字节数组
byte[] bytes = new byte[is.available()];
//将流读到字节数组中
is.read(bytes);
//创建HttpHeaders对象设置响应头信息
MultiValueMap<String, String> headers = new HttpHeaders();
//设置要下载方式以及下载文件的名字
headers.add("Content-Disposition", "attachment;filename=1.jpg");
//设置响应状态码
HttpStatus statusCode = HttpStatus.OK;
//创建ResponseEntity对象
ResponseEntity<byte[]> responseEntity = new ResponseEntity<>(bytes, headers, statusCode);
//关闭输入流
is.close();
return responseEntity;
}
(2)文件上传
文件上传要求form表单的请求方式必须为post,并且添加属性enctype=“multipart/form-data”,并且SpringMVC中将上传的文件封装到MultipartFile对象中,通过此对象可以获取文件相关信息。
① 在pom.xml中年添加相应的依赖:
<dependency>
<groupId>commons-fileuploadgroupId>
<artifactId>commons-fileuploadartifactId>
<version>1.3.1version>
dependency>
② 在SpringMVC.xml中添加如下配置:
<bean id="multipartResolver" class="org.springframework.web.multipart.commons.CommonsMultipartResolver">
<property name="defaultEncoding" value="UTF-8"/>
<property name="maxUploadSize" value="102400000"/>
bean>
③ 前端相应的代码:
<form th:action="@{/testUp}" method="post" enctype="multipart/form-data">
头像:<input type="file" name="photo"><br>
<input type="submit" value="上传">
form>
④ 对应的控制器方法:
//上传文件
@RequestMapping("/testUp")
public String testUp(MultipartFile photo, HttpSession session) throws IOException {
//获取上传的文件的文件名
String fileName = photo.getOriginalFilename();
//获取上传的文件的后缀名
String suffixName = fileName.substring(fileName.lastIndexOf("."));
//将UUID作为文件名
String uuid = UUID.randomUUID().toString().replaceAll("-","");
//将uuid和后缀名拼接后的结果作为最终的文件名
fileName = uuid + suffixName;
//通过ServletContext获取服务器中photo目录的路径
ServletContext servletContext = session.getServletContext();
String photoPath = servletContext.getRealPath("photo");
File file = new File(photoPath);
//判断photoPath所对应路径是否存在
if(!file.exists()){
//若不存在,则创建目录
file.mkdir();
}
String finalPath = photoPath + File.separator + fileName;
//上传文件
photo.transferTo(new File(finalPath));
return "success";
}
11.拦截器
有关拦截器相关的知识,可以查看我之前的这篇文章。
12.异常处理器
(1)基于配置的异常处理
① SpringMVC提供了一个处理控制器方法执行过程中所出现的异常的接口:HandlerExceptionResolver,它的实现类有:DefaultHandlerExceptionResolver和SimpleMappingExceptionResolver。
② SpringMVC提供了自定义的异常处理器SimpleMappingExceptionResolver,使用方式如下:
1)在SpringMVC.xml中进行相关配置:
<bean class="org.springframework.web.servlet.handler.SimpleMappingExceptionResolver">
<property name="exceptionMappings">
<props>
<prop key="java.lang.ArithmeticException">errorprop>
props>
property>
<property name="exceptionAttribute" value="ex">property>
bean>
2)error.html页面的代码如下:
DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en" xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>errortitle>
head>
<body>
出现错误<br>
<h1 style="color: red" th:text="${ex}">h1>
body>
html>
3)在下面的控制器方法中模拟异常:
@RequestMapping("/testExceptionHandler")
public String testExceptionHandler(){
//设置算术运算异常,此时会跳转到error.html页面
System.out.println(1/0);
return "success";
}
(2)基于注解的异常处理
package com.atguigu.mvc.controller;
import org.springframework.ui.Model;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ControllerAdvice;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ExceptionHandler;
//基于注解的异常处理器
//@ControllerAdvice将当前类标识为异常处理的组件
@ControllerAdvice
public class ExceptionController {
@ExceptionHandler(value = {ArithmeticException.class,NullPointerException.class})
public String testExceptionAnnotation(Exception ex, Model model){
model.addAttribute("ex",ex);
return "error";
}
}
注:该注解达到的效果与上面的一样。
13.注解配置SpringMVC
注解配置SpringMVC指的是使用配置类和注解来代替web.xml和SpringMVC配置文件。
(1)创建初始化类,代替web.xml
在Servlet3.0环境中,容器会在类路径中查找实现javax.servlet.ServletContainerInitializer接口的类,如果找到的话就用它来配置Servlet容器。 Spring提供了这个接口的实现,名为SpringServletContainerInitializer,这个类反过来又会查找实现WebApplicationInitializer的类并将配置的任务交给它们来完成。Spring3.2引入了一个便利的WebApplicationInitializer基础实现,名为AbstractAnnotationConfigDispatcherServletInitializer,当我们的类扩展了
AbstractAnnotationConfigDispatcherServletInitializer并将其部署到Servlet3.0容器的时候,容器会自动发现它,并用它来配置Servlet上下文。
package com.atguigu.mvc.config;
import org.springframework.web.filter.CharacterEncodingFilter;
import org.springframework.web.filter.HiddenHttpMethodFilter;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.support.AbstractAnnotationConfigDispatcherServletInitializer;
import javax.servlet.Filter;
//web工程的初始化类,用来代替web.xml
public class WebInit extends AbstractAnnotationConfigDispatcherServletInitializer {
//指定spring的配置类
@Override
protected Class<?>[] getRootConfigClasses() {
return new Class[]{SpringConfig.class};
}
//指定SpringMVC的配置类
@Override
protected Class<?>[] getServletConfigClasses() {
return new Class[]{WebConfig.class};
}
//指定DispatcherServlet的映射规则,即url-pattern
@Override
protected String[] getServletMappings() {
return new String[]{"/"};
}
//注册过滤器
@Override
protected Filter[] getServletFilters() {
CharacterEncodingFilter characterEncodingFilter = new CharacterEncodingFilter();
characterEncodingFilter.setEncoding("UTF-8");
characterEncodingFilter.setForceResponseEncoding(true);
HiddenHttpMethodFilter hiddenHttpMethodFilter = new HiddenHttpMethodFilter();
return new Filter[]{characterEncodingFilter,hiddenHttpMethodFilter};
}
}
(2)创建SpringConfig配置类,代替spring的配置文件
package com.atguigu.mvc.config;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
@Configuration
public class SpringConfig {
}
(3)创建WebConfig配置类,代替SpringMVC的配置文件
package com.atguigu.mvc.config;
import com.atguigu.mvc.interceptor.TestInterceptor;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.ComponentScan;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.web.context.ContextLoader;
import org.springframework.web.context.WebApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.web.multipart.MultipartResolver;
import org.springframework.web.multipart.commons.CommonsMultipartResolver;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.HandlerExceptionResolver;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.ViewResolver;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.config.annotation.*;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.handler.SimpleMappingExceptionResolver;
import org.thymeleaf.spring5.SpringTemplateEngine;
import org.thymeleaf.spring5.view.ThymeleafViewResolver;
import org.thymeleaf.templatemode.TemplateMode;
import org.thymeleaf.templateresolver.ITemplateResolver;
import org.thymeleaf.templateresolver.ServletContextTemplateResolver;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Properties;
/*
* 代替SpringMVC的配置文件:
* 1、扫描组件 2、视图解析器 3、view-controller 4、default-servlet-handler
* 5、mvc注解驱动 6、文件上传解析器 7、异常处理 8、拦截器
*/
//将当前类标识为一个配置类
@Configuration
//1、扫描组件
@ComponentScan("com.atguigu.mvc.controller")
//5、mvc注解驱动
@EnableWebMvc
public class WebConfig implements WebMvcConfigurer {
//4、default-servlet-handler
@Override
public void configureDefaultServletHandling(DefaultServletHandlerConfigurer configurer) {
configurer.enable();
}
//8、拦截器
@Override
public void addInterceptors(InterceptorRegistry registry) {
TestInterceptor testInterceptor = new TestInterceptor();
//拦截所有请求
registry.addInterceptor(testInterceptor).addPathPatterns("/**");
}
//3、view-controller
@Override
public void addViewControllers(ViewControllerRegistry registry) {
registry.addViewController("/hello").setViewName("hello");
}
//6、文件上传解析器
@Bean
public MultipartResolver multipartResolver(){
CommonsMultipartResolver commonsMultipartResolver = new CommonsMultipartResolver();
return commonsMultipartResolver;
}
//7、异常处理
@Override
public void configureHandlerExceptionResolvers(List<HandlerExceptionResolver> resolvers) {
SimpleMappingExceptionResolver exceptionResolver = new SimpleMappingExceptionResolver();
Properties prop = new Properties();
//出现算术错误后,跳转到error.html页面
prop.setProperty("java.lang.ArithmeticException", "error");
exceptionResolver.setExceptionMappings(prop);
exceptionResolver.setExceptionAttribute("exception");
resolvers.add(exceptionResolver);
}
//配置生成模板解析器
@Bean
public ITemplateResolver templateResolver() {
WebApplicationContext webApplicationContext = ContextLoader.getCurrentWebApplicationContext();
// ServletContextTemplateResolver需要一个ServletContext作为构造参数,可通过WebApplicationContext 的方法获得
ServletContextTemplateResolver templateResolver = new ServletContextTemplateResolver(
webApplicationContext.getServletContext());
//设置前缀
templateResolver.setPrefix("/WEB-INF/templates/");
//设置后缀
templateResolver.setSuffix(".html");
templateResolver.setCharacterEncoding("UTF-8");
templateResolver.setTemplateMode(TemplateMode.HTML);
return templateResolver;
}
//生成模板引擎并为模板引擎注入模板解析器
@Bean
public SpringTemplateEngine templateEngine(ITemplateResolver templateResolver) {
SpringTemplateEngine templateEngine = new SpringTemplateEngine();
templateEngine.setTemplateResolver(templateResolver);
return templateEngine;
}
//生成视图解析器并未解析器注入模板引擎
@Bean
public ViewResolver viewResolver(SpringTemplateEngine templateEngine) {
ThymeleafViewResolver viewResolver = new ThymeleafViewResolver();
viewResolver.setCharacterEncoding("UTF-8");
viewResolver.setTemplateEngine(templateEngine);
return viewResolver;
}
}