SpringBoot统一异常处理详解
文章目录
- 一、概述
-
- 1、统一异常处理介绍
- 2、原理和目标
- 二、Assert(断言)
-
- 1、概述
- 2、Assert自定义实战
-
- 2.1 自定义接口Assert
- 2.2 自定义异常
- 2.3 Enum整合
- 2.4 实战检测
- 三、统一异常处理器
-
- 1、异常处理器说明
-
- 1.1 handleServletException
- 1.2 handleBindException和handleValidException
- 1.3 handleBusinessException、handleBaseException
- 1.4 **handleException**
- 2、自定义统一异常处理器类
- 3、其他类型统一处理器
- 4、统一返回结果
一、概述
后端规范入门参考:Spring Boot后端接口规范
1、统一异常处理介绍
Spring在3.2版本增加了一个注解@ControllerAdvice,可以与@ExceptionHandler、@InitBinder、@ModelAttribute 等注解注解配套使用。不过跟异常处理相关的只有注解@ExceptionHandler,从字面上看,就是 异常处理器 的意思
2、原理和目标
简单的说,该注解可以把异常处理器应用到所有控制器,而不是单个控制器。借助该注解,我们可以实现:在独立的某个地方,比如单独一个类,定义一套对各种异常的处理机制,然后在类的签名加上注解@ControllerAdvice,统一对 不同阶段的、不同异常 进行处理。这就是统一异常处理的原理。
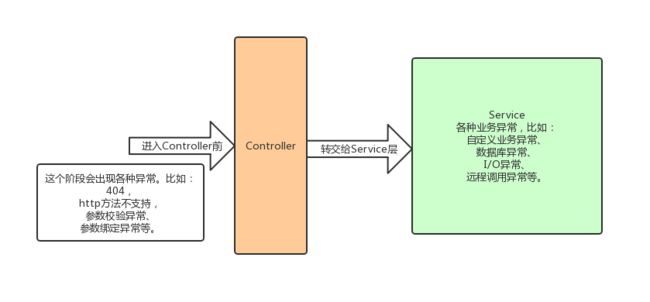
对异常按阶段进行分类,大体可以分成:进入Controller前的异常 和 Service 层异常
目标就是消灭95%以上的 try catch 代码块,并以优雅的 Assert(断言) 方式来校验业务的异常情况,只关注业务逻辑,而不用花费大量精力写冗余的 try catch 代码块。
二、Assert(断言)
1、概述
**Assert(断言)**是Spring 家族的 org.springframework.util.Assert,在我们写测试用例的时候经常会用到,使用断言能让我们编码的时候有一种非一般丝滑的感觉
Assert 的部分源码,可以看到,Assert 其实就是帮我们把 if {…} 封装了一下,抛出的异常是IllegalArgumentException()
public abstract class Assert {
public Assert() {
}
public static void notNull(@Nullable Object object, String message) {
if (object == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException(message);
}
}
}
2、Assert自定义实战
2.1 自定义接口Assert
Assert断言方法是使用接口的默认方法定义的,然后有没有发现当断言失败后,抛出的异常不是具体的某个异常,而是交由2个newException接口方法提供。因为业务逻辑中出现的异常基本都是对应特定的场景,比如根据用户id获取用户信息,查询结果为null,此时抛出的异常可能为UserNotFoundException,并且有特定的异常码(比如7001)和异常信息"用户不存在"。所以具体抛出什么异常,有Assert的实现类决定。
public interface Assert {
/**
* 创建异常
* @param args
* @return
*/
BaseException newException(Object... args);
/**
* 创建异常
* @param t
* @param args
* @return
*/
BaseException newException(Throwable t, Object... args);
/**
* 断言对象obj非空。如果对象obj为空,则抛出异常
*
* @param obj 待判断对象
*/
default void assertNotNull(Object obj) {
if (obj == null) {
throw newException(obj);
}
}
/**
* 断言对象obj非空。如果对象obj为空,则抛出异常
*
异常信息message支持传递参数方式,避免在判断之前进行字符串拼接操作
*
* @param obj 待判断对象
* @param args message占位符对应的参数列表
*/
default void assertNotNull(Object obj, Object... args) {
if (obj == null) {
throw newException(args);
}
}
}
2.2 自定义异常
public interface IResponseEnum {
int getCode();
String getMessage();
}
/**
* 业务异常
* 业务处理时,出现异常,可以抛出该异常
*/
public class BusinessException extends BaseException {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
public BusinessException(IResponseEnum responseEnum, Object[] args, String message) {
super(responseEnum, args, message);
}
public BusinessException(IResponseEnum responseEnum, Object[] args, String message, Throwable cause) {
super(responseEnum, args, message, cause);
}
}
2.3 Enum整合
代码示例中定义了两个枚举实例:BAD_LICENCE_TYPE、LICENCE_NOT_FOUND,分别对应了BadLicenceTypeException、LicenceNotFoundException两种异常。以后每增加一种异常情况,只需增加一个枚举实例即可,再也不用每一种异常都定义一个异常类了
public interface BusinessExceptionAssert extends IResponseEnum, Assert {
@Override
default BaseException newException(Object... args) {
String msg = MessageFormat.format(this.getMessage(), args);
return new BusinessException(this, args, msg);
}
@Override
default BaseException newException(Throwable t, Object... args) {
String msg = MessageFormat.format(this.getMessage(), args);
return new BusinessException(this, args, msg, t);
}
}
@Getter
@AllArgsConstructor
public enum ResponseEnum implements BusinessExceptionAssert {
/**
* Bad licence type
*/
BAD_LICENCE_TYPE(7001, "Bad licence type."),
/**
* Licence not found
*/
LICENCE_NOT_FOUND(7002, "Licence not found.")
;
/**
* 返回码
*/
private int code;
/**
* 返回消息
*/
private String message;
}
2.4 实战检测
使用枚举类结合(继承)Assert,只需根据特定的异常情况定义不同的枚举实例,如上面的BAD_LICENCE_TYPE、LICENCE_NOT_FOUND,就能够针对不同情况抛出特定的异常(这里指携带特定的异常码和异常消息),这样既不用定义大量的异常类,同时还具备了断言的良好可读性
private void checkNotNull(Licence licence) {
ResponseEnum.LICENCE_NOT_FOUND.assertNotNull(licence,"测试");
}
// 替代下面的方法
private void checkNotNull(Licence licence) {
if (licence == null) {
throw new LicenceNotFoundException();
// 或者这样
throw new BusinessException(7001, "Bad licence type.");
}
}
三、统一异常处理器
1、异常处理器说明
1.1 handleServletException
一个http请求,在到达Controller前,会对该请求的请求信息与目标控制器信息做一系列校验
-
NoHandlerFoundException:首先根据请求Url查找有没有对应的控制器,若没有则会抛该异常,也就是大家非常熟悉的404异常,但是实际上当出现404的时候,默认是不抛异常的,而是 forward跳转到/error控制器,spring也提供了默认的error控制器,如果要抛出异常,需要配置spring.mvc.throw-exception-if-no-handler-found=true spring.web.resources.add-mappings=false -
HttpRequestMethodNotSupportedException:若匹配到了(匹配结果是一个列表,不同的是http方法不同,如:Get、Post等),则尝试将请求的http方法与列表的控制器做匹配,若没有对应http方法的控制器,则抛该异常; -
HttpMediaTypeNotSupportedException:然后再对请求头与控制器支持的做比较,比如content-type请求头,若控制器的参数签名包含注解@RequestBody,但是请求的content-type请求头的值没有包含application/json,那么会抛该异常(当然,不止这种情况会抛这个异常); -
MissingPathVariableException:未检测到路径参数。比如url为:/licence/{licenceId},参数签名包含@PathVariable("licenceId"),当请求的url为/licence,在没有明确定义url为/licence的情况下,会被判定为:缺少路径参数; -
MissingServletRequestParameterException:缺少请求参数。比如定义了参数@RequestParam("licenceId") String licenceId,但发起请求时,未携带该参数,则会抛该异常; -
TypeMismatchException: 参数类型匹配失败。比如:接收参数为Long型,但传入的值确是一个字符串,那么将会出现类型转换失败的情况,这时会抛该异常; -
HttpMessageNotReadableException:与上面的HttpMediaTypeNotSupportedException举的例子完全相反,即请求头携带了"content-type: application/json;charset=UTF-8",但接收参数却没有添加注解@RequestBody,或者请求体携带的 json 串反序列化成 pojo 的过程中失败了,也会抛该异常; -
HttpMessageNotWritableException:返回的 pojo 在序列化成 json 过程失败了,那么抛该异常;
1.2 handleBindException和handleValidException
参数校验异常
1.3 handleBusinessException、handleBaseException
处理自定义的业务异常,只是handleBaseException处理的是除了 BusinessException 意外的所有业务异常。就目前来看,这2个是可以合并成一个的
1.4 handleException
处理所有未知的异常,比如操作数据库失败的异常。
注:上面的
handleServletException、handleException这两个处理器,返回的异常信息,不同环境返回的可能不一样,以为这些异常信息都是框架自带的异常信息,一般都是英文的,不太好直接展示给用户看,所以统一返回SERVER_ERROR代表的异常信息
2、自定义统一异常处理器类
将异常分成几类,实际上只有两大类,一类是ServletException、ServiceException,还记得上文提到的 按阶段分类 吗,即对应 进入Controller前的异常 和 Service 层异常;然后 ServiceException 再分成自定义异常、未知异常。对应关系如下:
-
进入
Controller前的异常: handleServletException、handleBindException、handleValidException -
自定义异常:handleBusinessException、handleBaseException
-
未知异常: handleException
@Slf4j
@Component
@ControllerAdvice
@ConditionalOnWebApplication
@ConditionalOnMissingBean(UnifiedExceptionHandler.class)
public class UnifiedExceptionHandler {
/**
* 生产环境
*/
private final static String ENV_PROD = "prod";
@Autowired
private UnifiedMessageSource unifiedMessageSource;
/**
* 当前环境
*/
@Value("${spring.profiles.active}")
private String profile;
/**
* 获取国际化消息
* 这里可以做处理
* @param e 异常
* @return
*/
public String getMessage(BaseException e) {
String code = "response." + e.getResponseEnum().toString();
String message = unifiedMessageSource.getMessage(code, e.getArgs());
if (message == null || message.isEmpty()) {
return e.getMessage();
}
return message;
}
/**
* 业务异常
*
* @param e 异常
* @return 异常结果
*/
@ExceptionHandler(value = BusinessException.class)
@ResponseBody
public ErrorResponse handleBusinessException(BaseException e) {
log.error(e.getMessage(), e);
return new ErrorResponse(e.getResponseEnum().getCode(), getMessage(e));
}
/**
* 自定义异常
*
* @param e 异常
* @return 异常结果
*/
@ExceptionHandler(value = BaseException.class)
@ResponseBody
public ErrorResponse handleBaseException(BaseException e) {
log.error(e.getMessage(), e);
return new ErrorResponse(e.getResponseEnum().getCode(), getMessage(e));
}
/**
* Controller上一层相关异常
*
* @param e 异常
* @return 异常结果
*/
@ExceptionHandler({
NoHandlerFoundException.class,
HttpRequestMethodNotSupportedException.class,
HttpMediaTypeNotSupportedException.class,
MissingPathVariableException.class,
MissingServletRequestParameterException.class,
TypeMismatchException.class,
HttpMessageNotReadableException.class,
HttpMessageNotWritableException.class,
// BindException.class,
// MethodArgumentNotValidException.class
HttpMediaTypeNotAcceptableException.class,
ServletRequestBindingException.class,
ConversionNotSupportedException.class,
MissingServletRequestPartException.class,
AsyncRequestTimeoutException.class
})
@ResponseBody
public ErrorResponse handleServletException(Exception e) {
log.error(e.getMessage(), e);
int code = CommonResponseEnum.SERVER_ERROR.getCode();
try {
ServletResponseEnum servletExceptionEnum = ServletResponseEnum.valueOf(e.getClass().getSimpleName());
code = servletExceptionEnum.getCode();
} catch (IllegalArgumentException e1) {
log.error("class [{}] not defined in enum {}", e.getClass().getName(), ServletResponseEnum.class.getName());
}
if (ENV_PROD.equals(profile)) {
// 当为生产环境, 不适合把具体的异常信息展示给用户, 比如404.
code = CommonResponseEnum.SERVER_ERROR.getCode();
BaseException baseException = new BaseException(CommonResponseEnum.SERVER_ERROR);
String message = getMessage(baseException);
return new ErrorResponse(code, message);
}
return new ErrorResponse(code, e.getMessage());
}
/**
* 参数绑定异常
*
* @param e 异常
* @return 异常结果
*/
@ExceptionHandler(value = BindException.class)
@ResponseBody
public ErrorResponse handleBindException(BindException e) {
log.error("参数绑定校验异常", e);
return wrapperBindingResult(e.getBindingResult());
}
/**
* 参数校验异常,将校验失败的所有异常组合成一条错误信息
*
* @param e 异常
* @return 异常结果
*/
@ExceptionHandler(value = MethodArgumentNotValidException.class)
@ResponseBody
public ErrorResponse handleValidException(MethodArgumentNotValidException e) {
log.error("参数绑定校验异常", e);
return wrapperBindingResult(e.getBindingResult());
}
/**
* 包装绑定异常结果
*
* @param bindingResult 绑定结果
* @return 异常结果
*/
private ErrorResponse wrapperBindingResult(BindingResult bindingResult) {
StringBuilder msg = new StringBuilder();
for (ObjectError error : bindingResult.getAllErrors()) {
msg.append(", ");
if (error instanceof FieldError) {
msg.append(((FieldError) error).getField()).append(": ");
}
msg.append(error.getDefaultMessage() == null ? "" : error.getDefaultMessage());
}
return new ErrorResponse(ArgumentResponseEnum.VALID_ERROR.getCode(), msg.substring(2));
}
/**
* 未定义异常
*
* @param e 异常
* @return 异常结果
*/
@ExceptionHandler(value = Exception.class)
@ResponseBody
public ErrorResponse handleException(Exception e) {
log.error(e.getMessage(), e);
if (ENV_PROD.equals(profile)) {
// 当为生产环境, 不适合把具体的异常信息展示给用户, 比如数据库异常信息.
int code = CommonResponseEnum.SERVER_ERROR.getCode();
BaseException baseException = new BaseException(CommonResponseEnum.SERVER_ERROR);
String message = getMessage(baseException);
return new ErrorResponse(code, message);
}
return new ErrorResponse(CommonResponseEnum.SERVER_ERROR.getCode(), e.getMessage());
}
}
3、其他类型统一处理器
@Slf4j
@RestControllerAdvice
public class GlobalExceptionHandler {
/**
* 没有登录
* @param request
* @param response
* @param e
* @return
*/
@ExceptionHandler(NoLoginException.class)
public Object noLoginExceptionHandler(HttpServletRequest request,HttpServletResponse response,Exception e)
{
log.error("[GlobalExceptionHandler][noLoginExceptionHandler] exception",e);
JsonResult jsonResult = new JsonResult();
jsonResult.setCode(JsonResultCode.NO_LOGIN);
jsonResult.setMessage("用户登录失效或者登录超时,请先登录");
return jsonResult;
}
/**
* 业务异常
* @param request
* @param response
* @param e
* @return
*/
@ExceptionHandler(ServiceException.class)
public Object businessExceptionHandler(HttpServletRequest request,HttpServletResponse response,Exception e)
{
log.error("[GlobalExceptionHandler][businessExceptionHandler] exception",e);
JsonResult jsonResult = new JsonResult();
jsonResult.setCode(JsonResultCode.FAILURE);
jsonResult.setMessage("业务异常,请联系管理员");
return jsonResult;
}
/**
* 全局异常处理
* @param request
* @param response
* @param e
* @return
*/
@ExceptionHandler(Exception.class)
public Object exceptionHandler(HttpServletRequest request,HttpServletResponse response,Exception e)
{
log.error("[GlobalExceptionHandler][exceptionHandler] exception",e);
JsonResult jsonResult = new JsonResult();
jsonResult.setCode(JsonResultCode.FAILURE);
jsonResult.setMessage("系统错误,请联系管理员");
return jsonResult;
}
}
4、统一返回结果
code、message 是所有返回结果中必有的字段,而当需要返回数据时,则需要另一个字段 data 来表示。所以首先定义一个 BaseResponse 来作为所有返回结果的基类
然后定义一个通用返回结果类CommonResponse,继承 BaseResponse,而且多了字段 data;为了区分成功和失败返回结果,于是再定义一个 ErrorResponse
最后还有一种常见的返回结果,即返回的数据带有分页信息,因为这种接口比较常见,所以有必要单独定义一个返回结果类 QueryDataResponse,该类继承自 CommonResponse,只是把 data 字段的类型限制为 QueryDdata,QueryDdata中定义了分页信息相应的字段,即totalCount、pageNo、 pageSize、records。其中比较常用的只有 CommonResponse 和 QueryDataResponse,但是名字又贼鬼死长,何不定义2个名字超简单的类来替代呢?于是 R 和 QR 诞生了,以后返回结果的时候只需这样写:new R<>(data)、new QR<>(queryData)
因为这一套统一异常处理可以说是通用的,所有可以设计成一个
common包,以后每一个新项目/模块只需引入该包即可
参考文章:
Spring Boot后端接口规范
减少 try catch ,可以这样干