tensorflow实现简单线性回归( Linear Regression)
tensorflow实现简单线性回归( Linear Regression)
线性回归过程
线性回归中线性的含义:因变量y对于未知的回归系数是线性的。
- 准备数据集
- 建立线性模型:
随机初始化w和b
y=w·x+b,目标:求出权重w和偏置b - 确定损失函数(预测值与真实值之间的误差)–均方误差
- 梯度下降优化损失:需要指定学习率(超参数)
(0)导入依赖包
import tensorflow.compat.v1 as tf
tf.disable_v2_behavior()
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
(1)创建模拟数据
创建一个线性回归的模拟数据,y = x,一共20个点,再在这些点上加一些随机的噪音,数据用numpy生成
x_data = np.linspace(0, 10, 20) + np.random.uniform(-1.5, 1.5, 20)
y_data = np.linspace(0, 10, 20) + np.random.uniform(-1.5, 1.5, 20)
(2)初始化w和b
y = W * x + b
线性回归中,训练的参数就是权重(weight)w 和偏移(bais)b,用numpy随机生成w和b的初始值。
w = np.random.uniform(-1, 1)
b = np.random.uniform(-1, 1)
w和b是tensorflow中训练的对象,需要转换成tensorflow的变量。
w_tf = tf.Variable(w)
b_tf = tf.Variable(b)
(3)确定损失函数
确定损失函数(预测值与真实值之间的误差)-均方误差(Mean Square Error MSE)
error = 0
for x, y in zip(x_data, y_data):
error += (w_tf * x + b_tf - y) ** 2
(4)优化损失
线性回归,需要通过Gradient Decendent(梯度下降方法)训练w和b,优化损失。
optimizer = tf.train.GradientDescentOptimizer(learning_rate=0.001)
train = optimizer.minimize(error)
(5)开始训练
init = tf.global_variables_initializer()
train_steps = 10
with tf.Session() as sess:
sess.run(init)
for step in range(train_steps):
sess.run(train)
w_final, b_final = sess.run([w_tf, b_tf])
(6)检验训练成果
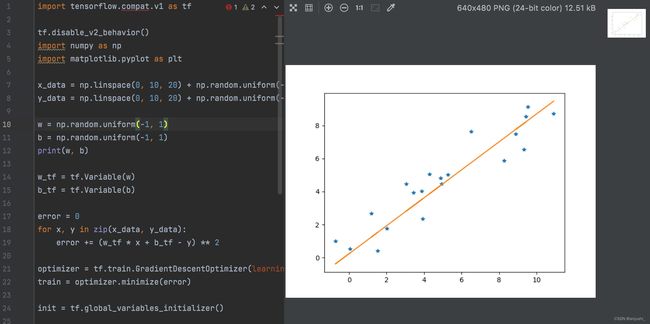
把原始数据和训练得到的结果通过plt.plot可视化
y_pred = w_final * x_data + b_final
print(w_final, b_final)
plt.plot(x_data, y_data, '*')
plt.plot(x_data, y_pred)
plt.show()
完整代码
import tensorflow.compat.v1 as tf
tf.disable_v2_behavior()
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# # ------------1. 获取训练数据--------------------------------------
x_data = np.linspace(0, 10, 20) + np.random.uniform(-1.5, 1.5, 20)
y_data = np.linspace(0, 10, 20) + np.random.uniform(-1.5, 1.5, 20)
# # ------------2.构造预测的线性回归函数 y = W * x + b------------------
w = tf.Variable(tf.random_uniform([1])) # 构造一个0~1的随机数
b = tf.Variable(tf.zeros([1])) # 设b的初始值为0
print(w, b)
w_tf = tf.Variable(w)
b_tf = tf.Variable(b)
# # ------------3.确定损失函数-----------------------------------------
error = 0
for x, y in zip(x_data, y_data):
error += (w_tf * x + b_tf - y) ** 2
# # ------------4.通过梯度下降方法优化损失--------------------------------
optimizer = tf.train.GradientDescentOptimizer(learning_rate=0.001)
train = optimizer.minimize(error)
# # ------------5.开始训练----------------------------------------------
init = tf.global_variables_initializer()
train_steps = 10
with tf.Session() as sess:
sess.run(init)
for step in range(train_steps):
sess.run(train)
w_final, b_final = sess.run([w_tf, b_tf])
# # ------------6.检验训练成果-----------------------------------------
y_pred = w_final * x_data + b_final
print(w_final, b_final)
plt.plot(x_data, y_data, '*')
plt.plot(x_data, y_pred)
plt.show()