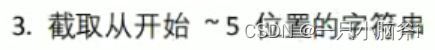Python 集合数据类型
第一章 变量类型
分为数字型和非数字型
- 数字型
- 整型(int)
- 浮点型(float)
- 布尔型(bool)
- 真True 非 0 数—非零即真
- 假 false 0
- 非数字型
- 列表
- 元组
- 集合
- 字典
- 字符串
在python 中,所有非数字类型都支持以下特点:
1、都是一个序列
2、通过变量名【索引】方式取值
3、通过 for in 遍历
4、可以计算长度、最大和最小值
第二章 变量进阶——列表
List (列表) 是Python 中使用最频繁的数据类型,在其他语言中叫做 数组,专门用于存储 一串信息。
列表的定义和使用
- 列表用 [ ] 定义
- 列表中多个成员用逗号隔开
- 列表可以使用 [索引] 方式访问指定成员
- 第一个成员的索引编号是 0
- 不能访问不存在的索引编号
# coding: utf-8
list1 = ['张三', '李四', '王五']
print(list1[0])
print(list1[1])
print(list1[2])
print(list1[3]) # 显示一个列表么有的成员会报错
空列表
- 通过 [ ] 定义一个空的列表
list2 = [] # 定义一个空列表变量叫 list2
print(list2[0]) # 对于空列表,不能访问成员
查看列表所有方法
- dir 列表变量名
print(dir(list1))
insert
* insert 作用是在列表指定位置插入指定的值
* 语法
insert(位置索引,要插入的值)
# coding: utf-8
list1 = ['张三', '李四', '王五']
list1.insert(3,'赵六')
print(list1)
append
- append作用是列表最后位置添加成员
- 语法
append(要添加成员的值)
# coding: utf-8
list1 = ['张三', '李四', '王五']
list1.insert(3,'赵六')
list1.append('孙七')
print(list1)
extend
- 把一个列表的成员追加到指定列表的后面
- 语法
extend(列表变量名)
# coding: utf-8
list1 = ['张三', '李四', '王五']
list1.insert(3,'赵六')
list1.append('孙七')
print(list1)
list2 = ['周八','吴九']
list1.extend(list2) # 把list2的所有成员,追加到list1的后面
print(list1)
修改成员列表的值
- 语法
列表变量名[索引] = 值
list1[1] = '郑十' # 修改第二个成员的值
删除成员值
- 语法
del(列表变量[索引])
del(list1[1])
- 语法
remove(要删除的值)
list1.remove('吴九')
- 语法
pop() # 删除列表最后一个成员
list1.pop()
- 语法
pop (索引) # 删除指定索引的值,功能与 del 类似
list1.pop(0) # 删除索引为 0 的成员
- 语法
clear() # 清空列表
list1.clear()
统计相同成员数量
- 语法
count (值) # 如果有多个值,返回值的数量,如果没有值,返回0
list1.count('张三')
返回指定值在列表中的索引编号
- 语法
index(指定的值,起始位置) # 如果不写起始位置,默认为 0,指定的值一定要存在,不然报错
list1.index('张三')
排序
- 语法
sort() # 对列表成员从小到大排序
list1.sort()
- 语法
sort(reverse=True) # 对列表成员从大到小排序
list1.sort(reverse=True)
逆置 / 反转
- 语法
reverse() # 把列表所有成员顺序颠倒
list1.reverse()
# coding: utf-8
list1 = ['张三', '李四', '王五']
list1.insert(3, '赵六')
list1.append('孙七')
print(list1)
list2 = ['周八', '吴九']
list1.extend(list2) # 把list2的所有成员,追加到list1的后面
print(list1)
list1[1] = '郑十' # 修改第二个成员的值
print(list1)
del (list1[1])
print(list1)
list1.remove('吴九')
print(list1)
list1.pop()
print(list1)
list1.pop(0) # 删除索引为 0 的成员
print(list1)
list1.clear()
print(list1)
list1 = ['张三', '李四', '张三', '王五', '张三']
print(list1.count('张三'))
print(list1.count('李四'))
print(list1.count('赵六'))
print(list1.index('张三'))
list1 = [1, 34, 64, 2, 7, 56, 98]
# list1.sort()
# list1.sort(reverse=True)
list1.reverse()
print(list1)
# coding: utf-8
list1 = []
list1.append(5)
list1.append(9)
list1.append(13)
print(list1)
孙七 改成 吴九
list2 = []
list2=['张三','李四','王五','赵六','孙七','周八']
list2[4]='吴九'
print(list2)
for遍历列表
- 语法
for 变量名 in 列表:
代码
列表中有多少成员,for就会循环多少次
变量名代表for 每次循环的时候,得到的列表成员的值
# coding: utf-8
list1=['张三','李四','王五']
for n in list1: # for循环三次,因为list1中有三个成员
print(n)
# for 第一次循环的时候 n 的值为'张三'
# for 第二次循环的时候 n 的值为'李四'
# for 第三次循环的时候 n 的值为'王五'
# coding: utf-8
list1=[0,3,3,9,10,3,5]
sum =0
for n in list1:
sum +=1
print(sum)
list1=[0,3,3,9,10,3,5]
sum = 0
for n in list1:
sum += n
print(sum)
拆包
- 语法
变量1,变量2,变量n = 列表变量
# 等号左边变量数量和等号右边的列表成员数量匹配
# coding: utf-8
list1=['张三','李四','王五']
# a=list1[0]
# b=list1[1]
# c=list1[2]
a,b,c=list1 # 等号左边变量数量和等号右边的列表成员数量匹配
print(a,b,c)
列表推导式
- 作用就是来快速的生成成员数量庞大的列表
- 语法
列表变量名 = [x for x in range(开始值,结束值,步长)]
列表变量名 = [x for x in range(开始值,结束值,步长) if 条件]
# coding:utf-8
list1 = [x for x in range(0,10)]
print(list1)
list1 = [x for x in range(0,100)]
print(list1)
list1 = [x for x in range(4,16,3)]
print(list1)
list1 = [x for x in range(6,-10,-2)]
print(list1)
list1 = [x for x in range(0,10)if x % 2==0]
print(list1)
# coding: utf-8
list1 = [x for x in range(0, 101, 10)]
print(list1)
list1 = [x for x in range(0, 101) if x % 10 == 0]
print(list1)
for遍历列表,处理列表成员为不同数据类型的情况
- 当列表中成员数据不统一,但又要在for中通过一条代码来处理不同类型的数据,需要把数据做一个强转
# coding: utf-8
list1 = ['张三', 2, 6.8, '曹操']
a = 1
for n in list1:
print('列表第%d成员的值是%s' % (a, str(n)))
a += 1
sum = 0
list1 = [56, '23','67',8]
for n in list1:
sum += int(n)
print(sum)
# coding: utf-8
list1 = ['笑眯眯', '乐呵', '嘎嘎乐', '笑哈哈','嘻嘻嘻']
num =0 # 存放为3 个字的,出现次数
for n in list1: # n 是列表中的每个成员,list1中有几个成员就循环几次
sum=0
for a in n: # a 是字符串中的每个字符,n 有几个字符for 就循环几次
sum += 1
if sum==3:
num += 1
print(num)
# sum出现3有多少次
# coding: utf-8
list1 = ['笑眯眯', '乐呵', '嘎嘎乐', '笑哈哈', '嘻嘻嘻']
# 判断列表中三个字的有几个
sum = 0
for n in list1:
if len(n) == 3:
sum+= 1
print(sum)
第三章 变量进阶——公共方法
len
- 返回非数字类型成员个数
- len(字符串)–返回字符串中字符的数量
- len(列表)–返回列表中成员的数量
list1=[1,3,5,8]
print(len(list1))
str1='hello'
print(len(str1))
list1=['张三','李四','王五']
print(len(list1))
# 如果Len 里面放的是列表,返回列表成员的数量
# 如果Len 里面放的是字符串,返回字符串中字符的个数
max
- 返回列表中最大值
max(列表) --列表中最大的值
max(字符串) --返回字符串中ASCII最大的那个字符
list1 = [23, 45, 77, 12, 99]
print(max(list1))
str2='hello'
print(max(str2))
min
- 返回列表中最小值
min(列表) --列表中最小的值
min(字符串) --返回字符串中ASCII最小的那个字符
list1 = [23, 45, 77, 12, 99]
print(min(list1))
str2='hello'
print(min(str2))
in
- 判断指定的值是否在列表中存在
指定的值 in 列表
# 这个操作对字符串同样有效
*** not in***
- 判断指定的值是否不在列表中
指定的值 not in 列表
# 这个操作对字符串同样有效
list3=[2,5,23,65]
if 5 in list3:
print('有5')
if 7 not in list3:
print('没有7')
str3 = 'hello'
if 'a' in list3:
print('有a')
if 'b' not in str3:
print('没有b')
练习——公共方法
定义一个列表变量
[‘张三’,‘李四’,‘王五’,‘赵六’,孙七’]
查找列表中是否有孙七,如果有将其删除
# coding: utf-8
list1=['张三','李四','王五','赵六','孙七']
if '孙七' in list1:
list1.remove('孙七')
print(list1)
list2 = [3, 5, 67, 2, 34, 12, 5, 11]
print(max(list2))
list2 = [3, 5, 67, 2, 34, 12, 5, 11]
# 求列表平均值
# 求平均值就是先求和,除以成员数量
sum = 0
for n in list2:
sum += n
print(sum/len(list2))
第四章 变量进阶——元组
元组定义
- 元组可以理解为一个只读的列表
- 成员不能修改,不能添加,不能删除的列表
- 语法
# coding: utf-8
tuple1 = ('张三', '李四', '王五', '赵六') # 定义一个元组,有四个成员
tuple2 = () # 定义一个空元组
tuple3 = ('张三',) # 如果元组中只有一个值,后面必须写逗号
tuple4 = '张三', '李四', '王五', '赵六' # 定义一个元组,有四个成员
tuple5 = '张三', # 如果元组中只有一个值,后面必须写逗号
tuple6 = '张三' # 定义的不是元组,是字符串
tuple7=('张三') # 定义的不是元组,是字符串
print(tuple1)
print(tuple2)
print(tuple3)
print(tuple4)
print(tuple5)
print(tuple6)
print(tuple7)
- 用小括号定义元组
- 小括号也可以省略
- 如果元组中有一个成员,那么成员后必须写一个逗号
元组的常用方法
- 元组[索引]
- 得到元组指定索引的值
- 但不能修改指定索引的值
- count
- index
- 公共方法
- len
- max
- min
- in
- not in
- 只要不涉及到修改成员的值,所有列表适用方法,元组通用
tuple1 = ('张三', '李四', '王五')
a = tuple1[1]
print(a)
# tuple1[1] = '赵六' # 元组的值不能修改
print(tuple1.count('张三'))
print(tuple1.index('张三'))
tuple2=(4,6,8.72)
print(len(tuple2))
print(max(tuple2) )
print(min(tuple2))
if 3 in tuple2:
print('3在元组tuple2中')
for遍历元组的方法
- for遍历元组的语法与遍历列表是一样的
for 变量名 in 元组名
代码
# coding: utf-8
tuple1=('张三','李四',2,34)
for n in tuple1:
print(n)
元组转列表
- 元组转列表
- list(元组)
- 列表转元组
- tuple(列表)
# coding: utf-8
list1 = [1, 2, 4, 8]
tuple1 = tuple(list1) # 把list1转为元组类型
print(tuple1)
tuple2 = (3, 5, 7, 9)
list2 = list(tuple2) # 把元组tuple2转为列表
print(list2)
练习
- 将元组 tuple1 元素追加到 list1 元素后面
# coding: utf-8
list1 = ['张三', '李四', '王五']
tuple1 = ('赵六', '孙七')
list1.extend(tuple1) # 改变的是list1,tuple1没改变
print(list1)
print(tuple1)
list1[3]='郑十'
print(list1)
print(tuple1)
把元组放到列表前
# coding: utf-8
list1 = ['张三', '李四', '王五']
tuple1 = ('赵六', '孙七')
a=0
for n in tuple1:
list1.insert(a,n)
a+=1
# 第一次循环a的值为 0insert(0.赵六)
# 第二次循环a的值为 1insert(1,孙七)
print(list1)
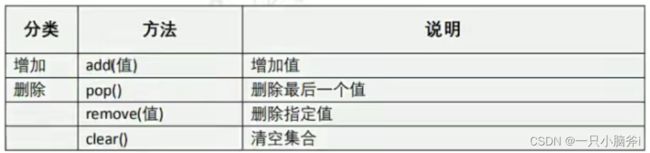
第五章 变量进阶——集合
集合定义
- 定义集合用{}
- 定义空集合用set()
- 集合与列表的区别
- 集合中所有成员是无序的,列表中所有成员是有序的
- 集合中成员的值不能重复,列表中成员的值可以重复
# coding: utf-8
set1={'张三','李四','王五'}
set2=set()
set3={'张三','李四','张三'}
print(set1)
print(set2)
print(set3)
- add添加值
- 集合变量.add(值)
set1.add('赵六')
print(set1)
- pop删除一个值
- 集合变量.pop()
set1.pop()
print(set1)
- remove删除指定的值
- 集合变量.remove(值)
set1.remove('张三')
print(set1)
- clear删除所有值
- 集合变量.clear()
set1.clear()
print(set1)
# coding: utf-8
set1 = set()
a = 0
while a < 5:
set1.add(int(input('请输入一个整数')))
a += 1
print(min(set1))
循环遍历集合
- 语法
for n in 集合变量:
循环中的代码
# coding: utf-8
set1={'张三','李四','王五'}
for n in set1:
print(n)
# 不管顺序是否对,遍历的结果,总能把集合中的每个成员都显示出来
# coding:utf-8
set1 = set()
a = 0
while a < 3:
set1.add(input('请输入字符串'))
a += 1
for n in set1:
print(n)
第六章 变量进阶——字典
字典的定义
- 用{}定义
- 用{}定义一个空字典
- 一个字典中可以存放多个键值对
- 键key,一个字典中键不能重复
- 值value
- 键和值用冒号分隔
- 字典和集合的区别
- 字典[键]=值
- 如果键存在,就是修改值
- 如果键不存在,就是新增键值对
# coding: utf-8
dict1 = {'name': '张三', 'age': '22', 'sex': '男'}
dict1['name']='李四' # 修改键name的对应值
print(dict1)
dict1['class']='1班' # 新增一个键值对,键为class,值为1班
print(dict1)
删除键值对
- pop(键)
dict1.pop('class') # 删除name键,一旦键被删除,对应的值也同时被删除
清空
- clear()
dict1.clear()
得到键对应的值 (查)
- 变量名=字典[键]
- 把键对应的值赋值给指定的变量
a=dict1['name'] # 得到键对应的值
print(a)
b=dict1['age'] # 得到键age 对应的值
print(b)
# coding: utf-8
dict1 = {'name': '周瑜', 'age': '32', 'id': '001'}
dict1['sex']='男'
dict1.pop('id')
dict1['age']='26'
print(dict1)
遍历字典
- 语法
for n in 字典:
代码
# n 是键
# coding: utf-8
dict1 = {'name': '周瑜', 'age': '32', 'id': '001'}
for n in dict1:
print(n,dict1[n]) # dict1[n] 意思是得到键对应的值
# 直接写n 代表输出键,dict1[n]代表输出键对应的值
通过items遍历字典
- 字典.items()返回一个包含键和值的元组
# coding: utf-8
dict1 = {'name': '周瑜', 'age': '32', 'id': '001'}
for n in dict1.items():
print(n)
# 使用字典items 方法, n 就是一个包含了键和值的元组
# n 是一个包含了两个成员的元组,第一个成员是键,第二个成员是值
# for循环3次
# for n in dict1.items():
# a, b = n # 对一个元组进行拆包
# print(a,b)
for a, b in dict1.items(): # a就是键,b就是键对应的值
print(a, b)
# coding:utf-8
dict1={'a':23,'b':4,'c':9,'d':3,'e':12}
for n in dict1:
print(n,dict1[n])
print('..........')
for a,b in dict1.items():
print(a,b)
练习–显示值9对应的键名
# coding:utf-8
dict1={'a':23,'b':4,'c':9,'d':3,'e':12}
for n in dict1:
if dict1[n]==9:
print(n) # 条件成立,就显示n,就是值9对应的键名
第七章 变量进阶——字符串
- 字符串中如果包含单引号,那么字符串用双引号引起来
- 字符串中如果包含双引号,那么字符串用单引号引起来
- 字符串中如果不包含引号,那么单双引号引字符无所谓
- 字符串中如果同时包含单双引号,那么必须用转义字符的方式实现
# coding: utf-8
str1 = '我"你'
print(str1)
str2 = "我'你"
print(str2)
str3 = "我\'你\"它"
print(str3)
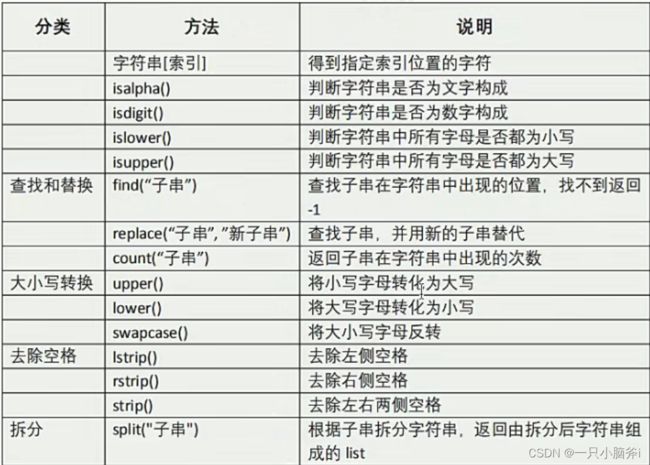
通过[索引]访问字符串中的指定位置字符
- 字符串[索引]
- 第一个字符的索引编号为 0
- 只能得到指定位置的字符,不能修改指定位置的字符
# coding: utf-8
str1='hello python'
a=str1[0] # a是字符串str1的第一个字符
print(a)
# str1[0]='b' 不能通过[索引]的方式修改字符串中具体字符的值
#字符串更像一个由字符串构成的元组
遍历字符串
- 语法
for n in 字符串:
代码
# coding: utf-8
str1='hello python'
for n in str1:
print(n)
得到字符串指定位置的字符
- 字符串[索引]
- 第一个字符的索引为 0
- 最后一个字符的索引为 -1
# coding: utf-8
str1='asdfgh'
print(str1[0])
print(str1[-1])
print(str1[-3])
判断字符串是否由纯字母组成
- isalpha()
- 如果条件成立,返回True,否则返回Flase
# coding: utf-8
str1='asdf123gh'
print(str1[0])
print(str1[-1])
print(str1[-3])
if str1.isalpha():
print('字符串都是由字母构成的')
判断字符串是否由纯数字组成
- isdigit()
- 如果字符串是纯数字组成,返回True,否则返回Flase
str2='1243asd45'
if str2.isdigit():
print('str2是由纯数字组成的')
练习
str1=input('请输入一个整数')
str2=input('请输入一个整数')
if str1.isdigit()and str2.isdigit():
a=int(str1)
b=int(str2)
print(a+b)
else:
print('只能数字不能其他')
islower
- 判断字符串是否全部由小写字母构成
isupper
- 判断字符串是否全部由大写字母构成
# coding: utf-8
str1='ajsnsjc'
if str1.islower():
print('str1全部使用小写构成')
str2='SDUSCJNJ'
if str2.isupper():
print('str2全部使用大写构成')
find
- 查找子串在字符串中的位置
- 找到返回子串位置,找不到返回-1
# coding: utf-8
str1='hello python'
a=str1.find('python')
print(a)
a=str1.find('nsansk')
print(a)
replace
- 替换子串
# coding: utf-8
str1='hello python'
a=str1.find('python')
print(a)
a=str1.find('nsansk')
print(a)
str2=str1.replace('python','world')
# 没有改变str1,只是把str1中的 python 变成 world给str2了
# str1 的值并没有改变
print(str2)
count
- 查找子串出现次数
- 找到返回次数,找不到返回 0
str3='hello worle hello python'
a=str3.count('hello')
print(a)
a=str3.count('b')
print(a)
upper
- 把字符串中的小写字母改成大写字母
lower
- 把字符串中的大写字母改成小写字母
swapcase
- 把字符串中大小写字母反转
# coding: utf-8
str1='AbCdEf'
str2=str1.upper() # str1的值并没有改变,str2是改变后的结果
print(str2)
str2=str1.lower()
print(str2)
str2=str1.swapcase()
print(str2)
lstrip
- 去除左侧空格
rstrip
- 去除右侧空格
strip
- 同时去除左右两侧空格
# coding: utf-8
str1 = ' aaaaaaa '
str2 = str1.lstrip()
print(str2)
str2 = str1.rstrip()
print(str2)
print("'%s'" % str1) # 格式化更清晰
print("'%s'" % str2)
str2=str1.strip()
print("'%s'" % str2)
split
- 根据子串拆分字符串
- 拆分后的结果,放到一个列表中
# coding: utf-8
str1='aaa_bbb_ccc_ddd'
list1=str1.split('_')
print(list1)
str2='123&345&324'
list2=str2.split('&')
print(list2)
去除字符串中间的空格
# coding: utf-8
str1='aaa nnn ffff wwww'
str2=str1.replace(' ','')
print(str2)
字符串形式的数学运算式(eval)
# print(eval("9*7+12-5"))
ope='9*7+12-5'
res=eval(ope)
print(res)
输出浮点数转化为整数
print (int(eval("9*7+12-5")))
ope='9*7+12-5'
res=int(eval(ope))
print(res)
格式化字符串
- %x意思是把一个十进制数按照十六进制方式显示,asdddfg用小写表示
- %X意思是把一个十进制数按照十六进制方式显示,ASDDDFG用大写表示
# coding: utf-8
print('%x' % 9)
print('%x' % 10) # 十进制的10就是十六进制的a
print('%x' % 16) # 十进制的16就是十六进制的10
print('%X' % 15) # 十进制的15就是十六进制的f
# 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 a b c d e f 10 11 12 13 14....
print('%X' % 10)
str1='我是%s,年龄是%d'%('小明',20) # 把格式化字符串的结果放到变量 str1 中
print(str1)
id = 1
name = '张三'
weight = 80.2
tel = '12345678909'
print('*' * 20)
print('编号%06d' % id)
print('姓名:%s' % name)
print('体重:%.3f' % weight)
print('电话:%s' % tel)
print('*' * 20)
字符串的切片
切片
- 只要可以使用[索引]访问成员数据类型,都可用切片
- [开始索引:结束索引:步长]
- 包含开始索引
- 不包含结束索引
- 省略开始索引,默认从0开始
- 省略结束索引,默认到最后
- 省略步长,默认步长为 1
# coding: utf-8
str1 = 'abcdefg'
str2 = str1[2:4:1]
print(str2)
str2=str1[:4:1]
print(str2)
str2=str1[2::1]
print(str2)
str2=str1[2:4:]
print(str2)
列表切片
list1=['张三','李四','王五','赵六','孙七']
list2=list1[1:4:]
print(list2)
切片练习
# coding: utf-8
list1 = ['孙七', '赵六', '王五', '李四', '张三']
list1 = list1[::-1]
print(list1)
# 列表成员逆置
# 遍历列表,把字符串逆置
for n in list1:
str1 = n[::-1]
print(str1)
index = 0 # 定义一个变量 index ,值为 0
for n in list1:
str1 = n[::-1] # str1是n 颠倒后的结果
list1[index] = str1
index += 1
print(list1)
索引值为一个变量的用例
- 列表或者元组、字符串都经常用 [索引] 的方式访问成员
- [索引] 可以是一个具体的数字,也可以是一个变量
a = 1
列表[a] = '张三' # 相当于列表[1] = '张三'
多维列表(了解)
- 一个列表的成员,又是一个列表,这种列表就是多维列表
# coding: utf-8
list1 = [['张三', '李四', '王五'], ['郑十', '吴九', '周八']]
# list1是一个多维列表,有两个成员
# 第一个成员是个列表['张三','李四','王五']
# 第二个成员也是个列表 ['郑十','吴九','周八']
a = list1[1] # a是一个列表 ['郑十','吴九','周八']
print(a)
print(a[1]) # 显示列表 a 的第二个成员