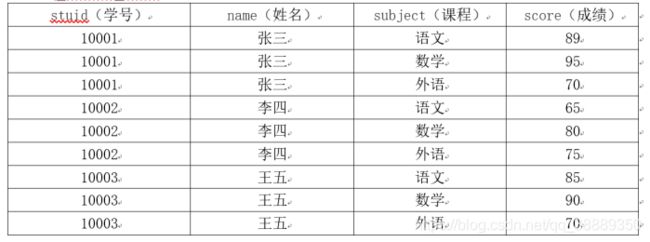
sql统计-关于学生成绩
-
计算每个人的总成绩并排名(要求显示字段:姓名,总成绩)
-
计算每个人的总成绩并排名(要求显示字段: 学号,姓名,总成绩)
-
计算每个人单科的最高成绩(要求显示字段: 学号,姓名,课程,最高成绩)
-
计算每个人的平均成绩(要求显示字段: 学号,姓名,平均成绩)
-
列出各门课程成绩最好的学生(要求显示字段: 学号,姓名,科目,成绩)
-
列出各门课程成绩最好的两位学生(要求显示字段: 学号,姓名,科目,成绩)
-
统计如下:
| 学号 | 姓名 | 语文 | 数学 | 英语 | 总分 | 平均分 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| . |
-
列出各门课程的平均成绩(要求显示字段:课程,平均成绩)
-
列出数学成绩的排名(要求显示字段:学号,姓名,成绩,排名)
-
列出数学成绩在2-3名的学生(要求显示字段:学号,姓名,科目,成绩)
-
求出李四的数学成绩的排名
-
12.统计如下:
| 课程 | 不及格(0-59)个 | 良(60-80)个 | 优(81-100)个 |
|---|---|---|---|
| . |
- 计算每个人的总成绩并排名
select name,sum(score) as allscore from stuscore group by name order by allscore
- 计算每个人的总成绩并排名
select distinct t1.name,t1.stuid,t2.allscore from stuscore t1,
(
select stuid,sum(score) as allscore from stuscore group by stuid
)t2
where t1.stuid=t2.stuid
order by t2.allscore desc
- 计算每个人单科的最高成绩
select t1.stuid,t1.name,t1.subject,t1.score from stuscore t1,
(
select stuid,max(score) as maxscore from stuscore group by stuid
) t2
where t1.stuid=t2.stuid and t1.score=t2.maxscore
4.计算每个人的平均成绩
select distinct t1.stuid,t1.name,t2.avgscore from stuscore t1,
(
select stuid,avg(score) as avgscore from stuscore group by stuid
) t2
where t1.stuid=t2.stuid
5.列出各门课程成绩最好的学生
select t1.stuid,t1.name,t1.subject,t2.maxscore from stuscore t1,
(
select subject,max(score) as maxscore from stuscore group by subject
) t2
where t1.subject=t2.subject and t1.score=t2.maxscore
6.列出各门课程成绩最好的两位学生
select distinct t1.* from stuscore t1
where t1.stuid in
(select top 2 stuscore.stuid from stuscore where subject = t1.subject order by score desc)
order by t1.subject
7.学号 姓名 语文 数学 英语 总分 平均分
select stuid as 学号,name as 姓名,
sum(case when subject='语文' then score else 0 end) as 语文,
sum(case when subject='数学' then score else 0 end) as 数学,
sum(case when subject='英语' then score else 0 end) as 英语,
sum(score) as 总分,(sum(score)/count(*)) as 平均分
from stuscore
group by stuid,name
order by 总分desc
8.列出各门课程的平均成绩
select subject,avg(score) as avgscore from stuscore
group by subject
9.列出数学成绩的排名
declare @tmp table(pm int,name varchar(50),score int,stuid int)
insert into @tmp select null,name,score,stuid from stuscore where subject='数学' order by score desc
declare @id int
set @id=0;
update @tmp set @id=@id+1,pm=@id
select * from @tmp
- 列出数学成绩在2-3名的学生
select t3.* from
(
select top 2 t2.* from (
select top 3 name,subject,score,stuid from stuscore where subject='数学'
order by score desc
) t2 order by t2.score
) t3 order by t3.score desc
- 求出李四的数学成绩的排名
declare @tmp table(pm int,name varchar(50),score int,stuid int)
insert into @tmp select null,name,score,stuid from stuscore where subject='数学' order by score desc
declare @id int
set @id=0;
update @tmp set @id=@id+1,pm=@id
select * from @tmp where name='李四'
- 课程 不及格(-59) 良(-80) 优(-100)
select subject,
(select count(*) from stuscore where score<60 and subject=t1.subject) as 不及格,
(select count(*) from stuscore where score between 60 and 80 and subject=t1.subject) as 良,
(select count(*) from stuscore where score >80 and subject=t1.subject) as 优
from stuscore t1 group by subject
- 数学:张三(50分),李四(90分),王五(90分),赵六(76分)
declare @s varchar(1000)
set @s=''
select @s =@s+','+name+'('+convert(varchar(10),score)+'分)' from stuscore where subject='数学'
set @s=stuff(@s,1,1,'')
print '数学:'+@s
从student表中查询年龄18~22岁的学生信息
第一种:
SELECT id,name,sex,2013-birth AS age,department,address
FROM student
WHERE 2017-birth BETWEEN 18 AND 22;
第二种:
SELECT id,name,sex,2013-birth AS age,department,address
FROM student
WHERE 2013-birth>=18 AND 2013-birth<=22;
从student表中查询每个院系有多少人
SELECT department, COUNT(id) FROM student GROUP BY department;
count(*) 和 count(1)和count(列名)区别 :
count(*)包括了所有的列,相当于行数,在统计结果的时候,不会忽略列值为NULL
count(1)包括了忽略所有列,用1代表代码行,在统计结果的时候,不会忽略列值为NULL
count(列名)只包括列名那一列,在统计结果的时候,会忽略列值为空(这里的空不是只空字符串或者0,而是表示null)的计数,即某个字段值为NULL时,不统计。
执行效率上:
列名为主键,count(列名)会比count(1)快
列名不为主键,count(1)会比count(列名)快
如果表多个列并且没有主键,则 count(1) 的执行效率优于 count(*)
如果有主键,则 select count(主键)的执行效率是最优的
如果表只有一个字段,则 select count(*)最优。