自动摘要生成 tf-idf+doc2vec+句子聚类
多文档自动摘要
目录
多文档自动摘要
1 计划
2 baseline+改进1+改进2
baseline:
文档格式如下:
python代码如下:
实现TF-IDF的计算:
改进1:
改进2:
1 计划
1.了解bat文件的作用,处理文件输入
2.先完成一个主题的自动摘要,再完成多个主题的摘要
3.与专家摘要进行对比,评估
2 baseline+改进1+改进2
baseline:
依次抽取10个文档中,每个文档的第一句话,组成摘要。
文档格式如下:
APW19981118.0276
NEWS
NEWSWIRE
Cambodian leader Hun Sen has guaranteed the safety and political freedom
of all politicians, trying to ease the fears of his rivals that they
will be arrested or killed if they return to the country. The assurances
were aimed especially at Sam Rainsy, leader of a vocally anti-Hun
Sen opposition party, who was forced to take refuge in the U.N. offices
in September to avoid arrest after Hun Sen accused him of being behind
a plot against his life. Sam Rainsy and the 14 members of parliament
from his party have been holed up overseas for two months. But a deal
reached between Hun Sen and his chief rival, Prince Norodom Ranariddh,
on forming a new government last week has opened the door for their
return. In a letter to King Norodom Sihanouk _ the prince's father
and Cambodia's head of state _ that was broadcast on television Tuesday,
Hun Sen said that guarantees of safety extended to Ranariddh applied
to all politicians. His assurances come a week before the first session
of Cambodia's new parliament, the National Assembly. Sam Rainsy said
Wednesday that he was unsatisfied with the guarantee. He said it contained
indirect language and loopholes that suggest he and his Sam Rainsy
Party members are still under threat of arrest from Hun Sen's ruling
party. ``It should be easy for them to say, `Rainsy and the SRP members
of the assembly have no charges against them and will not be arrested,'''
the opposition leader said in a statement. ``But instead they make
roundabout statements, full of loopholes that can easily be exploited
by a legal system that is completely in their control.'' Ranariddh
told reporters Wednesday that he believed it was safe for Sam Rainsy
in Cambodia. Speaking upon his return from a brief stay in Bangkok,
the prince said he would soon meet with Hun Sen to discuss the apportioning
of ministries in the new coalition government. Last week, Hun Sen's
Cambodian People's Party and Ranariddh's FUNCINPEC party agreed to
form a coalition that would leave Hun Sen as sole prime minister and
make the prince president of the National Assembly. The deal assures
the two-thirds vote in parliament needed to approve a new government.
The men served as co-prime ministers until Hun Sen overthrew Ranariddh
in a coup last year. ``I think Hun Sen has got everything. He's got
the premiership and legitimacy through the election and recognition
from his majesty the king. I don't think there is any benefit for
Hun Sen to cause instability for our country,'' Ranariddh said. The
prince also said that his top general, Nhek Bunchhay, would not be
given back his previous position as the second-ranking general in
the Cambodian military's general staff. Nhek Bunchhay's outnumbered
forces in the capital put up tough but unsuccessful resistance to
last year's coup.
python代码如下:
'''
Created by hjn On 2020.5.18
读取DUC数据集中一个主题,10个文档的text内容
'''
import os
# 遍历文件夹
for roots, dirs, files in os.walk("E:\pycharm_workspace\data_mining\data_classification\dataset"):
for dir in dirs:
# print(dir)
final_result = []
for file in os.listdir("E:\pycharm_workspace\data_mining\data_classification\dataset\\"+dir):
# print(file)
path = os.path.join("E:\pycharm_workspace\data_mining\data_classification\dataset", dir, file)
f = open(path)
result = []
while True:
lines = f.readline()
if not lines:
break
pass
else:
result.append(lines)
result_str = ' '.join(result).replace('\n', '')
text_temp = result_str.split("")
text = text_temp[1].replace(" ", "")
senetences = text.split(".")
final_result.append(senetences[0])
for row in final_result:
print(row, end='.')
print()
实现TF-IDF的计算:
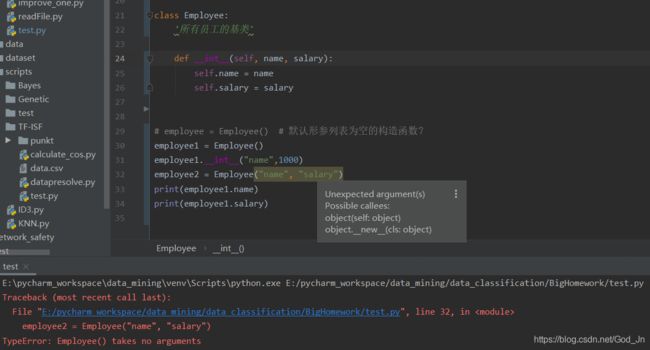
学习类的创建和使用
遇到的诡异问题,见图:
计算tf-idf和句子间的相似度:
"""
Created by hjn On 2020.5.30
读取DUC数据集中一个主题,10个文档的text内容,计算tf-idf
"""
# coding=utf-8
import os
from sklearn.feature_extraction.text import CountVectorizer, TfidfTransformer
from nltk import data
from nltk.corpus import stopwords
from nltk.tokenize import word_tokenize
from nltk.stem import PorterStemmer
# 离线加载nltk_data
data.path.append(r"C:/Users/HJN/nltk_data/tokenizers/punkt")
# 去除stopwords 和 词干化
set(stopwords.words('english'))
stop_words = set(stopwords.words('english'))
# 标点符号集合
punctuation = [',', '.', '“', '”', '(', ')', '‘', '’', '\'', '`']
def data_presolve(text):
"去除text中的停用词,并进行词干化"
word_tokens = word_tokenize(text)
filtered_sentence = []
for w in word_tokens:
if w not in stop_words:
filtered_sentence.append(w)
Stem_words = []
ps = PorterStemmer()
for w in filtered_sentence:
rootWord = ps.stem(w)
Stem_words.append(rootWord)
# print(filtered_sentence) # 去除停用词的结果
# print(Stem_words) # 词干化的结果
# 去除列表中的, . “ ”
for letter in punctuation:
while letter in Stem_words:
Stem_words.remove(letter)
return Stem_words
# 存储句子
short_sentence = []
# # 存储句子的分词结果
# short_sentence_split = []
# 存储长句子
doc_str = ""
# 遍历文件夹
for root, dirs, files in os.walk("E:/pycharm_workspace/data_mining/data_classification/data"):
# print(root)
# print(dirs)
# print(files)
for file in files:
path = os.path.join(root, file)
f = open(path)
result = []
while True:
lines = f.readline()
# print(lines)
if not lines:
break
pass
else:
result.append(lines)
#
# for row in result:
# print(row)
result_str = ' '.join(result).replace('\n', '')
# print(result_str)
text_temp = result_str.split("")
# print(text_temp[1])
text = text_temp[1].replace(" ", "")
doc_str += text
sentences = text.split(". ") # 问题:句子切分待优化
for sentence in sentences:
sentence_split = data_presolve(sentence) # 进行句子切分、去除停用词、单词词干化
sentence_str = ' '.join(sentence_split)
short_sentence.append(sentence_str) # 添加句子集合
sentence_split = data_presolve(doc_str) # 进行句子切分、去除停用词、单词词干化
sentence_str = ' '.join(sentence_split)
short_sentence.append(doc_str)
vectorizer = CountVectorizer() # 将文本中的词语转换为词频矩阵
X = vectorizer.fit_transform(short_sentence) # 计算词语出现的次数
word = vectorizer.get_feature_names() # 获取词袋中所有文本关键词
# print(X.toarray()) # 查看词频结果
transformer = TfidfTransformer()
tf_idf = transformer.fit_transform(X)
# print(tf_idf.toarray())
weight = tf_idf.toarray()
# for i in range(len(weight)): # 打印每类文本的tf-idf词语权重,第一个for遍历所有文本,第二个for便利某一类文本下的词语权重
# print(u"-------这里输出第", i, u"类文本的词语tf-idf权重------")
# for j in range(len(word)):
# print(word[j], " ", weight[i][j])
from sklearn.metrics.pairwise import linear_kernel
cosine_similarities = linear_kernel(tf_idf[-1:], tf_idf).flatten() # 计算长句子和短句子之间的句子相似度
# print(cosine_similarities)
# flatten把数组扁平化变成一维数组
# 假设一个数组z为[[0,1,19],[20,67,3]],
# 当使用numpy.argsort(z,axis=None)时,系统先用flatten()把z扁平化为[0,1,19,20,67,3]
related_docs_indices = cosine_similarities.argsort()[::-1]
print(related_docs_indices)
# [::-1]第一个冒号的作用是对整个字符串进行排序,::-1中的-1代表的是步长,作用是逆序
# related_docs_indices:与tf_idf[-1:](即十个文档合成的句子)句子相似度最接近的句子,order=降序
result = ""
topic_set = []
last_similarity = 0.0
similarity = 0.0
# print(cosine_similarities[related_docs_indices])
for i in related_docs_indices:
if i != 211: # 长句子不能放入摘要集合
for index in topic_set:
# 每选一个摘要句,需要和摘要集中的所有句子进行相似度比较,只有当相似度小于某个阈值的句子才能选入摘要集合
last_similarity = linear_kernel(tf_idf[index:index+1], tf_idf[i:i+1]).flatten()
if last_similarity > similarity: # similarity取最大值
similarity = last_similarity
if similarity < 0.8: # 该句子与摘要集合内的最大句子相似度
topic_set.append(i)
result += short_sentence[i]
result += ". "
if len(result.encode()) >= 665:
# 重复上述步骤,直到摘要集合中的词语数达到665bytes,算法终止。
break
# print(result)
改进1:
将切分后的句子进行聚类形成k个簇,
将各个簇看成一个句子
句子重要性度量
计算各个簇ci和簇中包含的句子sj之间的余弦相似度
计算各个簇ci和整个topic之间的余弦相似度
句子转化为向量,再进行k-means聚类:
"""
Created by hjn On 2020.6.2
分句之后,进行句子聚类
"""
# coding=utf-8
import os
import pandas as pd
import math
from gensim.models import Doc2Vec
from gensim.models.doc2vec import TaggedDocument
from sklearn.cluster import KMeans
from sklearn.feature_extraction.text import CountVectorizer, TfidfTransformer
from nltk import data
from nltk.corpus import stopwords
from nltk.tokenize import word_tokenize
from nltk.stem import PorterStemmer
# 离线加载nltk_data
data.path.append(r"C:\Users\HJN\nltk_data\tokenizers\punkt")
# 去除stopwords 和 词干化
set(stopwords.words('english'))
stop_words = set(stopwords.words('english'))
# 标点符号集合
punctuation = [',', '.', '“', '”', '(', ')', '‘', '’', '\'', '`']
def data_presolve(sentence):
"""
去除text中的停用词,并进行词干化
:param sentence:
:return:
"""
word_tokens = word_tokenize(sentence)
filtered_sentence = []
for w in word_tokens:
if w not in stop_words:
filtered_sentence.append(w)
Stem_words = []
ps = PorterStemmer()
for w in filtered_sentence:
rootWord = ps.stem(w)
Stem_words.append(rootWord)
# print(filtered_sentence) # 去除停用词的结果
# print(Stem_words) # 词干化的结果
# 去除列表中的, . “ ”
for letter in punctuation:
while letter in Stem_words:
Stem_words.remove(letter)
return Stem_words
def split_sentence(path):
"""
读取一个主题里的十个文档,并进行短句子划分
:param path:
:return:
"""
# 存储句子
short_sentence = []
# 存储长句子
doc_str = ""
# 遍历文件夹
for root, dirs, files in os.walk(path):
# print(root)
# print(dirs)
# print(files)
for file in files:
path = os.path.join(root, file)
f = open(path)
result = []
while True:
lines = f.readline()
# print(lines)
if not lines:
break
pass
else:
result.append(lines)
#
# for row in result:
# print(row)
result_str = ' '.join(result).replace('\n', '')
# print(result_str)
text_temp = result_str.split("")
# print(text_temp[1])
text = text_temp[1].replace(" ", "")
doc_str += text
sentences = text.split(". ")
for sentence in sentences:
sentence_split = data_presolve(sentence=sentence) # 进行句子切分、去除停用词、单词词干化
sentence_str = ' '.join(sentence_split)
short_sentence.append(sentence_str) # 添加句子集合
sentence_split = data_presolve(doc_str) # 进行句子切分、去除停用词、单词词干化
sentence_str = ' '.join(sentence_split)
short_sentence.append(doc_str)
return short_sentence
def sentence_k_means(short_sentence):
"""
用于生成句向量和对句子进行聚类
:param short_sentence:
:return:
"""
i = 0
sentenceLabeled = []
for sentence in short_sentence:
sentenceL = TaggedDocument(words=sentence, tags=['SENT_%s' % i])
i += 1
sentenceLabeled.append(sentenceL)
model = Doc2Vec(vector_size=300, window=10, min_count=0, workers=11, alpha=0.025, min_alpha=0.025, epochs=100)
model.build_vocab(sentenceLabeled)
for epoch in range(1):
print("epoch %s,training......" % epoch)
model.train(sentenceLabeled, total_examples=model.corpus_count, epochs=model.epochs)
model.alpha -= 0.002 # decrease the learning rate
model.min_alpha = model.alpha # fix the learning rate, no decay
textVect = model.docvecs.vectors_docs
## K-means ##
num_clusters = math.ceil(pow(i + 1, 0.5))
km = KMeans(n_clusters=num_clusters)
km.fit(textVect)
clusters = km.labels_.tolist()
## Print Sentence Clusters ##
cluster_info = {'sentence': short_sentence, 'cluster': clusters}
# for num in range(len(short_sentence)): # 输出每个句子和对应的类别号
# print(cluster_info['sentence'][num], " ", cluster_info['cluster'][num])
sentenceDF = pd.DataFrame(cluster_info, index=[clusters], columns=['sentence', 'cluster'])
'''
sentence cluster
2 cambodian leader hun sen friday reject opposit... 2
3 govern opposit parti ask king norodom sihanouk... 3
2 opposit leader princ norodom ranariddh sam rai... 2
2 hun sen howev reject 2
5 `` I would like make clear meet relat cambodia... 5
.. ... ...
4 the remain senat said select method agre upon ... 4
1 hun sen said monday cpp funcinpec agre senat w... 1
12 other detail senat includ much power given pro... 12
10 10
10 Cambodian leader Hun Sen on Friday rejected o... 10
[212 rows x 2 columns]
'''
# print(sentenceDF)
# for sentence in short_sentence:
# print(sentence, end=' ')
# for cluster in clusterDF.loc[sentence]['cluster'].values.tolist():
# print(cluster)
# print()
for num in range(num_clusters):
print()
print("Sentence cluster %d: " % int(num + 1), end='')
print()
'''
.ix is deprecated. Please use
.loc for label based indexing or
.iloc for positional indexing
'''
for sentence in sentenceDF.loc[num]['sentence'].values.tolist():
print(' %s ' % sentence, end='')
print()
print()
if __name__ == '__main__':
path = "E:/pycharm_workspace/data_mining/data_classification/data"
short_sentence = split_sentence(path=path)
sentence_k_means(short_sentence)
句子排序
对每个簇ci中的句子sj,按照相似度分值的大小进行排序
对每个簇ci,按照余弦相似度的大小进行排序
从排序最高的簇到排序最低的簇,依次选取每个簇的排序最高句子
一轮过后,再从排序最高的簇到排序最低的簇,依次选取每个簇的排序次高句子
改进1的实现
"""
Created by hjn On 2020.6.2
分句之后,进行句子聚类
"""
# coding=utf-8
import os
import pandas as pd
import math
from gensim.models import Doc2Vec
from gensim.models.doc2vec import TaggedDocument
from sklearn.cluster import KMeans
from sklearn.feature_extraction.text import CountVectorizer, TfidfTransformer
from nltk import data
from nltk.corpus import stopwords
from nltk.tokenize import word_tokenize
from nltk.stem import PorterStemmer
# 离线加载nltk_data
data.path.append(r"C:\Users\HJN\nltk_data\tokenizers\punkt")
# 去除stopwords 和 词干化
set(stopwords.words('english'))
stop_words = set(stopwords.words('english'))
# 标点符号集合
punctuation = [',', '.', '“', '”', '(', ')', '‘', '’', '\'', '`']
def data_presolve(sentence):
"""
去除text中的停用词,并进行词干化和句子切分
:param sentence: 输入的原始句子
:type sentence str
:return: 句子经过切分后的所有词语
"""
word_tokens = word_tokenize(sentence)
filtered_sentence = []
for w in word_tokens:
if w not in stop_words:
filtered_sentence.append(w)
Stem_words = []
ps = PorterStemmer()
for w in filtered_sentence:
rootWord = ps.stem(w)
Stem_words.append(rootWord)
# print(filtered_sentence) # 去除停用词的结果
# print(Stem_words) # 词干化的结果
# 去除列表中的, . “ ”
for letter in punctuation:
while letter in Stem_words:
Stem_words.remove(letter)
return Stem_words
def split_sentence(path):
"""
读取一个主题里的所有文档,并进行短句子划分
:param path: 主题的文件夹路径
:type path str
:return: 返回经过处理后的句子列表(最后一个是长句子)和原始句子列表(最后一个是长句子)
"""
# 存储句子
original_sentence = []
short_sentence = []
# 存储长句子
doc_str = ""
# 遍历文件夹
for root, dirs, files in os.walk(path):
# print(root)
# print(dirs)
# print(files)
for file in files:
path = os.path.join(root, file)
f = open(path)
result = []
while True:
lines = f.readline()
# print(lines)
if not lines:
break
pass
else:
result.append(lines)
#
# for row in result:
# print(row)
result_str = ' '.join(result).replace('\n', '')
# print(result_str)
text_temp = result_str.split("")
# print(text_temp[1])
text = text_temp[1].replace(" ", "")
doc_str += text
sentences = text.split(". ")
for sentence in sentences:
sentence_split = data_presolve(sentence=sentence) # 进行句子切分、去除停用词、单词词干化
sentence_str = ' '.join(sentence_split)
original_sentence.append(sentence) # 添加原始句子
short_sentence.append(sentence_str) # 添加经过处理后的句子集合
sentence_split = data_presolve(doc_str) # 进行句子切分、去除停用词、单词词干化
sentence_str = ' '.join(sentence_split)
original_sentence.append(doc_str)
short_sentence.append(sentence_str)
return short_sentence, original_sentence
def sentence_k_means(short_sentence):
"""
通过doc2vec,生成句向量;通过sklearn的k-mearns,对句子进行聚类
:param short_sentence: 经过处理后的句子列表(最后一个是长句子)
:type short_sentence list
:return: 返回一维列表,内容是:每个句子对应的类别号形成的列表和总的类别数
"""
i = 0
sentenceLabeled = []
for sentence in short_sentence:
sentenceL = TaggedDocument(words=sentence, tags=['SENT_%s' % i])
i += 1
sentenceLabeled.append(sentenceL)
model = Doc2Vec(vector_size=300, window=10, min_count=0, workers=11, alpha=0.025, min_alpha=0.025, epochs=100)
model.build_vocab(sentenceLabeled)
for epoch in range(20):
# print("epoch %s,training......" %epoch)
model.train(sentenceLabeled, total_examples=model.corpus_count, epochs=model.epochs)
model.alpha -= 0.002 # decrease the learning rate
model.min_alpha = model.alpha # fix the learning rate, no decay
textVect = model.docvecs.vectors_docs
## K-means ##
num_clusters = math.ceil(pow(i + 1, 0.5))
km = KMeans(n_clusters=num_clusters)
km.fit(textVect)
clusters = km.labels_.tolist()
# Print Sentence Clusters ##
# cluster_info = {'sentence': short_sentence, 'cluster': clusters}
# sentenceDF = pd.DataFrame(cluster_info, index=[clusters], columns=['sentence', 'cluster'])
# sentence_clusters = []
# for num in range(num_clusters):
# # print()
# # print("Sentence cluster %d: " % int(num + 1), end='')
# # print()
# sentence_cluster = []
# '''
# .ix is deprecated. Please use
# .loc for label based indexing or
# .iloc for positional indexing
# '''
# for sentence in sentenceDF.loc[num]['sentence'].values.tolist():
# # print(' %s ' % sentence, end='')
# # print()
# sentence_cluster.append(sentence)
# # print()
# sentence_clusters.append(sentence_cluster)
return clusters, num_clusters
def calculate_cosine(short_sentence):
"""
计算句子间的相似度
:param short_sentence: 经过处理后的句子列表(最后一个是长句子)
:type short_sentence list
:return: 返回最后一个句子和其他句子之间的句子相似度形成的列表,列表的长度等于short_sentence的长度
"""
vectorizer = CountVectorizer() # 将文本中的词语转换为词频矩阵
X = vectorizer.fit_transform(short_sentence) # 计算词语出现的次数
word = vectorizer.get_feature_names() # 获取词袋中所有文本关键词
transformer = TfidfTransformer()
tf_idf = transformer.fit_transform(X)
weight = tf_idf.toarray()
# for i in range(len(weight)): # 打印每类文本的tf-idf词语权重,第一个for遍历所有文本,第二个for便利某一类文本下的词语权重
# print(u"-------这里输出第", i, u"类文本的词语tf-idf权重------")
# for j in range(len(word)):
# print(word[j], " ", weight[i][j])
from sklearn.metrics.pairwise import linear_kernel
cosine_similarities = linear_kernel(tf_idf[-1:], tf_idf).flatten() # 计算长句子和短句子之间的句子相似度
# related_docs_indices = cosine_similarities.argsort()[::-1]
return cosine_similarities
def calculate_cosine_clusters(short_sentence, clusters, num_clusters):
"""
计算各个簇ci和簇中包含的句子sj之间的余弦相似度
计算各个簇ci和整个topic之间的余弦相似度
:param short_sentence: 经过处理后的句子列表(最后一个是长句子)
:type short_sentence list
:param clusters: 最后一个句子和其他句子之间的句子相似度形成的列表,列表的长度等于short_sentence的长度
:type clusters list
:param num_clusters: 聚类的数量
:type num_clusters str
:return: 返回两个列表,第一个是一维列表,内容为:按照余弦相似度的大小进行排序的簇的索引
第二个是二维列表,内容为:对每个簇ci中的句子sj,按照相似度分值的大小进行排序的句子的索引
"""
## Print Sentence Clusters ##
cluster_info = {'sentence': short_sentence, 'cluster': clusters}
sentenceDF = pd.DataFrame(cluster_info, index=[clusters], columns=['sentence', 'cluster'])
sentence_clusters = []
clusters_long_sentence = []
for num in range(num_clusters):
# print()
# print("Sentence cluster %d: " % int(num + 1), end='')
# print()
sentence_cluster = []
long_sentence = ""
'''
.ix is deprecated. Please use
.loc for label based indexing or
.iloc for positional indexing
'''
for sentence in sentenceDF.loc[num]['sentence'].values.tolist():
# print(' %s ' % sentence, end='')
# print()
long_sentence += sentence
long_sentence += ". "
sentence_cluster.append(sentence) # 获取短句子
sentence_cluster.append(long_sentence) # 加入每个簇形成的句子
clusters_long_sentence.append(long_sentence) # 为了计算各个簇ci和整个topic之间的余弦相似度,集合各个簇形成的长句子
short_sentence_cluster_cosine_similarities = calculate_cosine(sentence_cluster)
short_sentence_cluster_related_docs_indices = short_sentence_cluster_cosine_similarities.argsort()[::-1]
# 计算各个簇ci和簇中包含的句子sj之间的余弦相似度
sentence_clusters.append(short_sentence_cluster_related_docs_indices)
clusters_long_sentence.append(short_sentence[-1]) # 将整个topic加入列表中
topic_cluster_cosine_similarities = calculate_cosine(clusters_long_sentence)
# 计算各个簇ci和整个topic之间的余弦相似度
topic_cluster_related_docs_indices = topic_cluster_cosine_similarities.argsort()[::-1]
topic_cluster_related_docs_indices = topic_cluster_related_docs_indices[1:]
return topic_cluster_related_docs_indices, sentence_clusters
def generate_remark(topic_cluster_related_docs_indices, sentence_clusters, original_sentence, clusters):
"""
根据聚类结果、排序结果和原始句子,生成摘要
:param topic_cluster_related_docs_indices: 一维列表,内容为:按照余弦相似度的大小进行排序的簇的索引
:type topic_cluster_related_docs_indices list
:param sentence_clusters: 二维列表,内容为:对每个簇ci中的句子sj,按照相似度分值的大小进行排序的句子的索引
:type sentence_clusters list
:param original_sentence: 原始句子列表(最后一个是长句子)
:type original_sentence list
:param clusters: 一维列表,内容是:每个句子对应的类别号形成的列表和总的类别数
:type clusters list
:return: 返回生成的摘要
"""
cluster_info = {'sentence': original_sentence, 'cluster': clusters}
sentenceDF = pd.DataFrame(cluster_info, index=[clusters], columns=['sentence', 'cluster'])
result = "" # 摘要结果
# 计数变量
epoch_times = 0 # 第n次迭代
break_mark = 0 # 用来标记是否要退出循环
# 遍历topic_cluster_related_docs_indices
while 1:
for cluster_index in topic_cluster_related_docs_indices:
if epoch_times >= len(sentence_clusters[cluster_index]): # 有可能迭代次数已经超过列表中的长度上限了
break_mark = 1
break
sentenceDF_index = sentence_clusters[cluster_index][epoch_times]
sentenceDF_i = 0
for sentence in sentenceDF.loc[epoch_times]['sentence'].values.tolist():
if sentenceDF_i == sentenceDF_index:
result += sentence
result += ". "
break
sentenceDF_i += 1
if len(result) >= 665:
break_mark = 1
break
if break_mark == 1:
break
epoch_times += 1
return result
if __name__ == '__main__':
path = "E:/pycharm_workspace/data_mining/data_classification/data"
short_sentence, original_sentence = split_sentence(path=path) # 获得分句结果
print(short_sentence)
clusters, num_cluster = sentence_k_means(short_sentence=short_sentence) # 获得聚类结果
# print(num_cluster)
'''
clusters
输出结果:
[11, 3, 9, 14, 7, 6, 7, 12, 8, 2, 11, 8, 14, 4, 14, 11, 5, 11, 9, 6, 14, 13, 8, 14, 14, 12, 0, 8, 2, 8, 8, 9, 14, 2,
8, 8, 11, 9, 6, 10, 7, 8, 6, 7, 4, 3, 0, 8, 12, 2, 0, 2, 9, 11, 1, 12, 4, 8, 1, 14, 14, 9, 11, 4, 1, 8, 1, 2, 6, 4,
8, 1, 14, 7, 7, 1, 13, 8, 0, 6, 2, 1, 3, 1, 8, 2, 11, 13, 3, 1, 3, 11, 4, 13, 12, 9, 8, 6, 11, 11, 13, 2, 12, 13,
8, 2, 12, 11, 6, 4, 3, 12, 9, 7, 8, 14, 14, 8, 2, 8, 8, 9, 2, 8, 0, 0, 7, 9, 14, 2, 2, 14, 8, 6, 13, 14, 8, 3, 4,
0, 1, 8, 14, 6, 6, 11, 6, 0, 14, 2, 8, 2, 13, 7, 4, 11, 13, 14, 3, 8, 8, 2, 4, 8, 1, 13, 13, 2, 0, 13, 8, 10, 7, 0,
3, 11, 6, 6, 2, 10, 7, 3, 11, 4, 0, 2, 13, 11, 1, 13, 13, 8, 0, 2, 8, 2, 14, 14, 4, 3, 5, 11, 8, 2, 8, 8, 2, 8, 6,
2, 4, 4]
每个元素,代表所属类别的index
'''
topic_cluster_related_docs_indices, sentence_clusters = \
calculate_cosine_clusters(short_sentence=short_sentence, clusters=clusters, num_clusters=num_cluster)
# print(topic_cluster_related_docs_indices)
# print(len(sentence_clusters))
result = generate_remark(topic_cluster_related_docs_indices, sentence_clusters, original_sentence, clusters)
# print(result)
# cosine_similarities = calculate_cosine(short_sentence=short_sentence) # 获得每个短句子和长句子之间的cosine相似度
'''
cosine_similarities
输出结果:
[0.0369489 0.0645411 0.07572011 0.04469324 0.05598735 0.06870317
0.05517361 0.05667246 0.05911312 0.02421797 0.05752079 0.00959966
0.04805382 0. 0.05467164 0.12423966 0.03663924 0.01823689
0.06003995 0.04793762 0.03038719 0.0440952 0.0113016 0.08193282
0.03561778 0.05805447 0.04694088 0.01562031 0.07499985 0.03219183
0.01726291 0.06533694 0.04468038 0.01470686 0.03232685 0.03985583
0.03934646 0.01558247 0.0728808 0.02075386 0.07507461 0.04289326
0.02188341 0.08502677 0. 0.02619807 0.07092147 0.04638336
0.06053325 0.01434085 0.02972314 0.03417944 0.07873913 0.03417217
0.09039998 0.02288194 0.13840649 0.00276395 0.00497967 0.03165067
0.06479095 0.05420417 0.0478747 0. 0.0267854 0.03535918
0.09035666 0.02333625 0.05167437 0. 0.00361575 0.13283063
0.0503183 0.05491774 0.02951664 0.10343725 0.01561105 0.03868941
0.03710442 0.03825174 0.05673902 0. 0.01372241 0.09300941
0.03506926 0.08758283 0.10947296 0.08490101 0.04767494 0.16226998
0.02166416 0.02462259 0. 0.02384342 0.03126979 0.06866134
0.10552289 0.01901653 0.01929458 0.11052018 0.03393653 0.03849562
0.09774023 0.02777456 0.00959966 0.01043412 0.11917525 0.08025494
0.03052946 0. 0.06680314 0.08564869 0.04747937 0.03296444
0.02449389 0.02050697 0.09767556 0.12758946 0.11530088 0.12647082
0.03821594 0.09523041 0.1551513 0.00522573 0.08993113 0.0753947
0.07151088 0.07352524 0.04484816 0.03618936 0.11289245 0.02299431
0.10548842 0.11362721 0.03683305 0.11211793 0.02815374 0.01504682
0. 0.06973247 0.04124258 0.07253654 0.13036871 0.04785882
0.07818914 0.06542423 0.03910005 0.03848401 0.01613094 0.09102833
0.0616504 0.03377447 0.02487605 0.02097402 0.023759 0.04807775
0.04853745 0.11494868 0.06708912 0.02143509 0.03759268 0.02630726
0. 0.04301038 0.10535191 0.04004359 0.03541828 0.08568496
0.11709982 0.0373462 0.03307598 0.05807912 0.04714886 0.04790423
0.0507649 0.09458167 0.12110732 0.13280813 0.0433985 0.02626691
0.05731566 0.07593858 0.01909288 0. 0.04350831 0.05378095
0.04620767 0.06318009 0.04898741 0.04004359 0.09902095 0.09106616
0.03929769 0.06923411 0.17243096 0.10001141 0.05790366 0.09779317
0. 0.07918796 0.09136335 0.09914189 0.05560945 0.03055692
0.14330695 0.03289337 0.02399386 0.10450709 0.06948788 0.01891814
0. 1.]
'''
改进2:
用LexRank/DocHITS 对句子进行排序